JEANS exam 1: all about cell reps
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
difference in ploidy level tween a soma cella nd germ cell
soma- 2n or diploid
germ- haploid aka n
During cytokinesis of plant cells, a contractile ring assembles around the plasma membrane constricting it and forming a cleavage furrow.
t or f
f. this is for animals only
A diploid cell has two sets of 10 homologous chromosomes. How many pairs of sister chromatids does the cell have after its DNA have replicated (G2 phase)?
20
blank ammt of sets of chroms r found in human soma cell and blank ammt found within one set
two sets. 22
karyotype def and what stage of chroms r here
this is a visual rep of how chroms look. will show the 22 plus sex pairs. seen at metaphase.
it can help show counts, genetic badness, structure/size
procedure for making a karyotype FOUR STEPS
1- samp collection from wbc or bone marrow
2- make em grow in lab and make sure you keep them in metaphase by adding colchicine . then use centrifuge
3- harvest cells through hypotonic solution use.
4- anoter centrifuge round to concentrate cells. then put in a fixative, stain it and put on slide
binary fission is used by blank. this is when..
bacteria.
basically this is a way to do asex repro. the mom cell just divides into daughter cells thru formation of a septum
the blank tein is seen in binary fission
ftsZ
how similar are homolog chroms vs sex chroms
more than 99 cent identical
sex= verrryy different
how many diff arrangements could happen during meiosis 1 during prophase
8 million
binary fission vs mei 1 vs mei 2 vs mito
who has synapsis
who has diploid cells as end result
who has haploid cells as a result
who has a pair of sister chromatids on ONE pole only during meta
who aligns in a double row
who is usually with prokary
who is with euks
who has pair of sister chroms sepping during anaphase
who has chiasma
who makes four daughter cells
who makes 2 daughter cells
who is asexual
who has a pair of sister chroms on both poles during meta
who has sister chromatids (during metaphase)
who has bivalents
who aligns in a single row
who has synapsis- mei 1
who has two diploid cells as end result- mito
who has haploid cells as a result- the meiS and binary fiz
who has a pair of sister chromatids on ONE pole only- mei 1
who aligns in a double row- mei 1
who is usually with prokary- binary fiz
who is with euks- mito and the meiS
who has pair of sister chroms sepping during anaphase- mito and mei 2
who has tetrads sepping during anaphae- mei 1
who has chiasma- mei 1
who makes four daughter cells- mei 2
who makes 2 daughter cells- mito and binary fiz
who is asexual- bin fiz
who has a pair of sister chroms on both poles during metaphase - mito and mei 2
who has sister chromatids (during metaphase)- mito and mei 2
who has bivalents- mei 1
who aligns in a single row- mito and mei 2
synapsis seen in blank of blank. this means
zygotene of prophase mei 1. this is where mom pair and dad pair (must be homo in nature) begin to align themsleves along their lengths
chiasma seen in blank of blank. def HUH
pachytene. when the crossing over is seen at this spe site the connection that results from that crossover event is called chiasma
crossing over def
when chroms physically exchange w themselves
spermatogenesis vs oogenesis- describe the process
spermatogenesis- the spermatogonial cells divide by mito to make two of the same cells. one of remains a spermatogonial cell while the other becomes a primary spermatocyte. it will go thru mei 1 and 2 to make four haploid cells aka spermatids that mature int osperm cells
oogenesis- happening in the ovary;s oogonia where oogonia cells are made b4 birth. some of them go int o mei 1’s prophase and are ARRESTED (dormant phase). the cuffs turn them int oprimary oocytes. things get to continue when the female become sexually mature. moving on, we come to a first time meiotic div that is asyymm and makes a secondary oocyte and a much smaller cell called a polar body. the secondary oocyte go thru mei 2 as it released from the ovary aka ovulation to the uterus. if sperm hits this 2ndary oocyte meiosis 2 gets completed. the secondary oocyte makes a haploid egg and a second polar body.
order of bin fiz
five steps
Cells replicate their DNA.
The filamentous protein FtsZ (similar to a tubulin protein) moves to the division site.
The filaments assemble into a ring structure called the Z-ring.
The protein FtsZ recruits other proteins to form a septum. A septum is a wall between daughter cells.
The bacterial cell has divided into 2 daughter cells.
what is ftsZ doing
helping drive cell division as a protein that polymerizes into filamets which then form the z ring
when r chroms shown in sis dyad form
synthesis
after mei 1’s anaphase
mei 2’s prophase through metaphase shows sis chroms but with their gene info exchanged
kinetchore func
protein part on the chrom that links to the spindle appartus’s tubules during mito and mei
centromere
a region on the chrom where the kinetchore is housed
centrosome vs centrioles
a centrosome is a microtubule organizing center (where centrioles are located) in eukaryotic cells. both func to bring order to the tubules and form the mitotic spindle
match!
astral, kinetchore, polar (microtubs)
extend from each spindle pole and overlap at center of cell to push poles apart
attach to chroms at their kinetochores
extend outward from the centrosomes to the cell mem and help position the spindle
Kinetochore microtubules: Attach to the chromosomes at their kinetochores (a protein structure on the centromere).
Polar microtubules: Extend from each spindle pole and overlap at the center of the cell to push the poles apart.
Astral microtubules: Extend outward from the centrosomes to the cell membrane and help position the spindle.
mito or mei: myosin motor teins and actin filaments form at cyto shape of plas mem
mito. SEEN W A
which phase has duped the centrosome
syn
when does complete alignment happen
pachytene
mei 1 produces diploid cells t or f
f
meiosis 2 starts with the same set of cells as the mom cell t or f
f
. When a karyotype is prepared, which of the following steps is
carried out?
a. Treat the cells with a chemical that causes them to begin
cell division.
b. Treat the cells with a hypotonic solution that causes them to
swell.
c. Expose the cells to chemical dyes that bind to the chromosomes and stain them.
d. All of the above steps are carried out
d
How many sets of chromosomes are found in a human somatic cell, and how many chromosomes are within one set?
a. 2 sets, with 23 in each set
b. 23 sets, with 2 in each set
c. 1 set, with 23 in each set
d. 23 sets, with 1 in each set
a
Binary fission
a. is a form of asexual reproduction.
b. is a way for bacteria to reproduce
c. beings with mum cell and makes 2 identical daughter cells
d. all above
d
Which of the following is the correct order of phases of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
a. G1, G2, S, M
b. G1, S, G2, M
c. G1, G2, M, S
d. G1, S, M, G2
b
What critical event occurs during the S phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
a. The cell either prepares to divide or commits to not dividing.
b. DNA replication produces pairs of sister chromatids.
c. The chromosomes condense.
d. The single nucleus is divided into two nuclei.
B.
a- not a becuase its referring to gap 1
which phase of mito shows finally all the chroms condensed where it could even be seen with light microscopy
metaphse
anaphase
prophase
prometaphse
none of these
prophase
which mito phase shows the nucleus starting to become small vesicles and which one is when its completely all small vesicles
prophase- starting
prometaphse- all vessies
at this phase the chroms get to relax and decondense
anaphase
telphase
metphase
prophase
telophase
1. What is the function of the kinetochore during mitosis?
a. It promotes the attachment of monads to each other to form a dyad.
b. It is a location where a kinetochore microtubule can attach to a chromosome.
c. It promotes the condensation of chromosomes during prophase.
d. Both a and b are correct
d
when does crossover happen and what is end result
a- prophase of mei 1/shows pieces of chrom exchanged tween homo chroms
b- prometaphase of mei 1/ shows pieces of chrom exchanged tween homo chroms
c- prophase of mei 1 and shows sis sepping
d- none of these
a
mei 1 or mei 2 or mito
pairing of homo chroms happens
mei 1. this is cuz mom and dad are the homo chroms pairing
Prokaryotes divide through a process called binary fission. Because binary fission is a simpler process than mitosis, DNA replication does not occur.
t or f
f
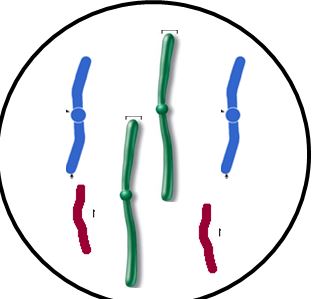
what phase is going on
anaphase
prophase
g2
g1
g1
What chromosomal regions are mainly composed of heterochromatin?
The centromeres and telomeres |
Which of the following proteins is not part of the core histone proteins (the octamer)?
H2B
H2A
H3
H4
H1
H1
The function of the kinetochore microtubules during cell division is to determine the positioning of the spindle apparatus.
t or f
false. ASTRAL DOES THIS
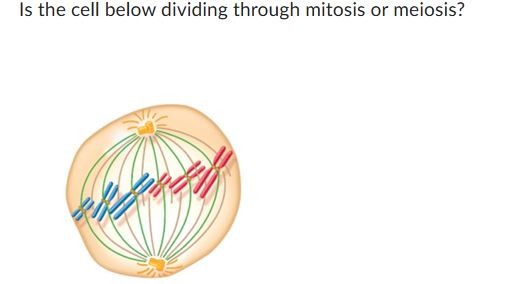
can be either mei 2 or mito. they both will look the same at the end of the day