17. GTP and Ring opening
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
What is Group Transfer Polymerisation?
GTP is a controlled (chain) polymerisation technique
Where a trialkylsilyl group from the initiator is transferred along the chain
A nucleophile is also required to increase the reactivity of the initiator.
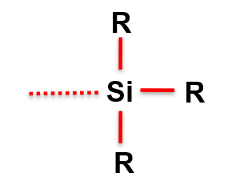
What does a trialkyl group look like?
What is GTP mostly used to polymerise?
acrylates, methacrylates, and has also been used for acrylonitrile and acrylamides
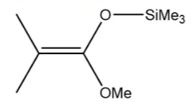
What is a typical GTP initiator?
MTS - 1-methoxy-1-(trimethylsiloxy)-2-methylpropene
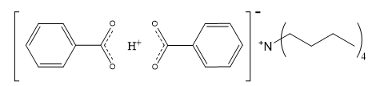
What is a typical GTP nucleophile?
TBABB - tetrabutylammonium bibenzoate
What is the GTP molar mass dispersity?
Mw/Mn < 1.20
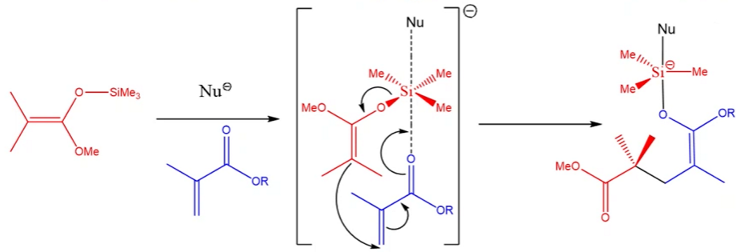
What is the initiation step for GTP?
INITIATION - complexation of the nucleophile with a monomer unit
nucleophile pushes electron density onto the silicon, which passes it to the oxygen, weakening the silicon-oxygen bond in the initiator
Then, electron density is pushed down the C=C double, which passes the density to the C=C bond on the monomer.
The monomer C=C bond pushes electron density to break the C=O bond and form a single S-O bond.
This cycle of passing electron density continues.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of GTP vs Anionic?
Advantages:
both controlled chain polymerisation so we can predict MW
GTP is not as stringent, no need for high vacuum
can be done under inert atmosphere
Disadvantages:
harder to achieve high molecular weights
monomers are limited
molar mass dispersity is higher than anionic (anionic is <1.1, GTP is <1.2)
What is ring opening polymerisation?
A controlled chain polymerisation where ringed monomers are opened to relieve strain
It can have an anionic or cationic active site passed along the chain. (a radical could also be used)
What can ROP be used to polymerise and what does it create?
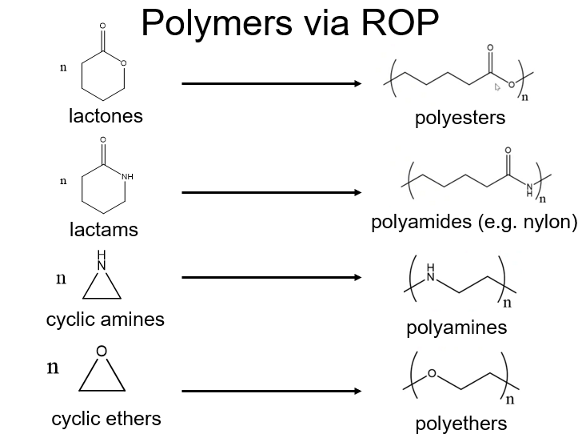
What is the initiation step for anionic ROP? What initiator is used for the anionic ROP mechanism? What is the termination species?
The initiator will be a salt of an alcohol (most commonly a potassium salt)
Initiation step: electron density is passed from initiating group to carbon and density is passes to open the ring at the oxygen, the oxygen becomes our anionic active site.
The termination species is excess alcohol.
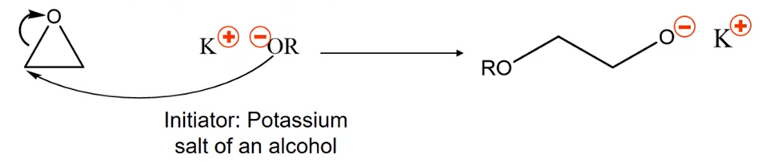
What is the initiation step for cationic ROP? What initiator is used for the cationic ROP mechanism? What is the termination species?
Initiator will be a Lewis acid (electron pair acceptor)
During initiation, density from the ring is given to the oxygen to open the ring, the oxygen passes the density to the lewis acid, the active site becomes a carbocation on the other end of the chain.
Excess alcohol is added to terminate.
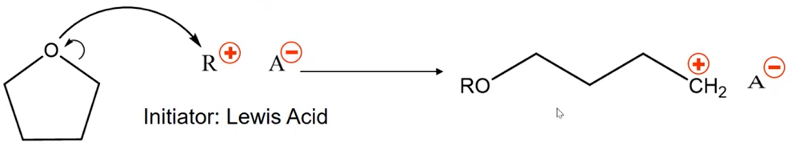
What are advantages and disadvantages of ROP?
Advantages:
controlled so we can predict MW (using MW = mole of monomer / mole of initiator)
Molar mass dispersity < 1.10 (same as anionic)
Very easy to obtain biodegradable polymers
Disadvantages:
Must be done under vacuum with all water removed as it is anionic/cationic.
Can also be explosive.
What is molar disperisty value for ROP?
< 1.10 (same as anionic)