Cerebral White Matter
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
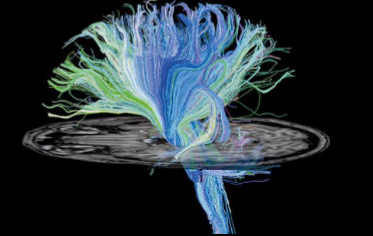
What kind of scan is this
Tractography
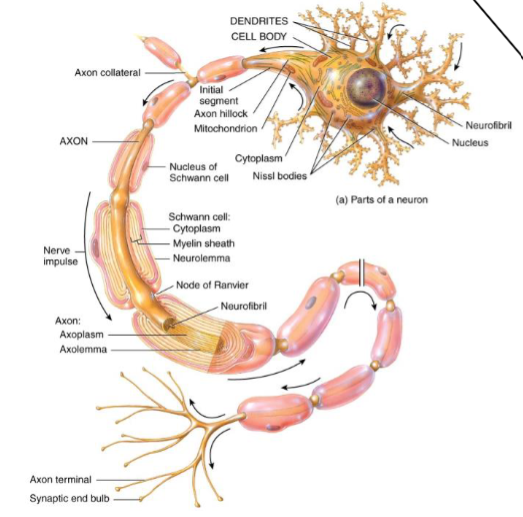
Myelin is formed by what where
Myelin formed by Oligodendrocytes - wraps around axons
How do we look at diffusion of molecules through the axons
Diffusion MRI
Why is diffusion MRI used in stroke
You see a spot where the microstructure of fibres is destroyed with a shadow around it - site of stroke
No motion = tissue that won’t be recovered
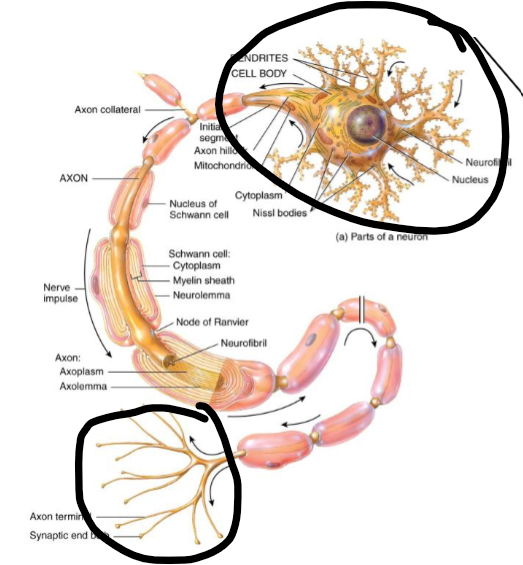
What part of this is grey/white matter
Circled = grey matter
The rest = white matter
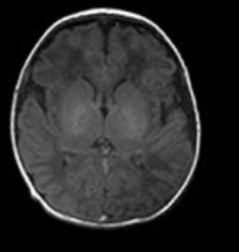
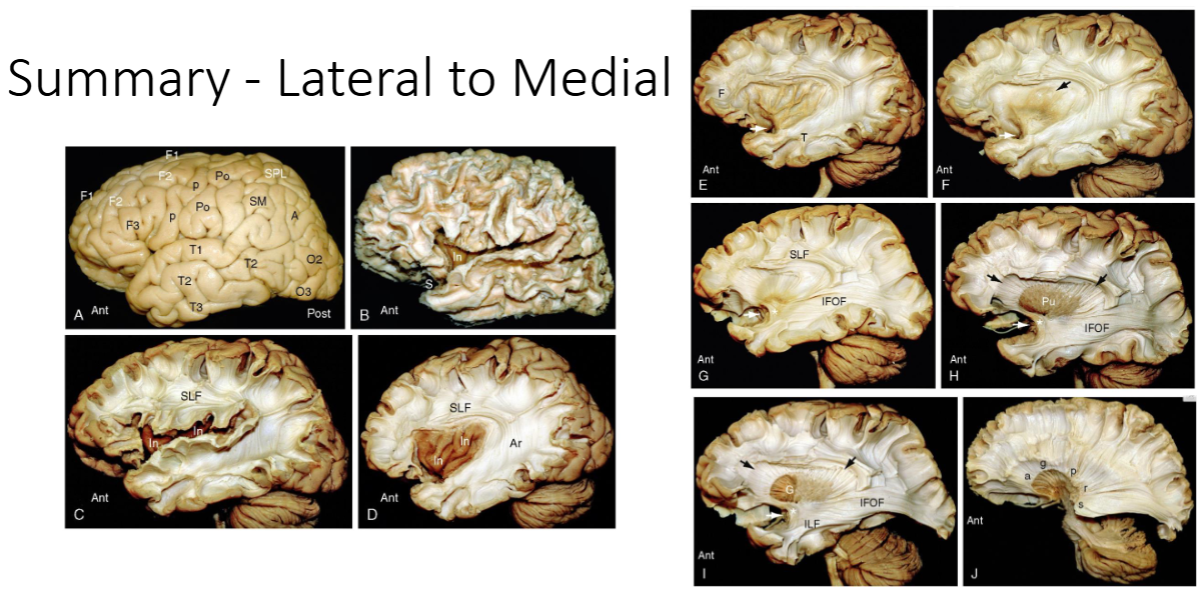
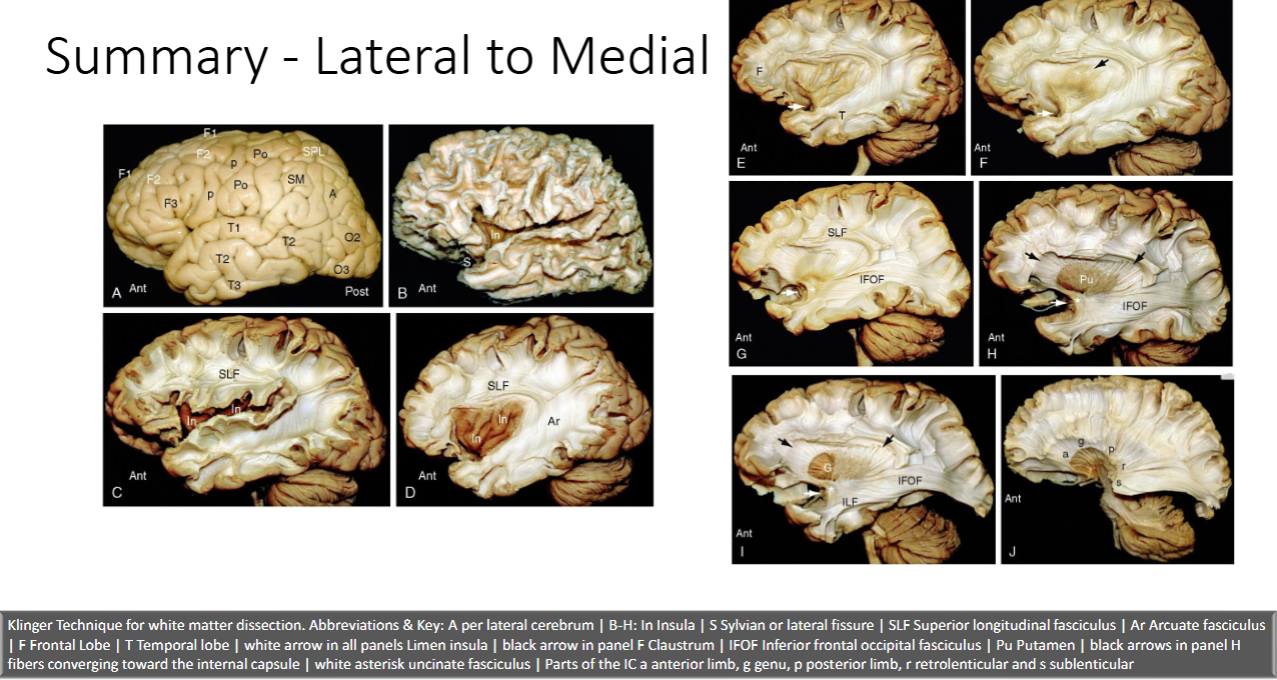
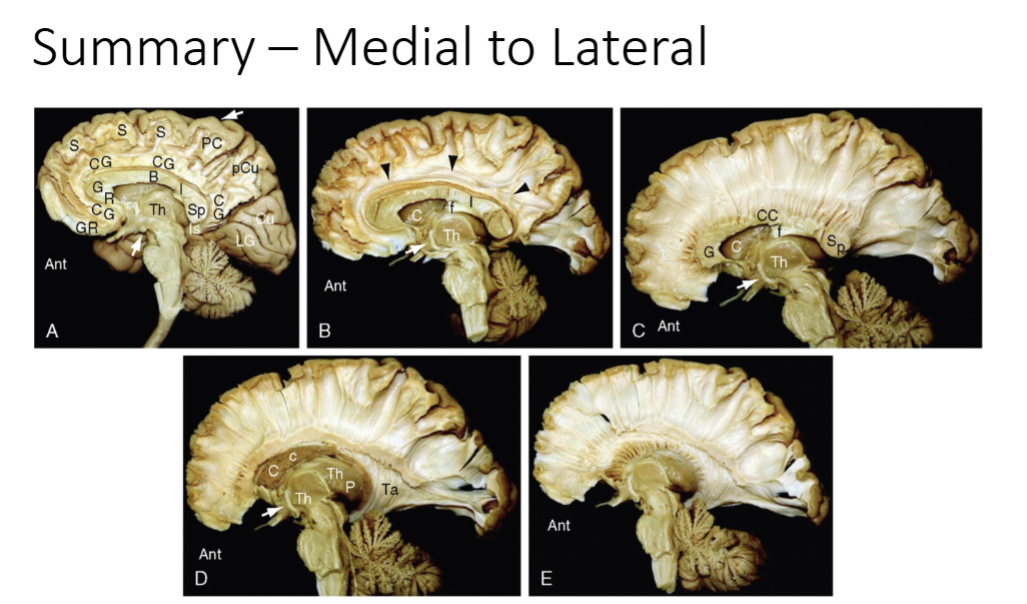
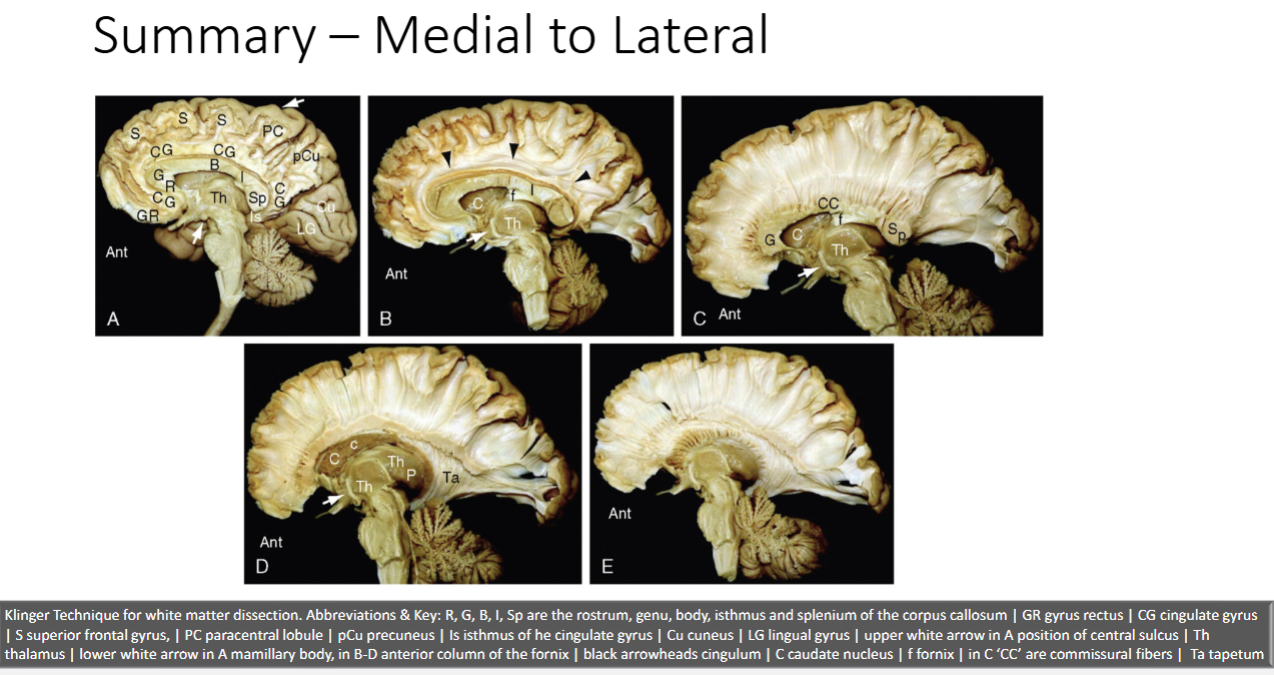
What technique is used to examine the brain post mortem
Klinger Technique
Why does the 1 week old brain look different on an MRI
Note much white matter - develops over time
At birth the brain myelination is minimal
It increases dramatically during the first and second year and continues to mature through life peaking at approximately 40 years
It then begins to degenerate thereafter
Striae defn
thin bundles of fibers that pass longitudinally across the brain
(white matter)
Fascicles defn
microscopically determined groups of fibers
You can have multiple tracts through a fascicle
Tracts defn
groups of axons subserving a similar or corresponding function
Lamina defn
relatively thin sheets of axons that proceed in a similar direction
Capsules
curved sheets of fibers that partially enclose a grey matter structure
Radiations
broad sheets of fibers that arch together to/from one target
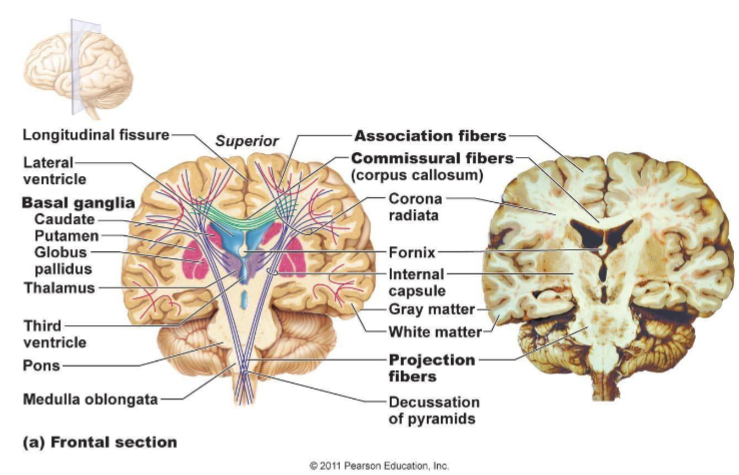
How are white matter tracts categorised
Commissural: Crossing the midline connecting cortical areas in one hemisphere to the other
Projection: Cortex to distant sites such as brainstem and spinal cord and visa versa
Association: Connecting cortical areas within the same hemisphere
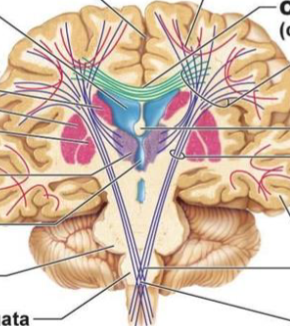
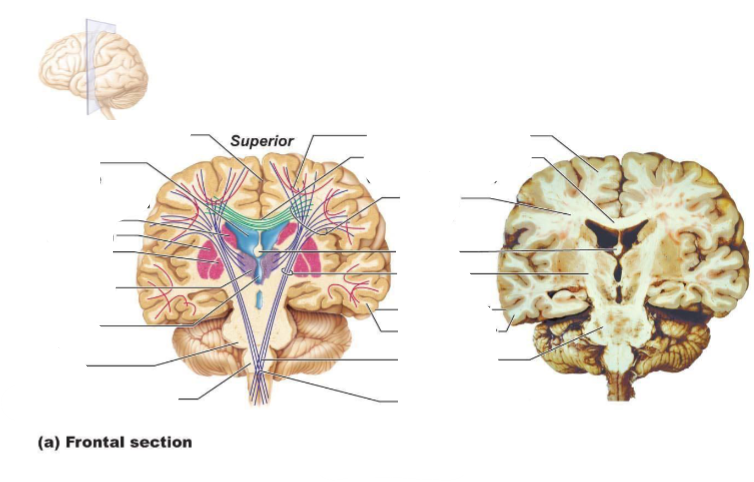
What categories of white matter tracts are seen here (what colour)?
Commissural = green
Projection fibres = purple
Association = pink
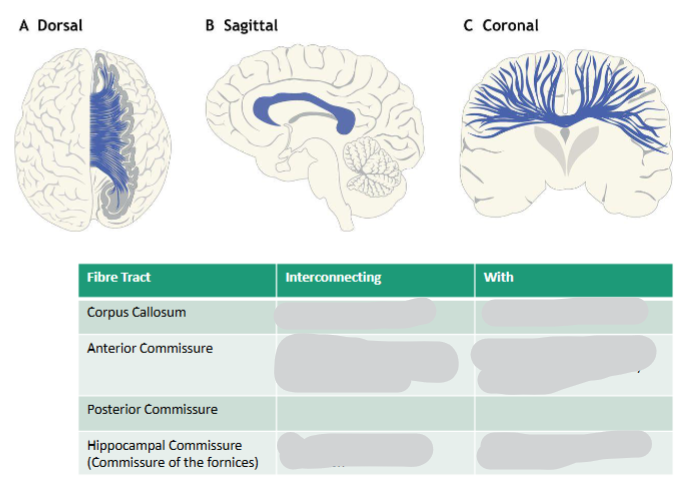
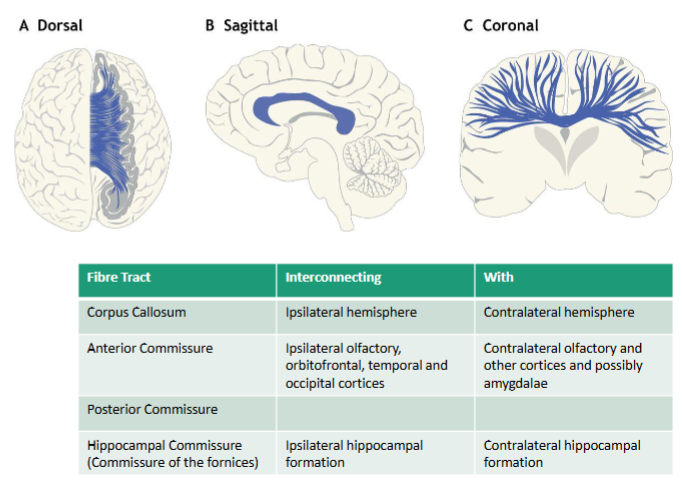
4 types of commissural white matter tracts
• Corpus Callosum
• Anterior Commissure
• Posterior Commissure
• Hippocampal Commissure
Location of the Anterior Commissure
Located on lamina terminalis
Posterior Commissure location
Epithalamic commissure
ACPC line
Hippocampal Commissure location
Commissure of the fornices
What do homotopic & heterotopic commissural fibres mean
Homotopic fibers are those that connect corresponding areas of cortex
Heterotopic fibers connect a non-corresponding area in the contralateral hemisphere
Corpus Callosum is Major white matter connecting the hemispheres. Name the 5 parts of it
• Rostal
• Genu
• Body
• Isthmus
• Splenium
Projection white matter tracts convey impulses from where to where
Projection fibers convey impulses from the cortex to distant sites or from distant sites to the cortex
Projection fibres pathway
Many fibers pass reciprocally through the brainstem (crus cerebri/cerebral peduncles) → travel compactly through the internal capsule at the basal ganglia level → relay in the thalamus → and finally reach the cortex
Allows for organized communication between the cortex and subcortical structures.
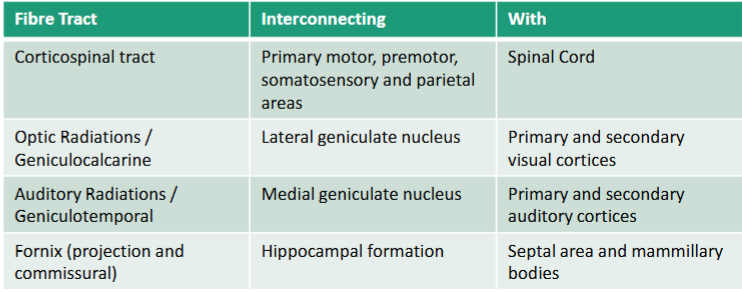
What are the 5 parts of the internal capsule
• Anterior Limb
• Genu of the IC
• Posterior Limb
• Retrolenticular part (Contains optic radiations)
• Sublenticular (Contains auditory radiations)
Capsules can be internal, external or what?
Extreme
Medullary Lamina are Middle, Lateral, and what is the last one called & its location
Internal - within thalamus projection
What is Corona radiata
Corona radiata is not a specific tract!
It is the collective term for all the fiber tracts connecting the brainstem to the thalamus (including the internal capsule area) and those connecting the thalamus and cortex termed thalamic peduncles
Name the thalamic peduncles
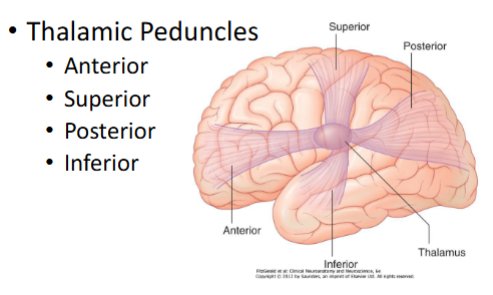
What is a stria
a tract or pathway — a visually or anatomically distinct band of axons connecting one part of the brain to another
Name the 4 main striae of the brain
• Olfactory Striae (CN1)
• Stria Medullaris
• Stria Terminalis
• Medial & Lateral Longitudinal Striae
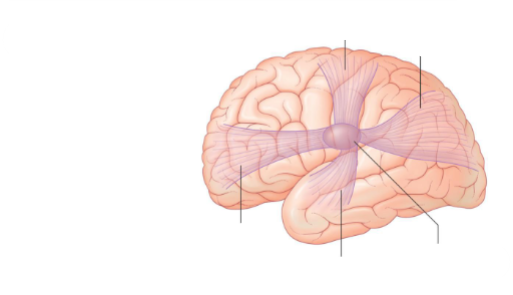
Role of association fibres
Association fibers connect diverse regions of the same hemisphere
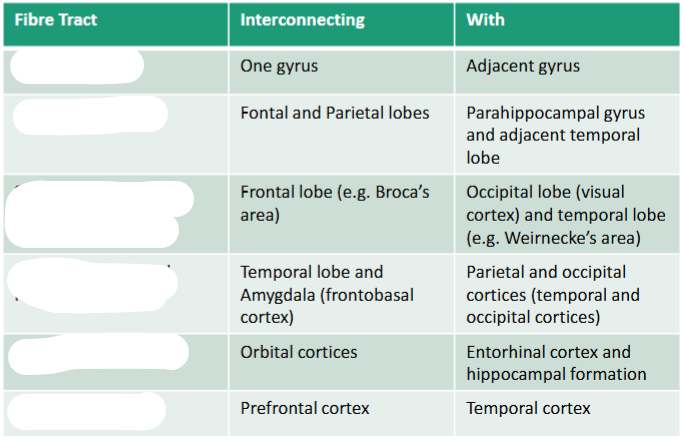
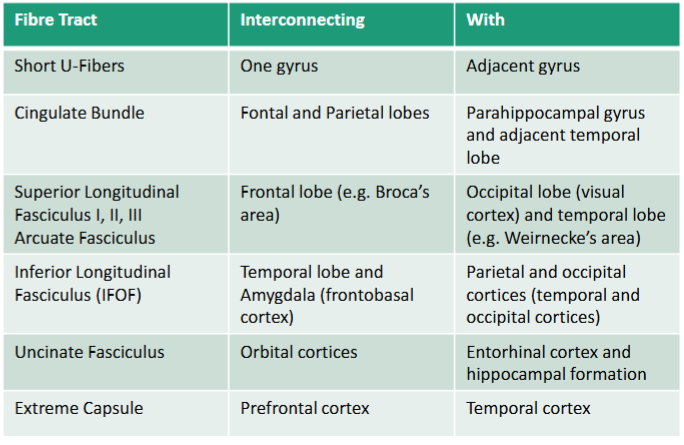
Fill in the names of the association fibres
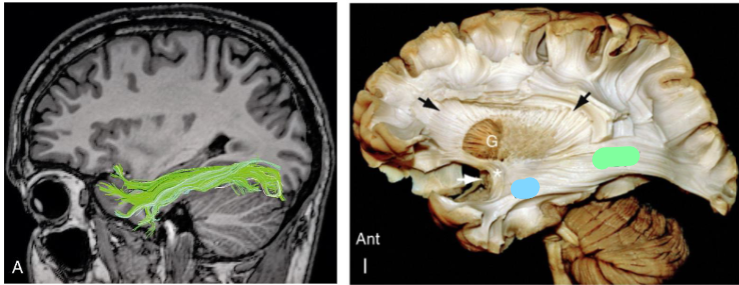
What association fibres are shown in the first image and as the blue in the second image
Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF)
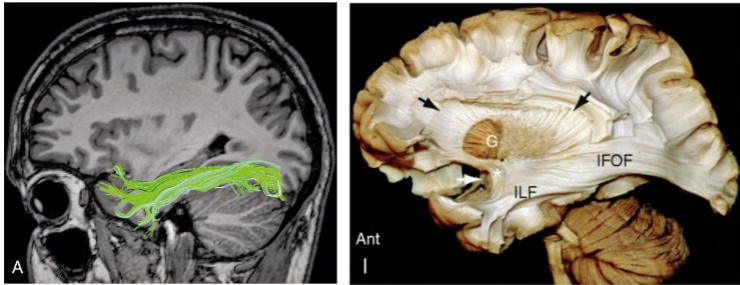
What does the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF) connect
Connects inferior posterior temporal and occipital cortices to anterior temporal areas both lateral and medial
Function of the the Inferior Longitudinal Fasciculus (ILF)
Object and face recognition
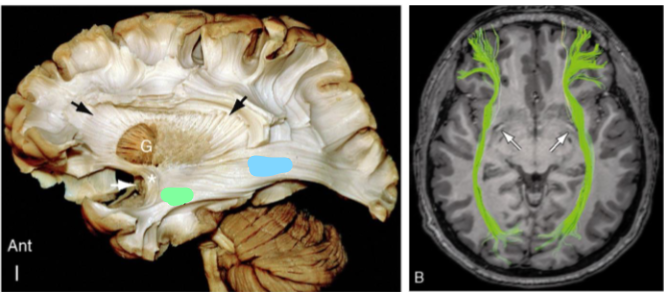
What association fibres are shown as blue in the first image and green in the second image
Inferior Frontal Occipital Fasciculus (IFOF)
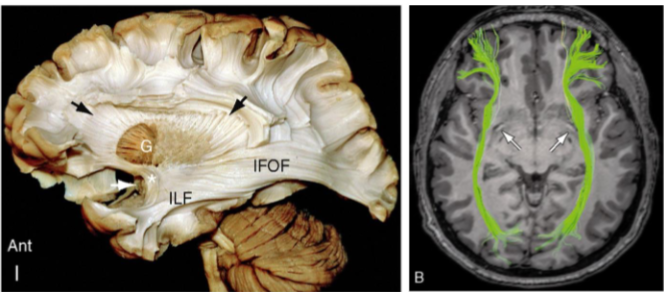
What does the Inferior Frontal Occipital Fasciculus (IFOF) connect
Connects broad areas of the temporal lobe and inferior occipital lobe to the frontal lobe
Function of the the Inferior Frontal Occipital Fasciculus (IFOF)
Object recognition, visuospatial and semantic processing
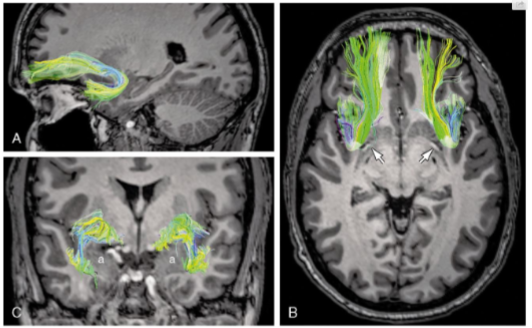
What association fibres are shown here
Uncinate Fasciculus
Describe the location & projection direction of Uncinate Fasciculus
Fibers arise anterior temporal lobe and curve to frontal areas
Uncinate Fasciculus functions
involved in processing novel information and emotional valence of stimuli
The ILF serves as the main white matter pathway linking the visual occipital areas to what, enabling high-level visual recognition and memory integration
The ILF serves as the main white matter pathway linking the visual occipital areas to the fusiform cortex, enabling high-level visual recognition and memory integration