Mangrove Ecosystems
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Mangrove Ecosystems
found closer to equator because can withstand heat better than salt marsh vegetation, transform around South Florida. important nurseries for fish and invertebrates. protects coast by slowing water limiting wave action and erosion. Also sequesters carbon
Mangrove Trees
tree/woody plant adapted to anoxic soil via air projecting and shallow but broad roots. contain trunk, stem, and leaves like terrestrial plants, but has root system projecting into air so underground roots can get oxygen.
Oxygen is transported from chambered upward roots to tissues below ground, protecting aerobic metabolism
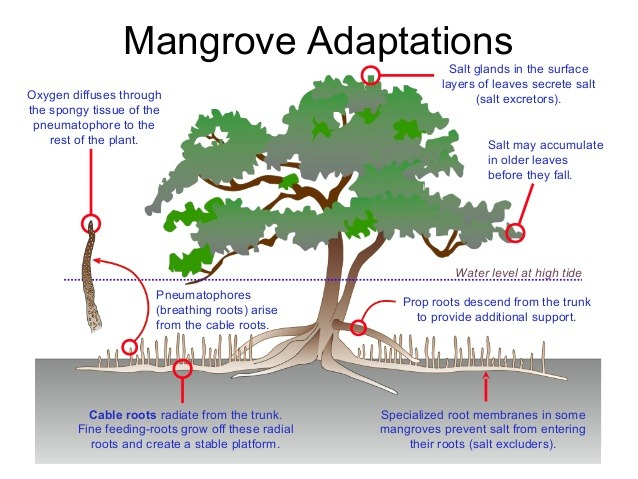
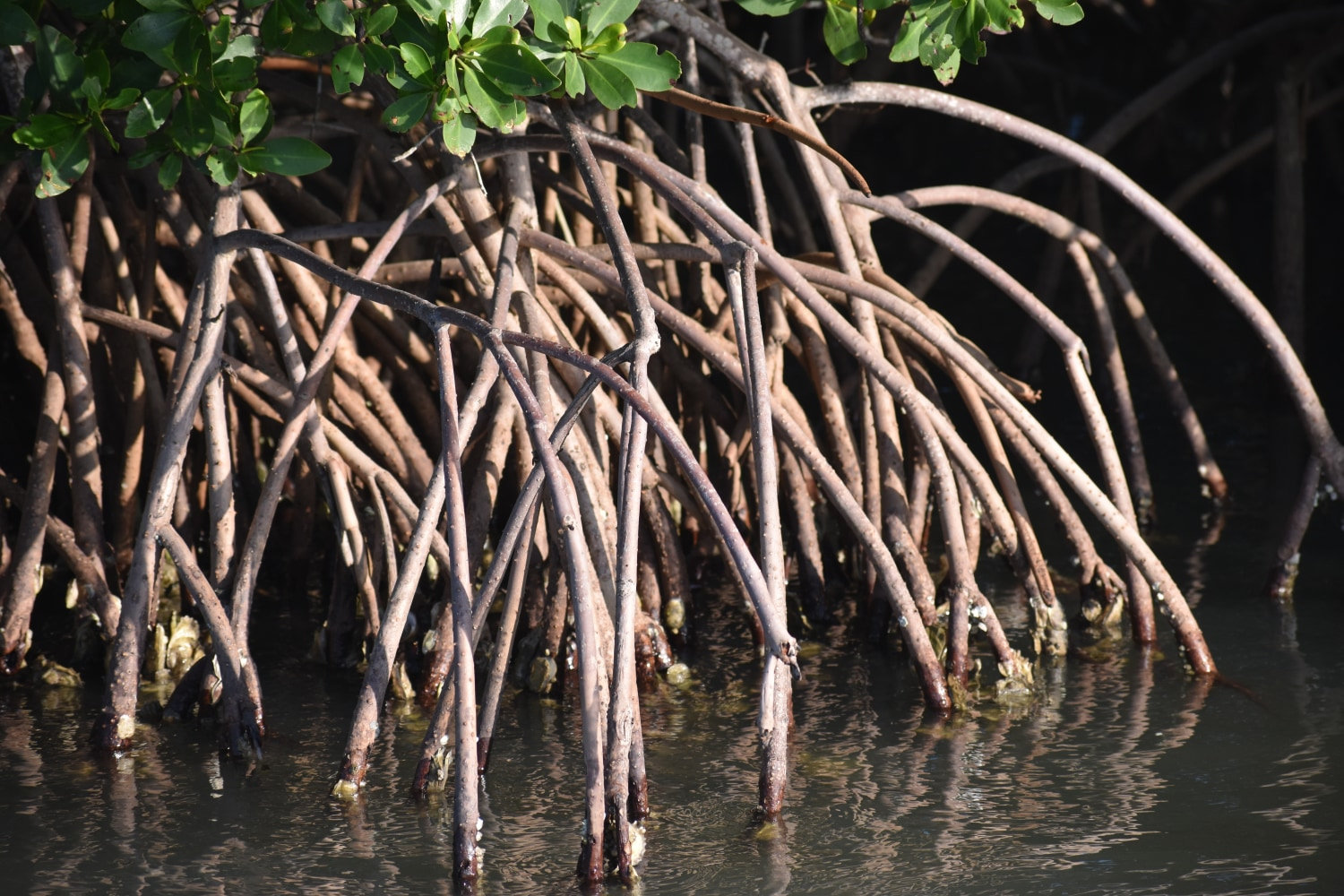
Prop roots
extend midway from trunk and arch down for support

Knee roots
also known as pneumatophores, project into air and shuttles oxygen

Finer roots
gather nutrients
Mangrove Saline Adaptations
high salinity in mangroves due to tidal inundation, so roots penetrate the validose layer
Species have salt glands excrete salt from leaves, can store Na+ in vacuoles, or roots will filter out salt when they take in other nutrients
Validose layer
high salt because top surface sediment, but has lower salinity than sea due to rainfall
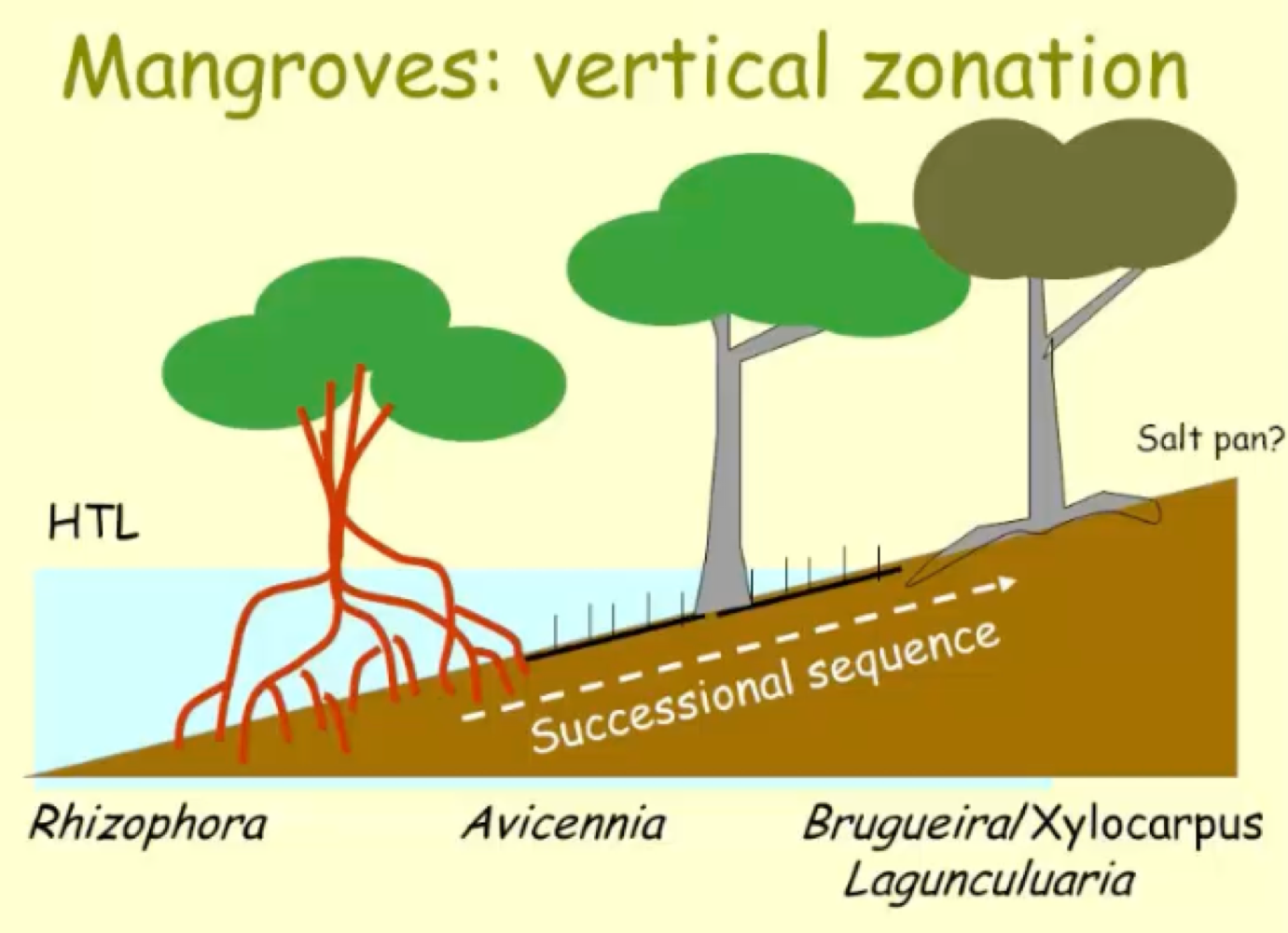
Vertical zonation
impacted by saltwater intrusion, seedling dispersal, and invertebrate predation on seeds.
In south Florida and Caribbean, Red Mangrove dominates seaward part, first to colonize shorelines and has prop roots. Tolerates tidal inundations → Black Mangrove lives shoreward of Red, tolerates occasional inundation (high tides) → White Mangrove rarely gets seawater inundation
Red Mangrove Seeds
germinate while still attached to parent plant, seedlings will fall into mud or water and get carried by wind. survival depends on Graspid crab predation, which could cause massive mortality.
Animal diversity
prop roots extend into open seawater to support invertebrates and provide shelter. Flat tree oysters (Isognomon alatus) attach to roots. Barnacles and snails live on trunks and leaves. Frequent leaf fall enhances supply of particulate matter/detrital material
Decline Factors
shoreline development and dredging for shrimp farms
sea level rises (drown → carbon release)
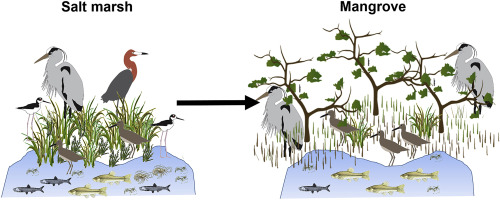
Marsh-mangrove ecotone
transitional area, shorter trees mixed in with grass
state-shift is driven by temperature changes (warming winter temperatures and less freezing events results in more mangroves) and nutrients.
community abundance stays similar, but nekton and bird species differed after state shift
Critical Threshold
-10ºC for state-shift reversal, but -4ºC caused damage