Male Reproductive Systems and Reproductive Systems
1/101
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANSC 410
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
list the structures of the male reproductive system
penis
prepuce
sheath
inguinal canal
peritoneum
testicles
scrotum
spermatic cord
epidiymis
vas deferens
accessory sex glands
what is the organ of copulation?
penis
what type of structure makes up the penis?
fibrous structure
describe the different shapes of the penis
bull- S-shaped (sigmoid flexure)
boar - corkscrew
dog - os penis (bone)
what is the main structure of penis tissue?
corpus cavernosum
(true/false) the corpus cavernosum is highly vascular and capable of trapping blood
true
erection
engorgement of blood in corpus cavernosum
what are the structures of the penis?
glans penis
sensitive area
tip of penis
urethra
runs through the middle
prepuce
double folded lining that covers the penis
sheath
external opening
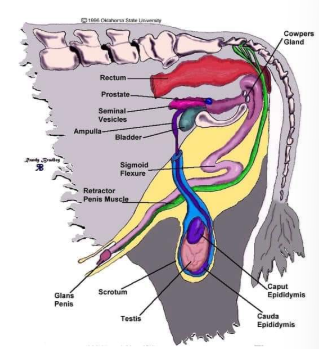
what are three functions of the penis?
transport of semen
urination
organ of copulation
what are two important muscles of the penis?
retractor penis muscle
ischiocavernosus muscle
function of testicles
produces sperm
where are the testicles located
descends from the kidney area to scrotum
what are the 2 types of cells of the testicles?
cells of leydig
sertoli cells
retractor penis muscle aids in…
retraction of the penis
ischiocavernosus muscle
aids in erection process
contracts penis against ischium of the pelvis causing blood to be trapped in the penis
cells of leydig produces…
hormone testosterone
sertoli cells provide…
nutrition for maturing sperm
list the structures of the testicles
tunica albuginea
tunica vaginalis
gubernaculum testis
seminiferous tubules
rete testis
epididymis
vas deferens
spermatic cord
cremaster muscle
tunica albuginea
outside covering of the testicles and penis thinner capsule
white and shiny
tightly adhered to the testicle
tunica albuginea was originally part of the ___________
peritoneum
the testicle becomes the tunica albuginea as it descends into the _________
scrotum
tunica vaginalis
also white and shiny thick capsule
also formed from the vaginal tunic and peritoneum
outside layer of the tunica albuginea
what is the first structure you will see after excising the scrotum?
tunica vaginalis
gubernaculum testis
ligament hooks the testicle to the scrotum and guides the testicle to scrotum
seminiferous tubules
tubes where spermatogenesis takes place
massive numbers of tubules in the testicle
rete testis
collection duct where maturing spermatozoa go to the epididymis
the epididymis has three parts. what are they?
head
body
tail
function of epididymis head
receives spermatozoa from the rete testis
storage and maturation of sperm
what does the epididymis tail turn into?
vas deferens
function of vas deferens
transports sperm from the tail of the epididymis to the urethra (ampulla)
where is the ampulla located?
where the epididymis joins the urethra (reservoir for sperm)
ampulla is present in all domestic animals except for ______
pigs
what is the spermatic cord made up of?
pampiniform plexus + vas deferens
function of spermatic cord
suspends the testicle
the spermatic cord contains:
arteries, nerves, veins (pampiniform plexus)
gubernaculum
common vaginal tunic
vas deferens
cremaster muscle
lymph structures
what is a muscle that lies near the spermatic cord?
cremaster muscle
function of cremaster muscle
allows the testicles to move closer or further away from the body for temperature regulation
where does spermatogenesis occur?
in the seminiferous tubules
how long does it take sperm to complete maturation?
13-17 days
what cells line the seminiferous tubules?
sertoli cells
what are the parts of sperm?
head
midpiece
tail
what does the head of sperm contain?
genetic material
acrosome contains enzymes to penetrate the ova
function of midpiece of sperm
powerhouse of sperm (contains mitochondria)
function of tail of sperm
responsible for locomotion
scrotum
outer sac that holds and encloses the testicles; has fibrous division
describe the appearance of the scrotum in stallions, bulls/rams, and boars
stallions - more attached to abdominal wall (more horizontal)
bulls/rams - more pendulous (more vertical)
boars - close to anus
the scrotum has one muscle called the _______
dartos
function of dartos
causes the scrotum to contract or relax; important for thermoregulation of the testicles*
inguinal canal
slit-like structure in groin area where the abdominal muscles join
what structure do testicles pass through when descending from the abdomen into the scrotum?
inguinal canal
peritoneum
lines the abdominal cavity; forms the vaginal tunic of the testicle as the testicle descends through the inguinal canal
list the accessory sex glands
bulbourethral
prostate
seminal vesicles
ampulla
bulbourethral
paired gland
in all domestic animals except dog
prostate
thick glandular structure that surrounds the urethra; located just over the pelvic arch
single gland - can have 2 lobes in some animals
found in all domestic animals
seminal vesicles
paired gland
all domestic animals except dog and cat
ampulla
not present in boar
sits at base of vas deferens
what are the functions of accessory sex glands?
add fluid to ejaculate (semen = sperm + fluid)
provide nutrients to the sperm by releasing sucrose
what animals have all 4 accessory sex glands?
horses, cows, sheep and goats
what animal has all accessory sex organs except for the ampulla?
pig
what are the 2 types of castration methods?
banding
cutting castration
banding
involves placing a rubber ring around the pampiniform plexus to restrict blood supply to the testicles
must make sure BOTH testicles are in the band
when is it best to band calves?
within 1st week of life
cutting castration
involves excising the scrotum with a blade and pull the testicles out of the body
open - excising the tunica vaginalis
closed - excising scrotum only
when is it best to perform a cutting castration on a calf?
done as a newborn or around 6 months of age at weaning
the entire penis must be examined on the ….
breeding soundness exam
paraphimosis
inability to retract the penis
what can paraphimosis cause?
preputial trauma and tumors
phimosis
inability to extend the penis
what can phimosis lead to?
adhesions, stenosis of the preputial opening, congenital abnormalities
cryptorchidism is an ___________ defect
inherited
what are the 2 types of cryptorchidism?
unilateral and bilateral
unilateral cryptorchidism
1 testicle is retained in the abdomen
may still be fertile
the descended testicle is usually larger
bilateral cryptorchidism
both testicles are retained in the abdomen
usually sterile
will still behave like an intact male and try to breed
increased chance for the testicles to develop tumors
what temperature do the testicles need to be to adequately produce viable sperm?
need to be 4 degrees cooler than the body temperature
hernias
condition when abdominal organs or tissues protrude through weak areas in the abdominal wall
where are hernias most commonly seen?
in the groin, scrotum, testicle, umbilicus
clinical signs of hernias depend on what?
what tissue is trapped in the hernia
what are clinical signs of a hernia?
swelling
pain
lethargy
depression
vomiting/diarrhea
what are the 2 types of hernias?
congenital
acquired
examples of how hernias can be acquired
bull fights
trauma
increased abdominal pressure
treatment for hernias
surgical correction
orchitis
inflammation of the testicles
what is orchitis a potential complication of?
giving the Brucellosis vaccine to bulls
causes of orchitis include:
Brucella abortis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Herpesvirus
trauma
clinical signs of orchitis
reluctance to move
swollen, painful, hot scrotum
reduced fertility
penile hematomas are most common in what cattle breed?
Bos Indicus
when do penile hematomas most commonly occur?
during the act of breeding
how does a penile hematoma occur during breeding?
cow moves
penis misses the cow
bull steps on the penis and or prepuce when trying to stand up
clinical signs of penile hematomas
decreased libido
infertile breedings
reluctance to breed
complications of penile hematomas
cellulitis
abcesses
fibrosis
what do penile hematomas often lead to?
preputial prolapse
when do lacerations most commonly occur?
occur due to violent ejaculatory lunge
where is the most common location of a laceration found on bulls?
the ventral aspect of the prepuce
lacerations often lead to…
preputial prolapse because fluid easily accumulates in the damaged portion
preputial prolapse is most common in what cattle species?
Bos Indicus
what is a preputial prolapse most commonly caused by?
a laceration that eventually allows so much fluid to accumulate in the penis/prepuce that the penis cannot be retracted back into the sheath
the longer the injured prepuce tissue remains prolapsed, what can it lead to?
secondary injuries such as necrosis, frostbite, extensive lacerations
how many classes of preputial injuries are there?
4
treatment options for a prolapsed prepuce?
surgical correction
hydrotherapy
pain control
antibiotics
urethral catheter
what often leads to bull fighting?
having multiple bulls in pastures with the same groups of cows