5=TOLERANCE & TRANSPLANTATION
1/182
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Learning Objectives ◼ Review central and peripheral developmental tolerance of lymphocytes that we explored earlier this semester ◼ Describe the role of immune privileged sites and T regs in tolerances ◼ Define the obstacles in organ transplantation and how we induce tolerance
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
183 Terms
TOLERANCE IS FAVORED WHEN: (3 L)
LONG BLANK
LACK BLANK
LOW BLANK
LONG TERM PERSISTENCE OF ANTIGEN
LACK OF ADJUVANT
LOW LEVELS OF CO-STIMULATION
IMMUNOGEN OR TOLEROGEN TABLE WRITE OUT
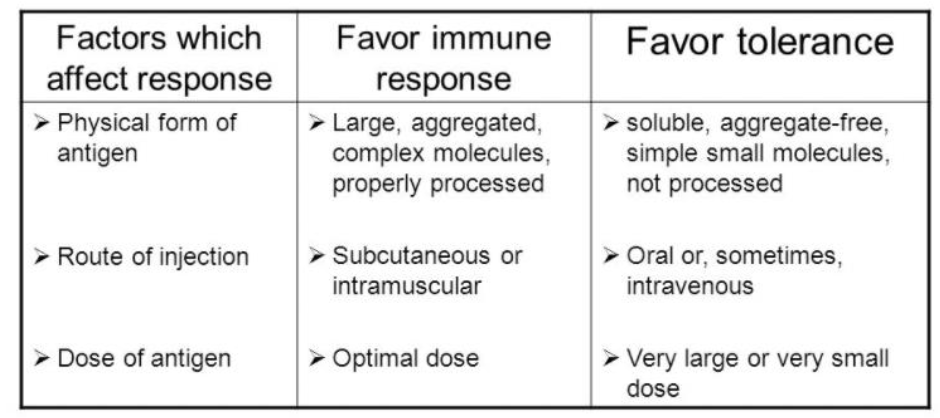
IMMUNOGEN OR TOLEROGEN
PHYSICAL FORM OF ANTIGEN, ROUTE OF INJECTION, DOSE OF ANTIGEN ARE ALL EXAMPLES OF BLANK
FACTORS WHICH AFFECT RESPONSE
IMMUNOGEN OR TOLEROGEN
LARGE, AGGREGATED, COMPLEX MOLECULES, PROPERLY PROCESSED
SUBCUTANEOUS OR INTRAMUSCULAR
OPTIMAL DOSE
ARE ALL EXAMPLES OF BLANK
WHAT FAVOR IMMUNE RESPONSE
IMMUNOGEN OR TOLEROGEN
SOLUBLE, AGGREGATE-FREE, SIMPLE SMALL MOLECULES, NOT PROCESSED
ORAL OR SOMETIMES INTRAVENOUS
VERY LARGE OR VERY SMALL DOSE
ARE ALL EXAMPLES OF BLANK
THOSE THAT FAVOR TOLERANCE
BLANK=PREVENTION OF AN IMMUNE RESPONSE AGAINST SELF STRUCTURES. MANY LAYERS OF THIS!
TOLERANCE (SELF TOLERANCE)
BLANK TOLERANCE-DELETION OF LYMPHOCYTES WITH RECEPTORS THAT RECOGNIZE SELF ANTIGENS BEFORE THEY MATURE DURING LYMPHOCYTE DEVELOPMENT
CENTRAL TOLERANCE
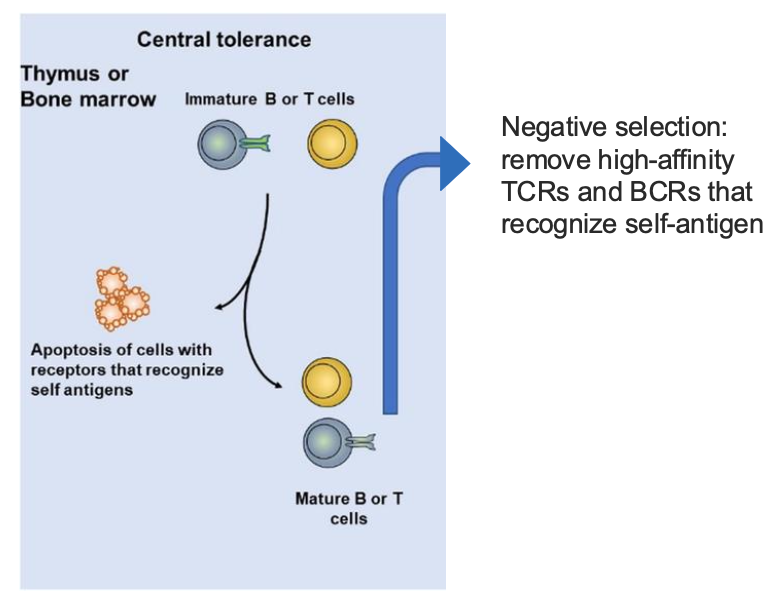
BLANK: REMOVE HIGH-AFFINITY TCRS AND BCRS THAT RECOGNIZE SELF-ANTIGEN
NEGATIVE SELECTION
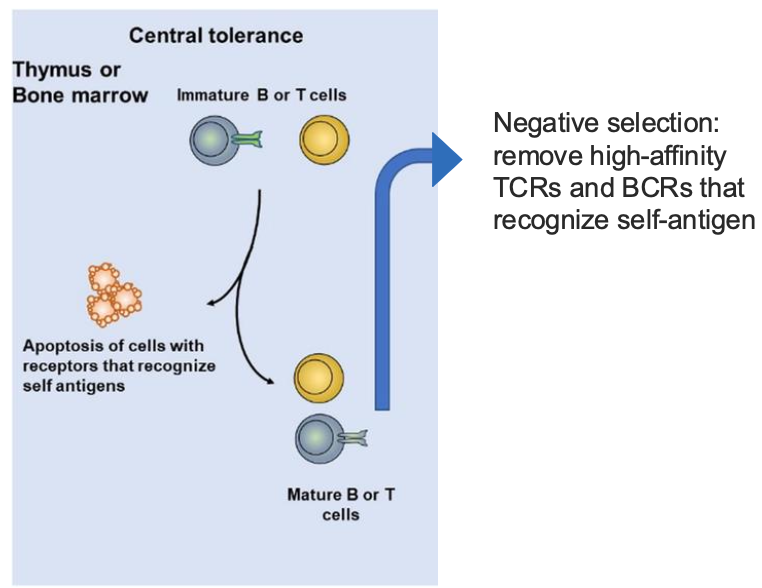
WHAT ARE THE 3 RESULTS OF CENTRAL TOLERANCE IN B CELLS?
NON-SELF REACTIVE B CELL
DELETION
ANERGC B CELKL
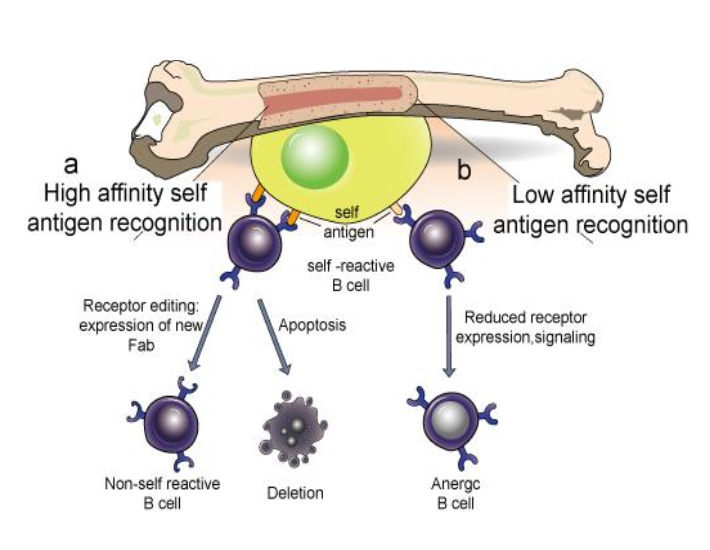
FOR CENTRAL TOLERANCE: NEGATIVE SELECTION OF B CELLS…
REMOVE OR EDIT BCRS THAT BIND TO ANTIGEN
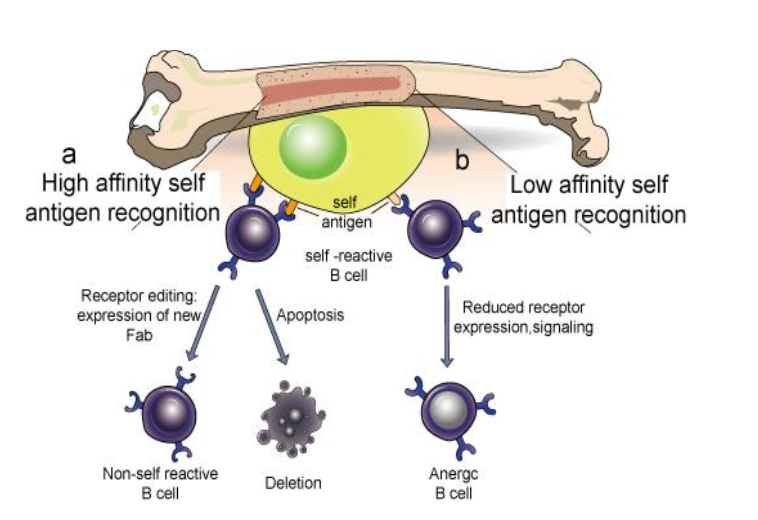
FOR CENTRAL TOLERANCE: T CELLS THYMIC SELECTION (LIST THE 2 BULLETS)
AFFINITY MODEL
USE OF MTEC AND AIRE+ CTECS
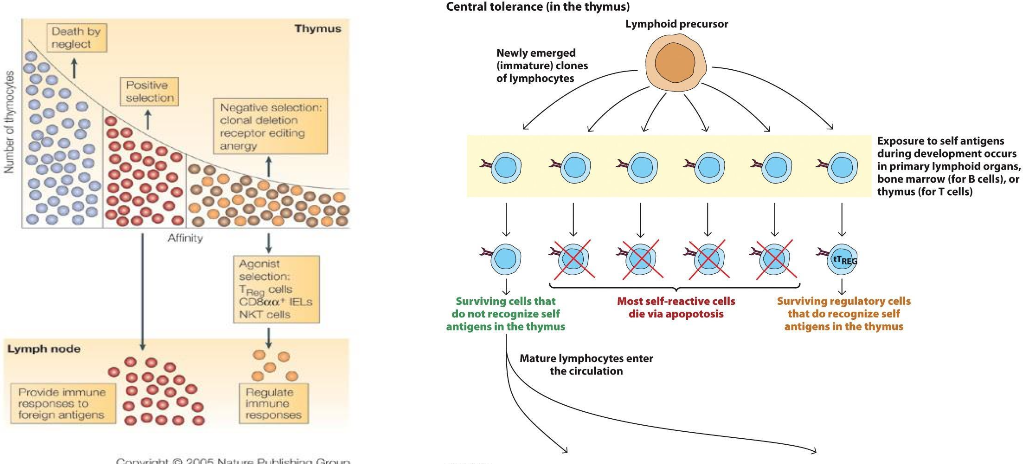
WHAT IS THE MAIN ISSUE WITH CENTRAL TOLERANCE?
“LEAKY” TOLERANCE MAY NOT ELIMINATE ALL SELF-REACTIVE CELLS
WHAT ARE THE REASONS “LEAKY” TOLERANCE TO SELF-REACTIVE CELLS HAPPENS? (HINT 4)
Not all self-antigens are expressed in central lymphoid organs: Tissue-Restricted Antigens
Weakly reactive cells may not be eliminated
Aging affects the thymic environment and this may impair proper negative selection
Genetic defects that impact apoptosis pathways or regulatory pathways
“LEAKY” CENTRAL TOLERANCE
BLANK AFFECTS THE THYMIC ENVIRONMENT—> IMPAIR PROPER NEGATIVE SELECTION
AGING
“LEAKY” CENTRAL TOLERANCE
GENETIC DEFECTS CAN IMPACT WHAT TWO PATHWAYS
APOPTOSIS OR REGULATORY PATHWAYS
WHAT ARE TISSUE-RESTRICTED ANTIGENS?
NOT ALL SELF-ANTIGENS ARE EXPRESSED IN CENTRAL LYMPHOID ORGANS
BLANK TOLERANCE: RENDERS SELF-REACTIVE LYMPHOCYTES NONRESPOSIVENESS OR ACTIVELY GENERATES INHIBITING LYMPHOCYTES (T-REGS)
PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE
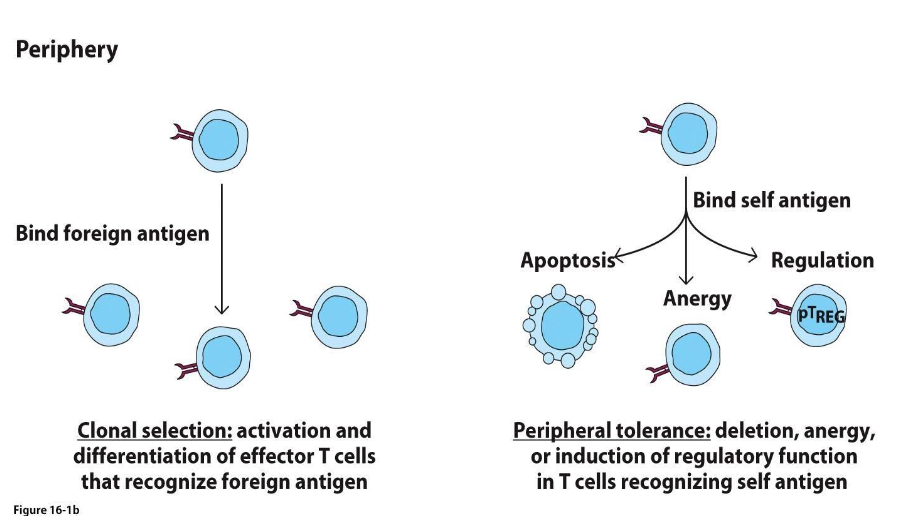
FOR PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE,
BLANK CAN ALSO ARISE FROM A LACK OF COSTIMULATION SIGNAL FROM APC
TREGS
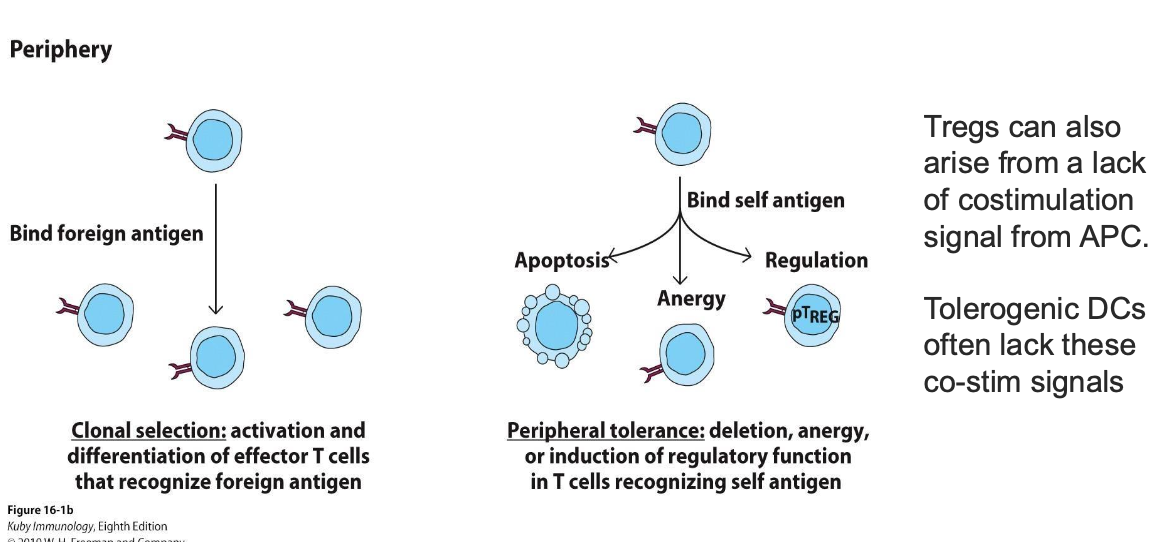
PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE
COMPARED TO TREGS, BLANK OFTEN LACK THESE COSTIMULATION SIGNALS FROM APC
TOLEROGENIC DCS
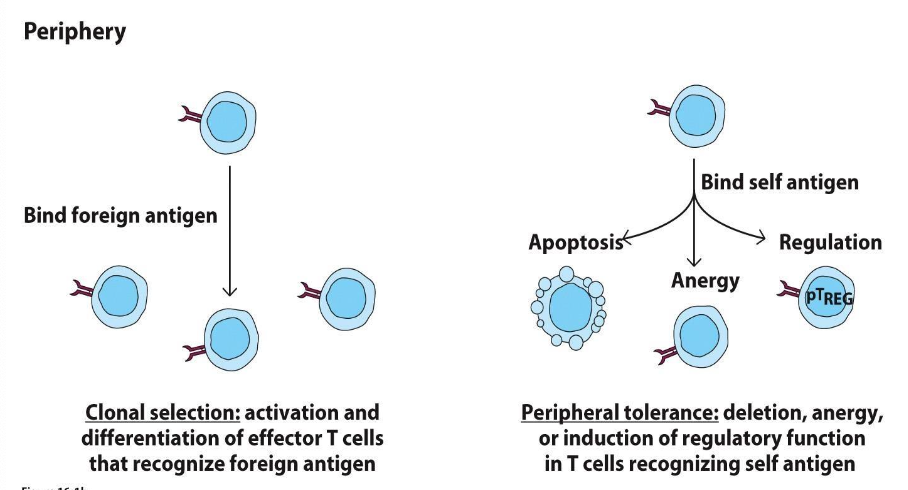
WHAT IS CLONAL SELECTION?
ACTIVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF EFFECTOR T CELLS THAT RECOGNIZE FOREIGN ANTIGEN
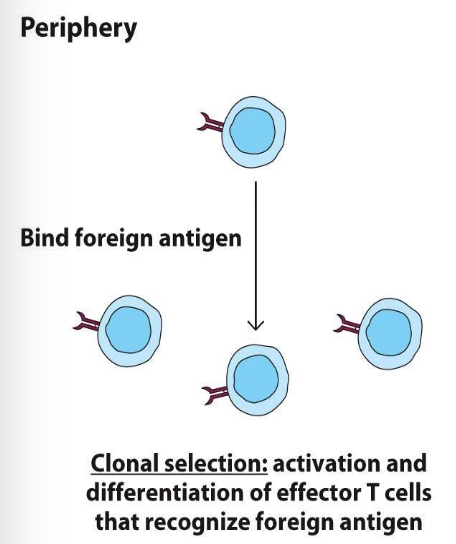
WHAT IS PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE?
DELETION, ANERGY, OR INDUCTION OF REGULATORY FUNCTION IN T CELLS RECOGNIZING SELF ANTIGEN
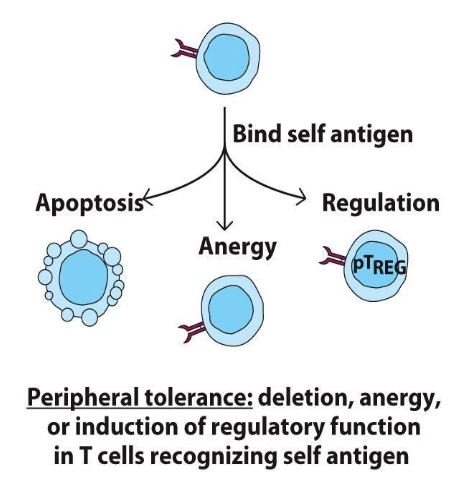
MATCH WHETHER PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE VS. CLONAL SELECTION
BLANK: ACTIVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF EFFECTOR T CELLS THAT RECOGNIZE FOREIGN ANTIGEN
BLANK: DELETION, ANERGY, OR INDUCTION OF REGULATORY FUNCTION IN T CELLS RECOGNIZING SELF ANTIGEN
CLONAL SELECTION: ACTIVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION OF EFFECTOR T CELLS THAT RECOGNIZE FOREIGN ANTIGEN
PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE: DELETION, ANERGY, OR INDUCTION OF REGULATORY FUNCTION IN T CELLS RECOGNIZING SELF ANTIGEN
THIS EXPERIMENT IN NOD (NON-OBESE DIABETIC) MICE IS CALLED WHAT
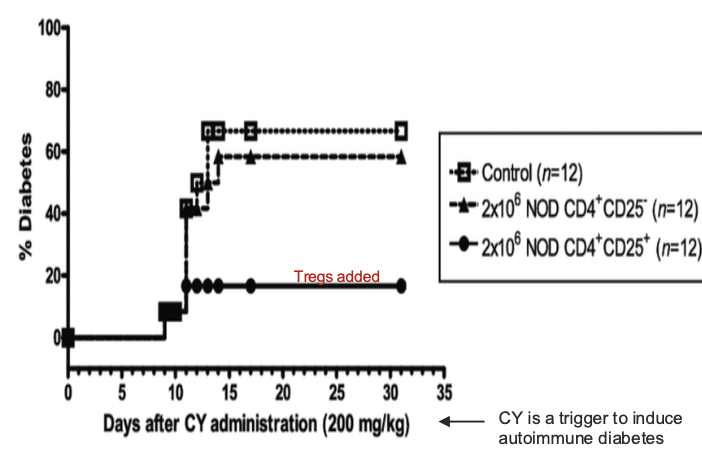
ADOPTIVE TRANSFER
WHAT DOES NOD STAND FOR?
NON-OBESE DIABETIC

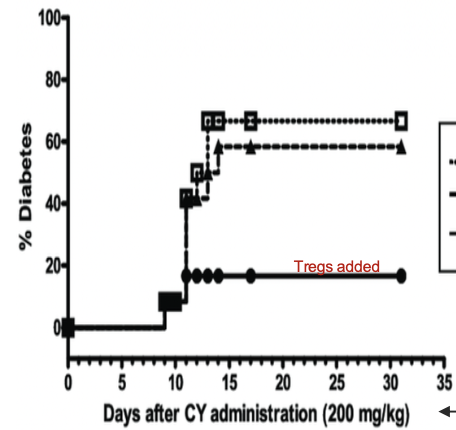
IN THIS DIAGRAM, WHAT DOES CY STAND FOR?
CY=TRIGGER TO INDUCE AUTOIMMUNE DIABETES
THESE ARE ALL CHARACTERISTICS OF WHAT?
Diverse cell type with affinity to self antigen
Defining molecules:
CD25+, CTLA-4, high levels of IL- 2R, and FoxP3 master transcription factor
Clinical significance: Mutation in FoxP3 (X-linked) cause multi-organ autoimmunity
CD4+ T reg
Clinical significance: Without these cells, IBD in mice is common
CD8+ T regs - recognize Ag/MHC and nonclassical lipids
TREGS
WHAT ARE THE 4 DEFINING MOLECULES OF TREGS?
CD25+
CTLA-4
HIGH LEVELS OF IL-2R
FOXP3 MASTER TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR
WHAT IS THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF TREGS?
MUTATION IN FOXP3 (X-LINKED) CAUSE MULTI-ORGAN AUTOIMMUNITY
WHAT IS THE CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CD4+ T REGS
WITHOUT THEM, IBD IN MICE IS COMMON
WHAT RECOGNIZE AG/MHC AND NONCLASSICAL LIPIDS?
CD8+ T REGS
WHAT ARE THE 5 TREG FUNCTIONS? (IHCMD)
1. Inhibitory cytokines (IL-10 & TGF−BETA)
2. High affinity IL-2R sequesters IL-2
3. Cytolysis: Perforin, Granzyme, FasL
4. Metabolism changes → decrease T cell function
Delivery cAMP via gap junctions
5. “Decommission” APCs. Block APCs that bind to same antigen. Engagement of CTLA-4
on Tregs causes the following:
Decrease pro-inflammatory cytokines,
Kynurenine production from tryptophan = immunoinhibitory microenvironment
Decrease surface expression of costimulatory molecules like CD80/86
Decrease MHC class II expression
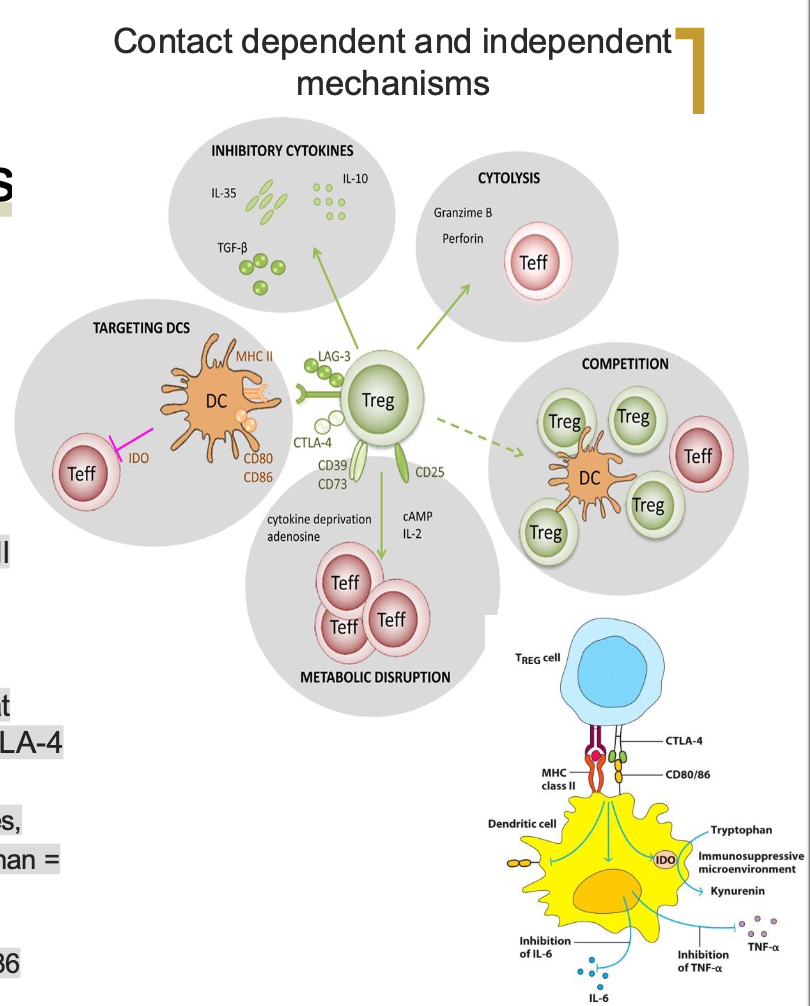
TREG FUNCTIONS:
BLANK PRODUCTION FROM TRYPTOPHAN = IMMUNOINHIBITORY MICROENVIRONMENT
TREG FUNCTIONS:
KYNURENINE PRODUCTION FROM TRYPTOPHAN = IMMUNOINHIBITORY MICROENVIRONMENT
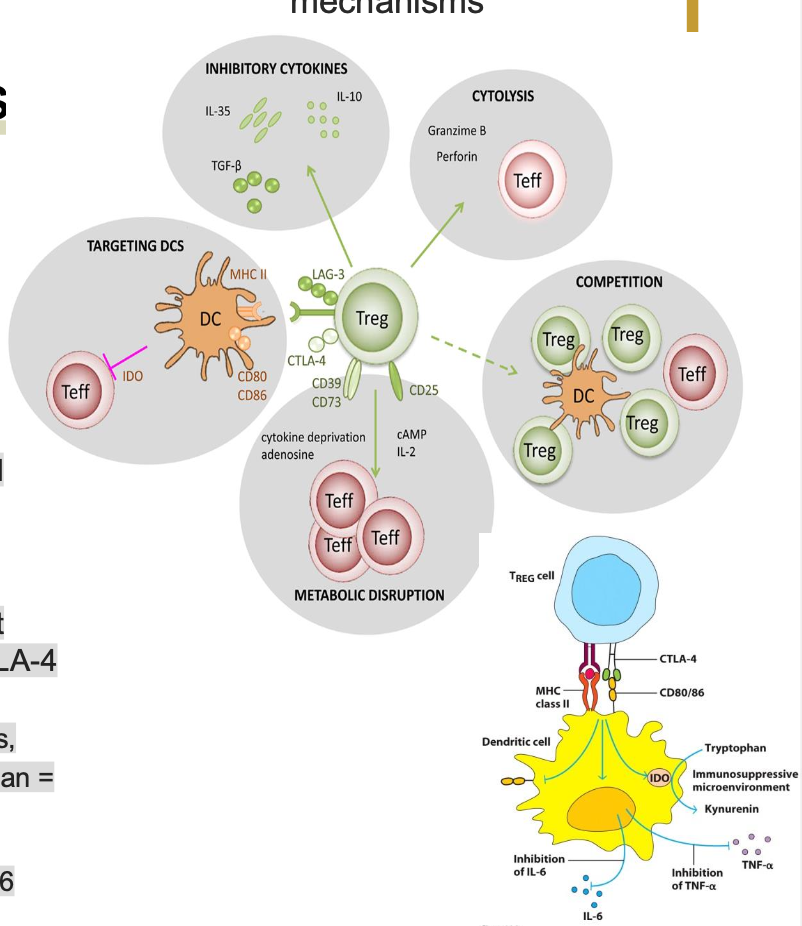
TREG FUNCTIONS
“DECOMMISSION” APCS. BLOCK APCS THAT BIND TO THE SAME ANTIGEN. ENGAGEMENT OF CTLA-4 ON TREGS CAUSES WHAT 4 THINGS? (DKDD)
DECREASE PRO-INFLAMMATORY CYTOKINES
KYNURENINE PRODUCTION FROM TRYTOPHAN=IMMUNOINHIBITORY MICROENVIRONMENT
DECREASE SURFACE EXPRESSION OF COSTIMULATORY MOLECULES LIKE CD80/86
DECREASE MHC CLASS II EXPRESSION
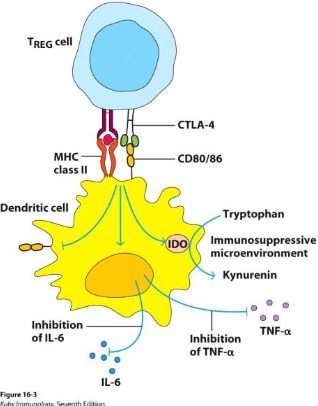
DRAW OUT TREG CELL AND DENDRITIC CELL

T REGS FUNCTION
An interesting “BLANK” effect can occur
A TREG that interacts with an APC can suppress T cells that engage with separate Ag-MHC class II complexes on the APC surface usually through down regulating APC costimulatory signals
T REGS FUNCTION
An interesting “BYSTANDER SUPPRESSION” effect can occur
A TREG that interacts with an APC can suppress T cells that engage with separate Ag-MHC class II complexes on the APC surface usually through down regulating APC costimulatory signals
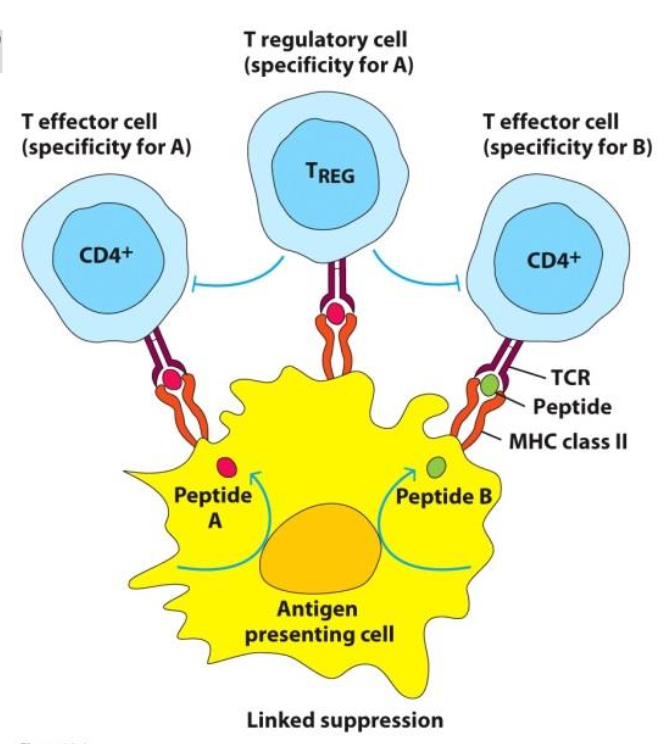
TREGS CAN ARISE FROM WHAT TWO THINGS?
CENTRAL OR PERIPHERAL TOLERANCE
WHAT HAPPENS TO TREG WHEN “BYSTANDER SUPPRESSION” EFEFCT OCCURS?
A TREG that interacts with an APC can suppress T cells that engage with separate Ag-MHC class II complexes on the APC surface usually through down regulating APC costimulatory signals

HOW DOES A TREG (THAT INTERACTS WITH AN APC) SUPPRESS T CELLS THAT ENGAGE WITH SEPARATE AG-MHC CLASS II COMPLEXES ON THE APC SURFACE?
BY DOWN REGULATING APC COSTIMULATORY SIGNALS

WHAT ARE REGULATORY CD8+ T CELLS (HINT: 3 BULLETS)
Complex, heterogenous cell population that is still under investigation
Appear after binding to self Ag-MHC class in the presence of TGF-β cytokine
Deficient mice = colitis (lack of tolerance to commensal
microbes?)
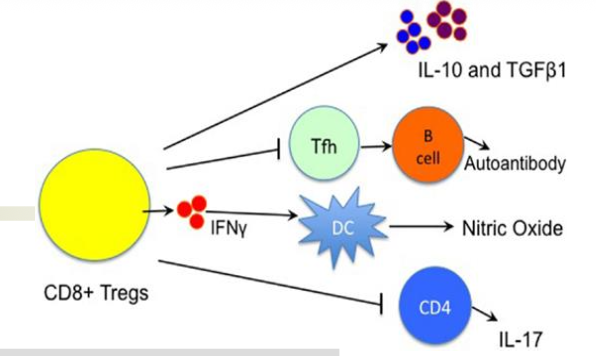
WHAT ARE COMPLEX, HETEROGENOUS CELL POPULATION THAT IS STILL UNDER INVESTIGATION?
REGULATORY CD8+ T CELLS

DEFICIENT MICE=
COLITIS (LACK OF TOLERANCE TO COMMENSAL MICROBES?)

WHEN DO REGULATORY CD8+ T CELLS APPEAR?
AFTER BINDING TO SELF AG-MHC CLASS IN THE PRESENCE OF TGF-BETA CYTOKINE

REGULATORY CD8+ T CELLS APPEAR AFTER BINDING TO SELF AG-MHC CLASS IN THE PRESENCE OF…
TGF-BETA CYTOKINE

HOW ARE CD8+ T REGS SIMILAR TO CD4+ T REGS MECHANISMS TO SUPPRESS ACTIVITY (4 WAYS)
KILL CD4+ T CELL WITH PERFORIN AND FASL
CYTOKINE SECRETION (IL-10 AND TGF-BETA)
INHIBITION AND LYSIS OF APCS
REGULATION OF EFFECTOR CELLS THAT BIND THE SAME AG

HOW DO CD4+ T REGS KILL CD4+ T CELLS?
WITH PERFORIN AND FASL
WHAT IS ANOTHER WAY TO SAY B REGULATORY CELLS
B10 CELLS
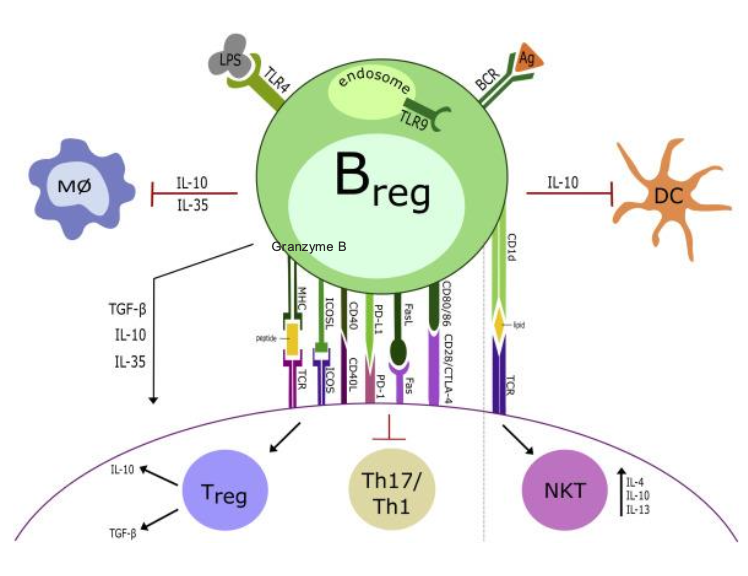
BLANK CELLS
Newly characterized and a lot yet to learn
Secrete IL-10, IL-35, TGf-BETA
They can present antigen in a tolerogenic fashion (low costimulatory molecule expression) → Treg formation
Engagement with Th17 cells may downregulate their function
PD-L1 and FasL expression on Bregs can suppress T cell activation or induce apoptosis
B REGULATORY CELLS (B10 CELLS)
Newly characterized and a lot yet to learn
Secrete IL-10, IL-35, TGf-BETA
They can present antigen in a tolerogenic fashion (low costimulatory molecule expression) → Treg formation
Engagement with Th17 cells may downregulate their function
PD-L1 and FasL expression on Bregs can suppress T cell activation or induce apoptosis
WHAT CELLS MAY GET DOWNREGULATED AFTER ENGAGEMENT WITH TH17 CELLS?
B REGULATORY CELLS (B 10 CELLS)

BLANK AND BLANK EXPRESSION ON BREGS CAN SUPPRESS T CELL ACTIVATION OR INDUCE APOPTOSIS
PD-L1 AND FASL EXPRESSION ON BREGS CAN SUPPRESS T CELL ACTIVATION OR INDUCE APOPTOSIS

HOW CAN B10 CELLS FORM TREGS?
THEY CAN PRESENT ANTIGEN IN A TOLEROGENIC FASHION (LOW COSTIMULATORY MOLECULE EXPRESSION)

WHAT 3 THINGS DO B10 CELLS SECRETE?
IL-10
IL-35
TGF-BETA

WHAT CELLS ARE NEWLY CHARACTERIZED AND A LOT TO LEARN
B REGULATORY CELLS (B10)

WHAT ARE MDSCS?
MYELOID DERIVED SUPPRESSOR CELLS
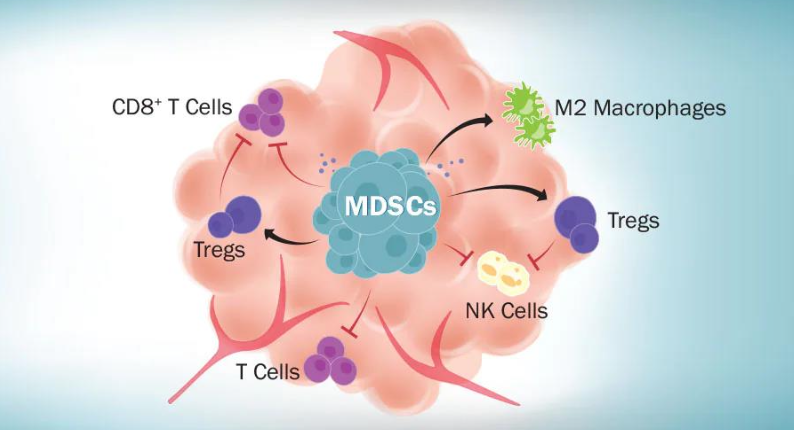
WHERE ARE MDSCS FOUND AND THIS LEADS TO WHAT?
AT TUMOR SITES—> POOR PROGNOSIS

HOW DO MDSCS REDUCE IMMUNE RESPONSE (HINT: 3 THINGS)
INHIBITORY CYTOKINES
CHEMICALS
IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE CELL RECEPTORS

BLANK ARE IMMATURE HETEROGENOUS GROUP OF MYELOID CELLS (GRANULOCYTES AND MONOCYTES) THAT ARRIVE AT SITES OF INFECTION, INFLAMMATION, OR TUMORS
MYELOID DERIVED SUPPRESSOR CELLS (MDSCS) ARE IMMATURE HETEROGENOUS GROUP OF MYELOID CELLS (GRANULOCYTES AND MONOCYTES) THAT ARRIVE AT SITES OF INFECTION, INFLAMMATION, OR TUMORS

MDSCS ARRIVE AT WHAT THREE SITES?
INFECTION, INFLAMMATION, TUMORS

JUST FOR REFERENCE: MYELOID DERIVED SUPPRESSOR CELLS: MECHANISMS OF IMMUNE INHIBITION, WHAT IS THIS DIAGRAM SHOWING?
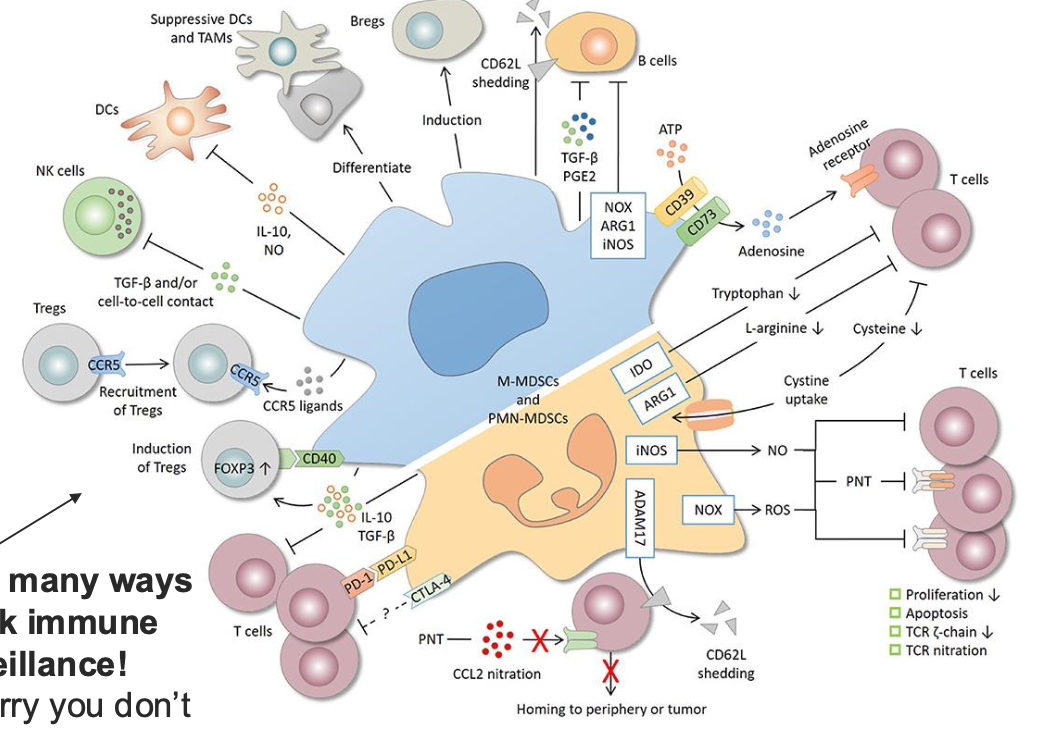
WOW, SO MANY WAYS TO BLOCK IMMUNE SURVEILLANCE!
TOLERANCE
BLANK-TISSUE THAT IS PROTECTED FROM IMMUNE ATTACK
TOLERANCE
IMMUNE PRIVILEGED SITES-TISSUE THAT IS PROTECTED FROM IMMUNE ATTACK
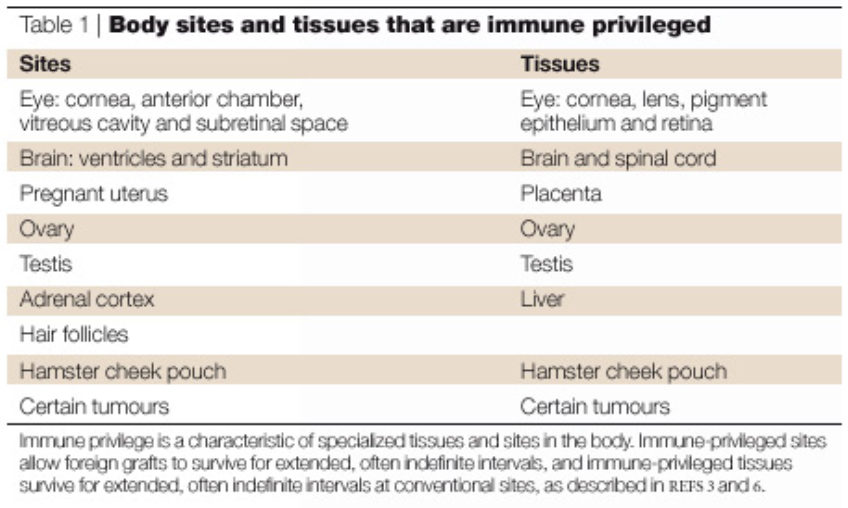
WHAT ARE IMMUNE PRIVILEGED SITES?
TISSUE THAT IS PROTECTED FROM IMMUNE ATTACK

What are the 3 major things in tolerace?
antigen sequestration
restricted immune entry
limited immune cells present
tolerance
what is antigen sequestration?
Lack of lymphatic drainage (anterior and lens of eye)
Ags are isolated from interaction with immune cells

tolerance
what is restricted immune entry?
blood-brain barrier

tolerance
what is limited immune cells present?
few immune cells (cornea)

in tolerance, damage to such areas may expose their blank to immune responses, initiating blank
antigen, damage potential

Immune tolerance in pregnancy
blank
Separate fetal and maternal blood systems
T regs present
Present only certain MHC I isotypes to avoid T cell and NK cell activation
Syncytium – fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through
Special uterine and fetal glycoproteins suppress immune response
Immune tolerance in pregnancy
Placenta-immunological barrier
Separate fetal and maternal blood systems
T regs present
Present only certain MHC I isotypes to avoid T cell and NK cell activation
Syncytium – fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through
Special uterine and fetal glycoproteins suppress immune response
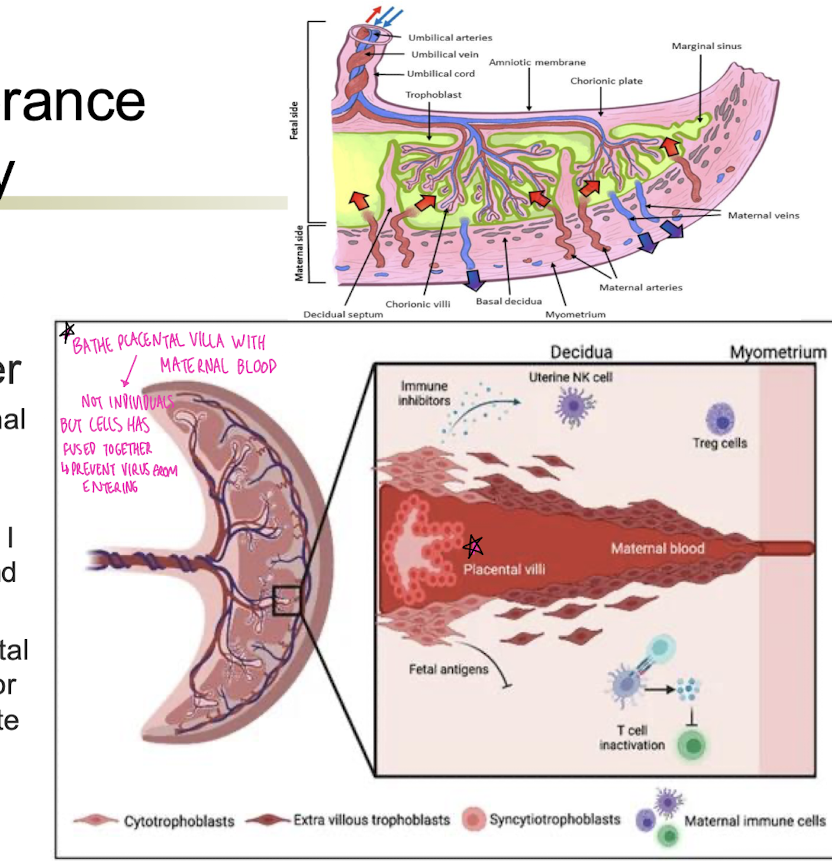
during pregnancy, more at risk for blank
during pregnancy, more at risk for infections!

immune tolerance in pregancy:
placentra-immunological barrier (list the 5 characteristics)
Separate fetal and maternal blood systems
T regs present
Present only certain MHC I isotypes to avoid T cell and NK cell activation
Syncytium – fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through
Special uterine and fetal glycoproteins suppress immune response

the placenta presents what to avoid t cell and nk cell activation?
only certain MHC I isotypes

immune tolerance in pregnancy, what suppress immune response?
special uterine and fetal glycoproteins

blank-fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through
syncytium-fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through

immune tolerance in pregnancy
placenta-immunological barrier
what is syncytium?
fused placental cells so no immune cells or maternal blood can migrate through

what induces tolerance?
transplantation

what are the current goals of transplantation?
minimize graft rejection
demand is high
availability of genetically identical donors is low
minimize rejection without suppressing entire immune response
for timeline of transplantation:
blank pioneered kidney transplantation and conducted the first non-twin living kidney transplant in 1960 and develop a perfusion instrument to preserve kidneys for up to 50 hours.
dr samuel kountz

dr samuel kountz (4 facts)
pioneered kidney transplantation
conducted first non-twin living kidney transplant
in 1960
develop a perfusion instrument to preserve kidneys for up to 50 hours

Who were the two doctors mentioned in regards to organ transplantations?
Dr Samuel Kountz
Dr Velma Scantlebury-White
transplantation immunology
how many corneal tissue grafts (2016)
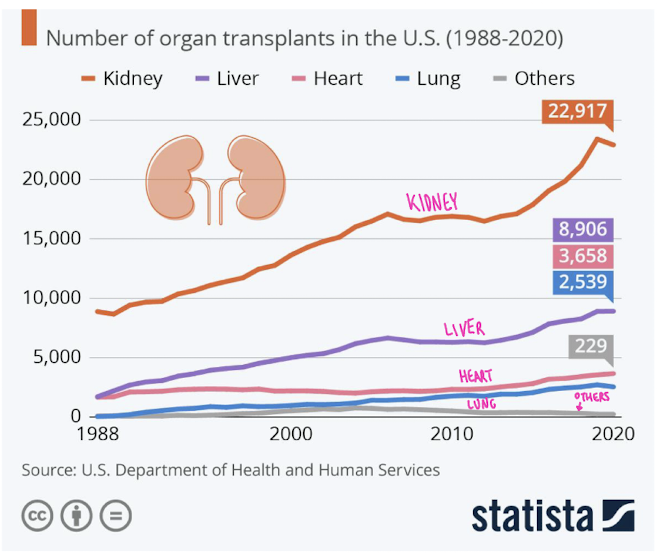
46,000!
Transplantation terminology
blank = self tissue grafted to another self area (skin grafts, blood vessels for bypass heart surgery)
blank = transplant between genetically identical individuals (inbred strains of mice, identical twins)
blank = tissue transferred between genetically different members of the same species (majority of transplant cases)
blank = tissue transferred between different species (baboon heart into a human)
blank – tissue that share sufficient antigen similarity to decrease chance of rejection
Transplantation terminology
Autograft = self tissue grafted to another self area (skin grafts, blood vessels for bypass heart surgery)
Isograft = transplant between genetically identical individuals (inbred strains of mice, identical twins)
Allograft = tissue transferred between genetically different members of the same species (majority of transplant cases)
Xenograft = tissue transferred between different species (baboon heart into a human)
Histocompatibility – tissue that share sufficient antigen similarity to decrease chance of rejection
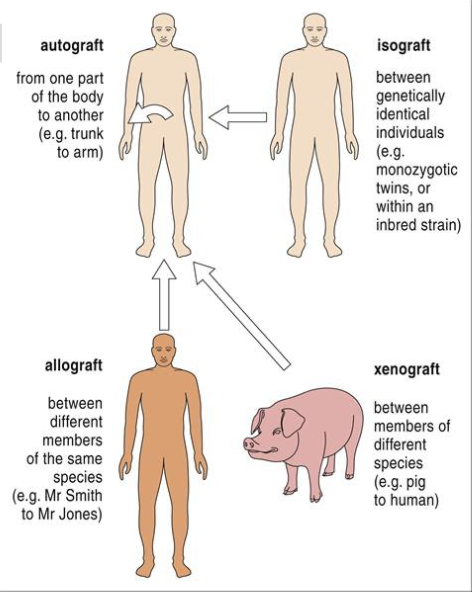
transplantation terminology
what is an autograft?
self tissue grafted to another self area
skin grafts, blood vessels for bypass heart surgery

transplantation terminology
what is an isograft?
transplant between genetically identical individuals
(inbred strains of mice, identical twins)

transplantation terminology
what is an allograft?
tissue transferred between genetically different members of the same species
(majority of transplant cases)

transplantation terminology
what is a xenograft?
tissue transferred between different species (baboon heart into a human)

transplantation terminology
what is histocompatibility?
tissue that share sufficient antigen similarity to decrease chance of rejection

List the xenotransplantation 4 facts with help
blank slices of chimpanzee testes in humans (1920s)
chimpanzee kidney survived blank months in one human (1963-64), rejected in blank # of other humans
blank animal liver survived 70 days in a human (1992)
genetically modified blank animal body part worked for 57 hours in 2 brain-dead patients
List the xenotransplantation 4 facts with help
“zest for life” slices of chimpanzee testes in humans (1920s)
chimpanzee kidney survived 9 months in one human (1963-64), rejected in 12 other humans
baboon liver survived 70 days in a human (1992)
genetically modified pig kidney worked for 57 hours in 2 brain-dead patients
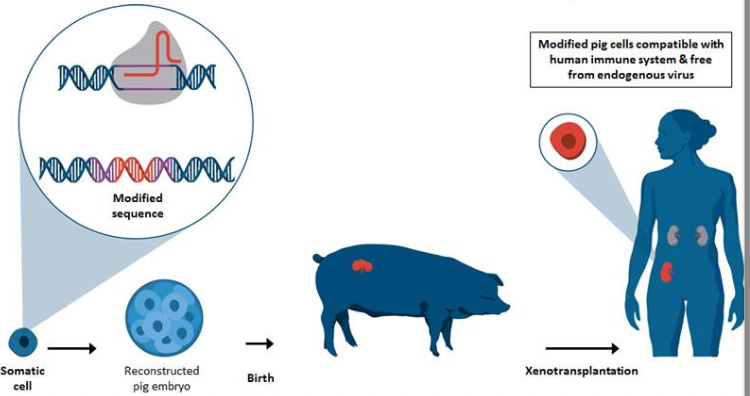
Xenotransplantation
Why did they do “zest for life” slices of chimpanzee testes in humans in 1920s?
to increase labido (sex drive)
macrophages clean this up after infection happened—> stopped doing it!
draw out the xenotransplantation model

What are the 2 reasons they use pig transplants in humans?
very fast to reproduce
similar organ size as humans

What are the 3 issues with pig transplants?
they have alpha-gal (sugar molecule) that we do not have
they lack complement inhibitors like DAF and protectin
Don’t know all their viruses

list the 4 facts about xenotransplantation (zcbg)
“zest for life” slices of chimpanzee testes in humans (1920s)
chimpanzee kidney survived 9 months in one human (1963-64), rejected in 12 other humans
baboon liver survived 70 days in a human (1992)
genetically modified pig kidney worked for 57 hours in 2 brain-dead patients

New breakthroughs in transplantation
face transplant (partial 2005, full 2010)
whole face and eye transplant (2023)
then showed video with patient one year later
From the video on new breakthroughs in transplantation what term did they use for transplant not rejected?
It was viable!
blank
“matching”
1. Blood group Ag differences = most intense graft rejections. They are the first items to be matched between donor/recipient.
2. MHC compatibility is determined next. Siblings/parents are first choice due to better matches
3. Cross-Matching. A blood test that determines compatibility. Analyzes circulating Abs, especially to HLA
4. Anti-rejection drugs allow organ transplants between completely mismatched people
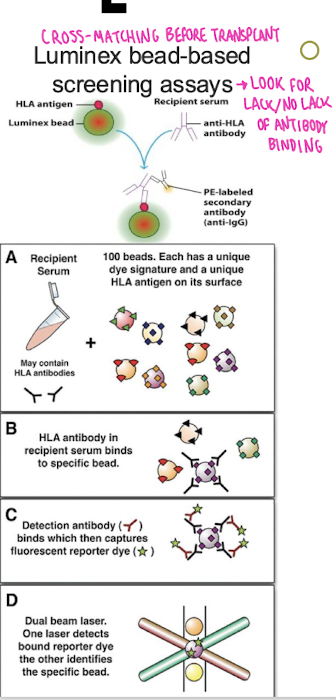
Transplant success
“matching”
1. Blood group Ag differences = most intense graft rejections. They are the first items to be matched between donor/recipient.
2. MHC compatibility is determined next. Siblings/parents are first choice due to better matches
3. Cross-Matching. A blood test that determines compatibility. Analyzes circulating Abs, especially to HLA
4. Anti-rejection drugs allow organ transplants between completely mismatched people

“matching” is part of what?
transplant success

what leads to the most intense graft rejections
blood group ag differences

what are the first items to be matched between donor/recipient
Blood group Ag differences

What does luminex bead-based screening assays look for?
look for lack/no lack of antibody binding

what is determined after blood group Ag differences in transplant success
MHC compatibility
siblings/parents are first choice in what due to better matches
MHC compatibility
What is the blood test that determines compatibility. Analyzes circulating Abs, especially to HLA
Cross-matching Department: Pediatrics
