SAM final - blood
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
Pathology of Non regenerative anemia
Primary Bone Marrow: intrinsic
Erythroid hypoplasia/aplasia
Myelophthisis
Myelofibrosis
Myelodysplasia
Secondary Bone Marrow: extrinsic
Anemia of Inflammatory disease (AID)-chronic dz
Renal disease
Endocrine disease
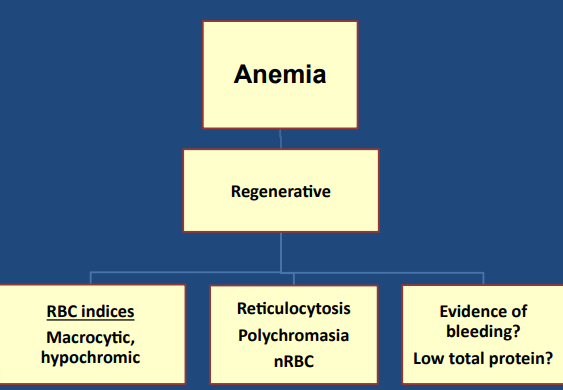
Iron deficiency anemia → regenerative early
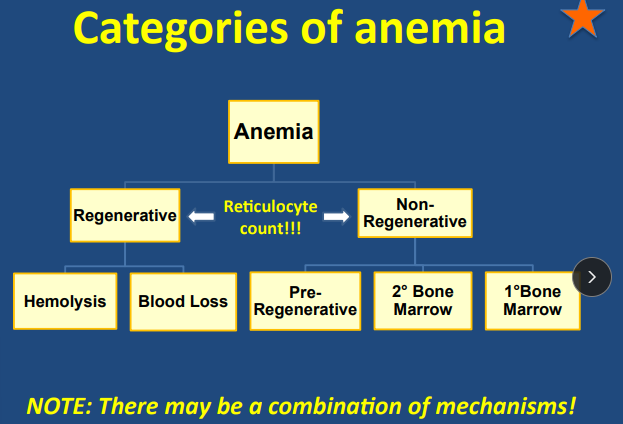
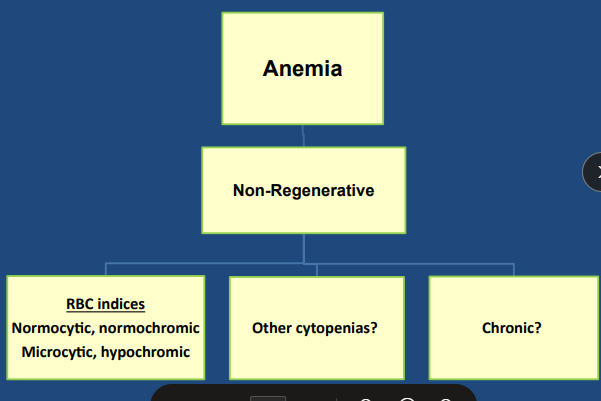
Non-Regenerative Anemia
Chronic
MANY causes!
– Pre-regenerative
– Primary bone marrow (“intrinsic”)
– Secondary bone marrow (“extrinsic”)
Cats > Dogs
Bone marrow sample may be needed!
Non-regeneration categories
pre-regen (acute) → takes 2-5d for making RBC
Primary bone marrow (intrinsic)
Erythroid hypoplasia/aplasia: Immune mediated destruction of RBC precursors (anemia only)
Myelophthisis
Myelofibrosis
Myelodysplasia
Secondary bone marrow (extrinsic)
Anemia of Inflammatory disease (AID)
Dogs never >30%
Cats <20% w/ severe renal dz
Renal disease ( EPO production)
Endocrine disease
Iron deficiency anemia (Often regenerative actually!) (anemia only)
Clinical Signs of Anemia
GET full history!!
May be normal depending on severity
Lethargy, Exercise intolerance, Weakness, Collapse
Pica (mainly cats)
Icterus, Bleeding, Pale, Melena
Tachycardia, Tachypnea, Bounding pulses, Heart murmur(physiologic)
Diagnostic Testing for Anemia Patients
#1 test: CBC / chem & PCV/TS!
Localizing:
Anemia only → secondary bone marrow disease
Iron deficiency: Microcytic hypochromic regenerative anemia
Anemia + cytopenias → primary bone marrow disease
Bone Marrow Aspirate #1 → Cellularity, Maturation,
Erythroid: myeloid ratio, Neoplasia, Infections
Bone Marrow Biopsy → Structure, Fibrosis, Necrosis, FeLV testing
CBC/ Chem → Coombs, RBC Ab, RBC indices, RBC morphology, Reticocytes, PCV/TP #1, smear + reticulocyte count, endocrine/renal panels
MCV- how big are the cells?
MCHC - how much hemoglobin in RBC?
Imaging → Rads, US
Infectious testing!! → FeLV/FIV, vector borne, fecal testing
Treating Anemia
General support: Transfusions, Vit B12, Iron, Folic acid, Erythropoietin
(2)Renal disease: Erythropoietin
(2)Iron deficiency: Deworm, Gastroprotectants, Iron supp
(1)PRCA: Immunosuppressive meds
(1)Myelophthisis: Chemo, Antimicrobials
(1)Myelofibrosis: Transfusions
Hemolytic Anemia
Immune-mediated hemolytic anemia → PREMATURE RBC destruction, type 2 reaction
CBC: Anemia of Inflammatory disease (AID), Hyperbilirubinemia
Hyperbilirubinemia does not differentiate extravascular vs. intravascular hemolysis
Many hemolytic anemias are not immune-mediated…
Erythrocyte organisms: Babesia(dogs), Mycoplasma, Cytauxzoon felis
DT: Organism ID, Blood smear, Blood PCR, Serology
Toxins: Zinc, Onions/garlic, Acetaminophen
Oxidative injury → Heinz bodies → decreased RBC deformability → increased fragility → hemolysis
Microangiopathic/fragmentation anemia: DIC, Hemangiosarcoma, Vasculitis, Heartworm
Mechanical trauma to RBC → schistocytes, keratocytes
Increased erythrocyte fragility
Hemophagocytic syndrome
Intravascular Vs Extravascular hemolysis
Extravascular hemolysis
IgG or IgM → Antibody bound to RBC → Premature RBC destruction
Spherocytosis, Hyperbilirubinemia, Bilirubinuria
Intravascular hemolysis
IgM → complement activation → MAC punches holes in RBC → Premature RBC destruction
Hyperbilirubinemia, Hemoglobinemia, Hemoglobinuria, Ghost cells
Worse prognosis
Canine IMHA
Et: Neoplasia, Infectious diseases, Drugs, Vaccines
Primary > secondary
Sig: Cockers, Min Schnauzers, Poodles, 2-7 years
Cs: Icterus, thromboembolism (leading cause of death), pigmenturia, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, lymphadenopathy, fever
Port wine: hemoglobinuria
Darker/orange: bilirubinuria
Dt: dx of exclusion! Spherocytosis, autoagglutination, rads, infectious testing, US, Anti-erythrocyte Ab (Coombs or flow cytometry)
#1: PCV/TS, saline agglutination, blood smear!, CBC/Chem → regen macroscopic, hypochromic anemia
Tx: immunosuppression + thromboprophylaxis (acute)
Supportive Care, Thromboprophylaxis(#2), Glucocortoid(#1) + Azathioprine or Cyclosporine, IVIg (Blocks Fc receptors), Rivaroxaban, Clopidogrel (irreversible platelet inhibition), Euthanasia
Chronic Tx: Gradual taper drugs → ALWAYS attempt full taper after PCV is NORMAL → ↓ 25% q4w
Px: Guarded, at risk for other IM diseases
Negative indicators → Intravascular hemolysis, Hemoglobinemia, Hemoglobinuria, Ghost cells, Autoagglutination, Hyperbilirubinemia, Thrombocytopenia, ↑ ALP
Feline IMHA
Et: Mycoplasma, FeLV, FIV, Cytauxzoon felis, Transfusion reaction, Neonatal isoerythrolysis
Secondary > Primary
Dt: Autoagglutination
Spherocytes difficult to see in cats
Rule out secondary causes first
Tx: immunosuppression + thromboprophylaxis
Primary: prednisolone, cyclosporine
Secondary: treat infection, prednisolone
Blood Loss Anemia
Et:
Acute: Hemoabdomen, Severe thrombocytopenia
Chronic: GI hemorrhage, Intestinal parasites, Ectoparasites → might have normal TP
Cs:
GI: melena, hematemesis, hematochezia, NSAID history
Urinary: hematuria, stranguria, pollakiuria
Epistaxis: nasal bleeding
Hemoabdomen: distention, weakness, decreased lung ventral sounds
Pulmonary / hemothorax: tachypnea, resp distress
Dt: Rads, U/S, Fecal float, Chem/CBC BMBT, vWF testing, Factor deficiency testing, UA, PT/PTT, Low TP, High BUN, Thrombocytopenia, PCV, RBC indices, Retic count, RBC morphology
Chronic might have normal TP
Tx: Blood transfusion, PPIs, sucralfate, barium, antiparasitics, plasma, vit K1
Transfusion + STOP the bleeding + treat underlying cause
Relative Erythrocytosis
Et: dehydration
Sighthounds have naturally higher PCV
Acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome (previously
HGE)
Dt: ↑ TP
Exception is acute hemorrhagic diarrhea syndrome
TP often low-normal or decreased
Tx: Treat with IV fluids
Absolute Erythrocytosis
Et:
Primary: Polycythemia rubra vera, Bone marrow RBC proliferation, Low/undetectable EPO
Secondary:
Appropriate → due to hypoxia → Pulmonary dz, Right-to-left shunts, High altitude
Inappropriate → no hypoxia → Renal mass, Neoplasia
Cs: PU/PD, neuro signs, epistaxis, hyphema, retinal hemorrhage, Bright red mucous membranes
may be normal
Dt: PCV >70%, Rads, US, Arterial blood gas → Evaluate underlying cause
Tx: Therapeutic phlebotomy, Hydroxyurea
Goal = reduce blood viscosity by lowering circulating RBCs
Nucleated RBCs
Often “mis-counted” as WBC
Et: Early marrow release
Strong regenerative anemia, heat stroke, neoplasia, extramedullary hematopoiesis, splenectomy, splenic dysfunction, lead toxicity
Dt: nRBCs per 100 WBC or % of total nucleated cells
Often miscounted as WBCs → Must correct WBC count if nRBCs elevated
Clot formation
Primary Hemostasis #1
Platelet plug formation at site of endothelial damage
Platelets + Adhesive proteins (vWF)
Secondary Hemostasis #2
Clotting factors assemble thrombus on platelet plug
Stabilize platelet plug
Intrinsic, extrinsic, and common cascaded
Clotting factors produced in liver
Clinical Presentation of Coagulopathy
Et: Medications, Toxins, Rodenticides, Previous surgery, Previous bleeding episodes, Recent vax, Inherited
Cs: Spontaneous bleeding, Prolonged bleeding, Hemothorax, Pulmonary hemorrhage, Neurologic, Anemia, Asymptomatic
Petechiae <3 mm → Primary hemostasis → Platelets
do not blanch
Ecchymosis → >1 cm → Primary + secondary hemostasis
do not blanch
Cavitary bleeding → coagulation factors → secondary hemostasis
Dt: CBC, Platelet count, PCV/TP, BMBT, PT/PTT
BMBT: vWF deficiency, thrombocytopathia → Not thrombocytopenia
PT: extrinsic + common pathway clotting disorders → first one to prolong (tests for factor 7)
aPTT: intrinsic + common pathway clotting disorders
ACT less sensitive
Special Considerations with Coagulopathy Patients
Use peripheral vein + hold off 5min
Do NOT blanch Petechia or ecchyosis
Avoid cystocentesis
Pseudothrombocytopenia
Et: Platelet clumping causes false decreased platlet count
Sig: Cats > dogs
Dt: Check smear manually
Macrothrombocytopenia
Et: Mutation in beta1-tubulin
Platelets 50k–150k but functional
Sig: Cavalier King Charles Spaniel
Cs: No spontaneous bleeding
Dt: Test at Auburn
Clinical Presentation of Thrombocytopenia
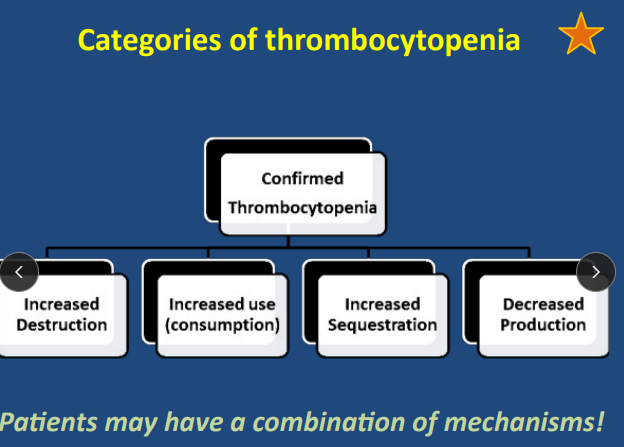
Et: Increased Destruction, Increased Use, Increased Sequestration, Decreased Production
Dt: Less than normal platelet count (175k-400k/µL)
Mild: 100k–175k
Moderate: 30k–100k
Severe: <30k → Spontaneous bleeding
Tx: treat underlying cause
IM: immunosuppressives(pred/cyclosporine), Vincristine(acute), Splenectomy
Neoplasia: chemotherapy
Infection:antibiotics
Px: ITP has a better prognosis than IMHA
Increased Destruction Thrombocytopenia
Et: Immune thrombocytopenia
Anti-platelet Ab + phagocytosis in spleen/liver + no complement fixation
Vector-borne diseases → Anaplasma platys
Sig: Middle-aged, Females, Cocker spaniels
Cs: Spontaneous bleeding
Dt: severe <30k platlets
Anti-platelet Ab → Flow cytometry
Anti-megakaryocyte Ab → Bone marrow sample
Tx: Pred, Cyclosporine, Azathioprine, Doxycycline, Human IVIG, Vincristine
Immunosuppression + antibiotics + Supportive care
Vincristine → Stim megakaryocyte frag
Px: Fair; neg prognostic factors → Melena, Increased BUN
ITP has a better prognosis than IMHA
Forms of Thrombocytopenia
Increased Destruction → IM
Anti-platelet Ab + phagocytosis in spleen/liver + no complement fixation
Vector-borne diseases → Anaplasma platys
Increased Use → Consumption
Normal response → Acute hemorrhage, GI bleed, Vit K antagonists, Thrombosis
DIC
Vasculitis → Pancreatitis, lepto, pneumonia, vector bone disease
Increased Sequestration → Splenomegaly, vector bone disease
Decreased Production(bone marrow) → Drugs, Infection, Neoplasia, IM
Vector-Borne Diseases and Thrombocytopenia
Most common lab abnormality → thrombocytopenia
Bleeding can occur even if platelets >30k
Mechanisms → Immune destruction, Consumption (vasculitis), Sequestration
Thrombocytopathia
Et: Congenital, drugs, systemic disease → Uncommon
NSAIDs, clopidogrel, aspirin, synthetic colloids, uremia, liver disease, hyperglobulinemia, iatrogenic
Cs: spontaneous severe hemorrhage
Dt: Genetic testing available (Auburn Lab), BMBT
vWF Disease
Et: Most common inherited bleeding disorder in dogs tho still → Uncommon
Type I: decreased vWF (#1) -mild
Type II: decreased large vWF - mod
Type III: absence of vWF - severe
Sig: Doberman
Cs: resemble platelet disorder
Dt: vWF assays, genetic testing, BMBT
Tx: Desmopressin, Fresh plasma, Cryoprecipitate
Buccal Mucosal Bleeding Time (BMBT)
Use: Evaluates primary hemostasis disorders
Spontaneous/prolonged bleeding with normal platelets + PT/PTT
Suspected vWF deficiency or thrombocytopathia
Not thrombocytopenia
Value: Measures time to platelet plug formation
Normal <3–4 minutes
Thrombocytosis
Excess glucocorticoids
Endogenous → Cushing’s
Exogenous → steroids
Inflammation
Iron deficiency
Clotting Cascade for Secondary Hemostasis
Vitamin K: activates 2, 7, 9, 10
Intrinsic pathway PTT
Activation: by contact with non-endothelial surfaces
Factors: 12, 11, 9, 8 → “In” walmart: Nothing is $12…everything is $11.98”
Extrinsic pathway PT
Activation: by contact with tissue factor
Factors: 7
Common pathway
Ends: in fibrin production
Factors: 10, 5, 2, 1 → 10/2=5, 1 left
Inherited Secondary Hemostatic Disorders
Signs of hemorrhage!
- Anywhere!
- Can be cavitary!!
Hemophilia A - genetic
Et: X-linked factor 8 deficiency
More common than B
Dt: Prolonged PTT + ACT
Hemophilia B - genetic
Et: X-linked factor 9 deficiency
Dt: Prolonged PTT + ACT
Factor XII deficiency - acquired
Sig: 20% of cats
Cs: No clinical bleeding
Dt: Very prolonged PTT
Rodenticide Toxicity
Et: Warfarin, Diphacinone, Brodifacoum, Bromadiolone
Vit K epoxide inhibition → effects factors 2 +7 + 9 + 10 → affects all 3 pathways
Most common acquired secondary hemostasis disorder
Cs: Cavitary bleeding, bleeding anywhere, hemothorax
Signs 4 days post ingestion
Dt: Prolonged PT (1st effected), Prolonged PTT
Tx: Induce vomiting Activated charcoal, Vit K1, Plasma
Liver Disease
Et:
Dysfunction: ↓ clotting factor production, Abnormal platelet function, DIC
Cholestasis: ↓ Vitamin K absorption
Cs: spontaneous hemorrhage
Tx: Treat cause, Vit K1, Plasma
Clinical Pathology of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Inappropriate activation of the coagulation system → coagulation & fibrinolysis imbalance
Excessive coagulation → Microthrombi formation → Consumption of platelets and clotting factors
Step 1: Hypercoagulable→ Thrombus, ischemia, necrosis, organ failure
Step 2: Hypocoagulable → hemorrhage
Mixed coagulation disorder of both primary and secondary hemostasis
Primary: Thrombocytopenia → increased consumption
Secondary: Prolonged PT + PTT → consumption of clotting factors
Clinical Presentation of Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Et: Not a specific disease → secondary to inflam or other dz
Endothelial damage → Vasculitis, Hemangiosarcoma, Sepsis
Activation of tissue factor → Neoplasia, Hemolysis, Heat stroke, Pancreatitis
Dt: clinical suspicion + thrombocytopenia + prolonged PT/PTT + decreased antithrombin, increased D-dimers or FDPs
Consumption: Thrombocytopenia, Prolonged PT/PTT, Decreased antithrombin
Fibrinolysis testing: Fibrin-degradation products + D-dimers
Whole blood viscoelastic coagulometry: ONLY test for “hypercoagulable phase”
TEG, Sonoclot, VCM
Tx: Treat underlying condition
IV fluids, plasma, whole blood, heparin
Virchow’s Triad
Endothelial injury
Valve disease, Endothelial damage from endotoxins, Heartworm disease, Neoplasia, Vasculitis
Changes in blood flow → Stasis or turbulence
heart disease, shock, hypotension
Hypercoagulability of blood → Loss of natural anticoagulants
Antithrombin loss with GI or glomerular disease
Hyperfibrinolysis
Sig: Greyhounds
Cs: excessive post-procedure or post-trauma bleeding
Tx: Antifibrinolytic agents → Epsilon aminocaproic acid or Tranexamic acid
Prevent activation of plasminogen to plasmin
Interpreting the Leukogram
Step 1: Is the total WBC ↑, normal, or ↓?
Step 2: Evaluate the differential (%)
Percentages used to calculate absolute numbers
Use absolute numbers, NOT percentages, for interpretation
Interpreting Neutrophil Values
Neutrophilia
Stress → Mature neutrophilia → No more than 2× upper RI
Inflam → Infection, Neoplasia, IM
Neutropenia
Decreased production
Consumption → dumping
IM destruction
Bands
Infection,systemic inflam, IMHA, Bone marrow rebound
Toxic Change
Typically infection, severe non-infectious inflammatory disease
Interpreting Monocyte Values
Monocytosis
Inflam, Infection, Neoplasia, IM, Non-infectious inflam
Monocytopenia - who cares
Not clinically relevant
Interpreting Lymphocyte Values
Lymphocytosis
Mild: Young, vax, stressed cats ONLY, addison’s
Dogs = lymphopenia (stress)
<8,000
Mod: Ehrlichiosis
< 10,000
High: Leukemia
Lymphopenia - who cares
Not clinically relevant
Stressed dogs
Interpreting Eosinophil Values
Eosinophilia
Parasites
Allergy
Eosinopenia - who cares
Not clinically relevant
Stress
Stress Leukogram
"LEMON”
idecreased Lymphopenia → Cats may have lymphocytosis or lymphopenia
decreased Eosinopenia
increased Monocytosis
increased Mature neutrophilia →Should not exceed >2× normal
Lymph Node Anatomy
Structure:
Cortex → B + T lymphocytes
Paracortical region → Small T lymphocytes, Macrophages
Medulla → Lymphocytes, Macrophages, Plasma cells
Function: Filtration, Phagocytosis, Lymphocyte production, Ab production
Location:
Superficial: Popliteal, Prescapular, Mandibular(palpable lymph nodes), Axillary, Inguinal
Thorax: Perihilar, Sternal (drains into abdomen)
Abdomen: Mesenteric, Sublumbar
Evaluating Lymph Nodes
PE: Size, Texture, Mobility, Temperature, Pain, Localization
Labs: CBC, Chem, UA
DI: rads, US, CT
FNA: Cell type/size, Infectious organisms, Culture
Biopsy: Tissue core, Open (wedge), Removal
often not req
Ancillary: Bone marrow, Infectious dz
Lymphadenopathy
Et:
Localized: pathologic process in region drained → inflammation or neoplastic
Round cell neoplasia, Carcinoma, Sarcoma, Lymphoma, Bacti
Generalized: Systemic disease → Infection, IM, neoplasia
Cs: Enlarged, tender, firm, Mobile or adherent, May be bi-lobed (neoplasia)
Dt: FNA #1, biopsy (often not req)
Lymphoma → Lg lymphocytes
Granulomatous → Macrophages + Neutrophils → Fungal, bacti
Reactive →Small lymphocytes + Plasma cellls → antigenic stimulation
Splenic Masses and Nodules
Et:
Benign: Hematoma, Hemangioma, Myelolipoma
Most are benign
Malignant: Hemangiosarcoma, Marginal cell lymphoma
Spontaneous bleeding = more likely malignant
Dt: US
Cannot determine malignancy visually
Splenomegaly
Et: Diffuse Splenic Enlargement
EMH, lymphoid hyperplasia, lymphosarcoma, anemia, thrombocytopenia, infectious disease, drugs
Usually hematopoietic neoplasia
Dt: Rads or US
Dog Blood Types
Class: Dog Erythrocyte Ag 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8
DEA 1 = clinically important
presence(+) or absence(-) of “dog erythrocyte
antigens” (DEA) on the RBC membrane
Immune: Dogs do not naturally have anti-DEA 1 Ab → Will form them after one exposure
First transfusion → No rxn → Repeated transfusions → Hemolytic rxn
Dog Blood Donors
At minimum, donor should be DEA 1 negative!
Universal Donor
Negative for DEA 1, 3, 5, 7
Positive for DEA 4
Characteristics
Friendly, healthy, young–middle aged.
>55 lb, able to give 450 mL safely.
No prior transfusions or litters.
Free of infectious disease.
Greyhounds ideal
large, cooperative, high PCV, easy venous access.
Cat Blood Types
Must type all cats!!
Types:
Type A: Most common
Has weak anti-B Ab
Type B: Has strong anti-A antibodies
Type A → Type B transfusion = fatal.
Type AB: Rare; no Ab; can receive A or B.
Immune:
No universal donor in cats ALL cats must be typed before transfusion.
In-house testing cards
Mik Antigen → Anti-Mik Ab are likely in Mik-negative cats.
Cat Blood Donors Selection
Friendly, healthy.
>10 lb, ages 1–8 years.
No previous transfusion.
Free of infectious disease.
RBC Transfusion Administration
Pre- Transfusion Testing
Dog:
No previous transfusion → no mandatory testing
Previous transfusion >3–5 days → MUST cross-match.
Cats: Always blood type
Dosing
Target: +10% PCV
pRBC: ~10 mL/kg
Whole blood dose: ~20 mL/kg
Administration
Do not warm RBCs.
Always use a blood filter
Administer alone in IV line over 4h
Monitoring
Minimum database → TPR, PCV/TP
Watch for reactions → vomiting, respiratory changes, facial edema, urticaria
Blood Products
Fresh Whole Blood → no processing
Stored: <8 hours.
Contents: RBCs, WBCs, viable platelets, full plasma
Indication: Any anemia
Refrigeration inactivates platelets!!
Stored Whole Blood
Stored: 4°C for 30–35 days.
Contents: RBC, WBC, inactive platelets
Lower labile factors (V, VIII, vWF)
Platelets inactive after refrigeration.
Indications: anemia, anemia + coagulopathy/hypoproteinemia.
Not indicated for severe thrombocytopenia or vWD
Packed Red Blood Cells
Stored: refrigerated 35 days at 4°C
Contents: RBC, some WBC and inactive platelets
Platelets inactive after refrigeration.
Indication: any anemia
Plasma Products
Fresh Frozen Plasma (FFP)
Product: Frozen within 6-8 hours; shelf life 1 year.
Contains: albumin, vWF, ALL clotting factors, fibrinogen, antithrombin.
Dose: 10–20 mL/kg over 4 hrs.
Frozen Plasma (FP)
Product: FFP frozen >8 hours; shelf life 5 years.
Contains: albumin, vWF, SOME clotting factors, fibrinogen, antithrombin.
Lacks Factor V, VIII, vWF.
Use: disorders not involving labile factor deficiencies
Plasma Transfusions
Indications: Coagulopathy with active bleeding or needing invasive Sx
Procedure:
Thaw in warm water bath
Filter before administration
Monitor for reactions
Vomiting, diarrhea, fever, tachycardia, tachypnea, urticaria
Platelet Products
Indications: life-threatening hemorrhage, invasive Sx
Not indicated for thrombocytopenia alone without bleeding.
Dose: 1 unit per 10 kg
Cryoprecipitate
pre-surgical
Production: Thaw FFP → centrifuge → collect precipitate.
Contents: rich in vWF, Factor VIII, Factor V.
Indications: vWF disease, Hemophilia A
Dose: 1 unit per 10 kg