AAMC section bank 2 bio/biochem
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
What is a characteristic of the infectious agent researchers analyzed?
“Researchers investigated the relationship between ABO gene polymorphism and susceptibility to contracting malaria in the Brazilian Amazon region. Researchers used PCR and restriction enzymes for restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis to assess the ABO genotype of each individual and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and blood smear analysis to verify the presence of the protozoan Plasmodium falciparum, the causative agent of malaria. Table 1 shows the relationship between the genotype and P. falciparum infection.”
1.absence of nucleus
absence of nucleic acid
presence of a capsid
presence of intracellular organelles
asking for a characteristic of the agent analyzed, locate what the agent is “protozoan plasmodium falciparum” now we know its a protozoan meaning it lacks capsid so not that, also have both nucleus and nucleic acid leaving choice 4 right
confocal microscope
uses laser based scanning and fluorescence to generate high resolution image, requires fluorescent labeling
light microscope
relies on visible light and uses staining protocols to highlight stuff in erythrocytes
scanning electron microscope
SEM, provides detailed three dimensional images
transmission electron microscope
TEM, high resolution of internal cells like organelles or viruses
Which microscope did researchers most likely use to verify the presence of the infective agent?
“enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and blood smear analysis to verify the presence of the protozoan Plasmodium falciparum, the causative agent of malaria.”
confocal
light
scanning
transmission
light microscope
polymorphic gene means
presence of two or more alleles at a locus, each occurring in at least 1% of the population
According to the passage, what best describes the gene encoding the antigens studied by researchers?
“The ABO gene encodes the enzyme glycosyltransferase, which catalyzes the final step in the synthesis of the A and B antigens on erythrocytes.”
one silent gene that originally duplicated from another gene
one gene encoding a similar protein with different functions in different species
one gene encoding similar proteins with unrelated functions in same species
one gene with more than one allele occurring in population at rate of at least 1%
4
what sequences do restriction enzymes recognize
palindromic sequences
palindromic sequence
sequence of nucleotides that reads the same from 5 to 4 on one strand and 5 to 3 on complementary strand
5′ - A G C T - 3′
3′ - T C G A - 5′
Which sequence do enzymes used for RFLP most likely recognize?
“RFLP is a restriction enzyme”
A
5′–GAAATTTC–3′
B
5′–CAAATTTC–3′
C
5′–GAATTAAC–3′
D
5′–GATTATTC–3′
A, G=C, A=t match the beginning and end going inwards they are the same which is what palindromic sequence is
What is the electron configuration for the metal ion used to obtain the 1H NMR spectrum?
“produce a neutral octahedral complex. Analysis of the 1H NMR spectrum for the Cu2+–Compound 2 complex indicated that the enol proton at 13.58 ppm is absent when compared to the 1H NMR spectrum of Compound 2.”
[Ar] 3d^9
[Ar] 4d^9
[Ar] 4s1 3d8
[Ar] 4s14d8
1, learn how to read a peridic table so normal copper is 4s2 3d9, since its cu 2+ we need to remove two electonrs so remove the 4s2 leaving 3d9
How much Co2+–Compound 2 was added to the agar plate?
“To test the antimicrobial activity of the metal–Compound 2 complexes, test solutions were prepared by dissolving the compounds in DMSO (100 μg/mL) and adding 20 μL to an agar plate loaded with the bacterium Bacillus subtilis (B. subtilis).”
0.02 ug
0.2 ug
2 ug
20 ug
3, convert 20 ul to ml by dividing by 100
20/100=0.02 ml
question is asking for mass, mass= volume *concentration
0.02 ml * 100ug/ml= 2 ug
what’s pyridine
mild base and nucleophilic catalyst that’s commonly used to neutralize HCL, the byproduct of reactions involving acid chlorides
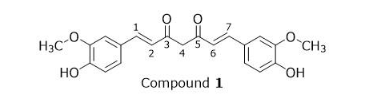
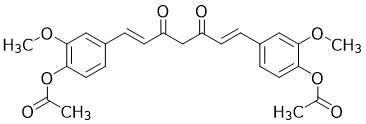
After a neutralization workup, which reagent is needed to produce the compound shown from Compound 1 in the presence of pyridine?
CH3Cl
CH3COCl
(CH3)2CO
CH3COCH2Cl
3, In which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does Compound 2 absorb?from compound 1 to the current compound acetylation occurred because OH became O2 CH3 thing leaving only answer choice 2 right it incorporates Cl which is in the problem because we were told about presence of pyridine and CH3CO matches acetylation description
In which region of the electromagnetic spectrum does Compound 2 absorb?
“Compound 2 was synthesized from Compound 1 and semicarbazide in methanol, and displays a strong absorption band at a wavelength of 423 nm in air.”
1.infared
visible
ultraviolet
x-ray
visible
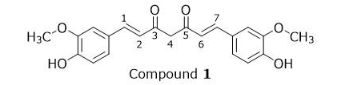
What are the E/Z designations for Compound 1?
A
1Z, 6Z
B
1Z, 6E
C
1E, 6Z
D
1E, 6E
D, bond 1 and 6 end in opposite directions meaning its E or trans
0.5-2ppm
Alkyl (–CH₃, –CH₂–) not near electronegative atoms
2-2.5 ppm
Allylic (next to C=C) or benzylic
3-4.5 ppm
Hydrogens on carbons attached to electronegative atoms (–O–CH₃, –CH₂–Cl, etc.)
4.5-6.5 ppm
Vinylic (C=C–H)
6-8.5 ppm
aromatic hydrogens
9-10 ppm
aldehyde (CHO)
10-12 ppm
carboxylic acid proton (COOH)
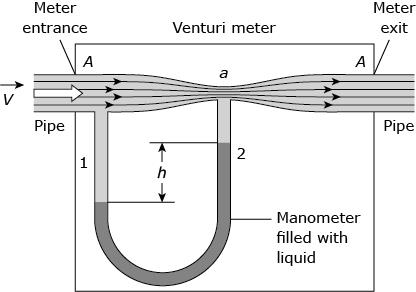
Which single modification to this Venturi meter increases the maximum air flow speed at the entrance that can be measured?
A) shortening the manometer tube
B) increasing the manometer liquid density
C) increasing the amount of manometer liquid
D) decreasing the amount of manometer liquid
B,Increasing the flow speed range means increasing the flow speed at the entrance that can be measured. According to the continuity equation. Increasing the liquid density ρ increases the maximum flow speed v that can be measured.
venturi meter
measures fluid flow speed by measuring the wider entrance and the narrower throat,
max flow speed is limited by height but can be overcome by influencing density so increase density to increase max air flow speed
Momentum is defined as mass multiplied by speed. If a large mass object and a small mass object have the same momentum, which object has the larger kinetic energy?
_
A
The small mass object
B
The large mass object
C
Either object, depending on their speeds
D
Both objects have the same kinetic energy
A
momentum mass and kinetic relationship
the smaller the mass the larger kinetic energy if momentum is same
Values for physical properties of water and mercury are given.
Density | Thermal expansion coefficient | Viscosity | Surface tension | |
Water | 1000 | 2.1 | 8.9 | 72 |
Mercury | 13500 | 1.8 | 15 | 500 |
Which property makes mercury better suited than water for use in clinical capillary thermometers?
A. density
b. viscisity
c. surface tension
d. thermal expansion coefficient
surface tension
what does thermometer rely on
consistent and measurable expansion of liquid with temp change and the liquid must move reliably through the capillaryWhat is the molar mass of CaM after its reaction with one equivalent of Compound 1? tube
What is the molar mass of CaM after its reaction with one equivalent of Compound 1?
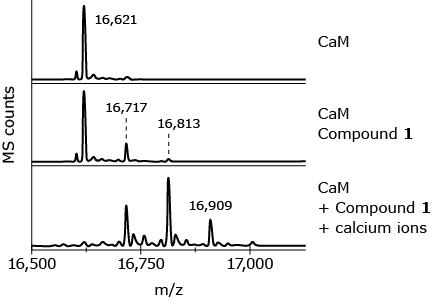
A
16621 g/mol
B
16717 g/mol
C
16813 g/mol
D
16909 g/mol
b
Which amino acid in CaM is expected to be responsible for binding the ion that triggers conformational changes in the protein?
“Calmodulin (CaM) is a ubiquitous eukaryotic calcium receptor containing two calcium-binding sites. Each site accommodates two calcium ions interacting mostly with acidic amino acid side chains.”
A
Arginine
B
Aspartate
C
Leucine
D
Phenylalanine
B
In terms of valency, metal/nonmetal classification, and ion type, what is the best description of the ion that induces conformational changes in CaM?
“Calmodulin (CaM) is a ubiquitous eukaryotic calcium receptor containing two calcium-binding sites. Each site accommodates two calcium ions interacting mostly with acidic amino acid side chains.”
A
Monovalent metal cation
B
Monovalent metal anion
C
Divalent metal cation
D
Divalent metal anion
C, it interacts with acidic or negative amino acids giving away two electrons making it an cation
break down what happens in chemical reaction
often excess reagents are used to drive the reaction to completion, any unreacted reagent must be removed to neutralized to prevent unwanted side chains
The protocol for CaM labeling by Compound 1 includes a step where Compound 4 is added to the reaction mixture. Why is this step needed?
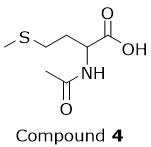
A
Compound 4 acetylates unreacted residues in CaM.
B
Compound 4 prepares protein residues for their reaction with Compound 1.
C
Compound 4 ensures that the reaction mixture does not have unreacted Compound 1.
D
Compound 4 sequesters the benzaldehyde byproduct of the reaction between CaM and Compound 1.
c, This is consistent with how labeling reactions are done. After the labeling step, you add a scavenger molecule that reacts with any leftover Compound 1 so it doesn’t nonspecifically keep modifying CaM or interfere in later steps.
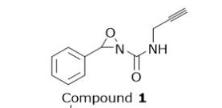
How many stereoisomers does Compound 1 have?
A
2
B
3
C
4
D
8
2, theres two N bonds which are stereoisomers, two stereogenic double bond E/Z
sterioisomers
A stereoisomer requires either (a) a stereogenic (chiral) center (sp³ carbon with four different substituents) or (b) a stereogenic double bond (E/Z).
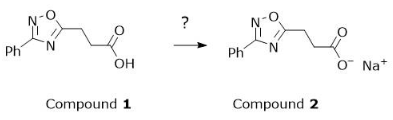
Which compound is most appropriate to accomplish the synthesis in Figure 2?
A
Sodium bromide
B
Sodium chloride
C
Sodium hydroxide
D
Sodium iodide
C, compound 1 was carboxylic acid (CooH) which became a salt. this process needs a strong base which answer C fulfils NaOH
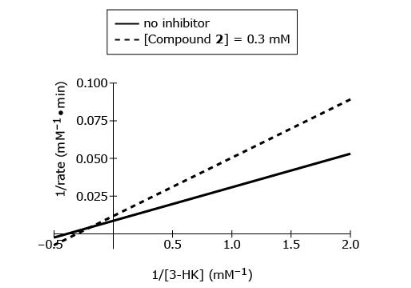
Which inhibition mechanism is exhibited by Compound 2 against HKT?
A
Competitive inhibition
B
Mixed inhibition
C
Noncompetitive inhibition
D
Uncompetitive inhibition
B, in the figure the two lines intersect with each other meaning both Vmax and Km is changed which is mixed
Which type of column chromatography was mentioned in the passage?
“To prepare for steady-state kinetic studies, His-tagged HKT was purified by column chromatography using a resin charged with NiSO4 solution. Compound 2 was synthesized and tested for its inhibitory activity against HKT. The last step in a three-step synthesis scheme is shown in Figure 2.”
A
Size exclusion chromatography
B
Antigen-antibody immunoaffinity chromatography
C
Hydrophobic interaction chromatography
D
Immobilized metal affinity chromatography
D, “his tagged HKT purified by column chromatography using resin charged with NiSo4”
immobilized metal affinity chromatography
relies on strong and selective interactions between histidine residues in His-tagged proteins and metal ions immobilized on resin
What is the Kb of 3-HK?
“Because an accumulation of 3-HK, a toxic compound with a predicted pKa of 1.0, is detrimental to the larval development of A. aegypti,”
A
0.1
B
13
C
10–13
D
10–14
C,Kb = 10–(14 – 1) , 14-pka
What is the IC50 of Compound 2 in nanomolar?
“an IC50 of 72 μM, Compound 2”
A
0.000072
B
0.072
C
7200
D
72,000
D, um is micromolar which is 1000nm/nanomolar so 72 × 1000 gives you 72,000 nanomolar
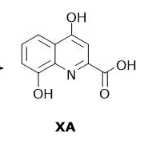
What is the number of hydrogen bond donors in XA?
A
3
B
4
C
5
D
6
3
ne mole of ideal gas undergoes a thermodynamic process in which pressure doubles and volume halves. What is the value of the molar heat capacity of the gas during the process?
_
A
0
B
∞
C
Undetermined
D
Ideal gas constant
infinity
molar heat capacity of ideal gas law
since temp doesn’t change and heat is exchanged the heat capacity is infinite
in alpha decay what do you
subtract from atoms mass number and atomic number, 4 from mass and 2 from atomic number
A hollow cube floats half submerged in oil of density 800 kg/m3. The cube edges are marked every 1 cm. What is the minimum density of a liquid that can be determined by reading the mark at which the cube floats?
_
A
100 kg/m3
B
200 kg/m3
C
400 kg/m3
D
600 kg/m3
C, cut density in half bc of Archimedes principal
Archimedes principal
Any object that is fully or partially submerged in a fluid experiences an upward buoyant force equal to the weight of the fluid that the object displaces.
Which process would be the first affected if dividing eukaryotic cells were treated with an inhibitor of spindle fiber elongation?
_
A
Aster formation
B
Attachment of fibers to centromeres
C
Positioning of chromosomes on the midline
D
Chromosome movement toward the poles
Aster formation
what are asters
star shaped microtubule arrays that form around each centrosome early in prophase prior nuclear envelope break down or spindle microtubule being to interact with chromosome
what are spindle fibers
microtubule based structures that form the mitotic spindle for proper chromosome alignment and segregation
mitosis is composed of what
-prophase
-prometaphase
-metaphase
-anaphase
-telophasepr
prophase
chromosome condense, spindle fibers begin forming, spindle assembly
prometaphase
spindle fibers attach to kinetochores
metaphase
chromosomes align at metaphase platean
anaphase
sister chromatids pulled apart, spindle fibers elongate to separate poles furthertel
telophase
nuclear envelope reform, cytokinesis follows
microtubule polymerization (elongation)
adding tubulin dimers yields growth
microtubule depolymerization (shortening)
removing dimers yields shrinkage
what are some inhibitors that mess with microtubule dynamics
colchicine or taxol used in cancer therapy
Which terms best define tRNA?
_
A
Molecule consisting of a double RNA strand of approximately 1000 nucleotides
B
Molecule consisting of a single RNA strand of approximately 1000 nucleotides
C
Molecule carrying the attachment site for an amino acid at its 3′ end
D
Molecule carrying the attachment site for the ribosome at its 5′ end
C
tRNA
-single stranded RNA 80 nucleotides
-carries amino acid at 3’ end
The table shows the conditions used to transform bacterial cells.
DNA concentration | Volume of DNA used | Volume of bacterial cells | Volume of transformation mixture plated |
0.005 µg/µL | 10 µL | 490 µL | 100 µL |
What is the transformation efficiency if the number of colony-forming units (CFU) is 4?
_
A
4000 CFU/µg DNA
B
400 CFU/µg DNA
C
40 CFU/µg DNA
D
4 CFU/µg DNA
B, calculate how much dna was added via: Dna conc volume used =Mass, 0.005 × 10 = 0.05 uG
next calculate total transformation volume
volume of dna used + volume of bacterial cell = 500 uL
calculate how many colonies are in the total volume we are given a number for colony forming units use it, 500/4= 20 CFUs total
use efficiency number to finish this, 20/0.05= 400 CFU/ ug DNA
The table shows kinetic parameters of an enzymatic reaction in the presence of various compounds.
Compound | KM (mM) | Vmax (mM/min) |
Control | 0.82 | 3.26 |
A | 1.6* | 3.38 |
B | 0.81 | 2.1* |
C | 0.41* | 3.30 |
D | 0.52* | 2.1* |
(Note: * indicates p < 0.05 compared to control.)
Which compound is a non-competitive inhibitor?
_
A
B
C
D
B, non comp inhibitors reduce v max while not impacting Km, after comparing to control only B doesn’t change kM
In Figure 1, which molecules represent 1 and 2, respectively?
“Clotting starts when signals released by the cells of a damaged blood vessel trigger a cascade of chemical reactions involving proenzymes and tissue factors.
fibrinolysis to occur, plasminogen is converted into an enzyme capable of degrading fibrin (Figure 1).”
A
Antithrombin and prothrombin
B
Prothrombin and antithrombin
C
Prothrombin and plasmin
D
Plasmin and prothrombin
C
plasmin
active enzyme that breaks down fibrin during fibrinolysis
whats prothrombin
inactive precursor thats cleaved to form thrombin during clotting cascade
According to the passage, which amino acid is responsible for the catalytic activity of the enzymes involved in the coagulation cascade? Amino acid is serine
A
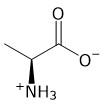
B
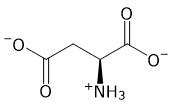
C
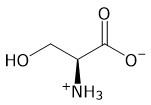
D
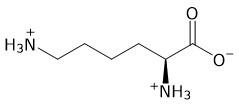
C
liver
clotting and fibrinolysis
spleen
immune function, blood filtration
pancreas
digestion and blood sugar regulation produces digestive enzymes like lipases and amylases and proteases to break down food
small intestine
responsible for nutrient absorption and digestion, produces digestive enzymes such as maltase, surcease, peptidases
Which cells are the precursors of the cellular fragments that are part of a clot?
A
Megakaryocytes
B
Monocytes
C
Lymphocytes
D
Progranulocytes
A
megakaryocyte
where platelet/thrombocytesmo that play a role in blood clotting is from
monocyte
white blood cells (leukocyte) function in immune system rather than clotting, largest type of leukocytes that can become macrophage and dendritic cells (involved in phagocytosis)
lymphocyte
T, B, NK cells key role in immune response and antibody production in body aren’t involved in platelet production nor clot formation
progranulocytes
develop from myeloblast r precursor of granulocyte such as nucleophiles, eosinophils and basophil
According to the passage, what is a characteristic of the hormone whose high plasma levels are associated with higher risks of thrombosis?
“Individuals treated with hormonal therapies containing high estrogen levels are more prone to thrombosis due to increased plasma levels of several clotting factors.”
A
It binds clotting factors in circulation to stimulate their secretion.
B
It binds a receptor in the cytosol to directly block protein degradation.
C
It is synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and, bound to its receptor, acts as an enzyme activator.
D
It is synthesized in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum and, bound to its receptor, acts as a transcription factor.
D
vasopressin
secreted in hypothalamus
hypothalamus
key neuroendocrine structure that regulates the body stress response by producing CRF which leads to production of ACTH leading to cortisol secretionc
cerebellum
located near brainstem, primarily responsible for motor coordination n balance
medulla oblongata
located at base of brainstem responsible for autonomic function such as respiration and heart rate
occipital lobe
located at the posterior part of brain responsible for visual processing
thalamus
major relay center for sensory and motor information in the brain
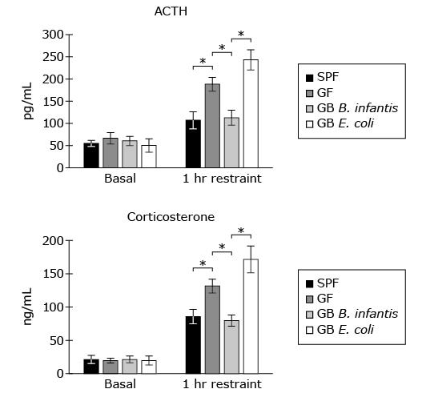
According to Figure 1, in GB E. coli mice, which type of hormone shows the highest fold increase after 1 h restraint, and how will it circulate in blood?
A
The lipid, which will circulate freely
B
The lipid, which will circulate bound to a carrier
C
The peptide, which will circulate freely
D
The peptide, which will circulate bound to a carrier
B, corticosteroids a peptide the figure shows higher level in ACTH which we can assume is the lipids now, its B because lipids are hydrophobic meanin they cannot travel freely and need to be bound to a carrier
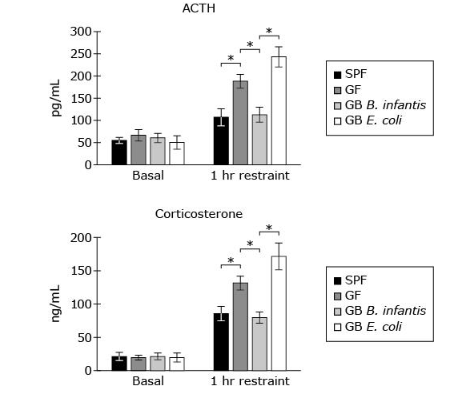
Which structure(s) is(are) present in both the microorganisms carried by the GB mice used in Experiment 3?
A
Membrane-bound organelles
B
Double membrane
C
Circular DNA
D
Thin cell wall
C, both are virsu’s meanin they lack cell wall, no double membrane and no membrane bound organelles
From which germ layer does the organ with high CRF levels originate? “CRF from hypothalamus”
A
Ectoderm
B
Endoderm
C
Mesoderm
D
Trophoderm
A
ectoderm
central nervous system components so brain, spinal cord, peripheral nerves
endoderm
forms epithelial linin of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract like liver and pancreas
mesoderm
blood vessels supplyin the brain, vessels in general
trophoderm
formin the placenta and extraembryonic structures
Which method did researchers most likely use to analyze adrenal and pituitary glands in Experiment 2?
“On prepared slides, researchers observed no structural differences in the adrenal and pituitary glands between GF and SPF mice after they had been restrained. However, they observed increased hypothalamic levels of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in GF mice when compared to SPF mice.”
A
Immunohistochemistry
B
Northern blot
C
Southern blot
D
Western blot
A
Which enzyme is required for the production of cDNA from an RNA template?
_
A
Deoxyribonuclease
B
Peptidyl transferase
C
Reverse transcriptase
D
RNA polymerase
C
deoxyribonuclease
used to breakdown dna molecules like cDNA
peptidyl transferase
link amino acids
reverse transcriptase
production of cDNA from RNA via reverse transcription
RNA polymerase
production of cDNA from RNA template,
A PCR reaction is performed using non-radioactive nucleotides and a DNA template labeled with radioactive phosphate on both strands. After two rounds of PCR, what percentage of DNA molecules will contain radioactive phosphate on at least one strand?
_
A
0%
B
25%
C
50%
D
100%
in a nutshell DNA replication is occurring which is a semi conservative process meaning its answer choice C 50 %
Which action will most likely increase FADH2 production in the citric acid cycle?
_
A
Inhibiting fumarase
B
Increasing fumarate levels
C
Decreasing succinate levels
D
Activating succinate dehydrogenase
D