S7 Bio 4 7.1.1 ATP Synthesis
1/71
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
in which transmembrane enzymes ATP synthesis takes place
ATP synthase
Thylakoids description
membranous sacs stacked to form a granum
What is the stroma?
the internal fluid
Where are chloroplasts found?
In leaves and other green organs of plants and algae
What do chloroplasts contain?
chlorophyll (the green pigment), enzymes, other molecules that function in photosynthesis
Two chloroplast structures
thylakoids and stroma
chemiosmosis definition
the use of energy in a H+ gradient to drive cellular work
What does synthesis of ATP require? (2 things)
Compartmentalization of an electrochemical gradient in a membrane space, electron transport chain that pumps H+ across a membrane generating a electrochemical gradient of hydrogen ions across a membrane.
What does an electron transport chain consist of?
a series of redox reactions
Difference of concentration of H+ (better phrase)
electrochemical gradient of hydrogen ions
What energy transfer happens in ATP synthesis
Mechanical energy into chemical energy
photosynthesis definition (simple)
The biochemical process by which plants and some bacteria capture light energy and use it to produce chemical bonds.
Balanced photosynthesis formula
6CO2 + 12H20 + light → C6H12O6 + 6H2O + 6O2
2 stages of photosynthesis
light dependent and light independent
Light dependent stage parts
ATP and NADPH2 synthesis
Light independent stage parts
Fixation of CO2 into carbohydrates using the energy in ATP and NADPH2
direct product of photosynthesis
glucose
fatty acids + glycerol =
lipids
nitrate + phosphate =
nucleotides, nucleid acids
NADP stands for
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
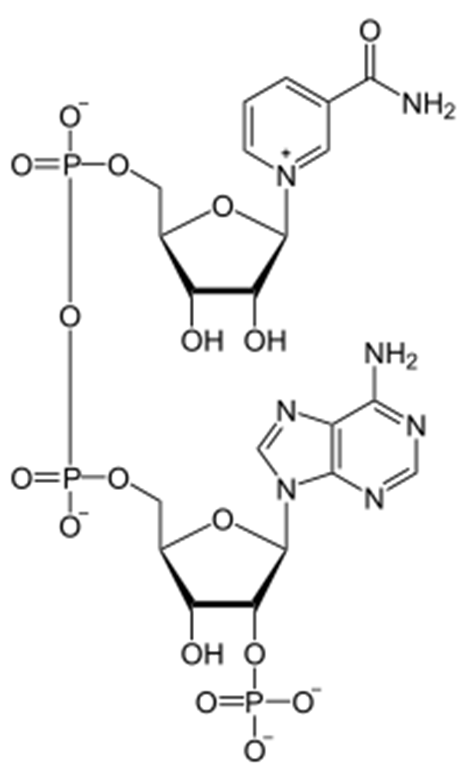
What is this molecule
NADP
NAD+ is a …
electron shuttle
NADH is a …
reducing agent
FAD+ stands for
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
What is the “synthesis” part of photosynthesis?
the Calvin cycle
Steps of light reactions (4 steps)
Split H20, release O2, reduce NADP+ to NADPH, synthesize ATP
Where do the light reactions take place?
thylakoids
Where does the Calvin cycle take place?
stroma
What does the Calvin cycle do?
Forms sugar from CO2 using ATP and NADPH
What is the first step of the Calvin cycle?
carbon fixation
What is carbon fixation?
incorporation of CO2 into organic molecules
What energy transformation happens in light reactions and by who?
thylakoids transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH
what does a photosystem consist of?
a reaction-center surrounded by light-harvesting complexes
what is a reaction-center complex?
A type of protein complex
what do light-harvesting complexes do?
transfer the energy of photons to the reaction center
what are light-harvesting complexes?
pigment molecules bound to proteins
Light dependent stage steps (in more detail) (till PSI)
Photon excites chlorophyll - P680 - primary electron accepor (PSII) - Pq - Cytochrome complex - Pc - PSI
Pq meaning
Plastoquinone
Pc meaning
Plastocyanin (protein)
Light dependent stage steps (in more detail) (from PSI)
PSI - P700 - Primary electron acceptor (PSI) - Fd- NADP+ reductase - Calvin cycle
photophosphorylation
the formation of ATP using light energy in photosynthesis
Where does the oxygen given off in photosynthesis come from?
water
What does the Calvin cycle do with its starting material after molecules enter and leave the cycle?
It regenerates them
In what form does carbon enter the Calvin cycle?
CO2
In what form does carbon leave the Calvin cycle?
PGAL
G3P definition
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
How many times does the cycle have to take place to get 1 G3P?
3
3 phases of the Calvin cycle?
Carbon fixation, reduction, regeneration of the O2 acceptor
What is carbon fixation catalyzed by (enzyme)
RuBisCo
Sequence of energy flow in cellular respiration
glucose - NADH - electron transport chain - proton-motive force - ATP
How much % of energy in glucose is transferred to ATP during cellular respiration?
34%
How many ATP are made from 1 glucose?
36-38 ATP
How much ATP is made each from both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle?
2 ATP
How much ATP is made from oxidative phosphorylation?
32-34 ATP
What is another name for the H+ gradient in mitochondria?
Proton-motive force