Biological and Genetic Foundations of Personality Psychology PSYC-2300
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What are the three biological factors that contribute to personality?
Evolutionary factors, genetic factors, and physiological factors.
What does the nature-nurture debate focus on?
Whether traits are inborn (nature) or learned (nurture).
What is the tabula rasa concept in the context of personality?
The idea that the mind begins as a blank slate, shaped by environmental influences.
What is the contemporary view on nature vs. nurture?
Both nature and nurture matter, and individual differences arise from their interaction.
What is the goal of behavioral genetics?
To determine the percentage of individual differences in traits attributed to genetic and environmental differences.
What does heritability (h²) measure?
The proportion of phenotypic variance explained by genetic variance.
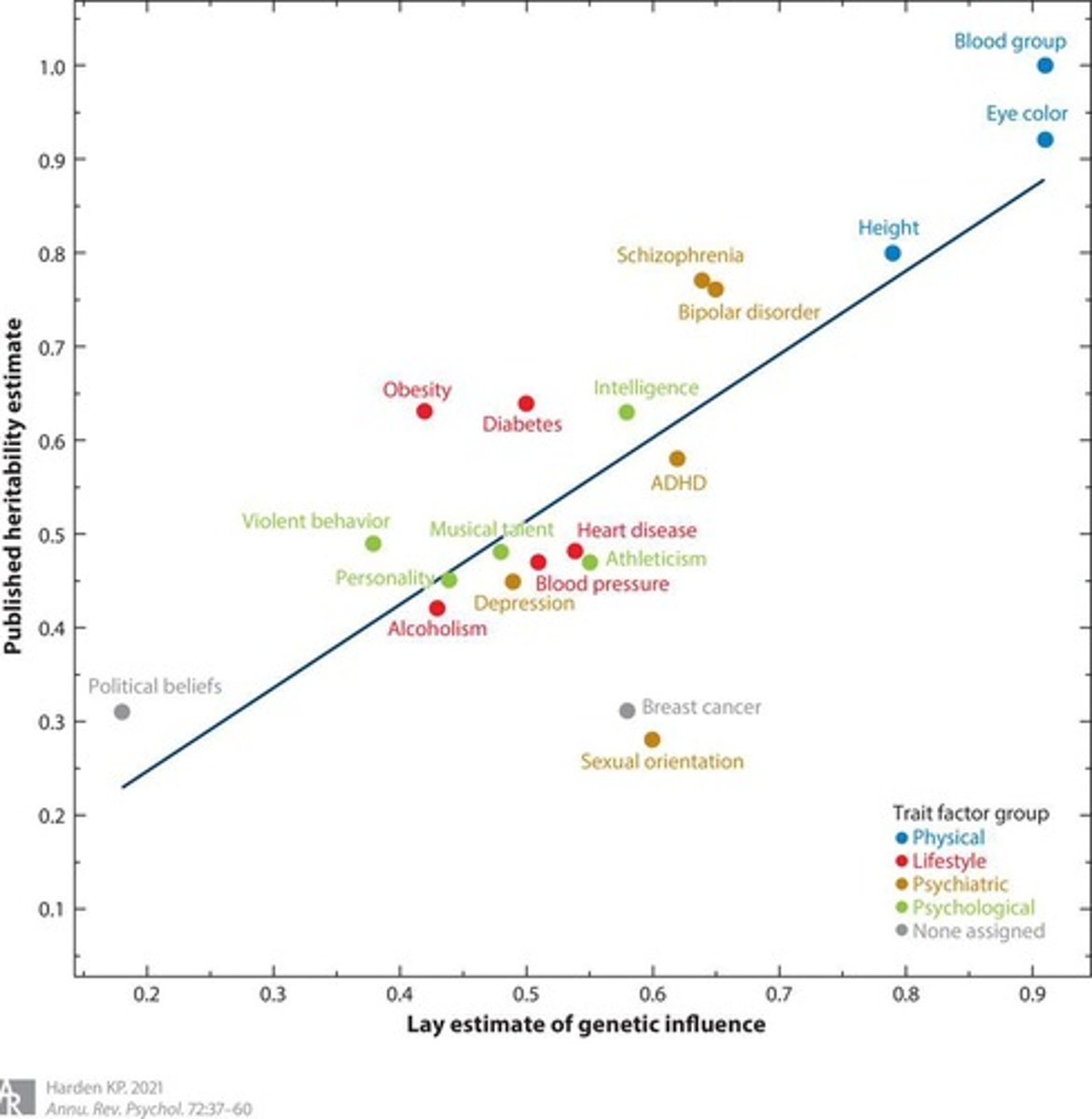
How is heritability calculated?
h² = 2(rmz - rdz), where rmz is the correlation of monozygotic twins and rdz is the correlation of dizygotic twins.
What does a heritability estimate of h² = 0.50 for extraversion indicate?
About half of the measurable variation in extraversion is due to genetic variation.
What are common misconceptions about heritability?
Heritability does not apply to individuals, is not constant, and is not a highly precise statistic.
What percentage of variance in happiness is attributed to genetics according to Lykken & Tellegen (1996)?
48% of variance in happiness is attributed to genetic factors.
What is the purpose of twin studies in behavioral genetics?
To gauge heritability by comparing the similarity of traits in identical (monozygotic) twins versus fraternal (dizygotic) twins.
What is the significance of the equal environments assumption in twin studies?
It assumes that MZ and DZ twins raised together experience equally similar environments.
How do adoption studies measure heritability?
By examining the similarity of adoptees to their biological versus adoptive parents.
What is the benefit of using adoption studies?
They do not require the equal environments assumption, allowing for a clearer assessment of genetic versus environmental influences.
What are the laws of behavior genetics?
1. All human behavioral traits are heritable. 2. The environment also plays a significant role.
What is a limitation of behavioral genetics methods?
They assume that genes and environment are independent, which may not always be the case.
What does the term 'environmentality' refer to?
The proportion of phenotypic variance that is attributed to environmental variance, calculated as (1 - h²).
What is the relationship between genetic dispositions and environmental selection?
Certain genotypes may be associated with the selection of specific environments.
What is the role of reactions from others in behavioral genetics?
Genetic dispositions can evoke reactions from others, influencing an individual's environment.
What is the significance of studying twins reared apart?
It combines the strengths of both twin and adoption studies, providing insights into genetic and environmental influences.
What is the heritability of happiness as found in the study by Lykken & Tellegen?
Genes account for 48% of the variance in happiness, with environmental factors contributing 43%.
What is the main question addressed by the nature-nurture debate at the population level?
Which is more important in accounting for variation in traits: genes or environment?
What has a larger effect on personality: genes or being raised in the same family?
Genes have a larger effect than being raised in the same family.
What are the three different influences on personality?
Genetic, Shared Environment, Non-Shared Environment.
What is an example of a non-shared environmental influence?
Friend groups or unique aspects of parenting not shared by siblings.
What is an example of a shared environmental influence?
Socioeconomic status (SES) or overall parenting styles.
What is the heritability estimate range for major personality traits?
Heritability estimates range from .30 to .50.
What is the heritability estimate for extraversion?
The heritability estimate for extraversion is .49.
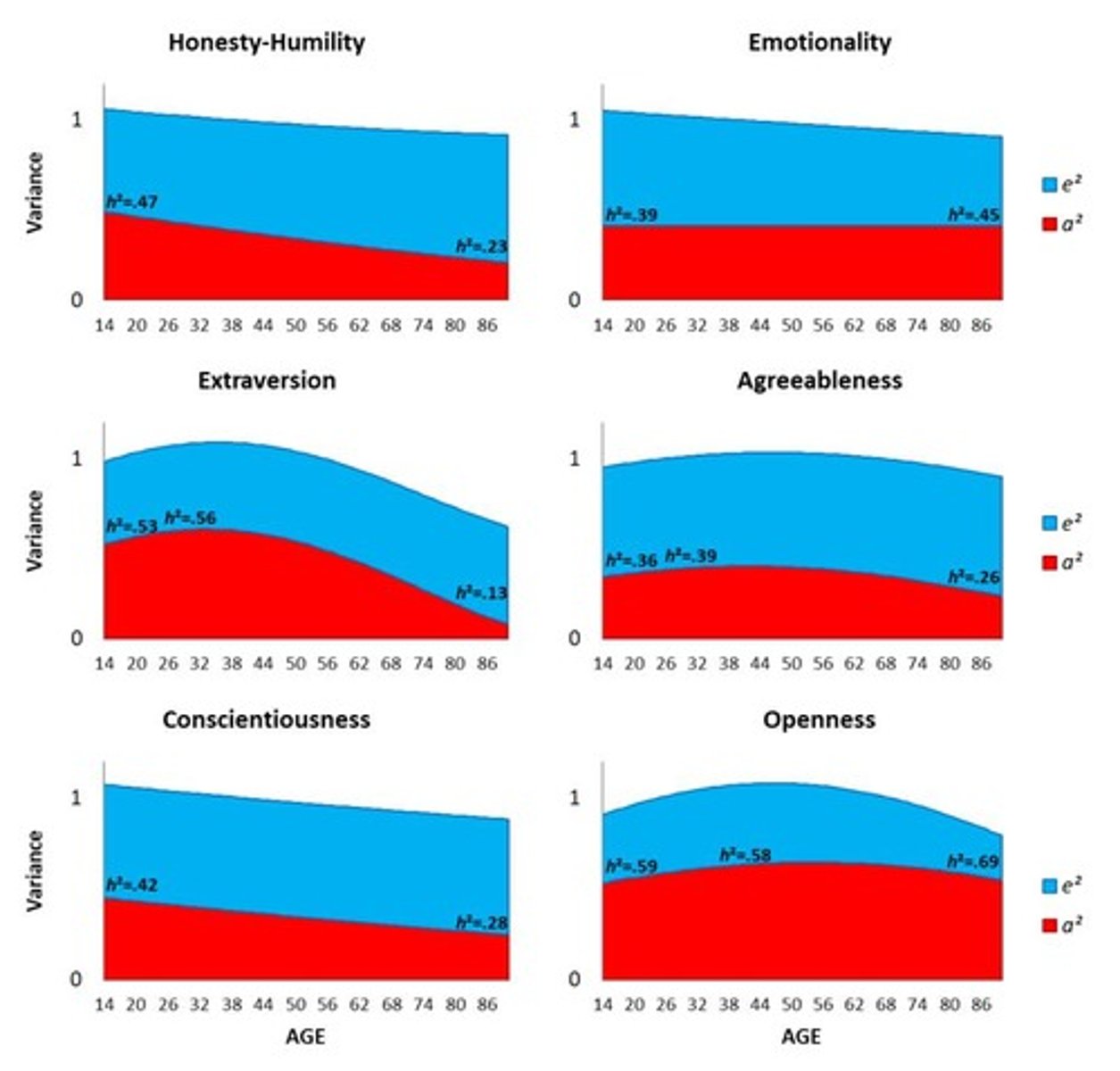
How does heritability of personality traits change across the lifespan?
Heritability generally declines with age, with increased importance of life experiences.
What is the heritability estimate for tendencies to drink alcohol and smoke cigarettes?
The heritability estimate is greater than .50.
What is the heritability of traditionalism as an attitude?
The heritability of traditionalism is about .60.
What percentage of political orientation is explained by genetic variation?
Genetic variation explains about 40% of differences in political orientation.
What is the overlap percentage between heritable aspects of political orientation and personality?
The overlap is 60-70%, especially with openness to experience.
What gene is associated with impulsivity and novelty-seeking?
The DRD4 gene, located on chromosome 11.
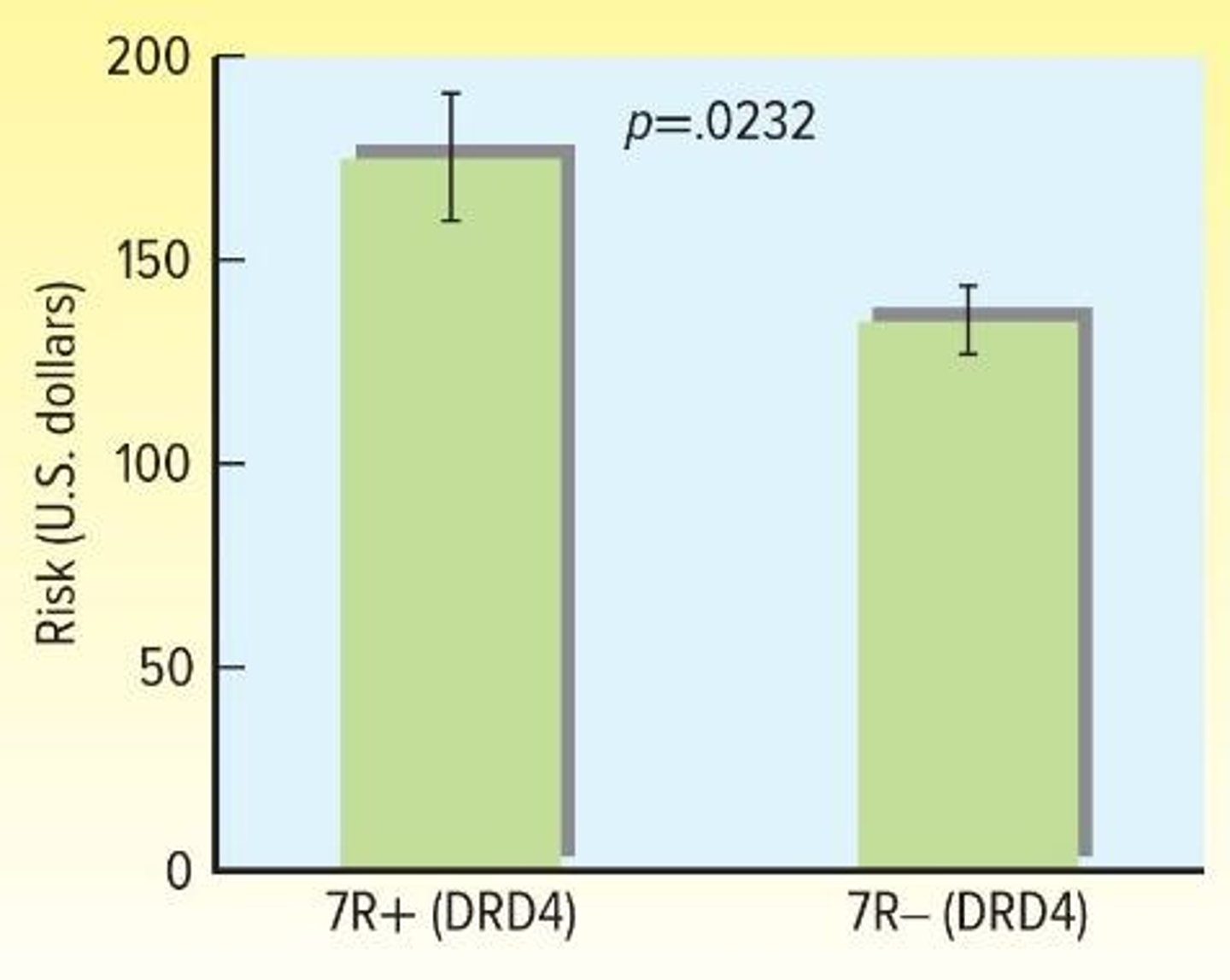
What does the genotype-environment interaction refer to?
Differential responses of people with different genotypes to the same environments.
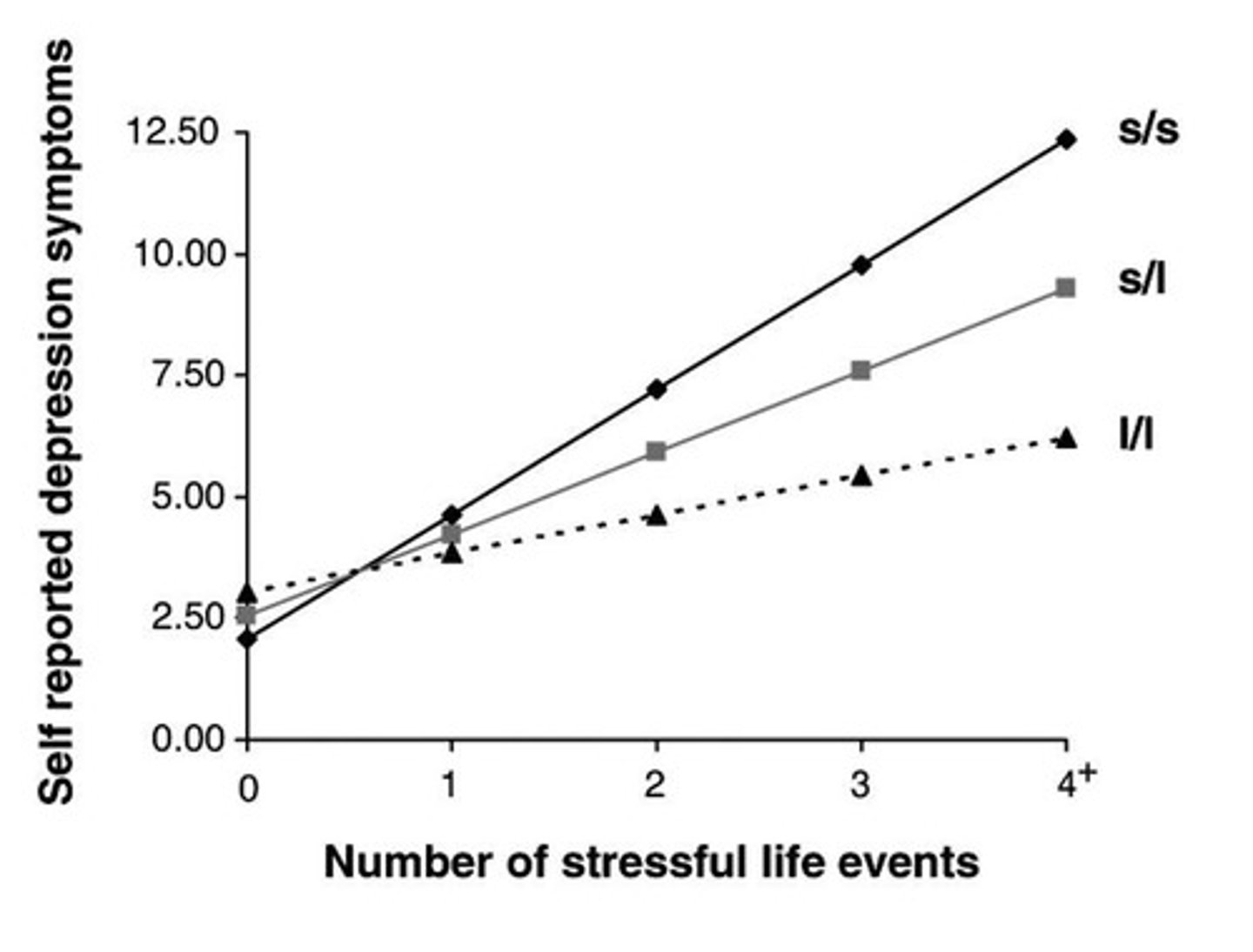
What was the significant finding of Caspi et al. (2003) regarding depression?
The effect of negative life events on depression was stronger for individuals with the short allele of the serotonin-related gene 5-HTT.
What does the Triple Vulnerability Theory propose?
It suggests that genetic and environmental factors interact to influence the development and expression of neuroticism.
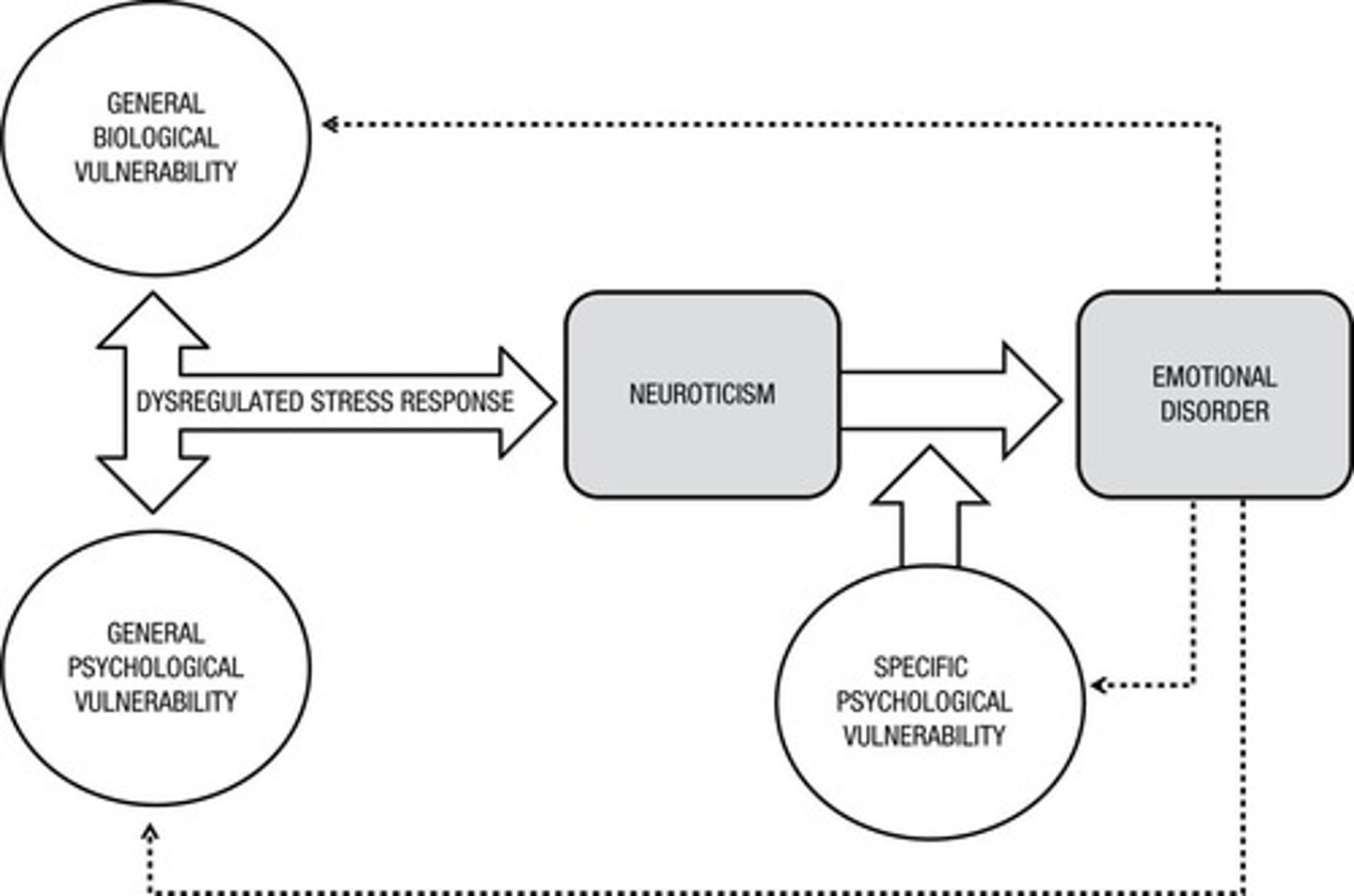
What are the three types of genotype-environment correlations?
Passive, Reactive, and Active correlations.
What does a passive genotype-environment correlation involve?
It involves the exposure of individuals to environments that are influenced by their parents' genotypes.
What is a reactive genotype-environment correlation?
It occurs when individuals with different genotypes evoke different responses from their environment.
What is an example of a non-heritable attitude?
Beliefs in God show low or no heritability.
What is the significance of the Minnesota Twin Family Registry in behavioral genetics?
It is a key resource for studying the heritability of various traits, including personality and political orientation.
What is passive genotype-environment correlation?
Parents provide both genes and environment to children, but children do not actively seek that environment. Example: A child's verbal ability and the number of books in the home.
What is reactive genotype-environment correlation?
Parents or others respond to children differently based on the child's genotype. Example: A baby's preference for cuddling influences the mother's cuddling behavior.
What is active genotype-environment correlation?
Individuals with a particular genotype seek out environments that match their traits. Example: High sensation seekers expose themselves to risky environments.
How do personality traits relate to genetics?
Personality traits are generally heritable, with much environmental influence stemming from nonshared variables unique to siblings.
What physiological systems can influence psychological functioning?
Nervous, cardiac, and musculoskeletal systems.
What physiological measures are used to study personality?
Electrodermal activity, cardiovascular activity (blood pressure, heart rate, EKG), brain activity (EEG, PET scan, fMRI), and biochemical analyses of blood and saliva.
Which neurotransmitter is associated with extraversion?
Dopamine.
What brain structures are linked to extraversion?
Substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, medial orbitofrontal cortex, and amygdala.
Which neurotransmitter is associated with neuroticism?
Serotonin.
What brain regions are involved in neuroticism?
Amygdala, hypothalamus, insula, medial prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and hippocampus.
What is the Behavioral Activation System (BAS)?
A system that drives individuals to approach rewards, associated with impulsivity and positive emotions.
What does the Fight-Flight-Freeze System (FFFS) do?
It motivates individuals to move away from threats or punishing stimuli, associated with fear-proneness and avoidance.
What is the Inhibition System (BIS)?
It assesses risk and produces anxiety and rumination, associated with neuroticism facets like anxiety and depression.
How does high BAS influence learning?
Impulsive individuals with a strong BAS learn better from rewards.
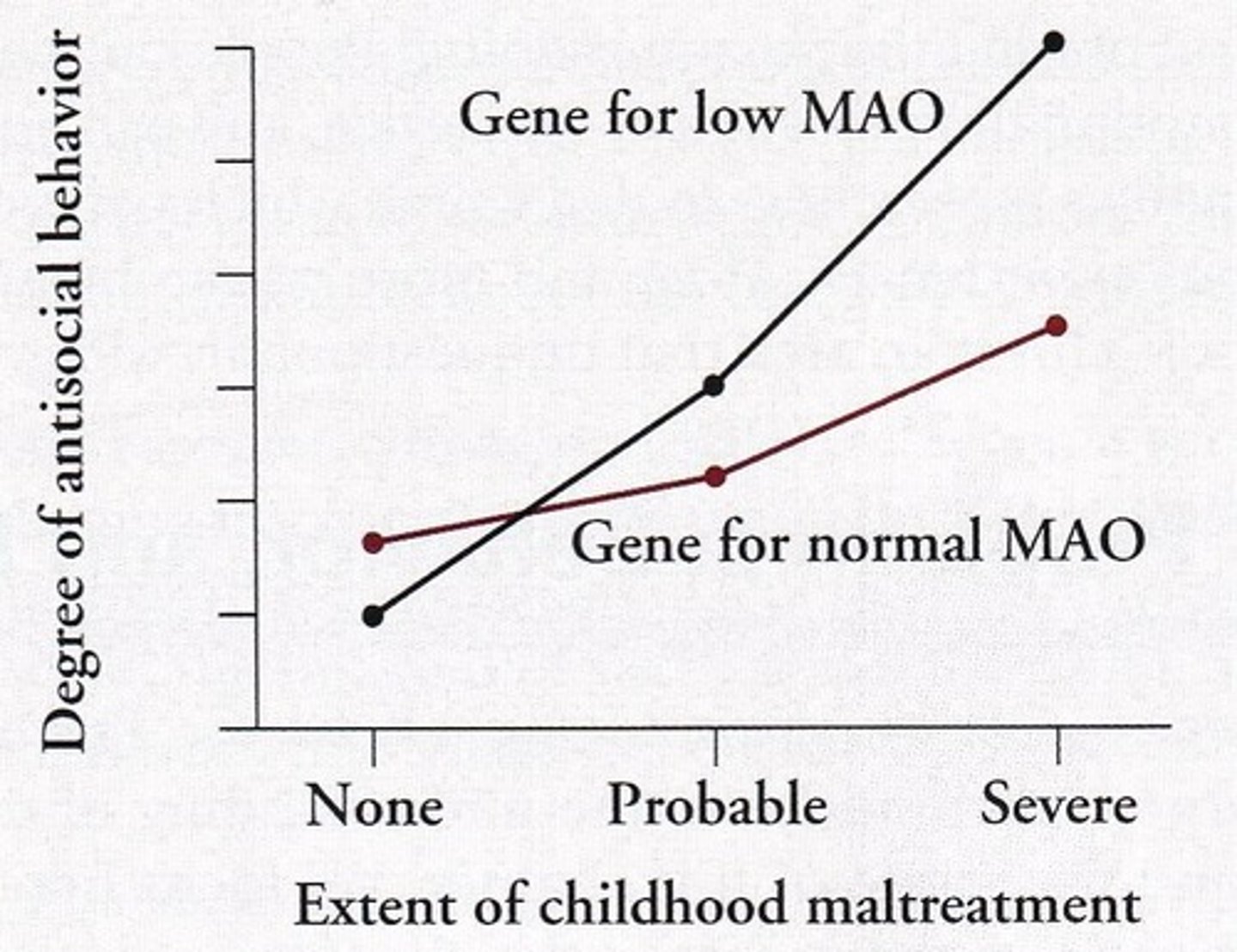
What is the relationship between low MAO and sensation seeking?
High sensation seekers have low levels of MAO, which produces a need for stimulation.
What is Cloninger's Tridimensional Personality Model?
A model categorizing personality traits into novelty-seeking, harm avoidance, and reward dependence.
What is the significance of morningness-eveningness in personality?
It relates to individual differences in circadian rhythms affecting sleep and alertness patterns.
What are the characteristics of evening chronotypes?
Higher impulsivity, risk-taking, sensation-seeking, and extraversion, along with lower conscientiousness and agreeableness.
How does brain asymmetry relate to affective style?
Dispositionally positive individuals show greater left frontal EEG activity, while negative individuals show greater right frontal activity.
What is the role of physiological variables in personality?
Physiological variables may correlate with personality traits or underlie distinct behavior patterns that define personality.