Molec Cell Ch. 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/62
Earn XP
Last updated 7:59 PM on 1/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
1
New cards
What is the critical characteristic of the macromolecule from which life evolved?
The ability to replicate itself
2
New cards
What are two major macromolecules?
Nucleic acids and proteins
3
New cards
Which macromolecule is capable of self-replication?
Nucleic acids
4
New cards
What did Altman and Cech first discover?
RNA is capable of catalyzing chemical reactions, including the polymerization of nucleotides
5
New cards
What is RNA able to do for its replication?
RNA is able to both serve as a template for, and to catalyze its own replication.
6
New cards
What may be the initial genetic system?
RNA
7
New cards
What is RNA world?
A period of evolution
8
New cards
All present-day cells…
use DNA as the genetic mateiral and have the same mechanisms for replication and gene expression.
9
New cards
Genes
segments of DNA that encode proteins or DNA
10
New cards
Transcription
Nucleotide gene sequence is copies into RNA
11
New cards
Translation
Nucleotide sequence of RNA is used to specify the order of amino acids in a protein
12
New cards
What was part of the first cell?
Self-replicating RNA and phospholipid membrane
13
New cards
Phospholipids
Basic components of all present-day biological membranes
14
New cards
Amphipathic
a chemical compound containing both polar (water-soluble) and nonpolar (not water-soluble) portions in its structure
15
New cards
Are phospholipids amphipathic?
* Water-insoluble (hydrophobic) **hydrocarbons chains**
* water-soluble (hydrophilic) **head groups** that contain phosphate
* water-soluble (hydrophilic) **head groups** that contain phosphate
16
New cards
What happens when phospholipids are placed in water?
Phospholipids spontaneously aggregate into a bilayer
17
New cards
What do all cells use as their source of metabolic energy?
Adenosine 5’-triphosphate (ATP)
18
New cards
What are the mechanism that generate ATP?
Glycolysis, photosynthesis, oxidative metabolism
19
New cards
Glycolysis
Glucose → lactic acid (generates 2 ATP)

20
New cards
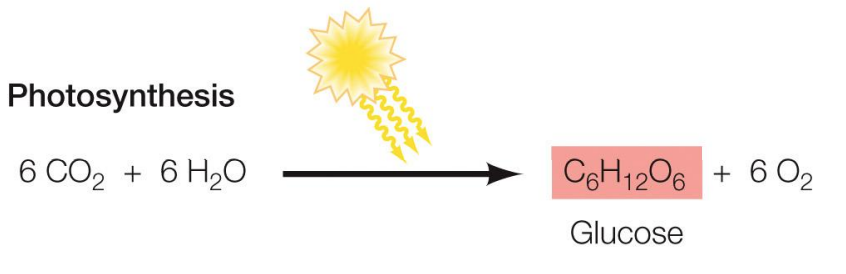
Photosynthesis
CO2 + H2O + sunlight → Glucose + O2
21
New cards
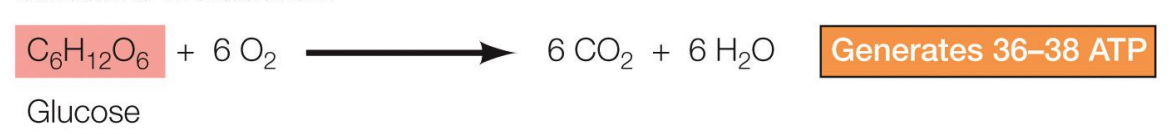
Oxidative Metabolism
Glucose + O2 → CO2 + H2O (Generates 36-38 ATP)
22
New cards
How did glycolysis evolve?
* Glycolysis evolved when the Earth’s atmosphere was anaerobic.
* Glucose broke down to lactic acid, with 2 ATP gained.
* All present-day cells carry out glycolysis
* Glucose broke down to lactic acid, with 2 ATP gained.
* All present-day cells carry out glycolysis
23
New cards
Photosynthesis allowed…
Some cells to harness energy from sunlight
24
New cards
Use of H2O in photosynthesis…
changes Earth’s atmosphere by making free O2 available
25
New cards
Complete oxidative breakdown of glucose yields how many ATP molecules?
36-38 ATP
26
New cards
What are the two types of cells?
Prokaryotic (bacteria) and Eukaryotic
27
New cards
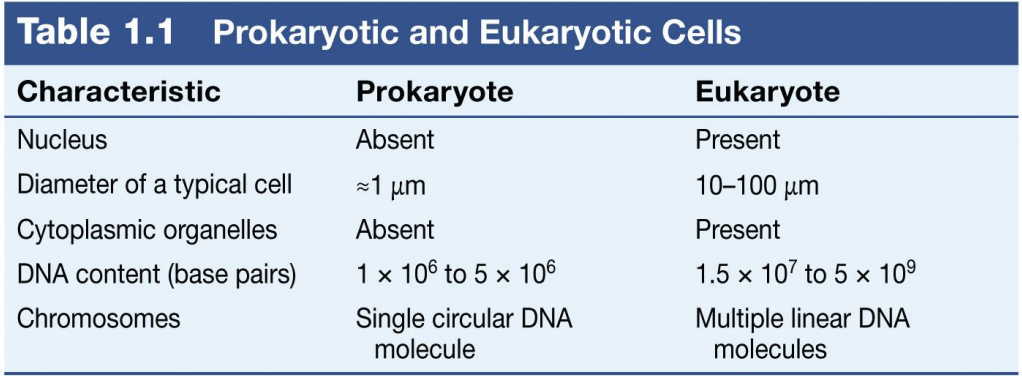
Prokaryotic
lack a nuclear envelope
28
New cards
Eukaryotic
Have a nucleus that separates genetic material from cytoplasm?Wha
29
New cards
What is the difference of the 2 cell types?
30
New cards
What is a typical prokaryotic cell?
E. Coli
31
New cards
What are some key features in prokaryotes, especially in E. coli?
1. **Cell wall:** polysaccharides + peptides
2. **Plasma membrane:** phospholipid bilayer + associated proteins
3. DNA: **single circular molecule in the nucleoid** - **not surrounded by a membrane**
4. Cytoplasm: 30,000 **ribosomes**
32
New cards
Present-day prokaryotes are:
* Archaea
* Bacteria
* Prokaryotes
* Cyanobacteria
* Bacteria
* Prokaryotes
* Cyanobacteria
33
New cards
Archaea habitat?
extreme environments (ex: hot sulfur springs)
34
New cards
Bacteria…
* include the common forms of present-day prokaryotes
* in a wide range of environments
* in a wide range of environments
35
New cards
Prokaryotes… (size and DNA)
* Most are small, diameters: 1 to 10 um
* DNA ranges from 0.6 million to 5 million base pairs, encodes about 5000 different proteins
* DNA ranges from 0.6 million to 5 million base pairs, encodes about 5000 different proteins
36
New cards
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthesis evolved, largest and most complex prokaryotes
37
New cards
Eukaryotic cells are…
much larger and more complex, with a nucleus, other organelles, and cytoskeleton
38
New cards
What are the key organelles in euks?
1. Nucleus
2. Mitochondria
3. Chloroplasts
4. Lysosomes and Peroxisomes
5. Vacuoles: in plant cells
6. Endoplasmic Reticulum
7. Golgi apparatus
8. Cytoskeleton
39
New cards
What is the largest organelle in euks? What does it do?
* Nucleus is the largest organelle
* contains the linear DNA molecules
* site of DNA replication and RNA synthesis
* contains the linear DNA molecules
* site of DNA replication and RNA synthesis
40
New cards
What do mitochondria do in euks?
site of oxidative metabolism
41
New cards
What do chloroplasts do in euks?
site of photosynthesis
42
New cards
what do Lysosomes and peroxisomes do in euks?
specialized metabolic compartments for the digestion and macromolecules and for various oxidative reactions
43
New cards
What do vacuoles do in euks?
in plant cells
\
Do a variety of functions: digestion of macromolecules and storage of waste products and nutrients
\
Do a variety of functions: digestion of macromolecules and storage of waste products and nutrients
44
New cards
What does the endoplasmic reticulum do in euks?
* Network of intracellular membranes, extending from the nuclear membrane throughout the cytoplasm
* Functions in processing and transport of proteins and lipid synthesis
* Functions in processing and transport of proteins and lipid synthesis
45
New cards
What does the golgi apparatus do in euks?
* Proteins are further processed and sorted for transport to their final destinations
* site of lipid synthesis; and (in plant cells) synthesis of some polysaccharides that compose the cell wall
* site of lipid synthesis; and (in plant cells) synthesis of some polysaccharides that compose the cell wall
46
New cards
What does the cytoskeleton do in euks?
a network of protein filaments extending throughout the cytoplasm
* provides structural framework
* determines cell shape and organization
* involved in movement of whole cells, organelles, and chromosomes during cell division
* provides structural framework
* determines cell shape and organization
* involved in movement of whole cells, organelles, and chromosomes during cell division
47
New cards
How are eukaryote organelles thought to have arisen?
Endosymbiosis → prokaryotic cells living inside the ancestors of eukaryotes
48
New cards
What organelles support endosymbiosis? Why?
Mitochondria and chloroplasts:
* similar to bacteria in size
* like bacteria: reproduce by dividing in two
* both contain their own DNA
* DNA is replicated when the organelle divides. Genes are transcribed within the organelle and translated on organelle ribosomes
* Ribosomes and ribosomal RNAs are more closely related to those of bactiera than to those encoded by the eukaryote nuclear genome
* similar to bacteria in size
* like bacteria: reproduce by dividing in two
* both contain their own DNA
* DNA is replicated when the organelle divides. Genes are transcribed within the organelle and translated on organelle ribosomes
* Ribosomes and ribosomal RNAs are more closely related to those of bactiera than to those encoded by the eukaryote nuclear genome
49
New cards
Are there any unicellular euks?
Yes
50
New cards
What are the simplest eukaryotes?
Yeasts
51
New cards
Approx how many germ cells and somatic cells do multicellular organisms have?
16 germ cells and 2000 somatic cells
52
New cards
What is another example of the transition to multicellularity?
amoeba *Dictyostelium discoideum* is able to **alternate between unicellular and multicellular forms** depending on the availability of food
53
New cards
What led to the complexity and diversity of present-day plants and animals?
Increasing specialization and division of labor among the cells of multicell organisms
54
New cards
What are the main tissue systems in plants?
1. Ground Tissue
2. Dermal Tissue
3. Vascular Tissue
55
New cards
Ground Tissue
* Has parenchyma cells - site of metabolic reactions, including photosynthesis
* Collenchyma and sclerenchyma - have thick cell walls and provide structural support
* Collenchyma and sclerenchyma - have thick cell walls and provide structural support
56
New cards
Dermal Tissue
covers the surface of the plant; forms a protective coat and allows absorption of nutrients
57
New cards
Vascular Tissue
Xylem and Phloem - elongated cells which transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
58
New cards
What are the 5 main tissue types in animals?
1. Epithelial cells
2. Connective tissues
3. Blood
4. Nervous Tissue
5. Muscle Cells
59
New cards
Epithelial Cells
Can form sheets that cover the surface of the body and line internal organsCo
60
New cards
Connective Tissue
Includes bone, cartilage, and adipose tissue.
\
Loose connective tissue is formed by fibroblasts.
\
Loose connective tissue is formed by fibroblasts.
61
New cards
What types of cells does blood have?
* Red blood cells (erthrocytes) function in oxygen transport
* White blood cells (granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes) function in inflammatory
* White blood cells (granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and lymphocytes) function in inflammatory
62
New cards
Nervous Tissue
Composed of supporting cells and nerve cells, or neurons, and various types of sensory cells
63
New cards
Muscle Cells
Rresponsible for the production of force and movement