Headwork Part 2: Facial & Nasal Bones
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
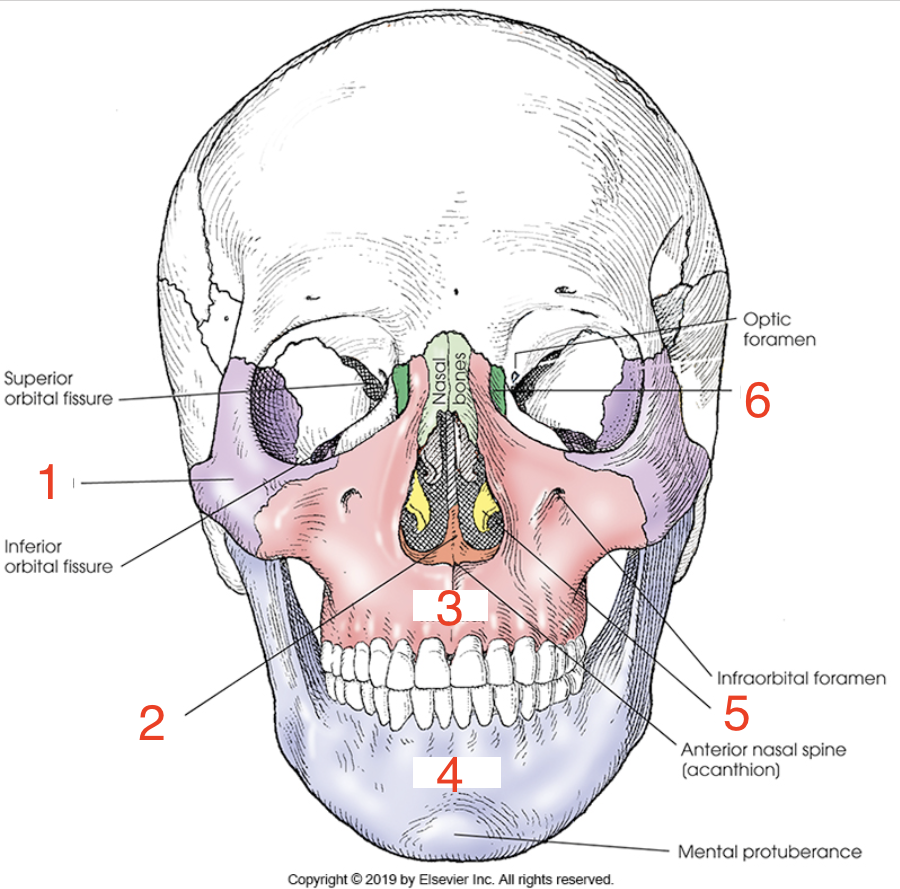
1?
Zygoma
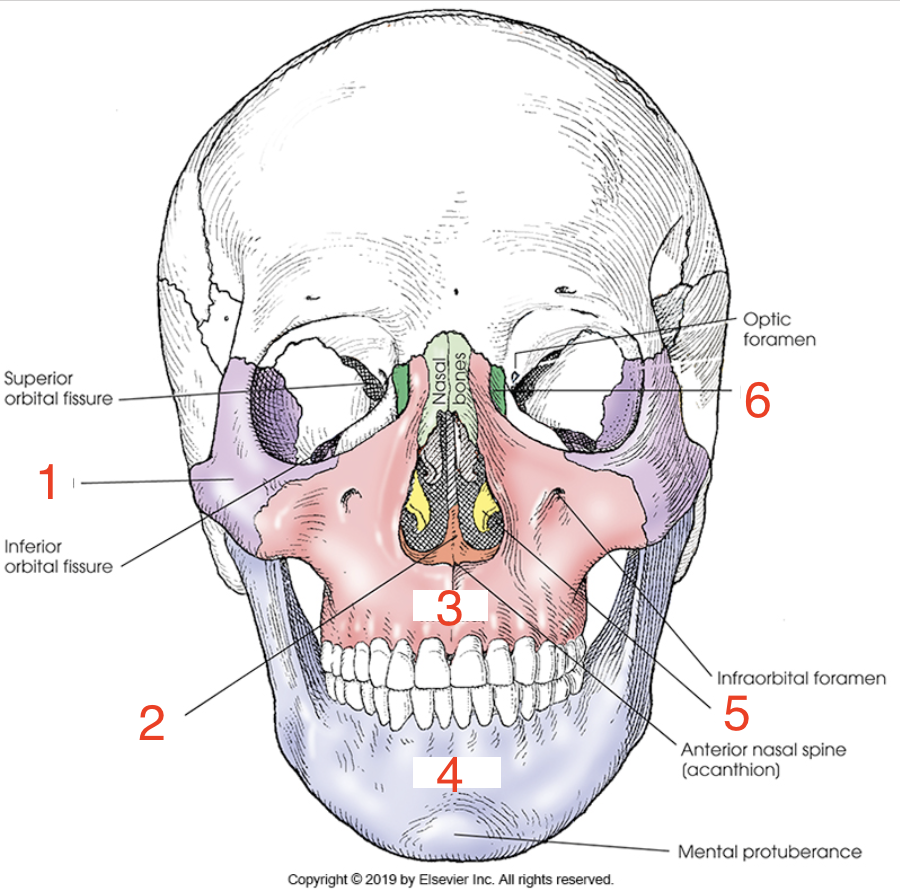
2?
Vomer
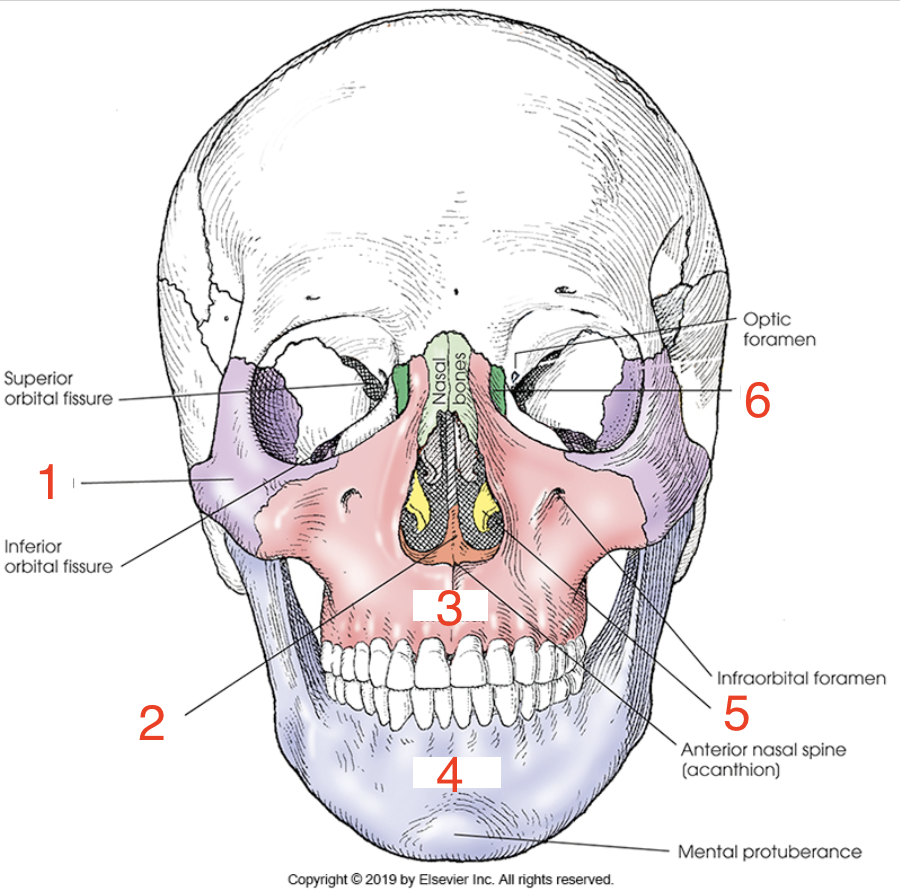
3?
Maxilla
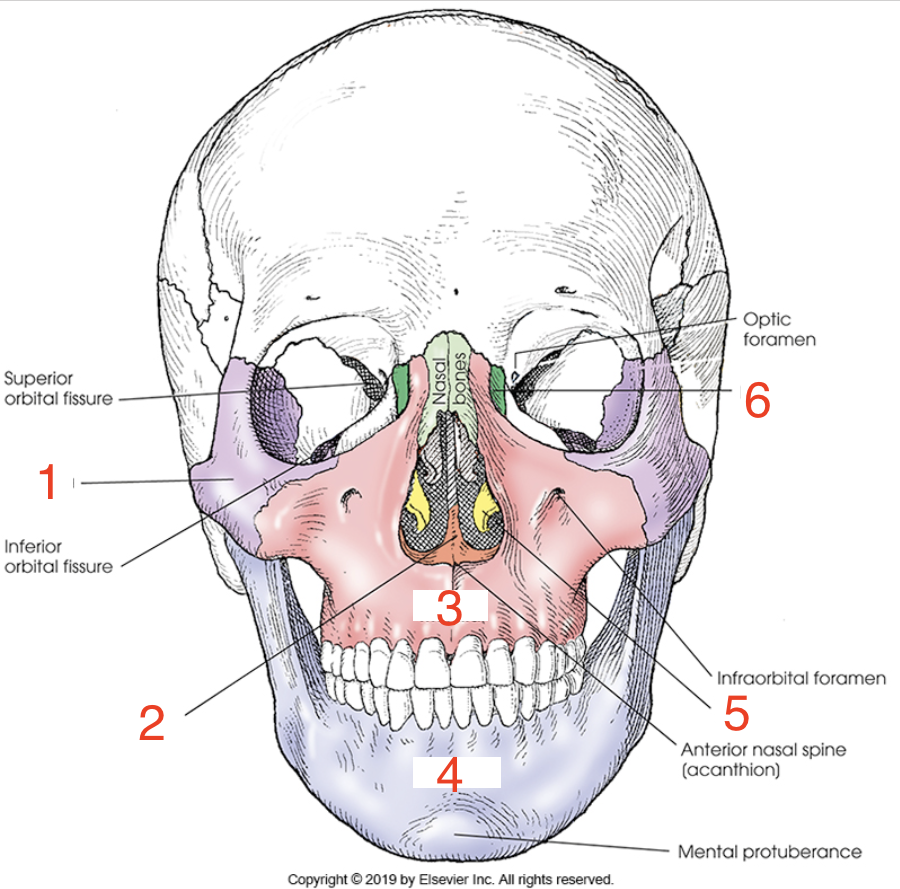
4?
Mandible
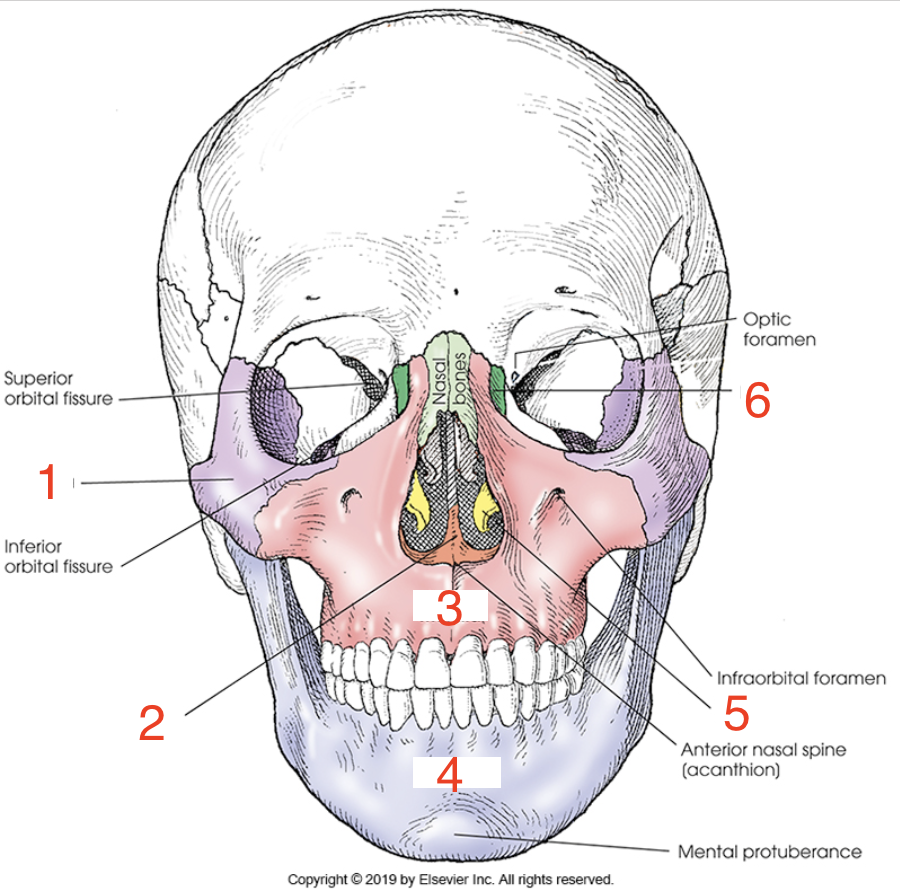
5?
Inferior nasal concha
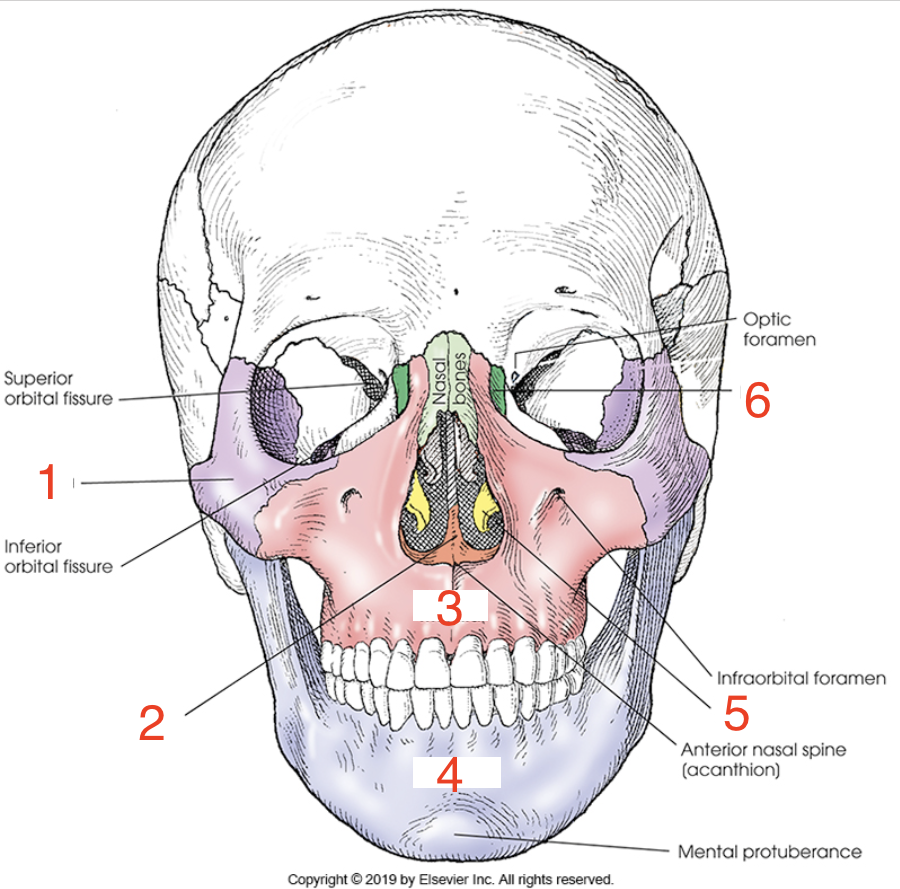
6?
Lacrimal bone
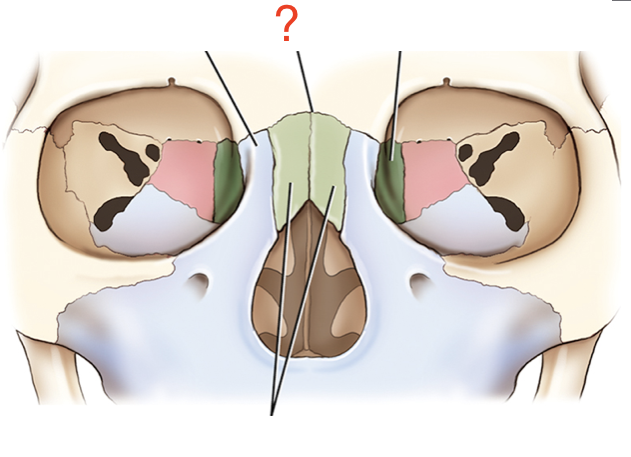
Nasion
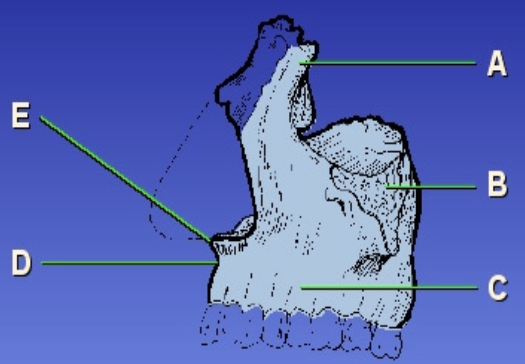
A?
Frontal bone
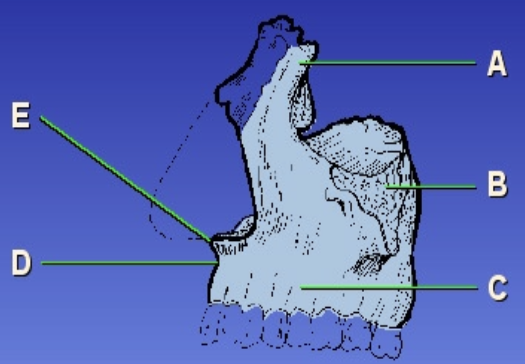
B?
Zygomatic bone
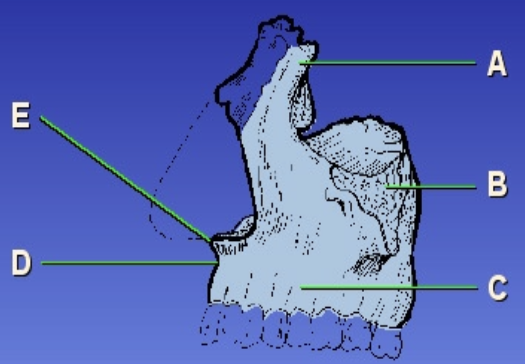
C?
Alveolar
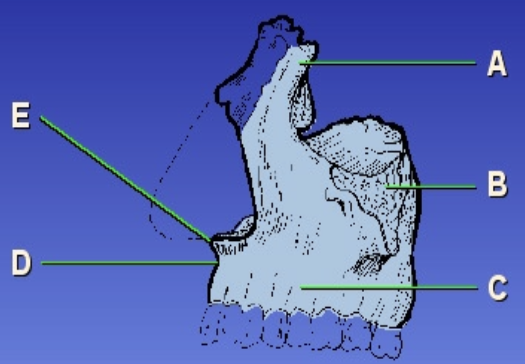
D?
Acanthion
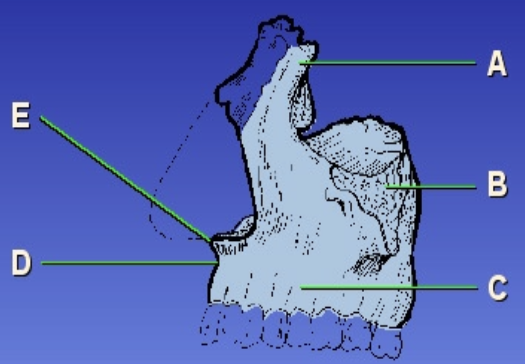
E?
Anterior nasal spine
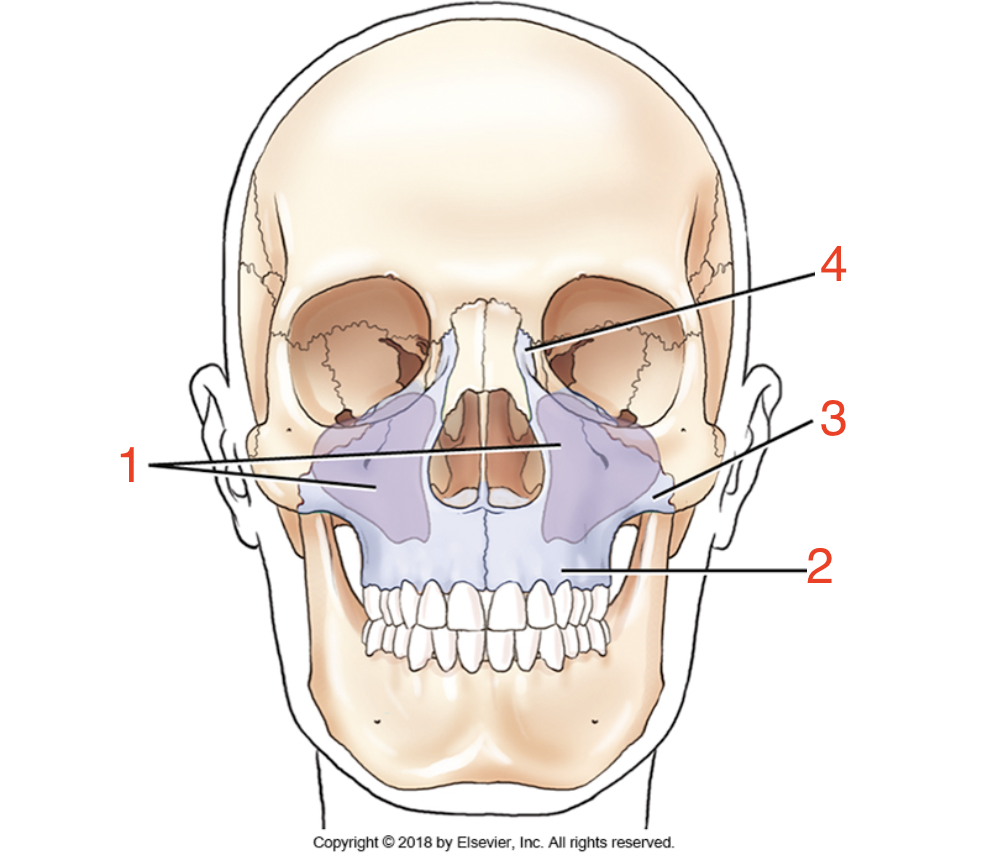
1?
Maxillary sinuses
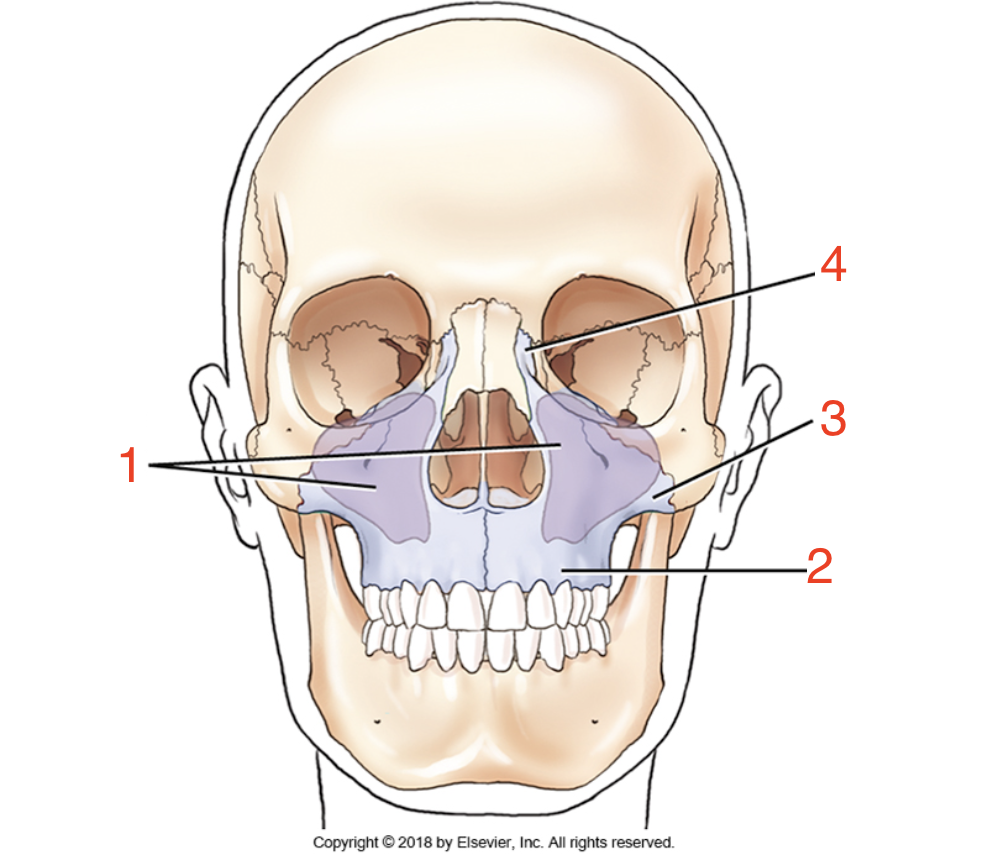
2?
Alveolar process
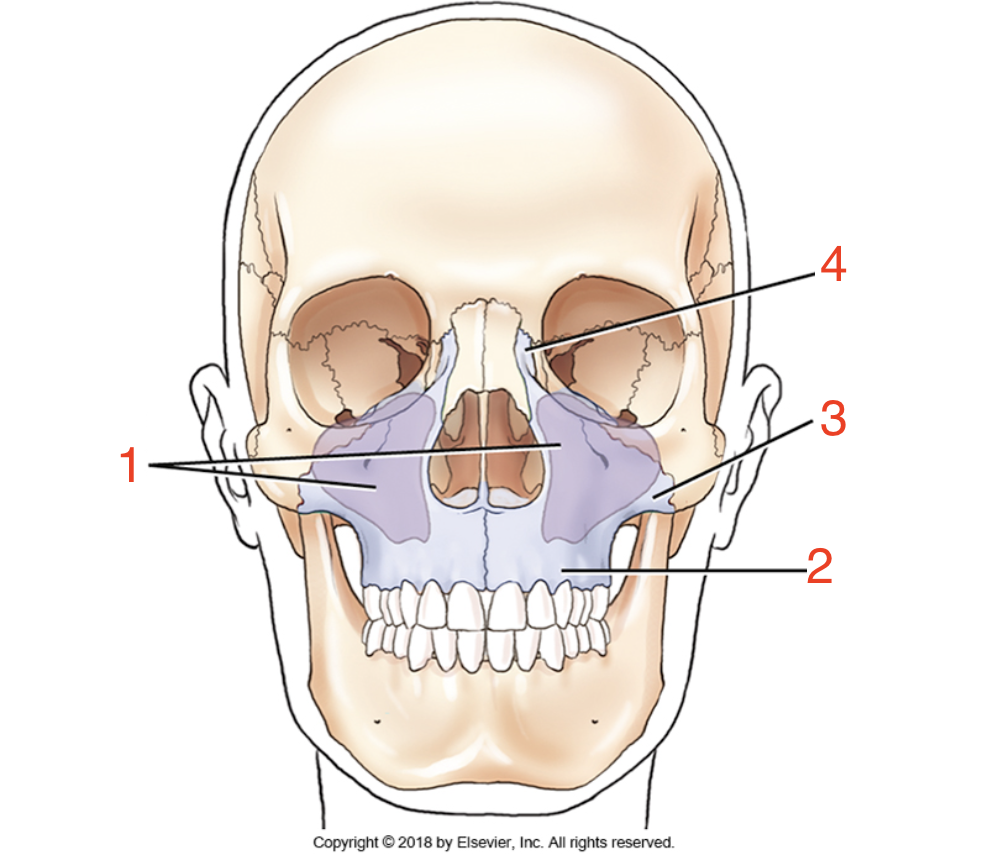
3?
Zygomatic process
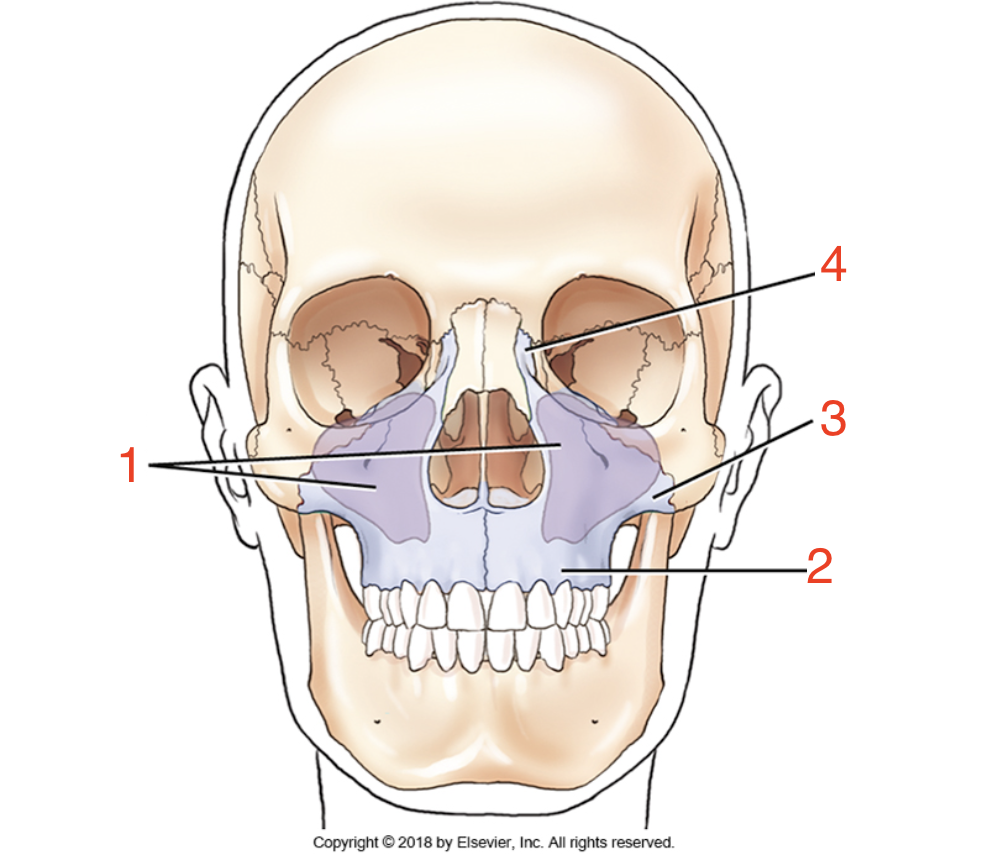
4?
Frontal process
Zygomatic Arch
Formed by zygomatric bone and temporal bone
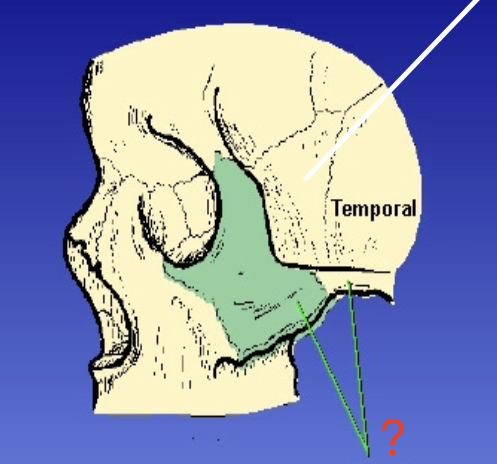
Zygomatic arch
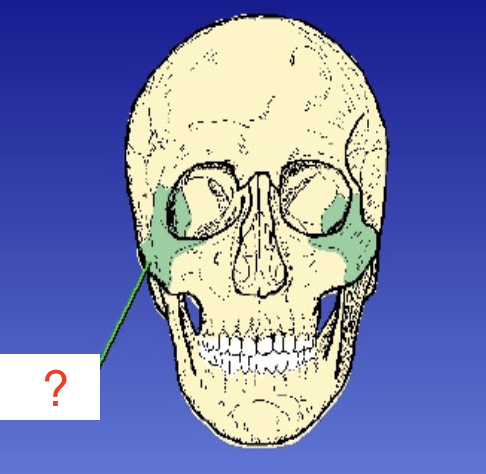
Zygomatic prominence
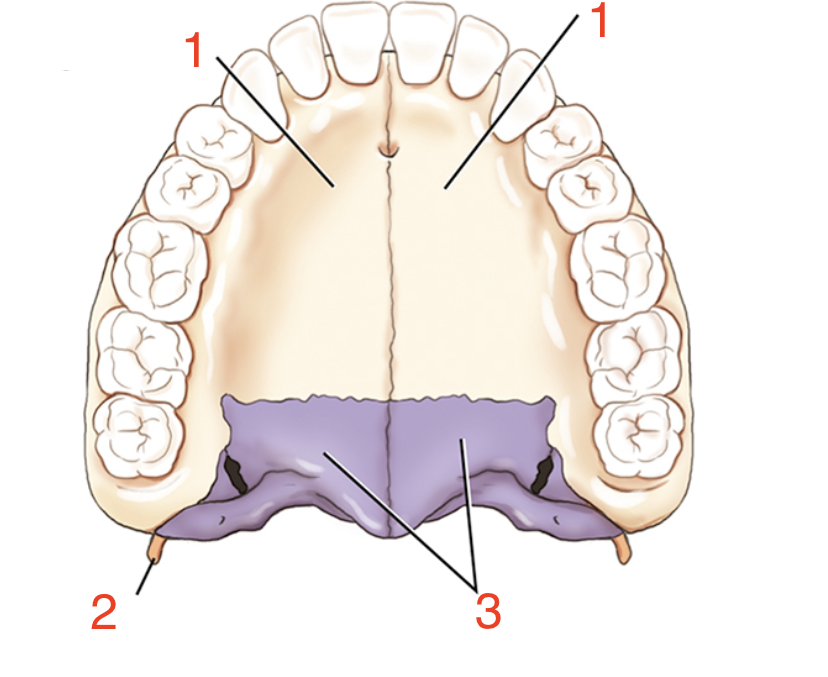
1?
Palatine process
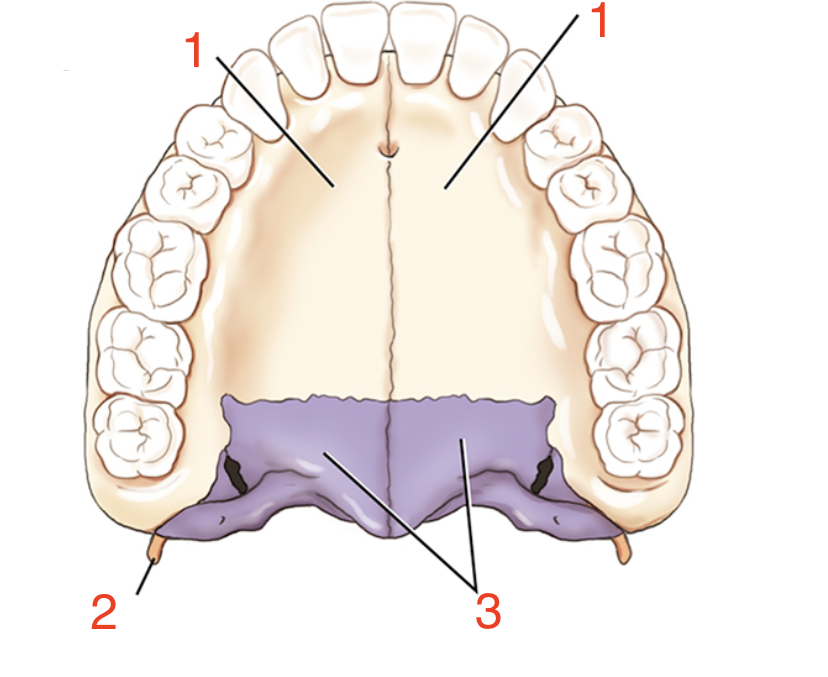
2?
Pterygoid hamulus
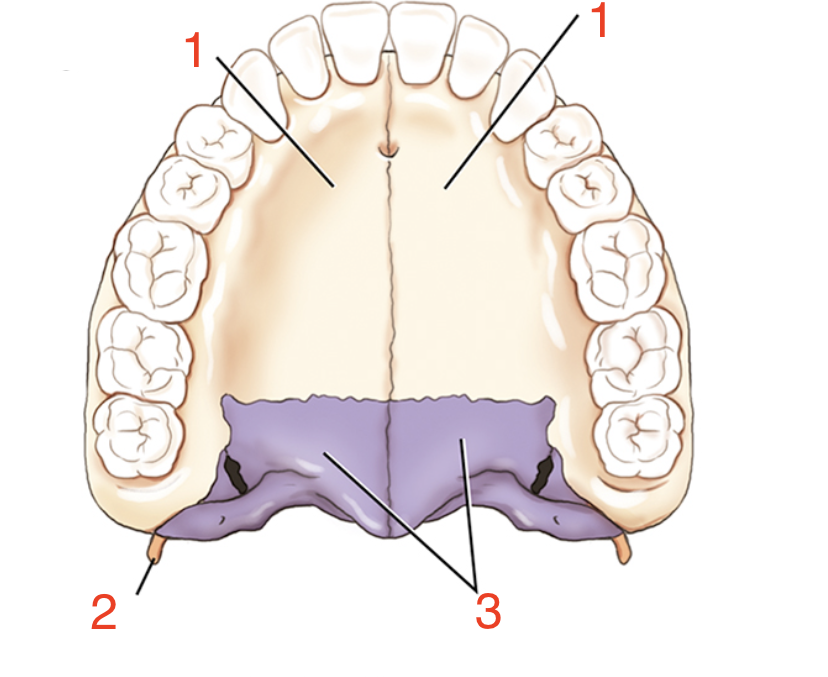
3?
Palatine bones
What is the green?
Superior nasal concha
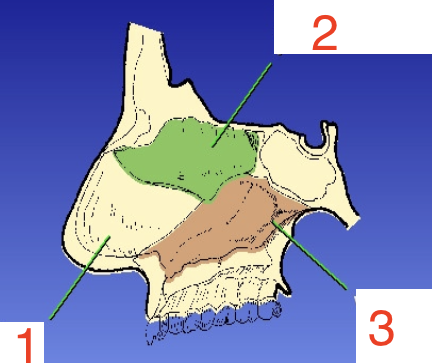
1?
Septal cartilage
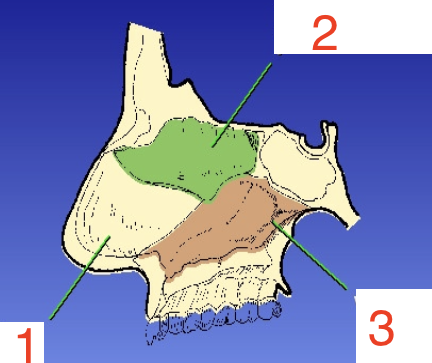
2?
Perpendicular plate
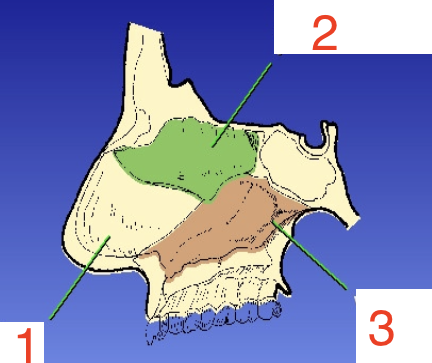
3?
Vomer
How many facial bones are there?
14
Facial Bones
Maxillae (2), zygoma (2), lacrimal (2), nasal (2), inferior nasal conchae (2), palatine (2), vomer (1), mandible (1)
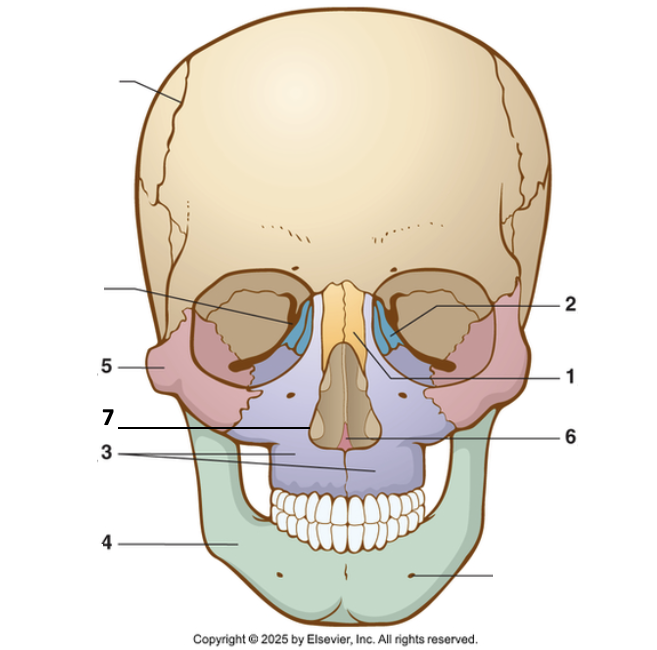
1?
Nasal bone
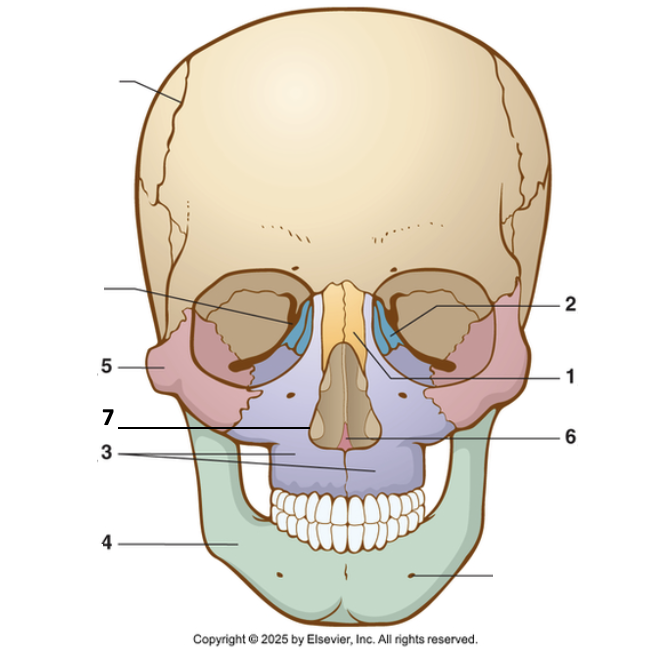
2?
Lacrimal
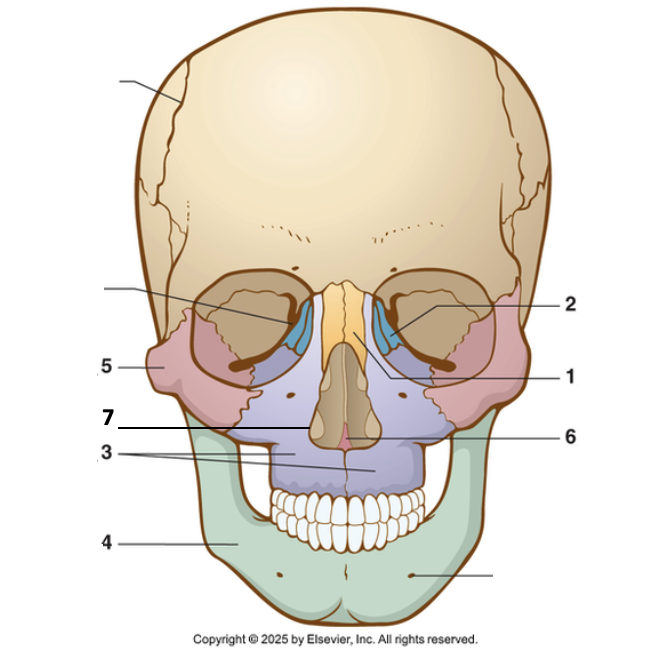
3?
Maxilla
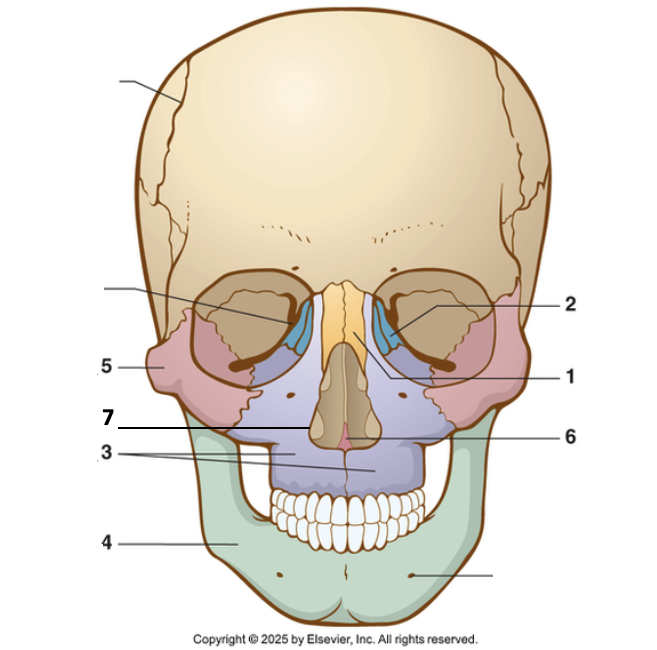
4?
Mandible
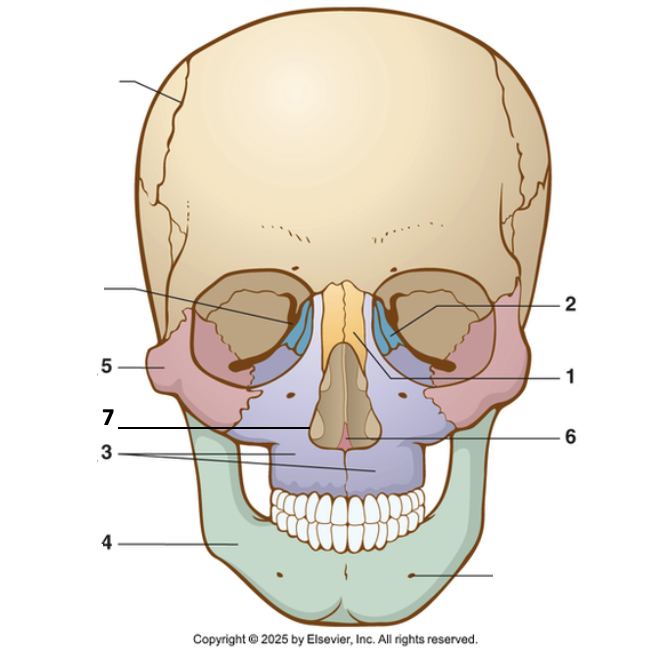
5?
Zygoma
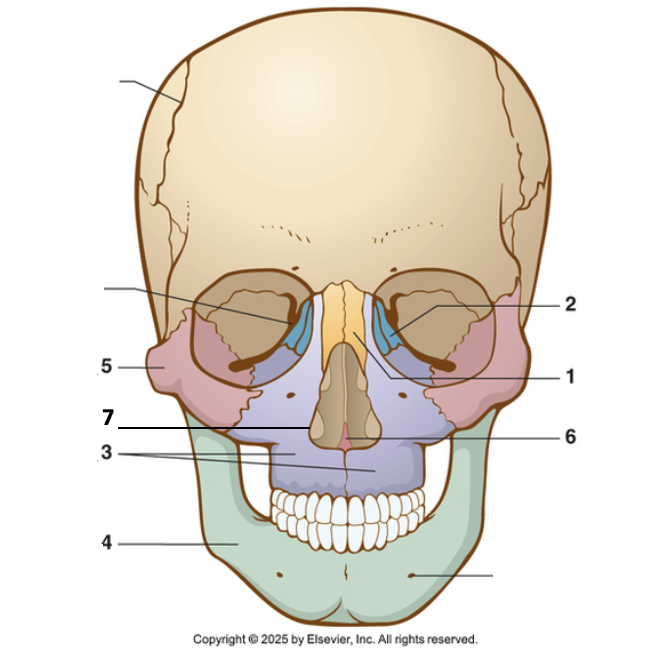
6?
Vomer
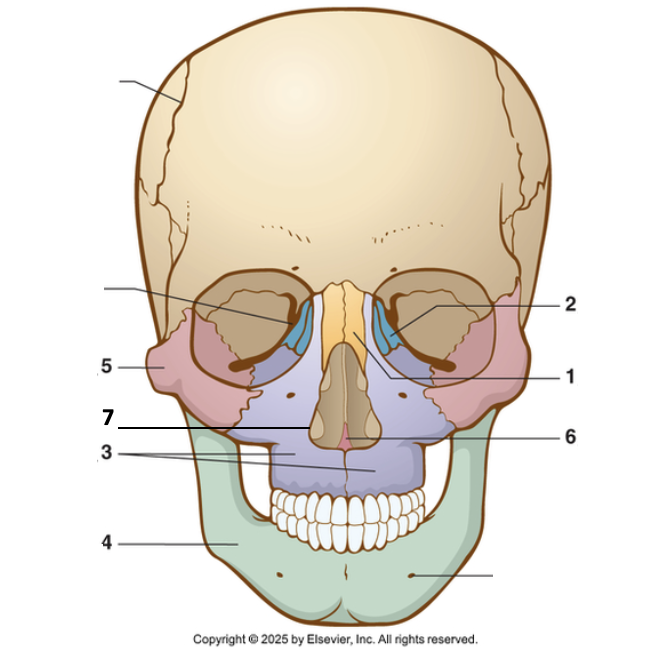
7?
Inferior nasal concha
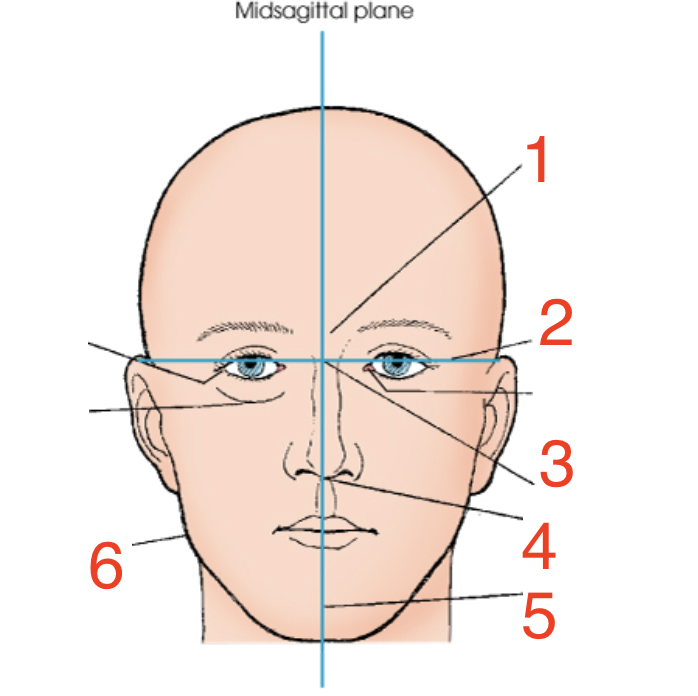
1?
Glabella
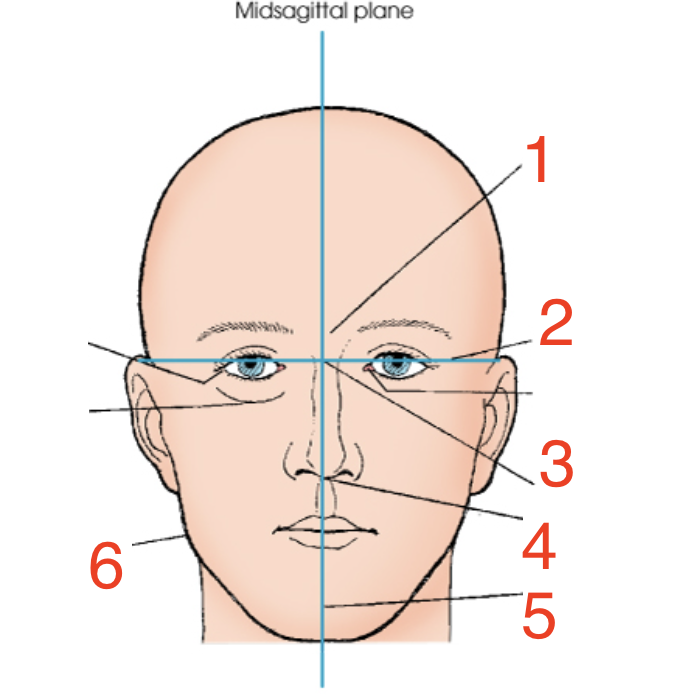
2?
Interpupillary line
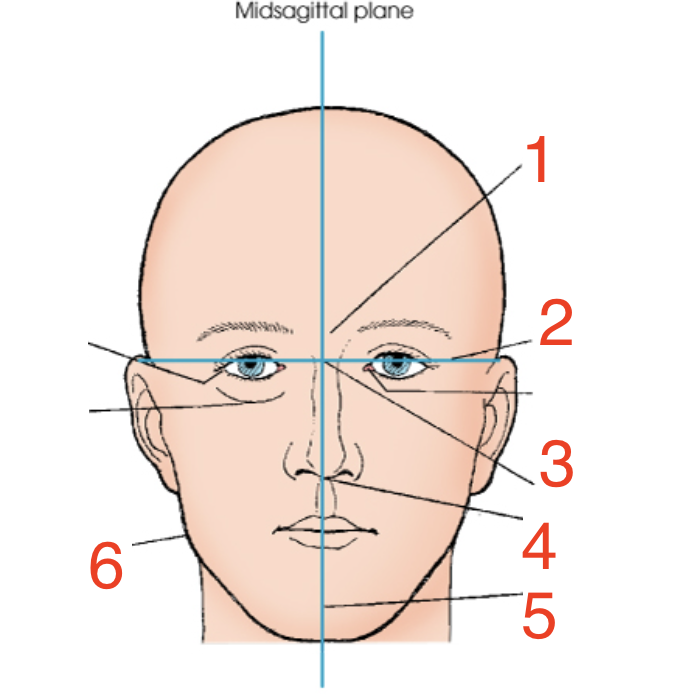
3?
Inner canthus
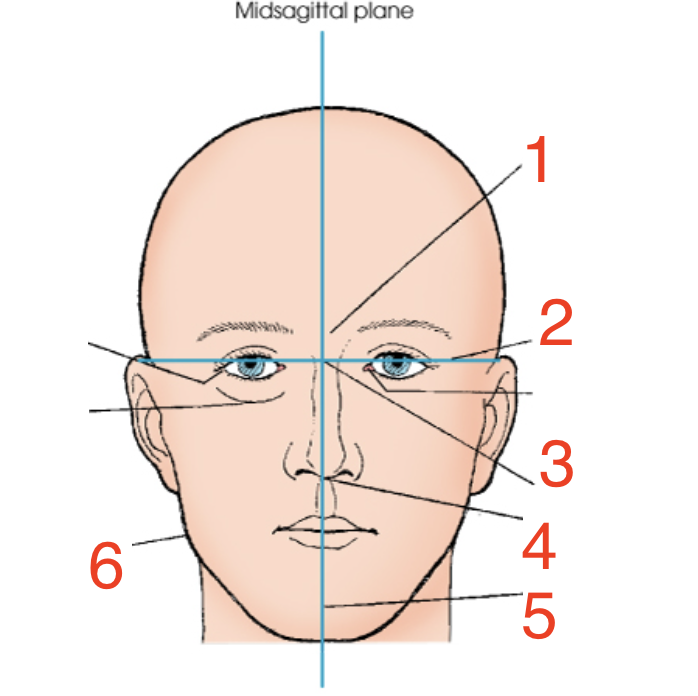
4?
Acanthion
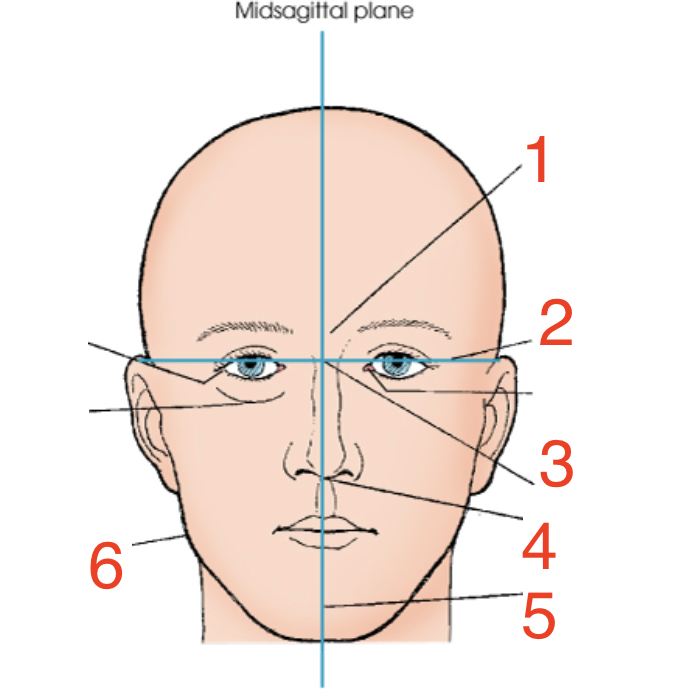
5?
Mental point
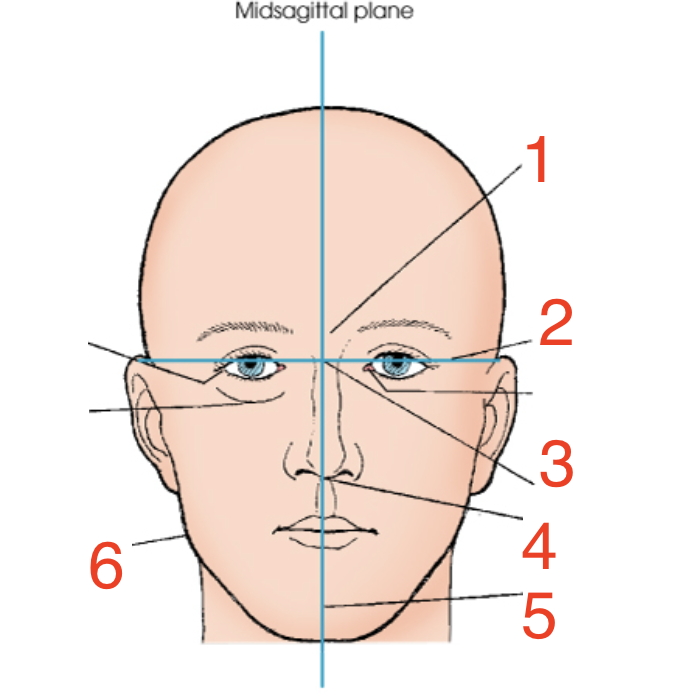
6?
Gonion
Facial bone joint classification
Fibrous, synarthrodial (immovable)
Mandible joint classification
Synovial, hinge and gliding
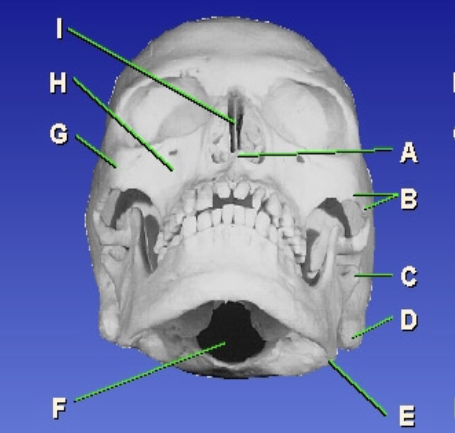
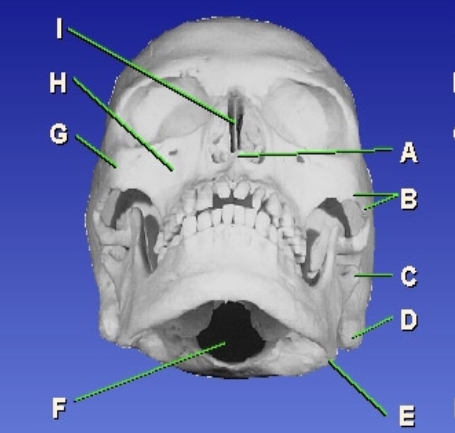
A?
Anterior nasal spine
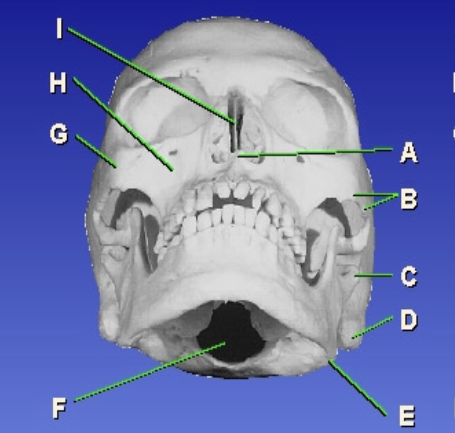
B?
Zygomatic arch
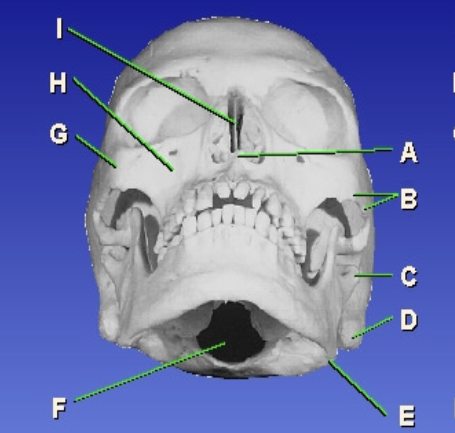
D?
Mastoid process
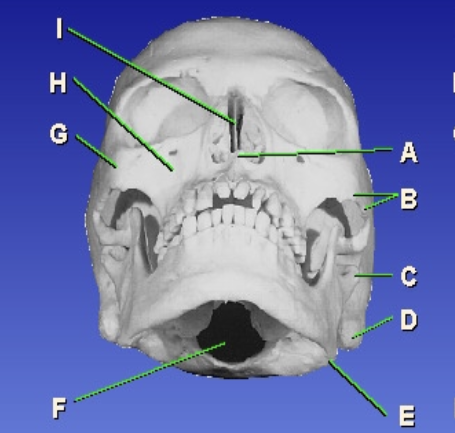
E?
Gonion
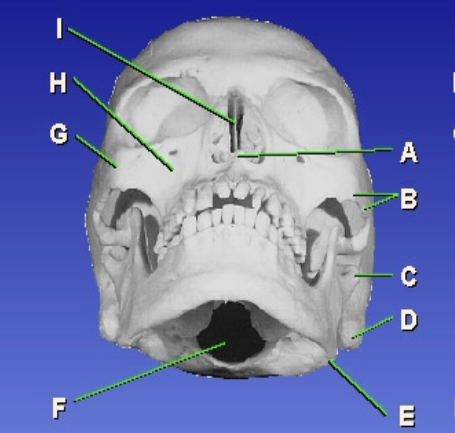
F?
Foramen magnum
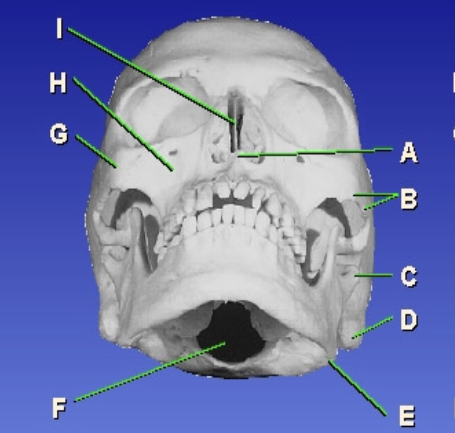
G?
Zygomatic prominence
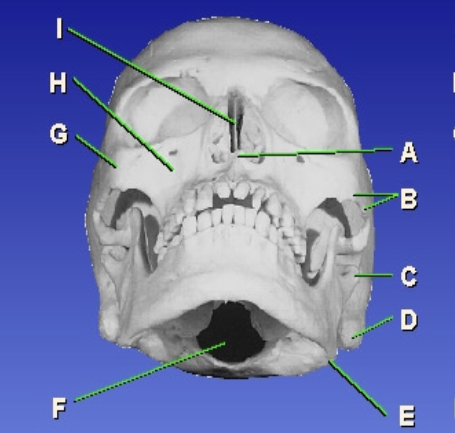
H?
Maxillary sinus
I?
Bony nasal septum
Orbit Composition
Ethmoid bone, frontal bone, sphenoid bone, lacrimal bone, maxilla, palatine, zygoma
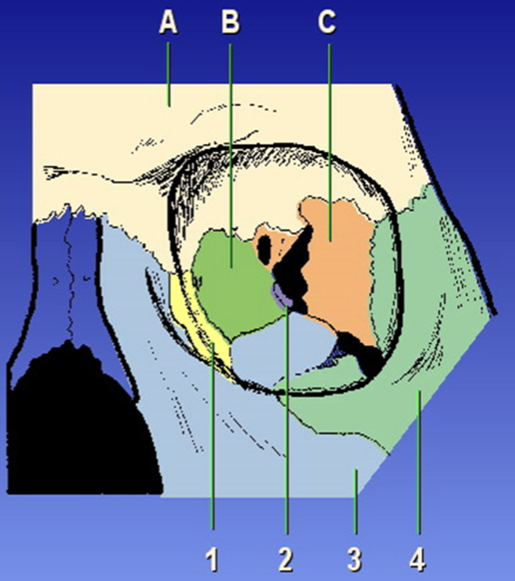
A?
Frontal bone
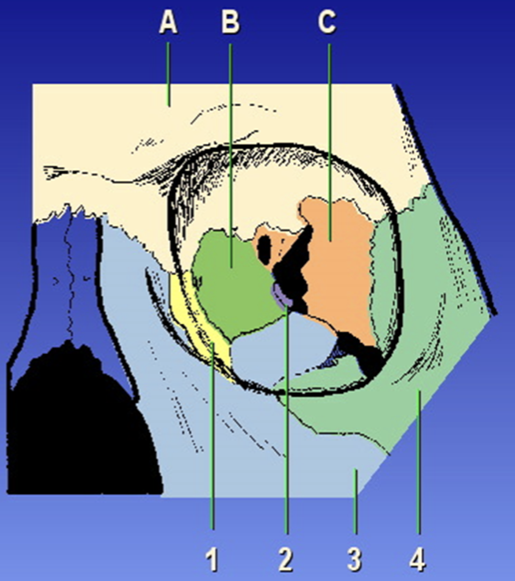
B?
Ethmoid bone
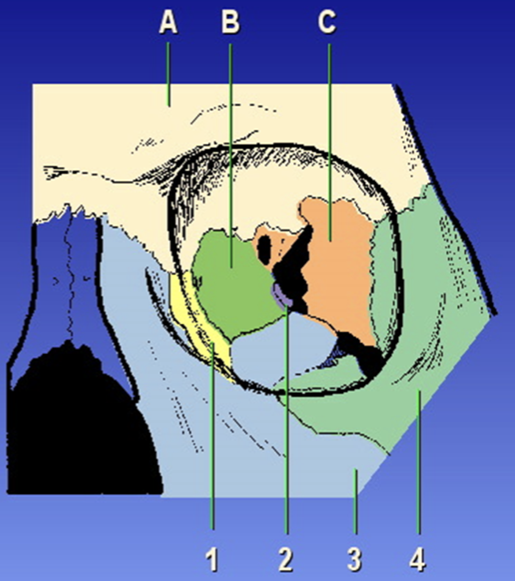
C?
Sphenoid bone
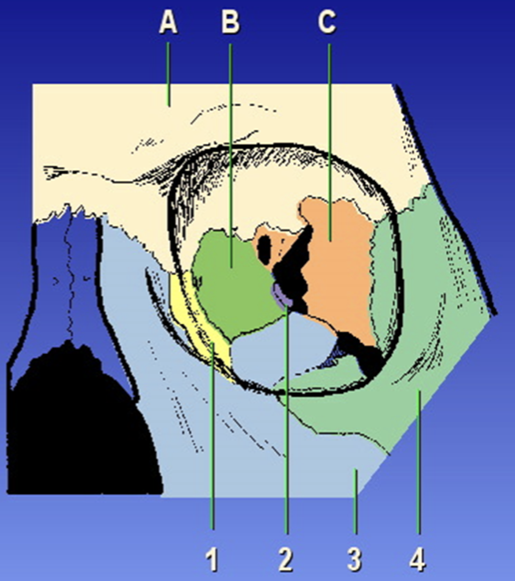
1?
Lacrimal
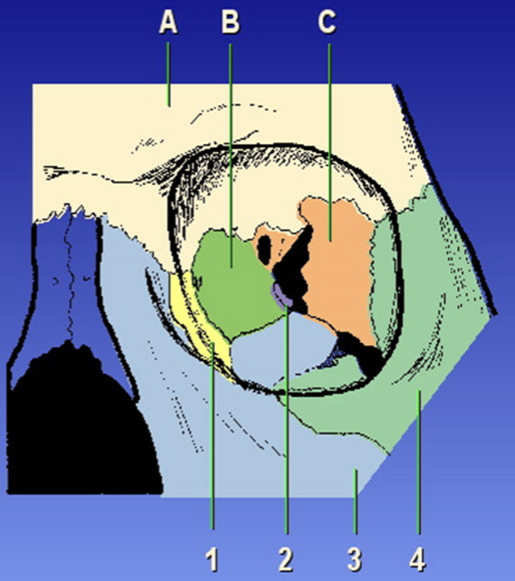
2?
Palatine
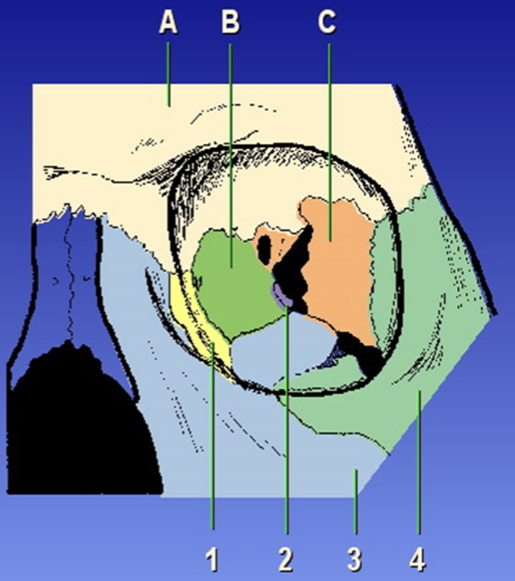
3?
Maxilla
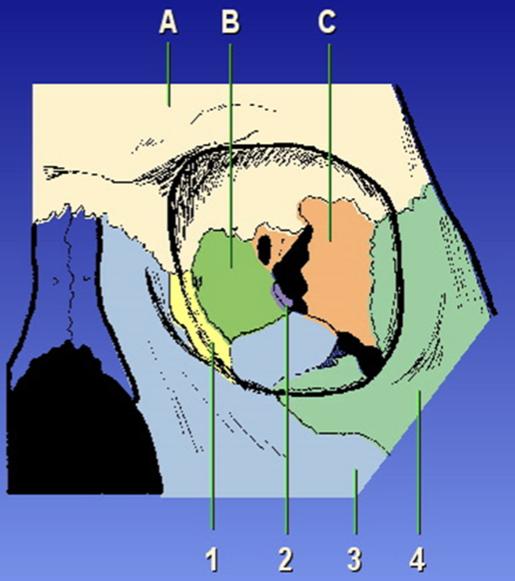
4?
Zygoma
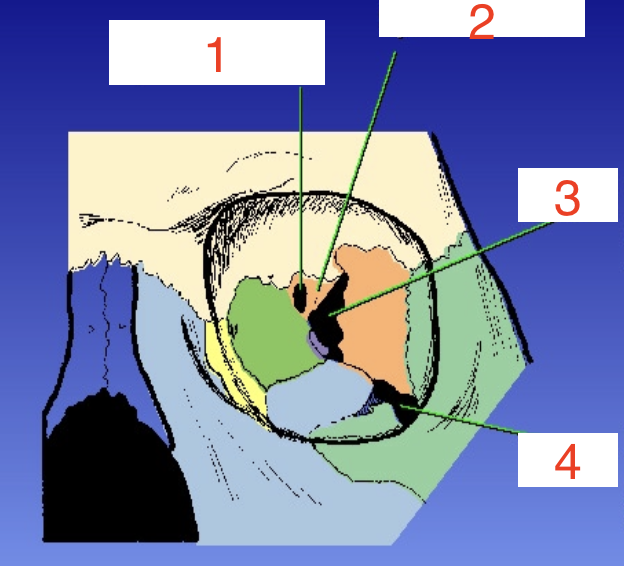
1?
Optic foramen
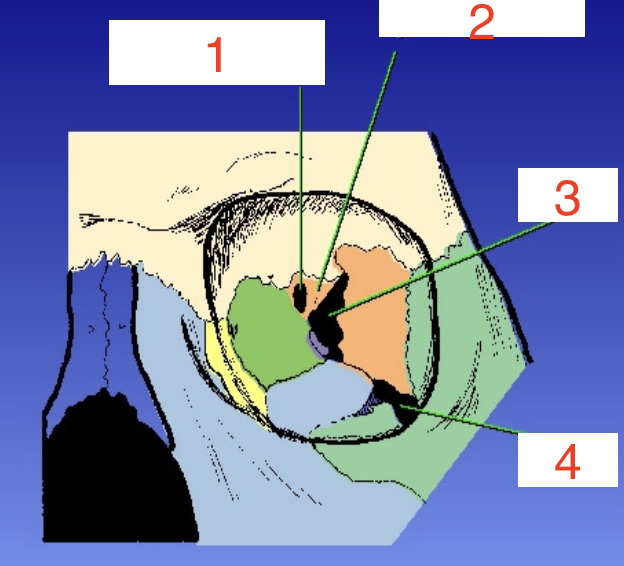
2?
Sphenoid strut
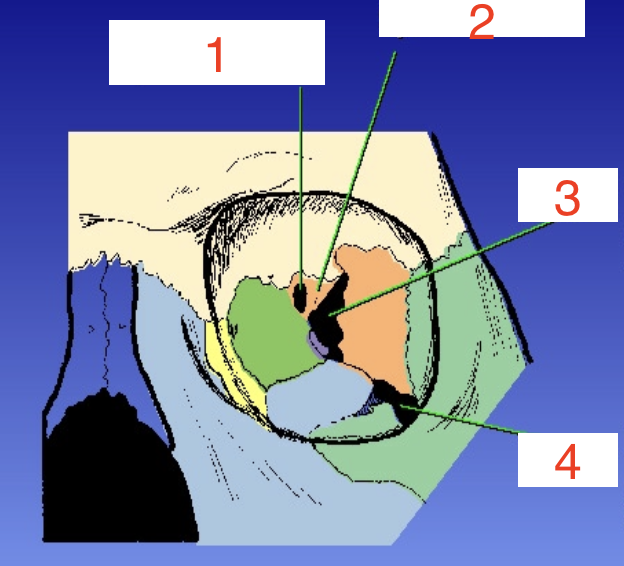
3?
Superior orbital fissure
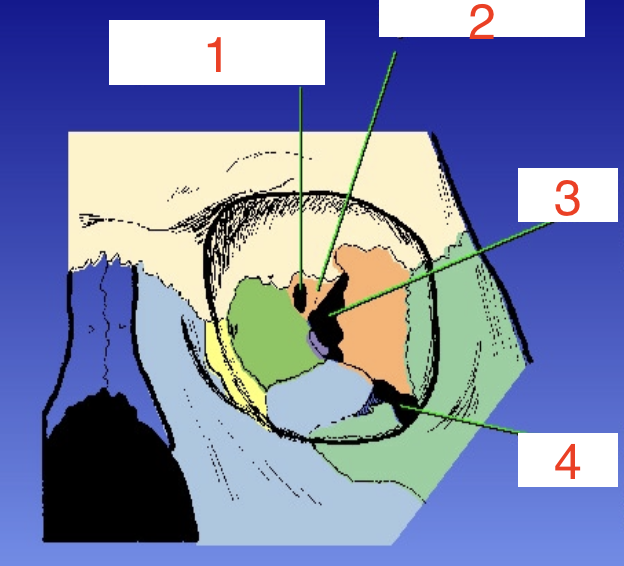
4?
Inferior orbital fissure
What is the superior angle of the orbits?
30°
What is the medial angle of the orbits?
37°
What is the wide, round anterior half of the orbits called?
Base
What is the long, narrow posterior part of the orbits called?
Apex
Blowout Fracture
Result of a forceful blow to the orbit (ex. fist or baseball); causing one or more of the orbital walls to fracture, but the orbital rim stays intact
What “sign” on a CT shows a blowout fracture?
Tear drop
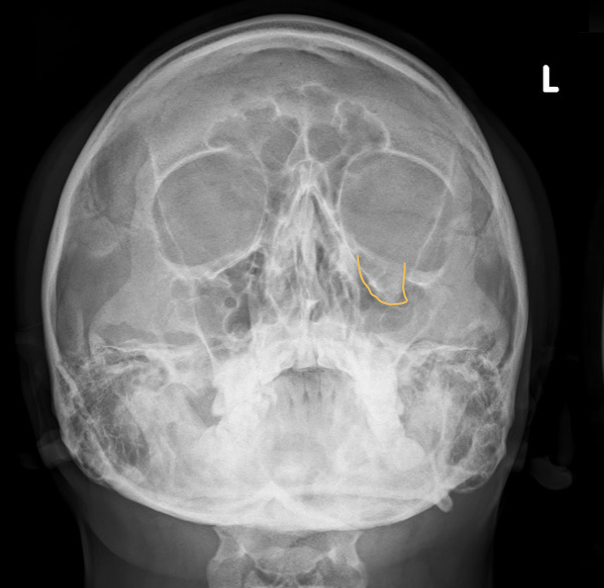
Blowout fracture
Tripod Fracture (ZMC Fracture)
Comprise fractures of the zygomatic arch, inferior orbital rim/anterior and posterior maxillary sinus walls, lateral orbital rim
What does ZMC fracture stand for?
Zygomaticomaxillary complex
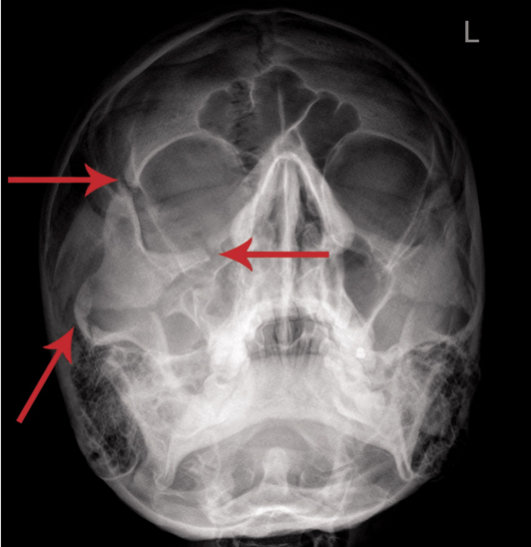
Tripod fracture (ZMC Fracture)
Le Fort Fracture
Bilateral horizontal fracture of the maxillae that causes instability; 3 levels
Le Fort I
Separation of the hard palate from the upper maxilla due to a transverse fracture running through the maxilla and pterygoid plates at a level just above the floor of the nose
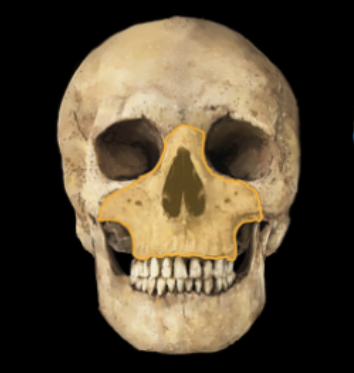
Le Fort II
Fractures transect the nasal bones, medial-anterior orbital walls, orbital floor, inferior orbital rims and finally transversely fracture the posterior maxilla and pterygoid plates
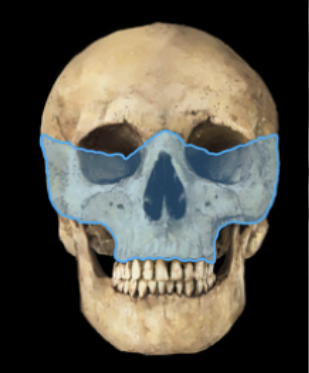
Le Fort III
Highest level Le Fort fracture; results in craniofacial disjunction (essentially separates the maxilla from the skull base)
Le Fort I
Le Fort II
Le Fort III
Zygomatic Arch Fracture
A fracture of the zygomatic arch; may be simple or comminuted
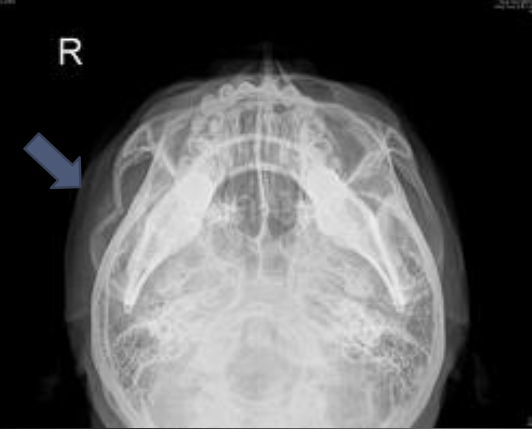
Zygomatic arch fracture
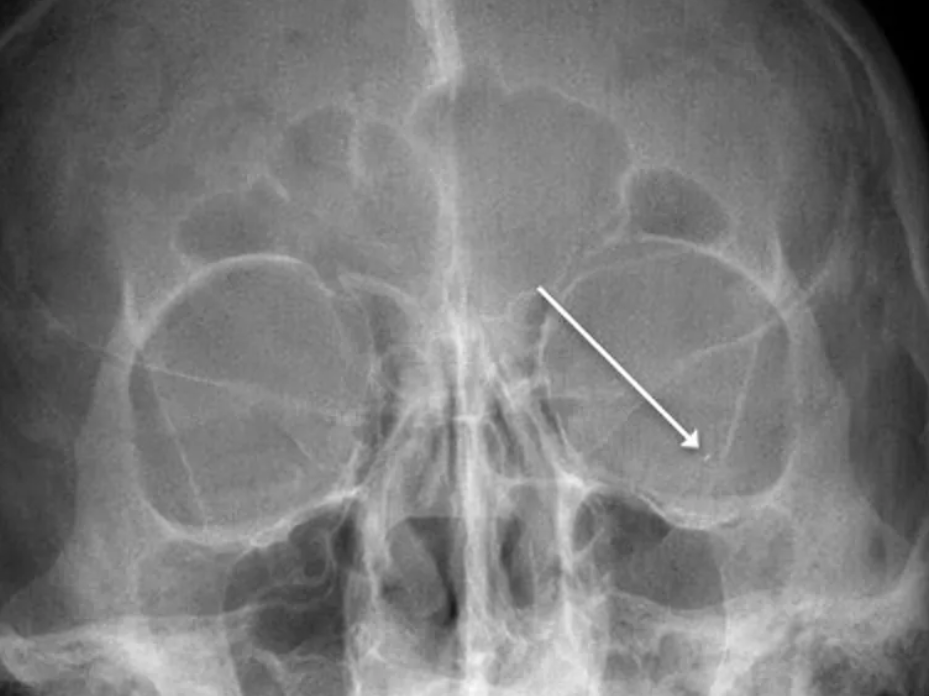
Metal foreign body
Nasal Bone Fracture
Fracture to the nasal bone; often a transverse fracture
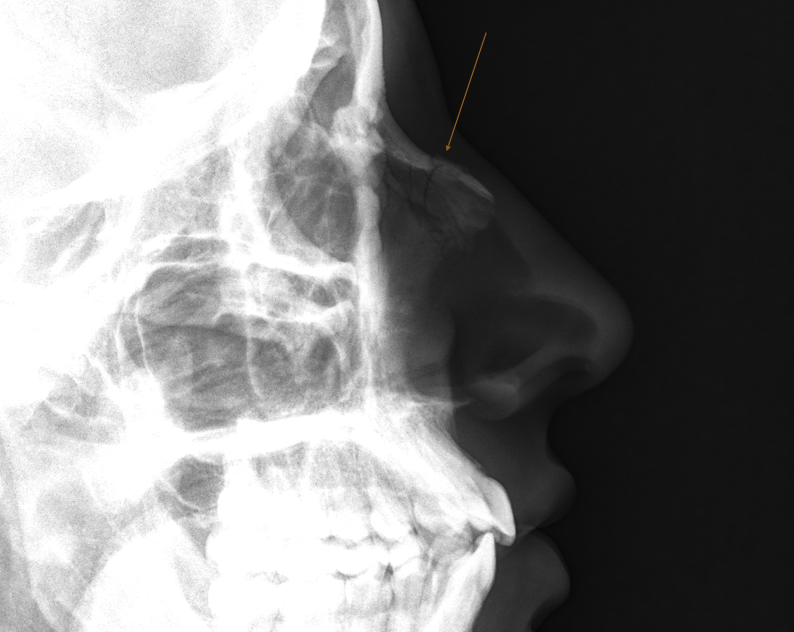
Nasal bone fracture
Parietoacanthial waters collimation
10×12
Left lateral collimation
8×10
PA Axial Exaggerated Caldwell collimation
9×6
SMV collimation
12×10
Facial Bones Routine
Parietoacanthial waters
Left lateral
PA axial exaggerated caldwell
SMV
Nasal Bones Routine
Parietoacanthial waters
Right and left laterals
Parietoacanthial waters (nasal bone) collimation
6×6
Right and left lateral (nasal bone) collimation
4×4
Parietoacanthial Waters
Neck hyperextended
OML 37° with IR
MML & MSP perpendicular to IR
CR exiting acanthion
Left Lateral
Anterior oblique
MSP parallel to IR
IPL & IOML perpendicular to IR
CR at point halfway between outer canthus and EAM
Right and Left Lateral (nasal bone)
Anterior oblique
MSP parallel to IR
IPL & IOML perpendicular to IR
CR at point ½ distal to the nasion
PA Axial Exaggerated Caldwell
Forehead and nose against IR
OML perpendicular to IR
30° caudad tube angle
CR exits the infra-orbital rim
SMV
Hyperextend neck
IOML nearly parallel with IR
Head rested on vertex - MSP perpendicular
CR perpendicular to IOML through gonion, ¾ in superior to EAM
Parietoacanthial Waters Evaluation
Distance between the lateral border of the skull and the orbits should be equal on both sides
Petrous ridges should be projected immediately below the maxillary sinuses
Left Lateral Evaluation
Zygomatic bone centered
Superimposed mandibular rami
Superimposed orbital roofs
Sella turcica in profile