AP BIO UNIT 3 - Enzymes
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What are some physical indicators of a reaction? (4)
1) Fizzing
2) Gas
3) Color Change
4) Temperature
Exothermic Reaction
When heat energy is released
Endothermic
When heat energy is absorbed
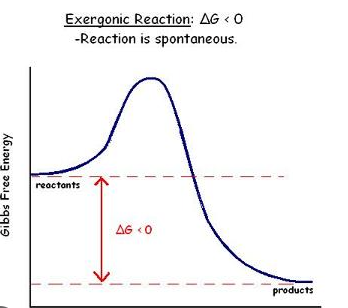
Exergonic Reaction (Spontaneous)
Occurs when reactions come close to each other;
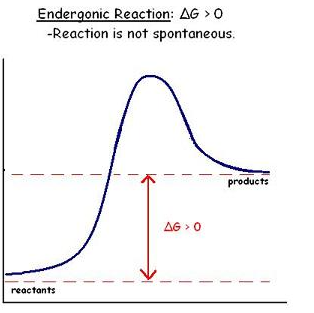
Endergonic Reaction (Not Spontaneous)
Reactions that require a sort of activation energy to occur.
When an exergonic reaction releases heat energy….
That energy can be used to power an endergonic reaction
Name the two ways to start a reaction
1) Activation energy
2 Enzymes
Enzymes
biological organic catalysts
ALWAYS PROTEINS
Allow for chemical reactions to occur by lowering the Activation Energy
What are some environmental factors that decrease enzyme activity?
1) temp
2) PH
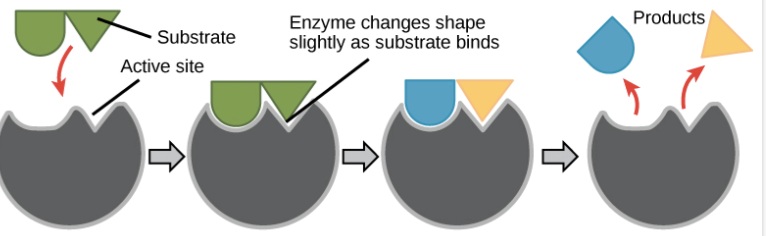
Active Site
the part of the enzyme where the reaction occurs
Hydrolytic Enzymes
enzymes that break things down
Induced Fit Model
enzymes can slightly change/adjust to its active site so that it can fit the substrate (the enzyme flexes)
Macromolecule →(hydrolysis) building block
←(synthesis)
The types of enzymes.
What happens to an enzyme if you increase and decrease the temperature?
the rate of the reaction occurs faster, then the enzyme will denature. If temp decreases, the rate of the reaction becomes slower, so there will be no collisions at all.
Coenzyme
an organic compound that binds to the active site of the enzyme and assists the enzyme.
Cofactors
Coenzymes that are inorganic
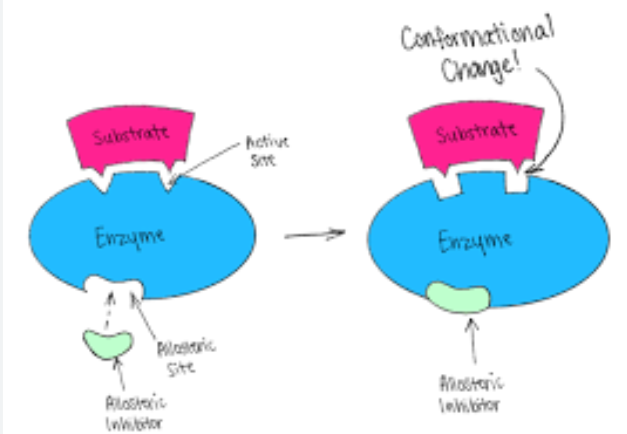
Allosteric site
the product of the enzyme that attaches to a different part of the enzyme to temporarily shut it off, until it starts again to repeat the process..
Feedback Inhibition
The product binds to the allosteric site and deactivates the enzyme
Inhibitors (name the types and definition)
inhibit chemical reactions
1) competitive inhibitor
2) non-competitive inhibitor
competitive inhibitor
competes with the substrate for the active site
noncompetitive inhibitor
particle binds to the allosteric site.
Aerobic Respiration (what is the formula, where does it occur, and what kind of reaction is it?)
Occurs in the mitochondria
C6H12O6 + O2 →(enzymes) CO2 + H2O + 38/36 ATP
This is an exergonic,exothermic, spontaneous reaction. It releases heat energy
You can only transfer 33% of chemical energy (not efficient)
What cells go through Aerobic respiration?
ALL EUKARYOTIC CELLS,
some prokaryotic cells go through this across their cell membrane
Anaerobic Respiration (what is the formula, where does it occur, and what kind of reaction is it?)
Occurs in the cytosol
C6H12O6 →alcohol/ethanol + CO2 + 2ATP
Another word for anaerobic Respiration?
Fermentation
2 Types of Anaerobic Respiration
Fermentation (yeast does this)
Lactid Acid Fermentation (animals do this) : C6H12O6 →lactid acid + 2ATP
Oxidation
hydrolysis: losing electrons and breaking bonds increasing the charge and making smaller molecules
Reduction
Synthesis: gaining electrons and forming bonds (reducing the charge and making a bigger molecule)
High energy oxidizes to…
Low energy
ATP →
ADP+ inorganic molecule
NADH →
NAD+
FADH2→
FAD
NADPH
NADP+
In order for cellular respiration to occur, what HAS to occur?
Glycolysis
When you add a phosphate to a molecule its called
Phosphorylation: makes the molecule more energetic and unstable so that it can split
Enzymes are the cause of
Phosphorylation
What class of enzymes Phosphorylate, and what does it break into?
kinases
It breakes molecules into 2 , 3 carbon sugars(PGAL)
PGAL
Phosphoglyceraldehyde
Intermediates
the middle reactions in the oxidation process.

Glycolysis Reaction
-
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
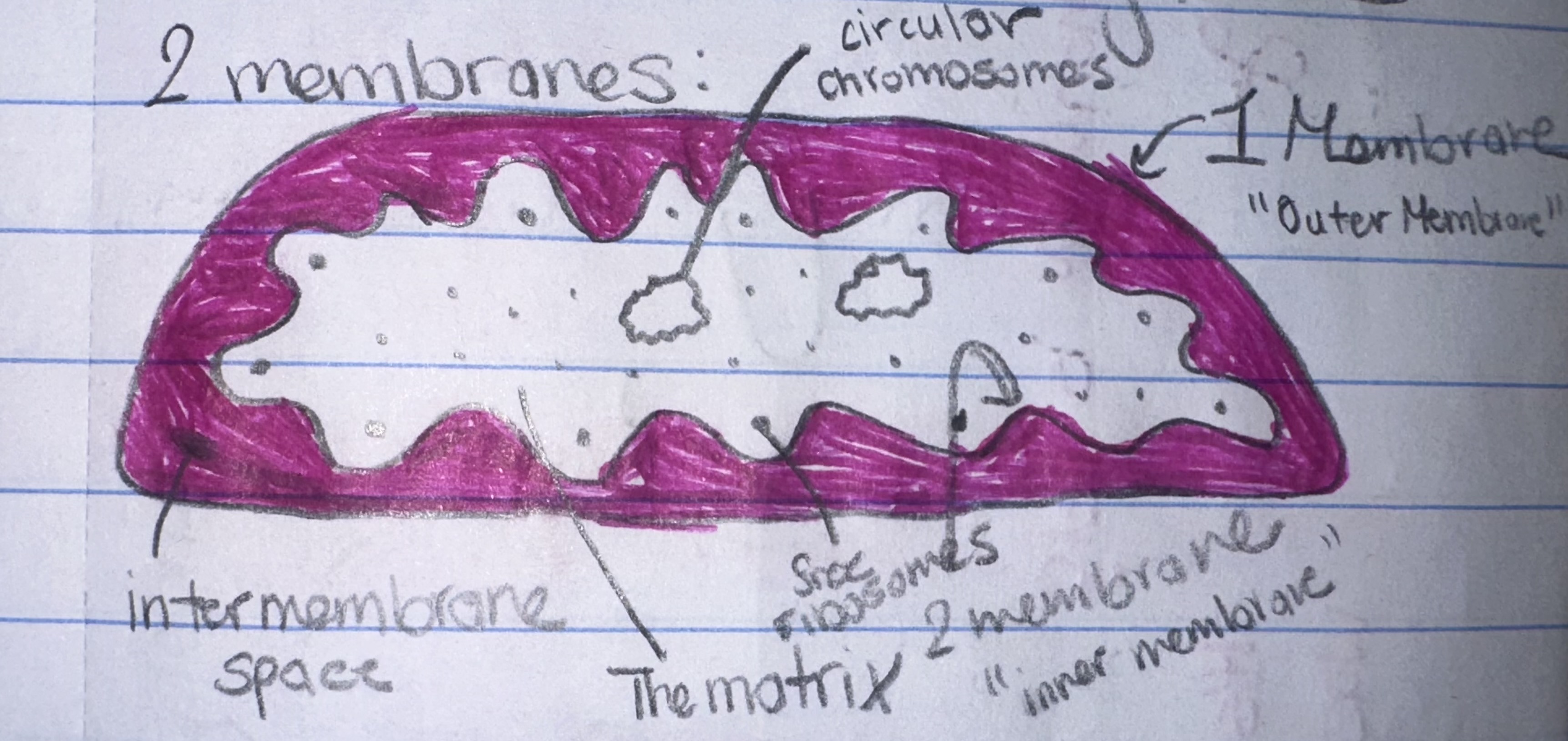
The Mitochondria
Has 2 membranes
1) The outer membrane
2) intermembrane space
Self replicating
Name the compartments(spaces) of the mitocondria
The intermembrane space
the matric
How do Prokaryotic cells resemble the mitocondria?
they have free ribosomes
When you hear double membrane, think of
endocytosis
The Endosymbiotic Theory
There is a symbiotic relationship b/w the cell and the mitochondria
(They CANNOT live w/o each other)
Membrane Bound Organelle Diagram
-
Apoptosis
The suicide program
If there is something wrong with the cell, the cell will die.
In order for cellular respiration to occur…
glycolysis has to occur.
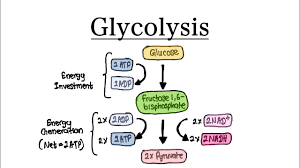
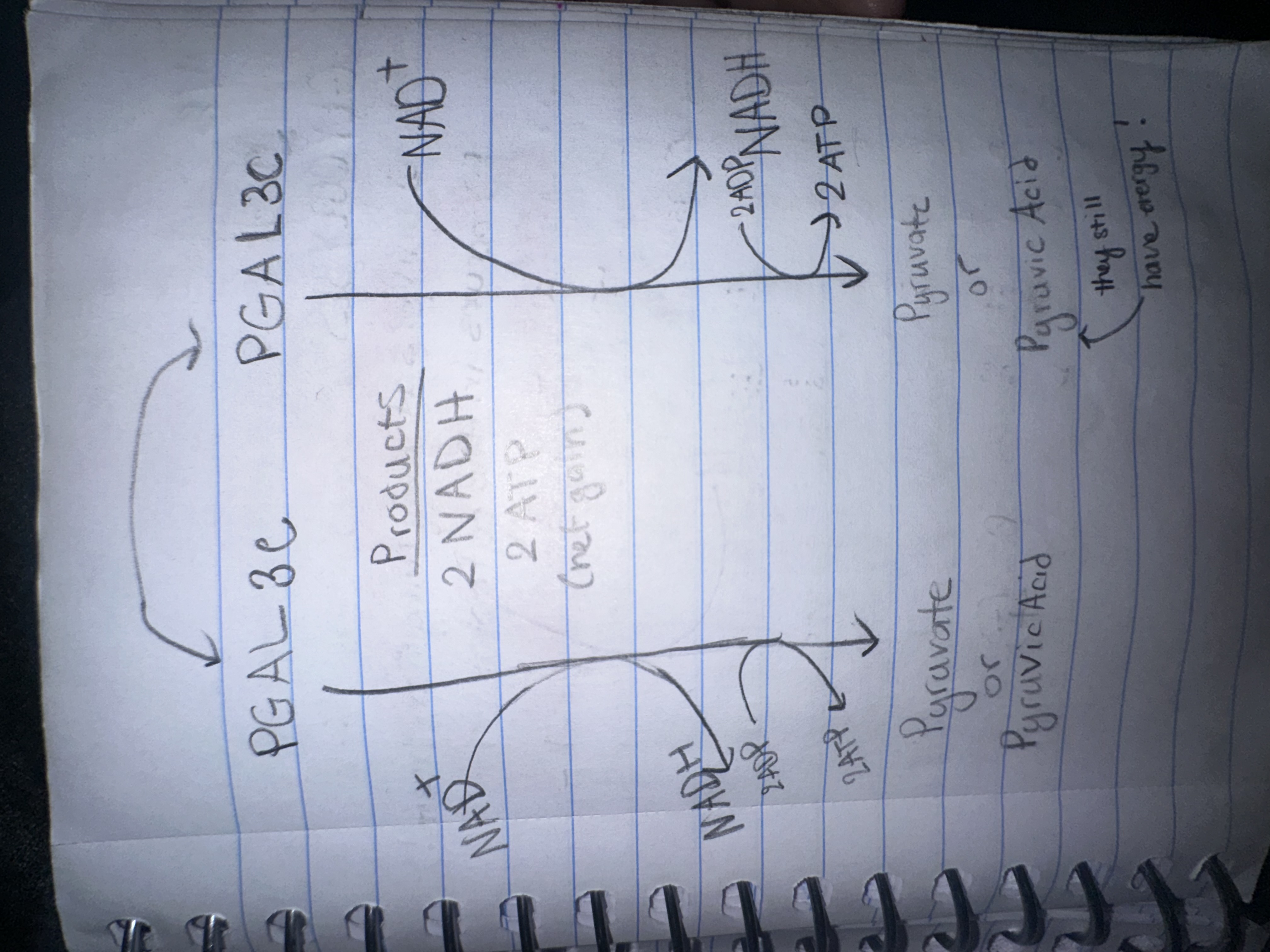
Glycolysis breakdown
Glucose →(Oxidizes 2 ATP into ADP) → 2 PGAL
2 PGAL → (2NAD+ and 4ADP gets REDUCED to 2NADH and 4ATP (2 ATP net gain) → Pyruvate

Kreb Cycle break down
Acetyl CoA and oxaloacetate react to produce citric acid, then breaks it down into smaller organic compounds.
WHEN CITRIC ACID IS BREAKING DOWN, 2 ATP is produced, 6 NAD+ and 2 FAD+ is being reduced to 6NADH and FADH2 , and 4CO2 is being released.
Pyruvate →Acetyl CoA breakdown
Pyruvate is broken down into Acetyl CoA (a coenzyme)
Pyruvate →( 2 NAD+ gets reduced to NADH, & 2 CO2 is being released) → acetyl CoA is produced.
what is the functional group of pyruvate?
Acetyl group! (put the picture)
Where does the Kreb Cycle Occur
Matrix of the Mitochondria
Where does glycolysis occur?
the cytoplasm
Where does the pyruvate to Acetyl CoA occur?
matrix of the mitochondria?
Intermediate steps of Aerobic Respiration to making ATP
Glycolysis (2 ATP Made) → Pyruvate to Acetyl CoA (0) → Kreb Cycle(2) → ETC (34)
ETC (stand for?)
Electron Transport Chain
cytrochromes
proteins that transport electrons
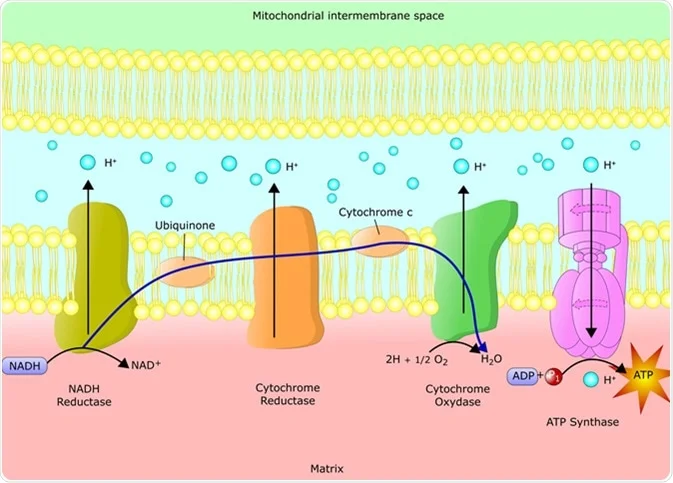
electrochemical gradient
electrical gradient - the charge
chemical gradient - the concentration of H+ (the protons)
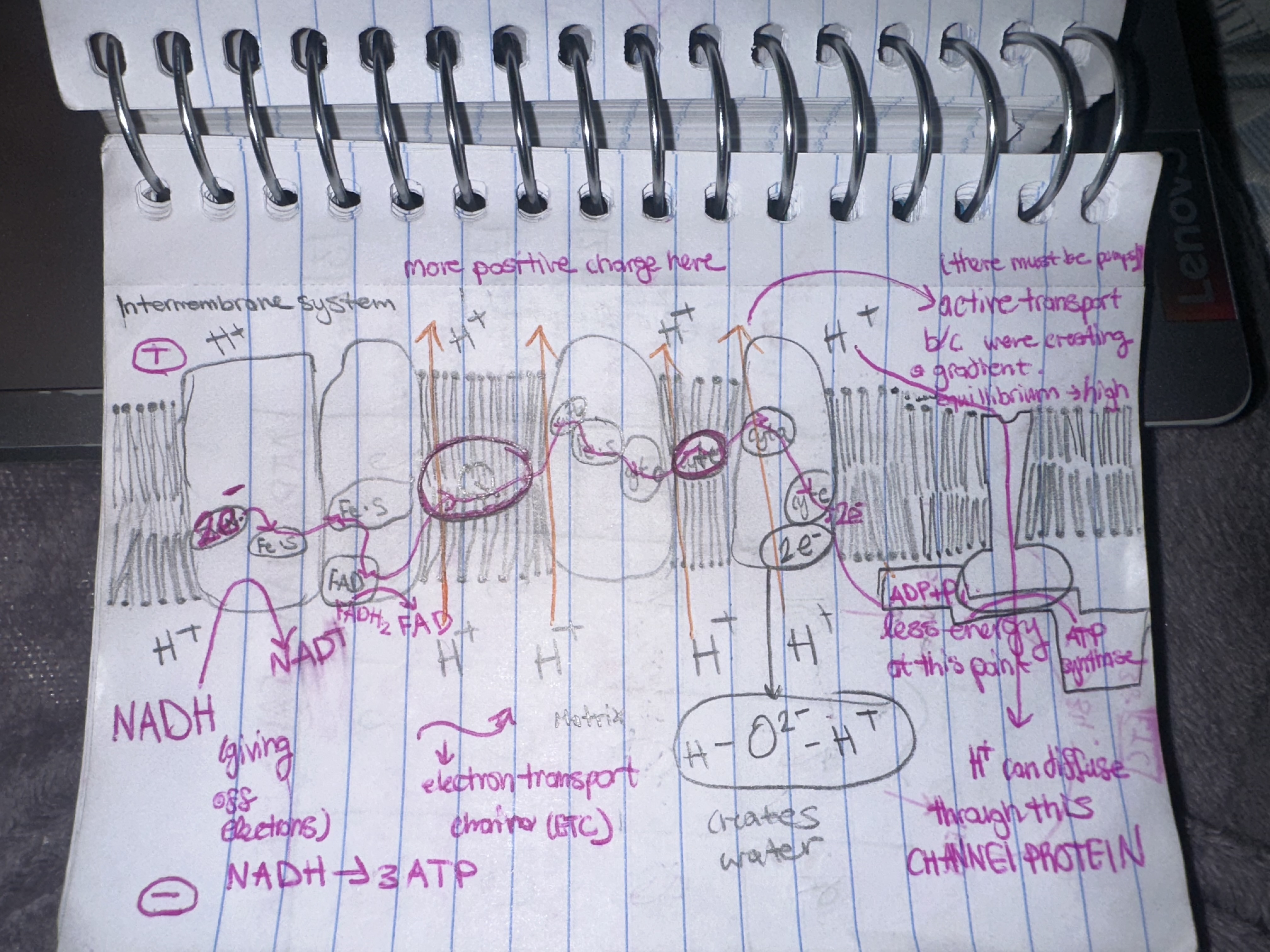
THE ETC breakdown
electrons are transferred from NADH and FADH2 to travel through the membrane by cytochromes. Once they travel, H+ are being pumped out from the matrix to the intermembrane space which creates an electrochemical gradient.
WHY? - there is a higher concentration of protons on the intermembrane space than in the matrix. Also, the charge in the intermembrane space is more positive than in the matrix.
The H+ diffuse back into the matrix (chemiosmosis) through ATP synthase, which is a channel and enzyme that creates ATP. When the H+ go through the ATP synthase channel, the channel gets charged and oxidative phosphorylation occurs. Phosphates are attached to ADP to make ATP. H+ that go through the channel are picked up by the final electron acceptor (oxygen) to create WATER.
where does the ETC occur?
The intermembrane system. (b/w the inner membrane and the matrix)
What is the final electron acceptor in the ETC chain?
oxygen
Chemisosmosis
Diffusion of H+ DOWN their concentration gradient.
if ATP synthase wasn’t there, why cant H+ move back into the matrix?
the membrane is IMPERMEABLE to H+
Oxidative Phosphorylation
when ATP synthase produces ATP. the energy comes from the ORIGINAL glucose oxidation process.
Substrate-level phosphorylation
directly adding a phosphate to ADP to make ATP
What is the function of Chlorophyll?
its a pigment that absorbs all light but reflects green for photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
the conversion of light energy to chemical energy.
Plants can use what light for photosynthesis? (in order from best to worst)
blue, violet, red, orange
they can die from green/yellow (prevents them from performing photosynthesis).
When you see/hear Chlorophyll think of
double peaks!
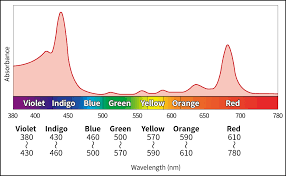
what macromolecule is chlorophyll?
Chlorophyll
Where does photosynthesis occur?
In the chloroplasts
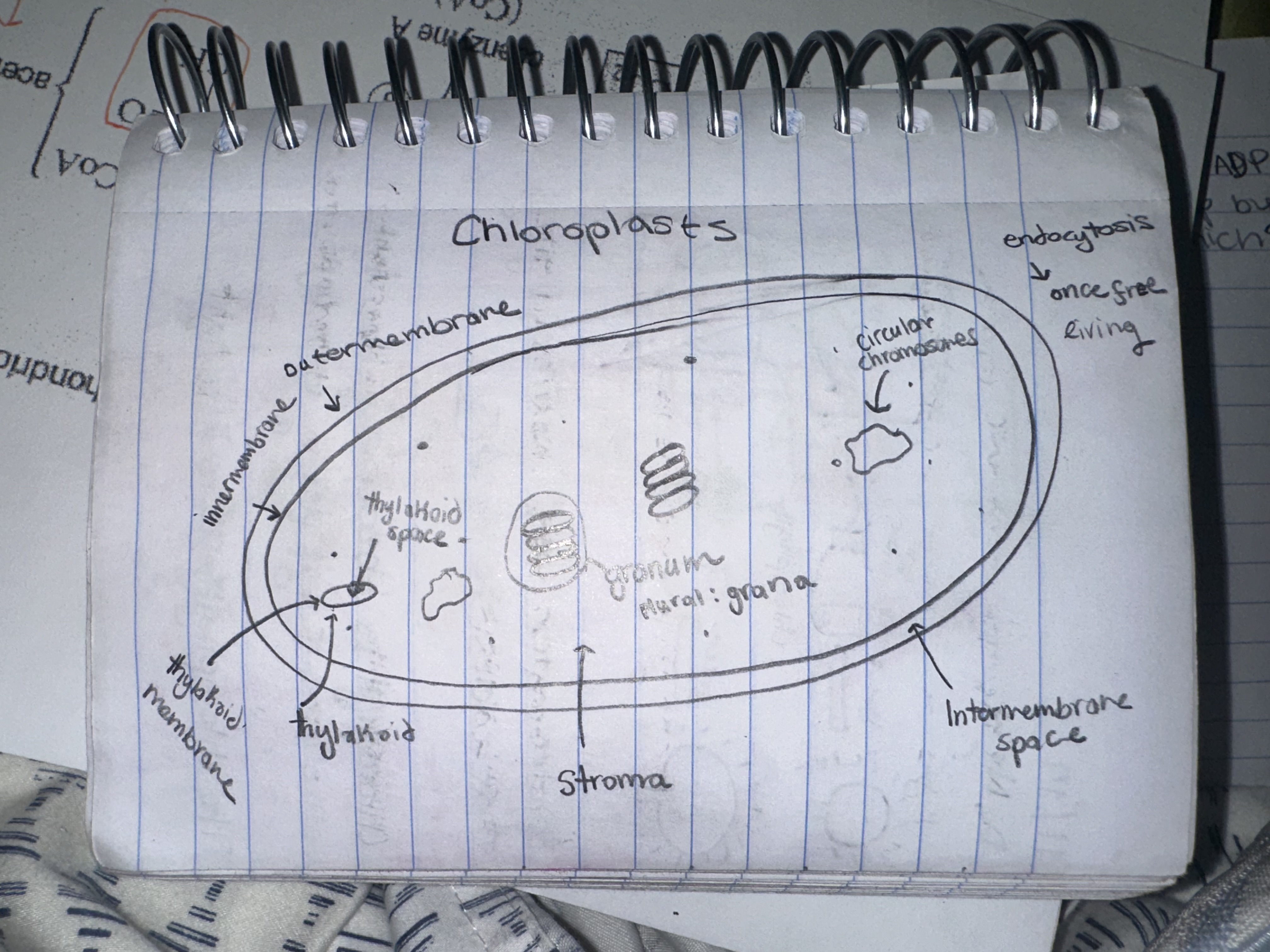
Chloroplasts (picture)
Membrane:
outer
inner
thylakoid
Compartments (spaces):
intermembrane space
stroma
thylakoid space
What is the final electron acceptor in the chloroplasts?
NADP+
Photolysis
splitting of water to return elections back to chlorophyll.
How many reactions are in photosynthesis
2: light and dark reaction
Ingedients of the light reaction
light, H2O, CO2 → C6H12O6 +6O2
Ingredients of the Dark reaction
light, H2O + CO2 → C6H12O6 + 6O2
What reaction needs to happen first before the other does?
The light reaction needs to happen first before the dark reaction.
Calvin Cycle (Dark Reaction) break down
6 CO2 (from the light cycle) + 6 RuBP + Rubisco(enzym) → 12 PGA
PGA → (12 ATP is oxidized to 12 ADP and 12 NADPH is oxidized to 12 NADP+) → 12 PGAL
10 PGAL goes baack and is turned into 6 RuBP to repeat the process while the other 2 PGAL is turned back into glucose
In the dark reaction, where does the 12 NADP+ go ?
They get reused in the light reaction
Where does the light reaction occur?
the thylakoid membrane
Where does the dark reaction occur?
the stroma