Chemistry PPQs got wrong 4
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
steam AND acid/H+ catalyst
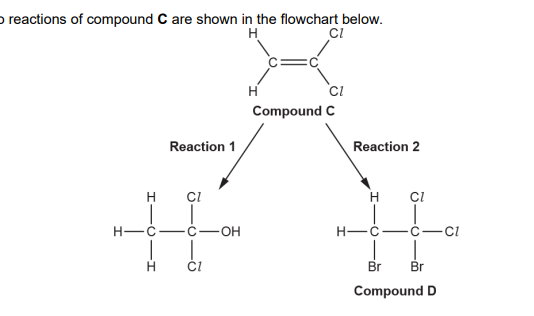
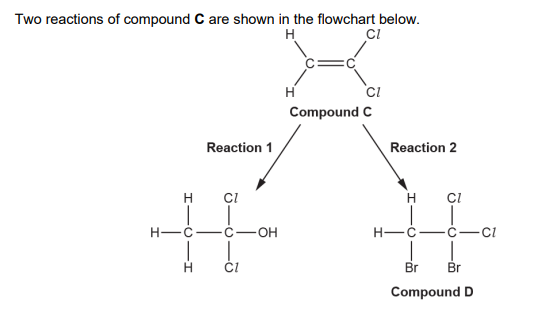
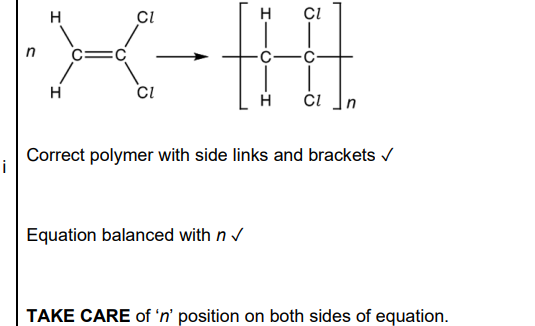
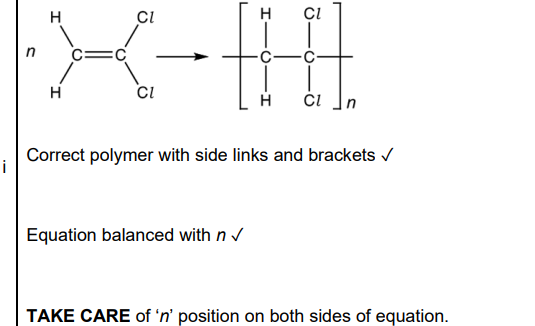
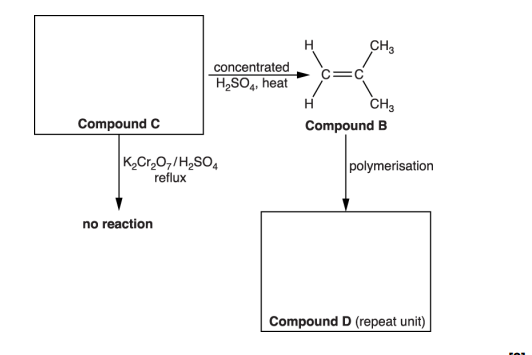
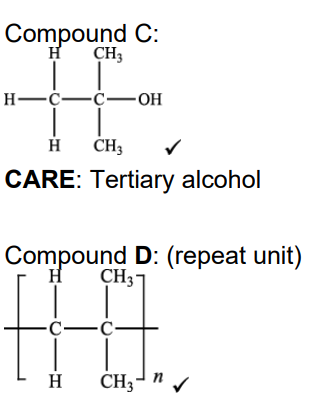
(c). Compound C forms an addition polymer E. i. Write a balanced equation for this reaction. Show displayed formulae (2)
State one advantage and one disadvantage of using combustion as a method for the disposal of waste polymer E. (waste polymre E in picture)
Advantage - Energy production/energy used to produce electricity
Disadvantage
formation of HCl/ products of combustion cause acid rain
OR formation of CO2/ gases that cause global warming/ greenhouse gases
OR formation of CO
After polymers have been used for packaging, the waste polymers need to be processed to save resources, for example, by recycling. Describe two other ways in which waste poly(propene) can be processed in a sustainable way (2)
combustion for energy production (alternative to fossil fuels)
Use as an organic feedstock
. After their useful life, waste polymers can be disposed of by combustion. State one particular problem with disposal of poly(2-chloropropene) by combustion (1)
Formation of HCl
OR Chlorine
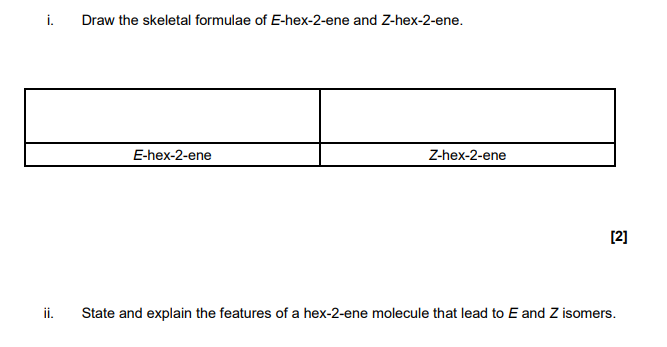
carbon-carbon double bond does not rotate OR has restricted rotation
each carbon atom of the double bond attached to 2 different groups/atoms
(ii)
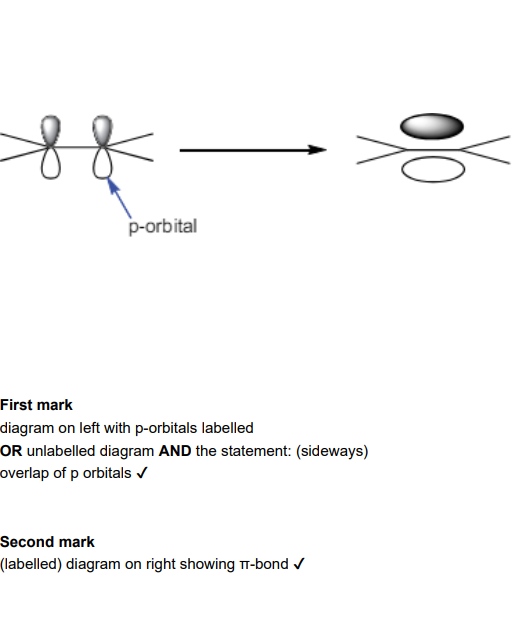
Describe the differences between the sigma and pi bond
a sigma bond is between bonding atoms/nuclei AND pi bond is above and below the bonding atoms/ nuclei
sigma bond has direct / head on overlap of orbitals AND pi bond has sideways overlap
pi bond has a lower bond enthalpy / is weaker than a sigma bond
sigma bond has electron density between bonding atoms AND pi bond has electron density above and below bonding atoms
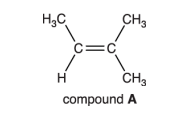
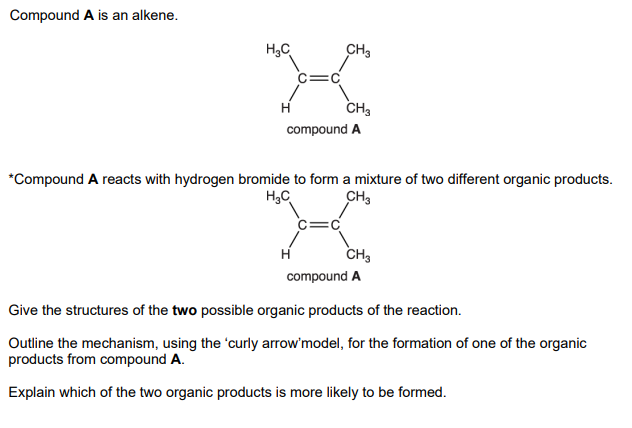
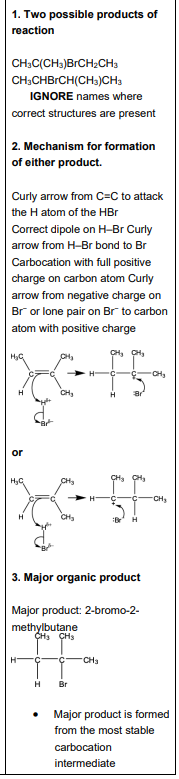
Explain why compound A does not have E/Z isomerism
one carbon atom in the double bond is attached to 2 groups which are identical / the same
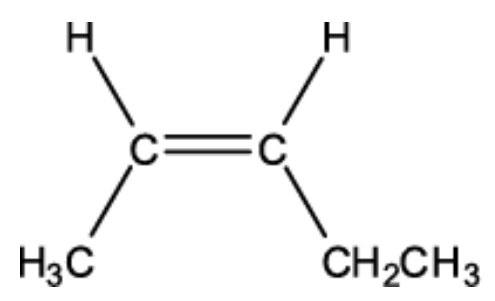
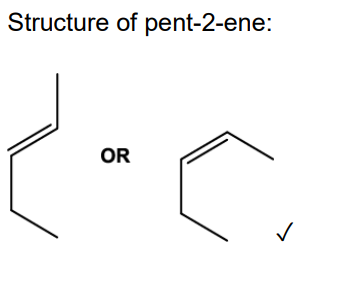
Name this isomer
Z - pent - 2 - ene
Allyl bromide, CH2=CHCH2Br, is used in the production of polymers. Part of the C=C double bond in allyl bromide is called a π-bond. Draw a labelled diagram to show the formation of the π-bond. (2)
In radical substitution why is a mixture of organic products produced?
further substitution OR produces different termination products OR more than one termination step
substitution at different positions along chain
Incineration of plastics containing poly(chloroethene) produces waste gases that can damage the environment. Incineration carried out in the presence of oxygen produces carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide and hydrogen chloride as waste gases and one other non-toxic product. ii. Chemists have developed ways of removing hydrogen chloride from these waste gases. Sodium hydrogencarbonate, NaHCO3(s), is frequently used in industry for this purpose. Explain how sodium hydrogencarbonate removes hydrogen chloride.
sodium hydrogencarbonate neutralises HCl
What do curly arrows represent in a mechanism
movement of a pair of electrons
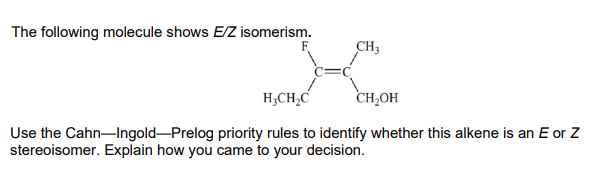
E isomer
AND F takes priority over carbon on the left hand side (as it has a higher atomic number)
AND C2H2OH takes priority over CH3 group on the right hand side
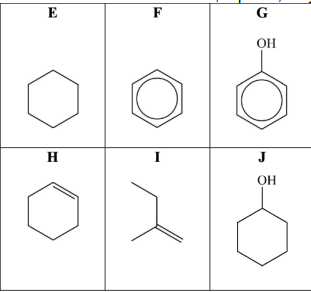
Compound H can be prepared in an elimination reaction by heating compound J with an acid catalyst. A student carries out this preparation using 7.65 g of compound J. The student obtains 2.05 g of compound H. i. Write an equation for this reaction, using molecular formulae. Calculate the percentage yield of compound H. Give your answer to one decimal place.

Combustion of a polymer produces HCl, which is a toxic gas. Describe how HCl is removed from waste gases produced
HCl gas is passed through alkali/carbonate
State the advantages of using polymers made from natural foods
reduces dependency on finite resources
OR biodegradable
OR photodegradable
Outline how a catalyst increases the rate of a chemical reaction
it allows the reaction to proceed via a route with a lower activation energy
so that a greater proportion of molecules exceed the activation energy
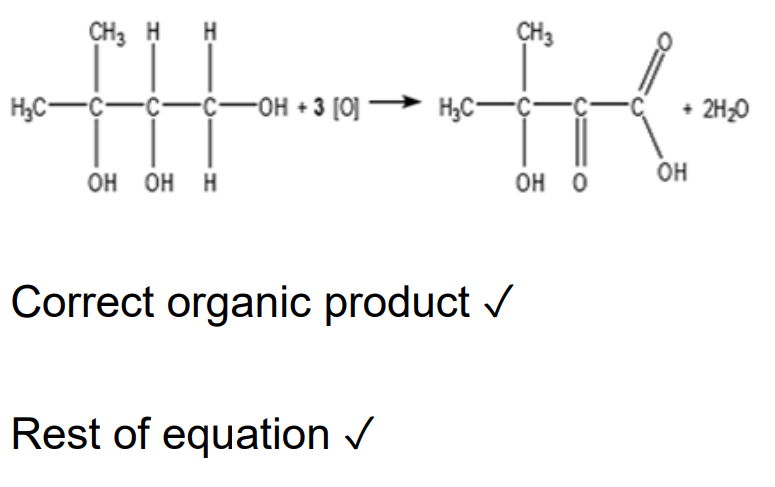
Alcohols can be used to prepare organic compounds with different functional groups. HO(CH2)4OH can be oxidised to form HOOC(CH2)2COOH. i. State the reagents and conditions and write an equation for this oxidation. In the equation, use [O] for the oxidising agent (3)

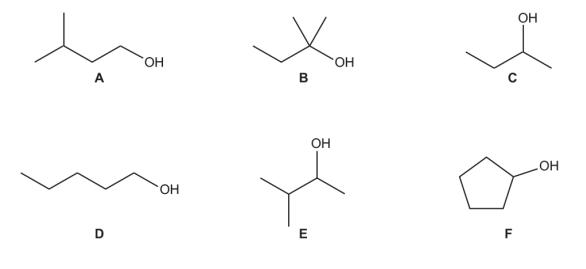
C, E and F
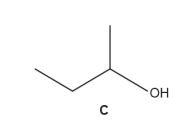
What is the systematic name for alcohol C
Butan-2-ol
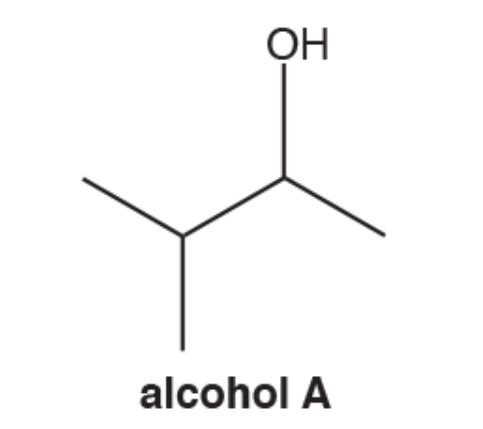
What is the systematic name of this alcohol
3 - methylbutan - 2 - ol
The chemist heats alcohol A with an acid catalyst to form a mixture containing two alkenes. Draw the structures of the two alkenes formed in this reaction

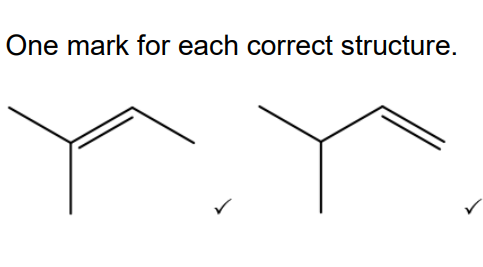
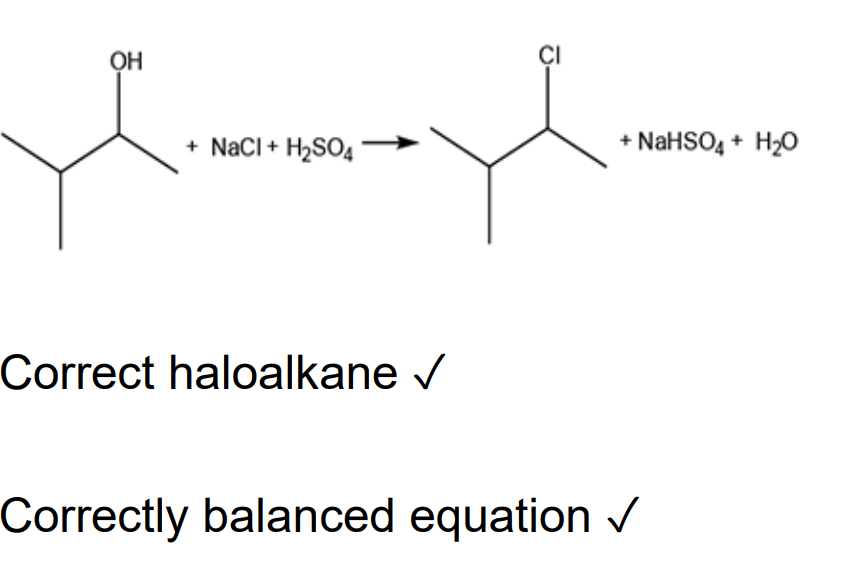
The chemist heats alcohol A with sodium chloride and sulfuric acid. Construct a balanced equation for this reaction. Show structures for the organic compounds in your equation.


1-Bromobutane is an organic liquid with a boiling point of 102 °C. A student prepares 1-bromobutane by reacting butan-1-ol with sulfuric acid and sodium bromide. The student boils the mixture for one hour. The equation is shown below. CH3CH2CH2CH2OH + H+ + Br− → CH3CH2CH2CH2Br + H2O The student obtains a reaction mixture containing an organic layer (density = 1.27 g cm−3) and an aqueous layer (density = 1.00 g cm−3). i. * Draw a labelled diagram to show how you would safely set up apparatus for the preparation. Outline a method to obtain a pure sample of 1-bromobutane from the reaction mixture.
Apparatus set up for reflux
round - bottom / pear shaped flask
heat source
condenser
detail: water flow in condenser bottom to top; open system
Purification
use of separating funnel to separate organic and aq layers
detail: collect lower organic layer density greater
Drying with an anhydrous salt
deatil e.g. MgSO4, CaCl2
Redistillation
Detail : collect fraction distilling at 102°C
Alcohols can be converted into alkenes in an elimination reaction. The elimination of H2O from pentan-2-ol forms a mixture of organic products. Give the names and structures of all the organic products in the mixture. Your answer should explain how the reaction leads to the different isomers. (6)

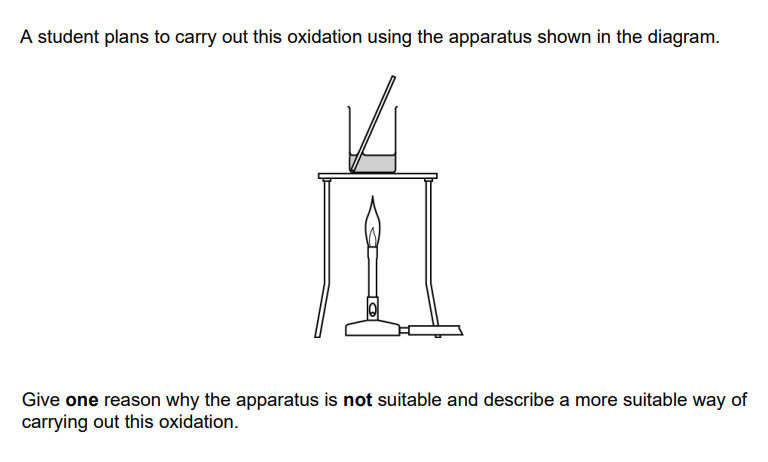
Oxidation of alcohols (2)
Butan - 2 - ol / butanone is flammable OR butan - ol / butanone is volatile / low boiling point OR Butan - 2 - ol / /butanone will evaporate / boil away
heat under reflux OR a description of reflux with vertical condenser and a round bottomed or pear shaped flask with a source of heat
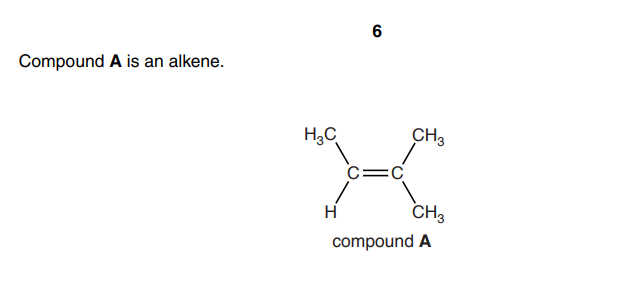
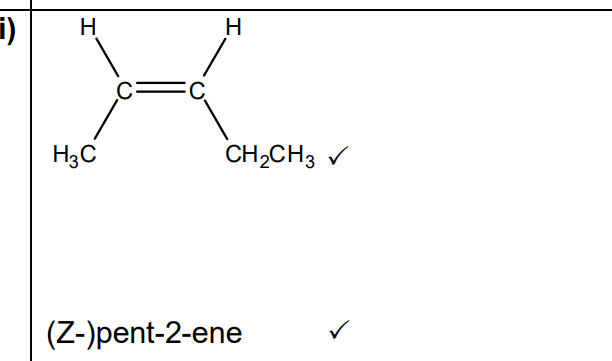
A structure isomer of compound A has E/Z isomers
Draw the structure of the Z isomer and then name this isomer
State one particular problem with disposal of poly(2-chlropropene) by combustion (1)
Formation of HCl / hydrochloric acid OR chlorine
How does free radical substitution show an example of homolytic fission?
One electron from the bond pair goes to each atom
What is meant by the term homologous series (2)
(series of compounds with the) same functional group OR same / similar chemical properties OR same / similar chemical reactions
Each successive / subsequent member differs by the addition of CH2
Describe the oxidation reaction of propan-1-ol when using a suitable oxidising agent. Indicate how the use of different reaction conditions can control which organic product forms. Include reagents, observations and equations in your answer. In your equations, use structural formulae and use [O] to represent oxidising agent. (6)
Reagents: Acid / H+ and (potassium or sodium) dichromate / Cr2O7 2-
observations: orange to green OR orange to blue
distillation / distil produces aldehyde
CH3CH2CH2OH + [O] → CH3CH2CHO + H2O (do displayed though)
reflux produces carboxylic acid
CH3CH2CH2OH + 2[O] → CH3CH2COOH + H2O (do displayed though)
This question is about alkenes. When alcohol A is heated with an acid catalyst, a reaction takes place forming alkene B. The equation for this reaction is shown below as Equation 16.1.
CH3CH(CH3)CH2CHOHCH3 → CH3CH(CH3)CHCHCH3 + H2O Equation 16.1 alcohol A alkene B
* A student carries out the reaction in Equation 16.1 using 9.26 g of alcohol A. The student obtains a liquid reaction mixture containing a mixture of organic products and the acid catalyst. The student purifies the reaction mixture to obtain the liquid alkene B with a percentage yield of 75.0%. Describe a method to obtain a pure, dry sample of alkene B from the reaction mixture and calculate the mass of alkene B that the student produced.
