U3: Energy and momentum
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
formula for work done by a constant force
units
W = |F||d|cos(ø)
w = J (Nm)
F = N
*make sure to do magnitude of force and displacement
what is the meaning of Fcosø
force in the direction of displacement
positive and negative work
positive and negtive work depend on the angle:
cos(0) = +1
cos(180) = -1
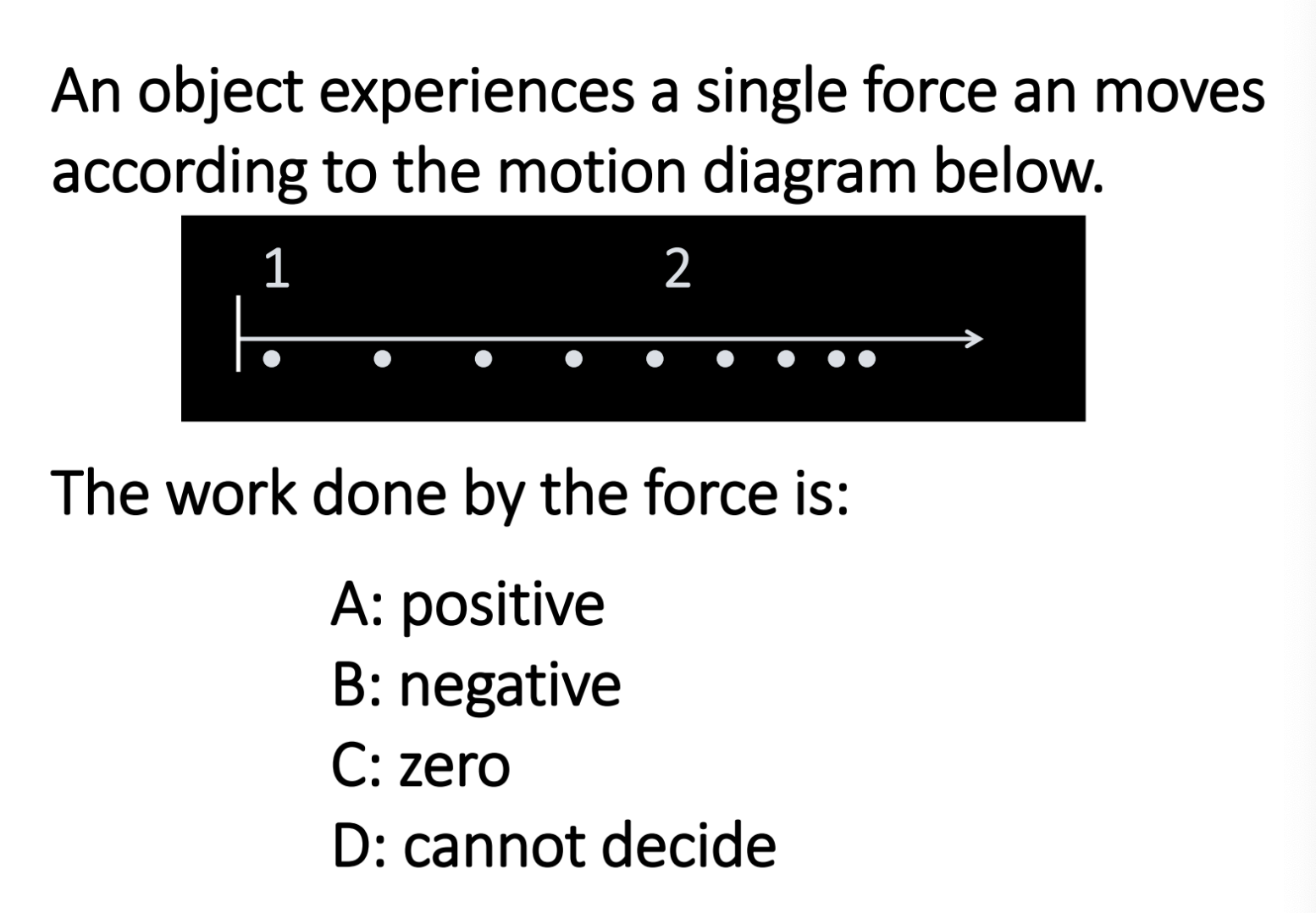
negative
force is going according to the acceleration (net force results in acceleration not displacement) which is negative
displacement is positive
opposite directions means negative work
what are energy flow diagrams
can you have energy added and taken away in a system
give an example of adding energy
example of taking away energy
energy flow diagrams show if energy is added to or taken away from the system. energy can be added and taken away for 1 system
adding energy: Fa → adding energy by adding work to the system
removing energy: Ff → removing energy by removing work from the system
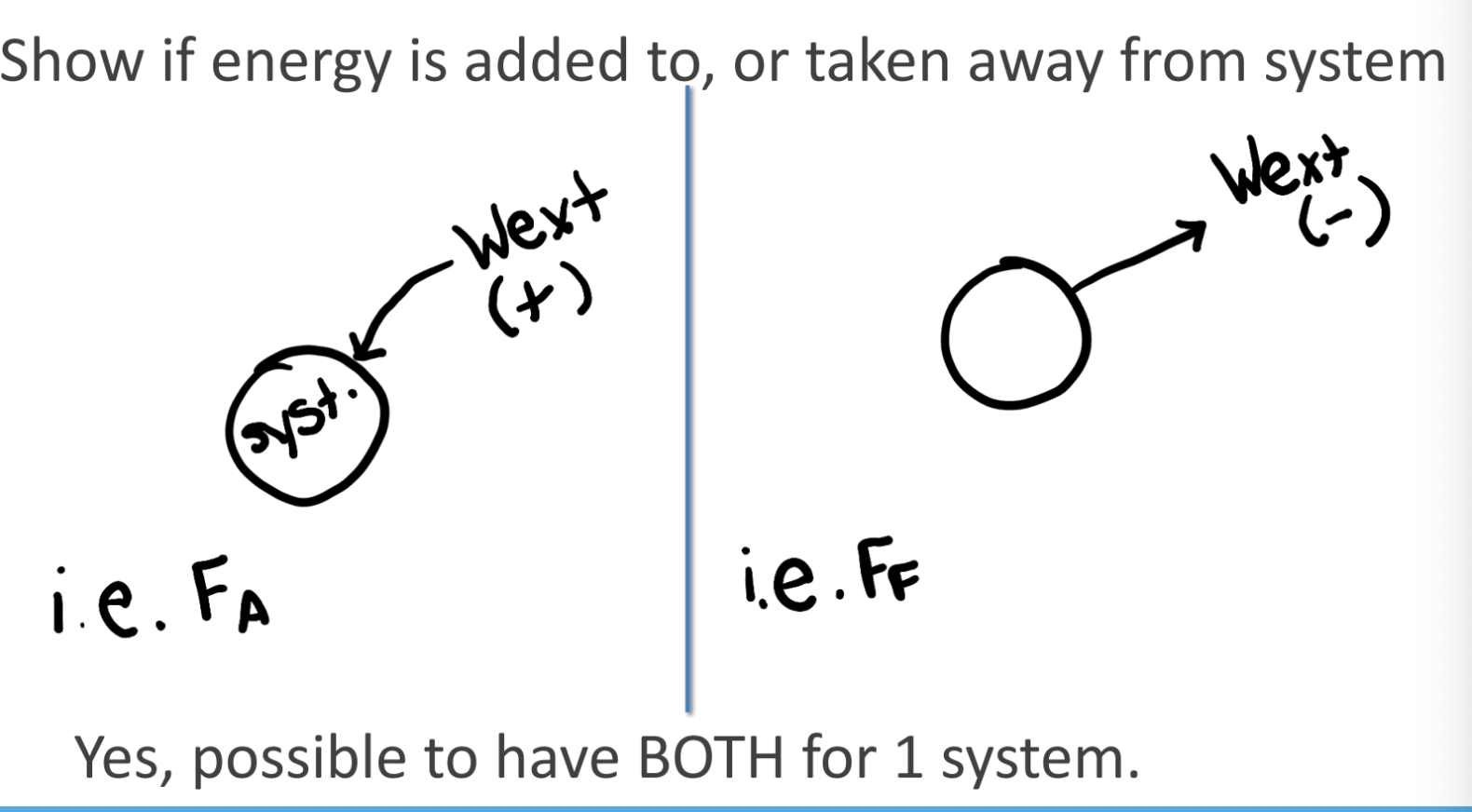
draw an energy flow diagram with energy going in and out
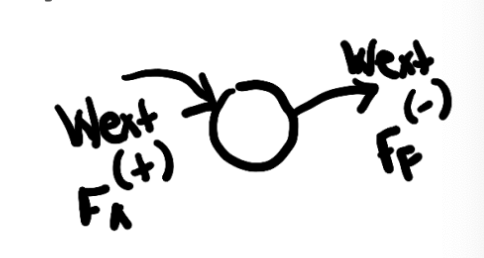
how do you know if you have external work?
if you have
an applied force
friction
air resistance
this is why you can have multiple Wext in equations of energy conservation. if multiple of these questions are answered, like there is an applied force and friction, youd have Wext1 and Wext2.
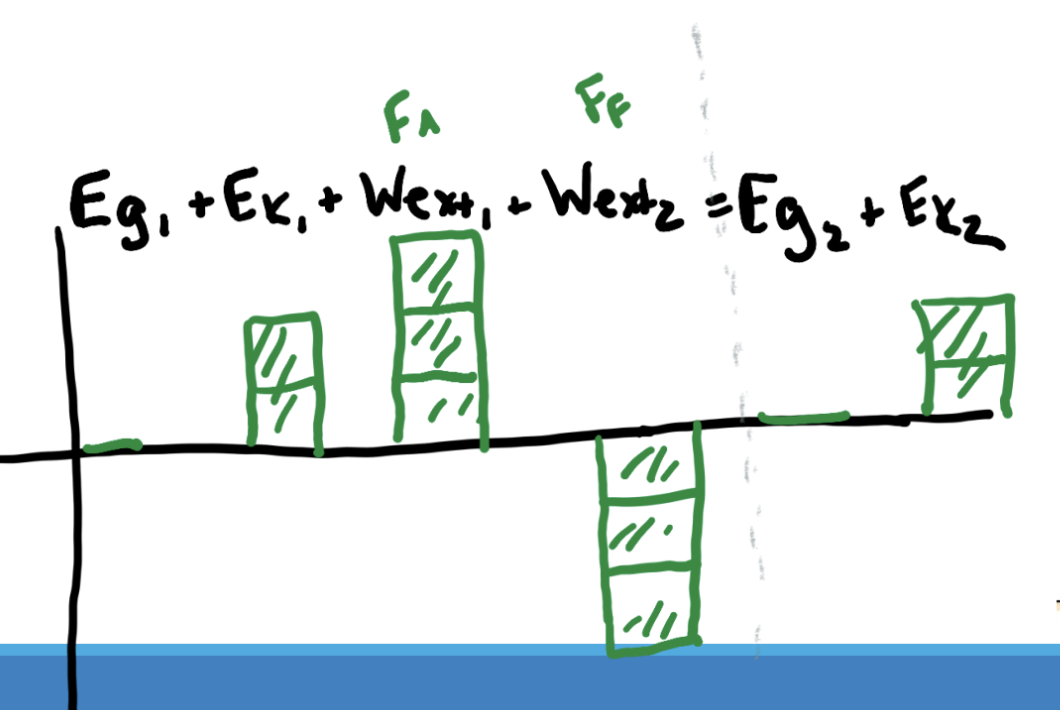
draw an energy bar chart for pushing a box at a constant velocity with friction
energy bar charts show the amount of energy and work gained or lost between 2 events. they should be equal.
the chart matches the energy conservation equation:
how do you calculate work when its:
constant
non constant
constant: W = |F||d|cosø
non constant: the graph is not a rectange, you can only get work by getting the area under the graph
on an F,d graph, the area under the graph is the work done (sum all the areas, including negatives)
example: write the full equation from 1 to 3
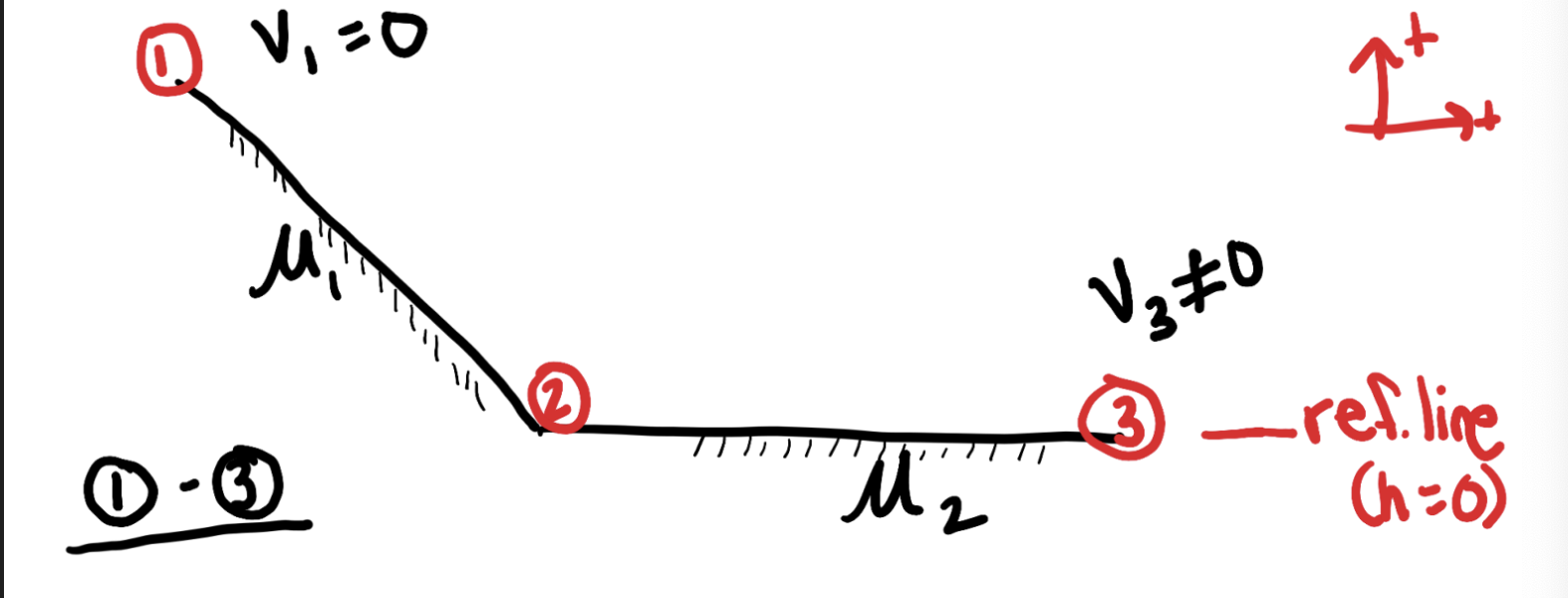
key idea: you need to account for external work 2x because energy is moved out of the system 2x between event 1 and 3
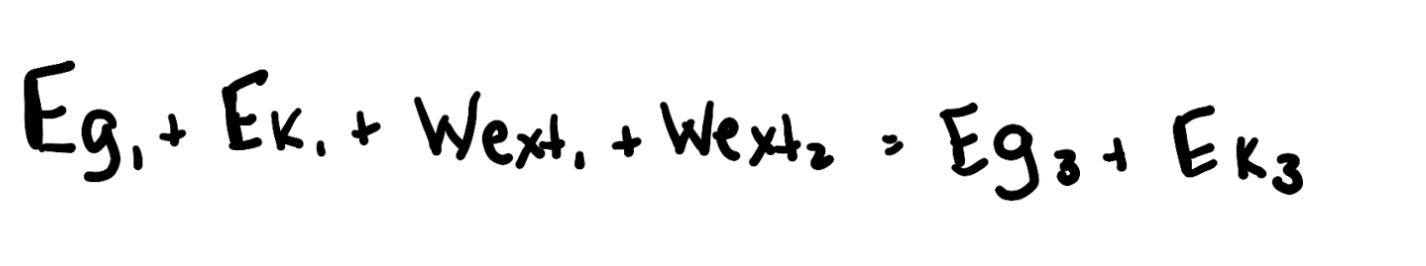
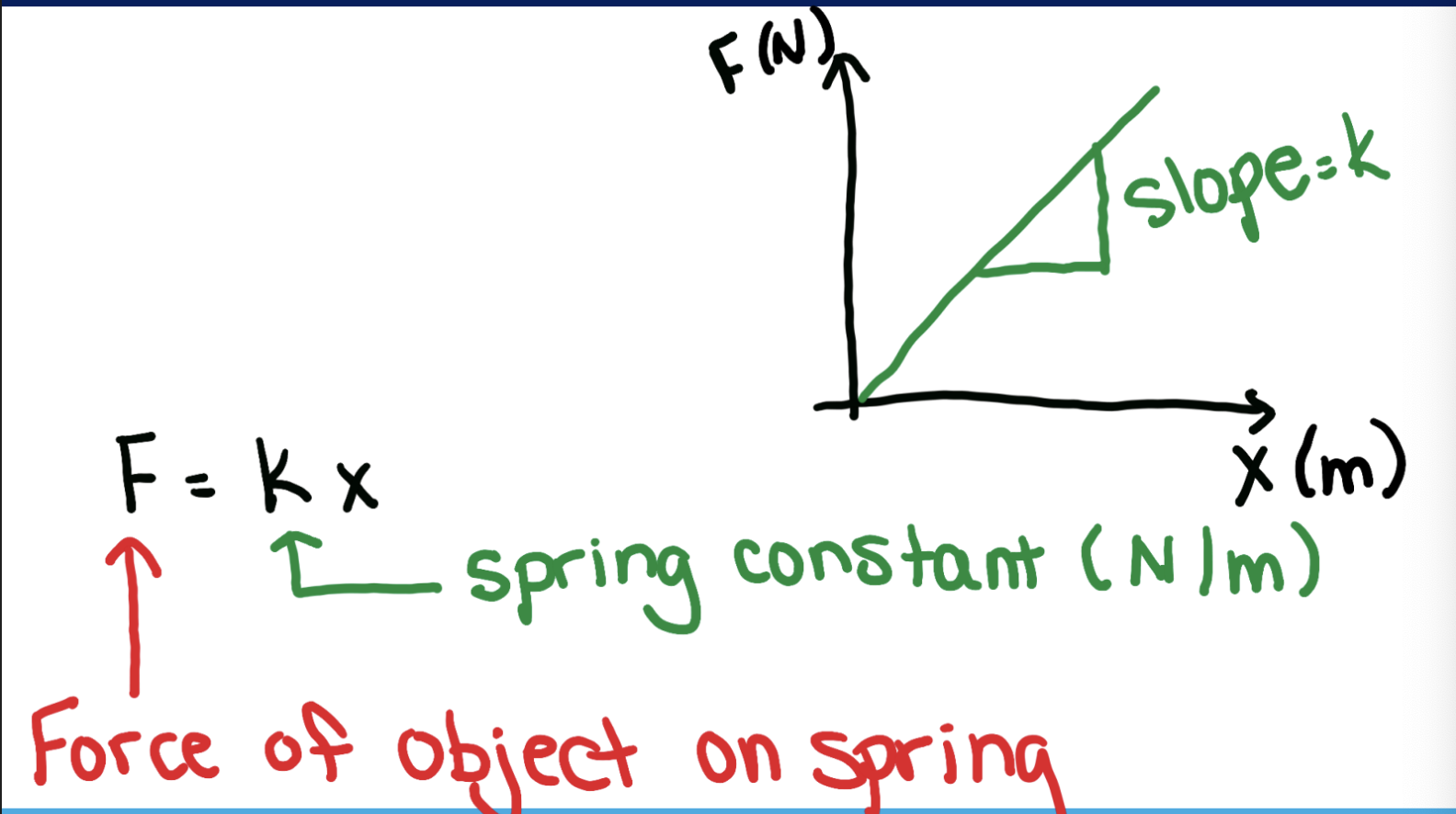
what is hookes law
Fos = kx
force of object on spring
K = spring constant (N/m)
x = how much the spring was stretched
how do you calculate k (spring constant) graphically
the formula F=kx tells you that on a F vs x graph the slope is k
what is the restoring force
Frest = -Fos
the restoring force is the force the spring exterts on the object (Fso) which tries to restore the object back to equilibrium
Fso = -kx → the restoring force is negative bc the force is in the opposite direction of x
what is the formula for elastic energy? how did we derive it?
Ee = 1/2kx²
work = area under an F-d graph, so Ee (work done by spring)= area under a F-x graph
for a non constant force:
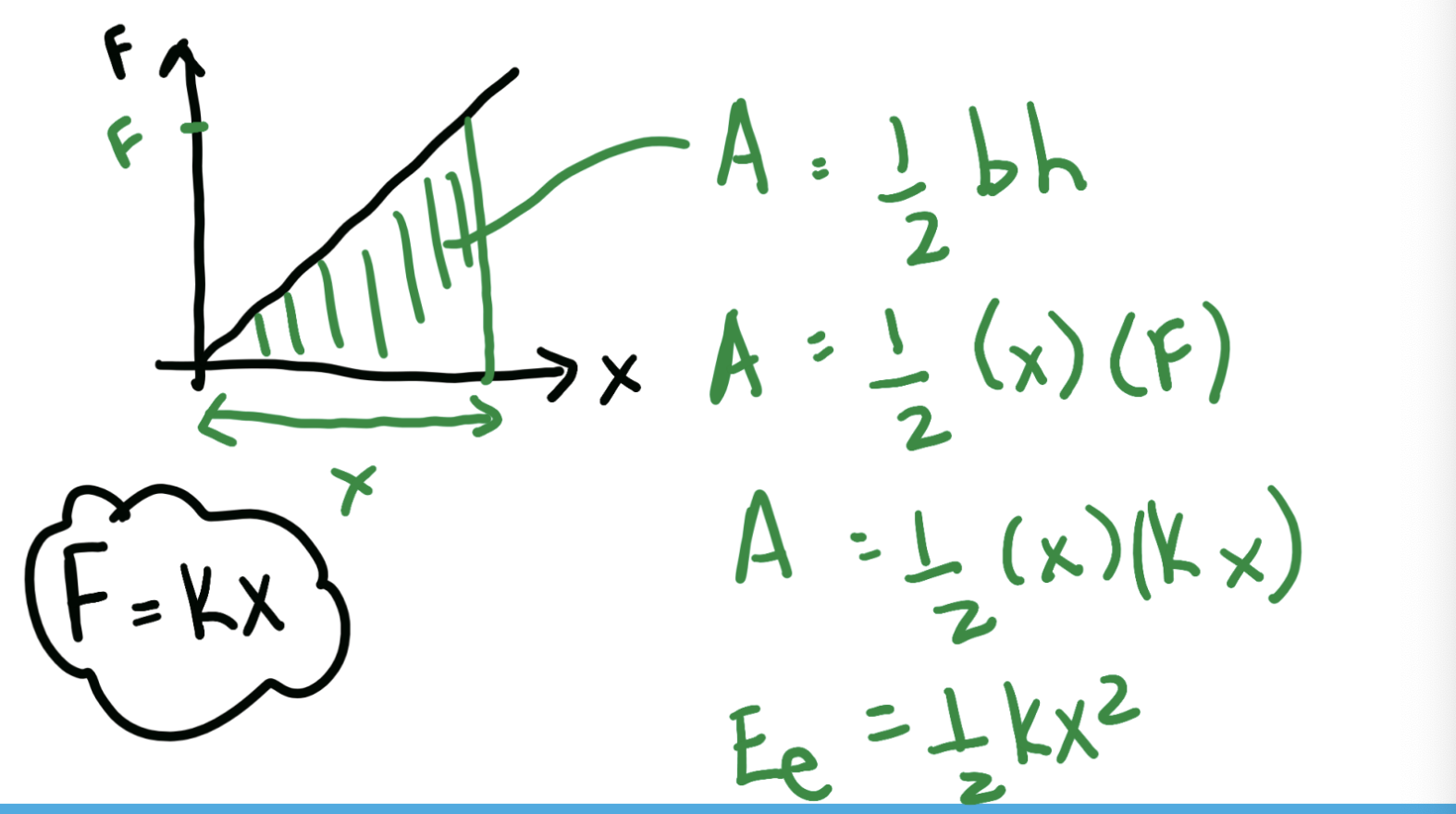
how should you label your events in an elastic energy question
label at top and bottom of ramp
at the beginning of spring and at the end of spring (for stretch/compression)
what does the word “max compression” tell you?
tells you at the event of max compression, the velocity of object is 0
what is the acceleration of a mass on a spring
the acceleration is measured from an equilibrium point
Fnet= ma = -kx → its the accleration of the object thats being measured, so we need to use the restoring force because thats Fs,o
using: ma = -kx
a = -k/m (x) → this is the acceleration of a mass on a spring
accleration of the mass on a spring is proportional to ?
accleration is in the opposite dirrection of ?
accleration is ____ constant?
accleration of the mass on a spring is proportional to x, the position
accleration is in the opposite dirrection of displacement
accleration is NOT constant because x is always changing
cant use the big 5 kinematics equations
acceleration of object is in the direction of ___
net force
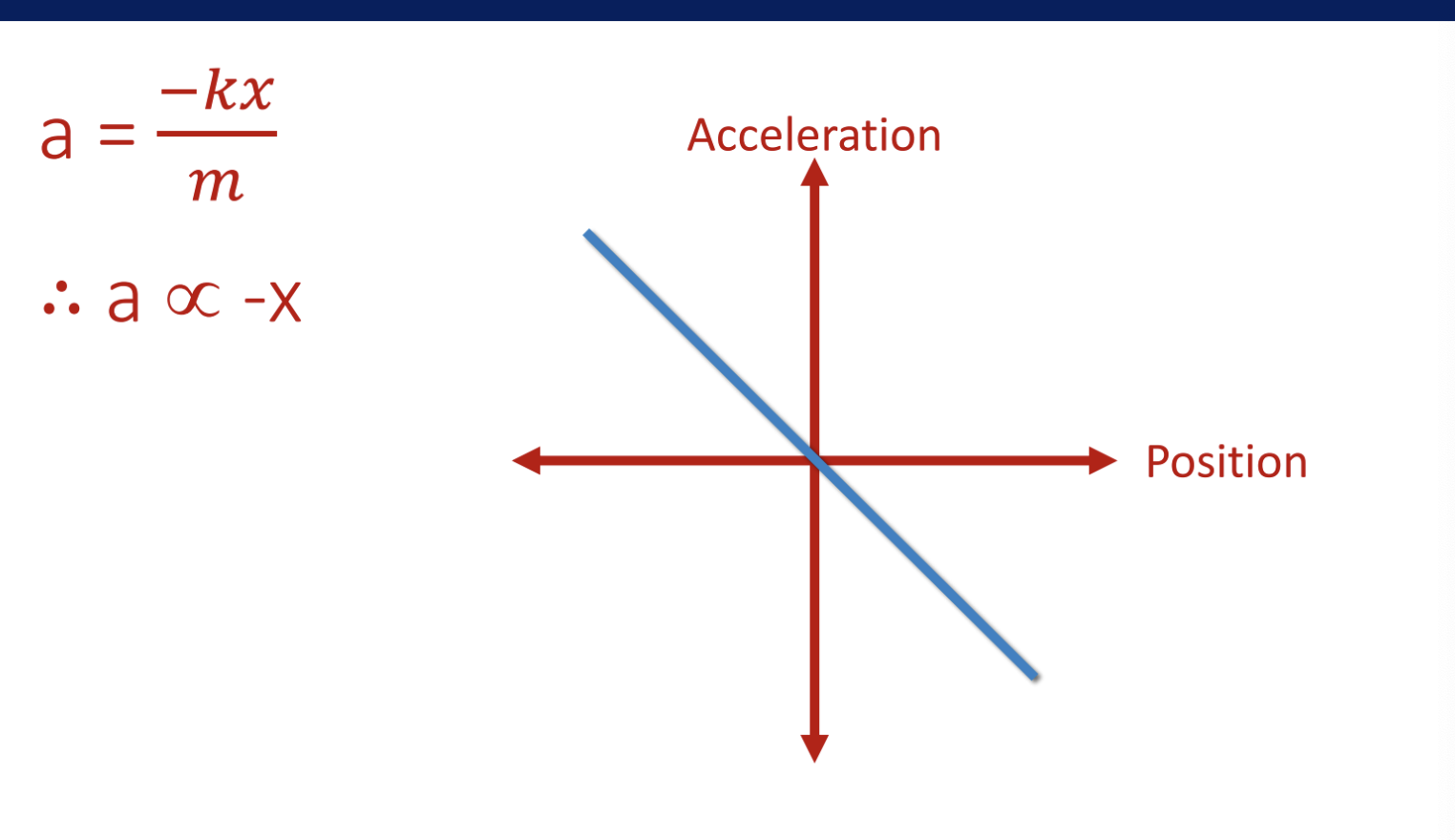
describe the acceleration of a mass on a spring
accleration is proportional to displacement and directed toward the equilibrium
graph of a vs x, accleration of object on spring vs position
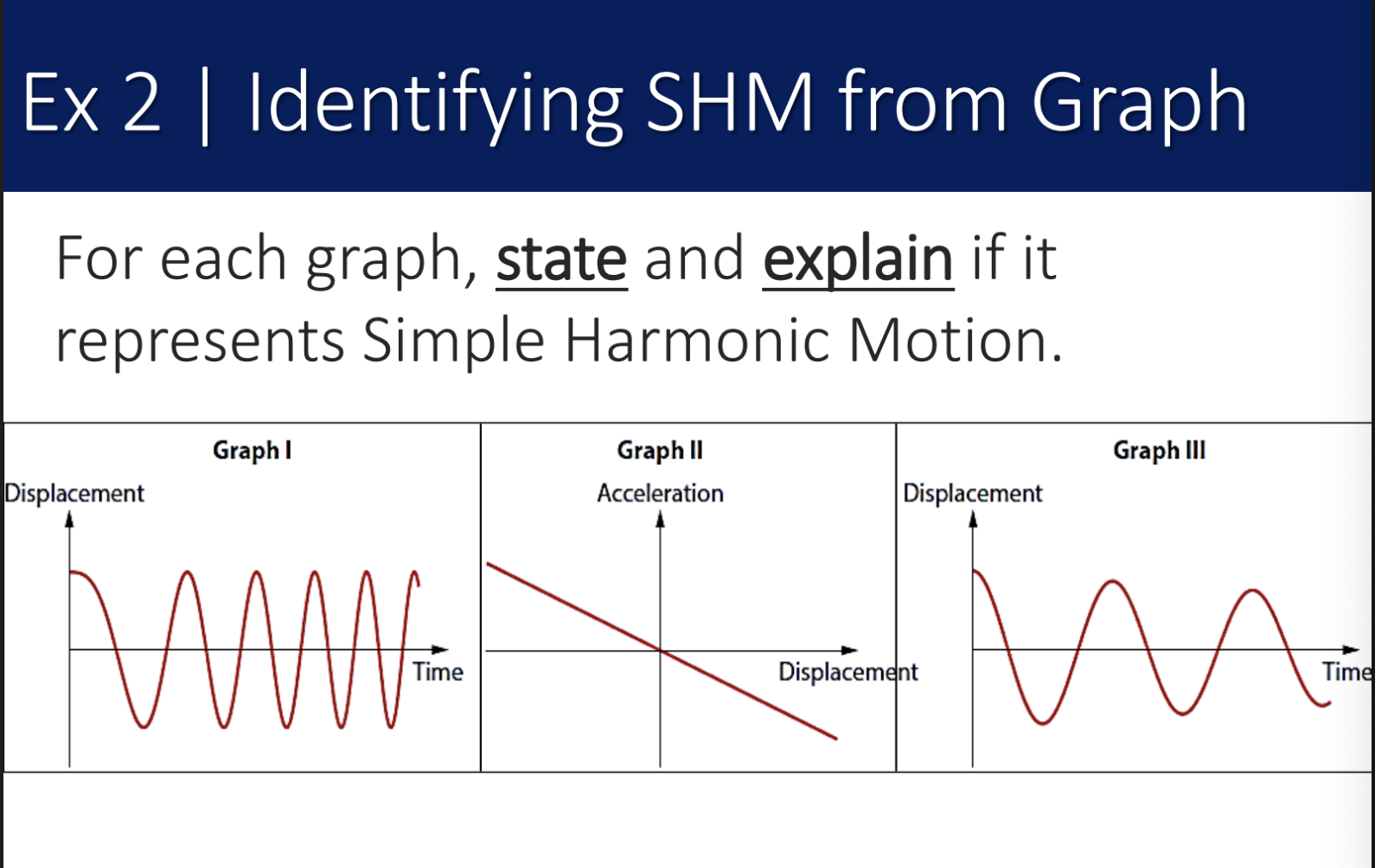
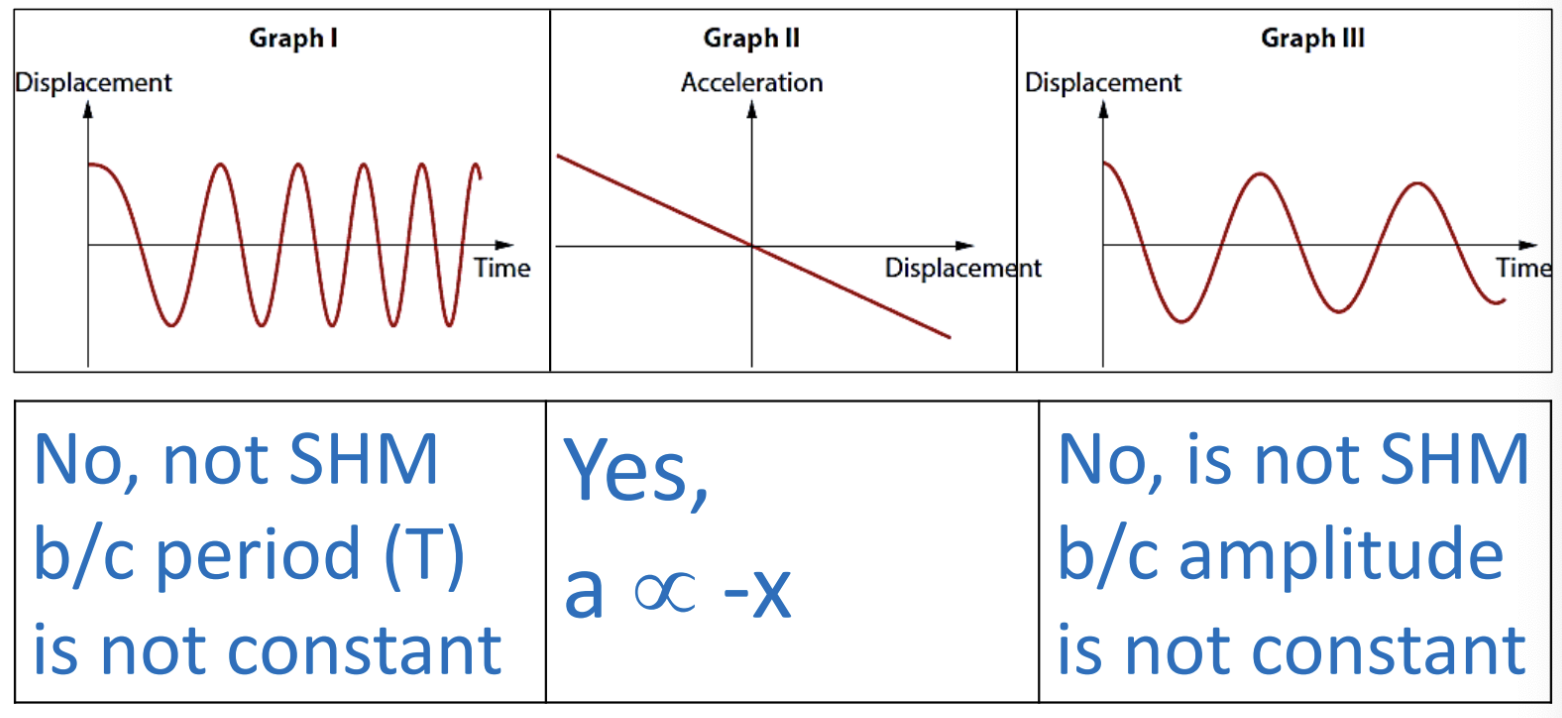
simple harmonic motion
the repeating motion of an oscillting mass where the restoring force is proportional to the displacement but in the opposite direction
characteristics of SHM (3)
period (T) and amplitude (A) are constant
period is independent of amplitude
position, velocity and acceleration vs time graphs are sinusoidal functions
you can find the period and amplitude from a ____ vs time graph
you can find the period and amplitude from a displacement vs time graph
period
frequency
period: the time it takes to complete 1 cycle (T) (s)
frequency: the number of cycles per second, f = 1/T (Hz)
T= 1/f
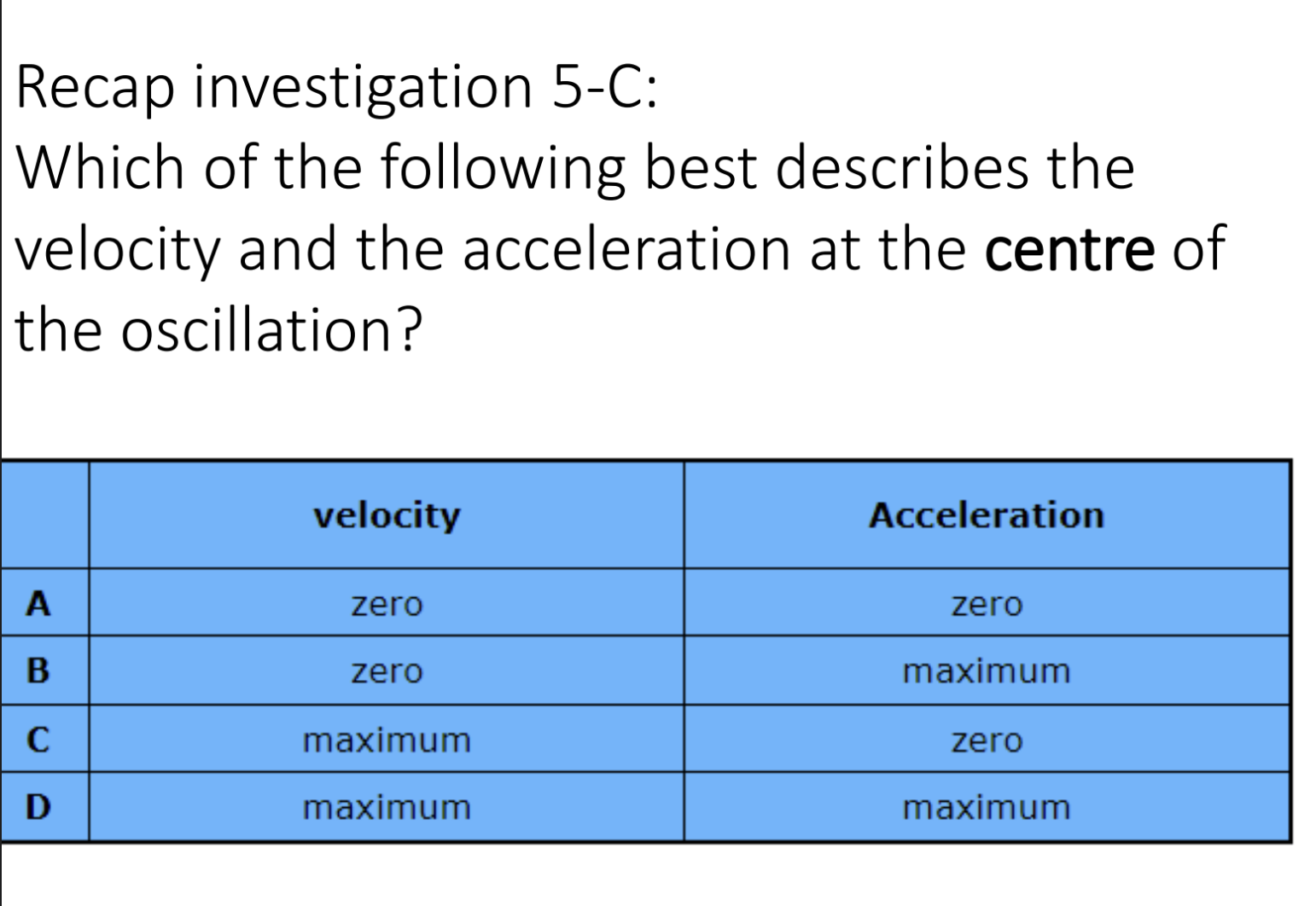
C
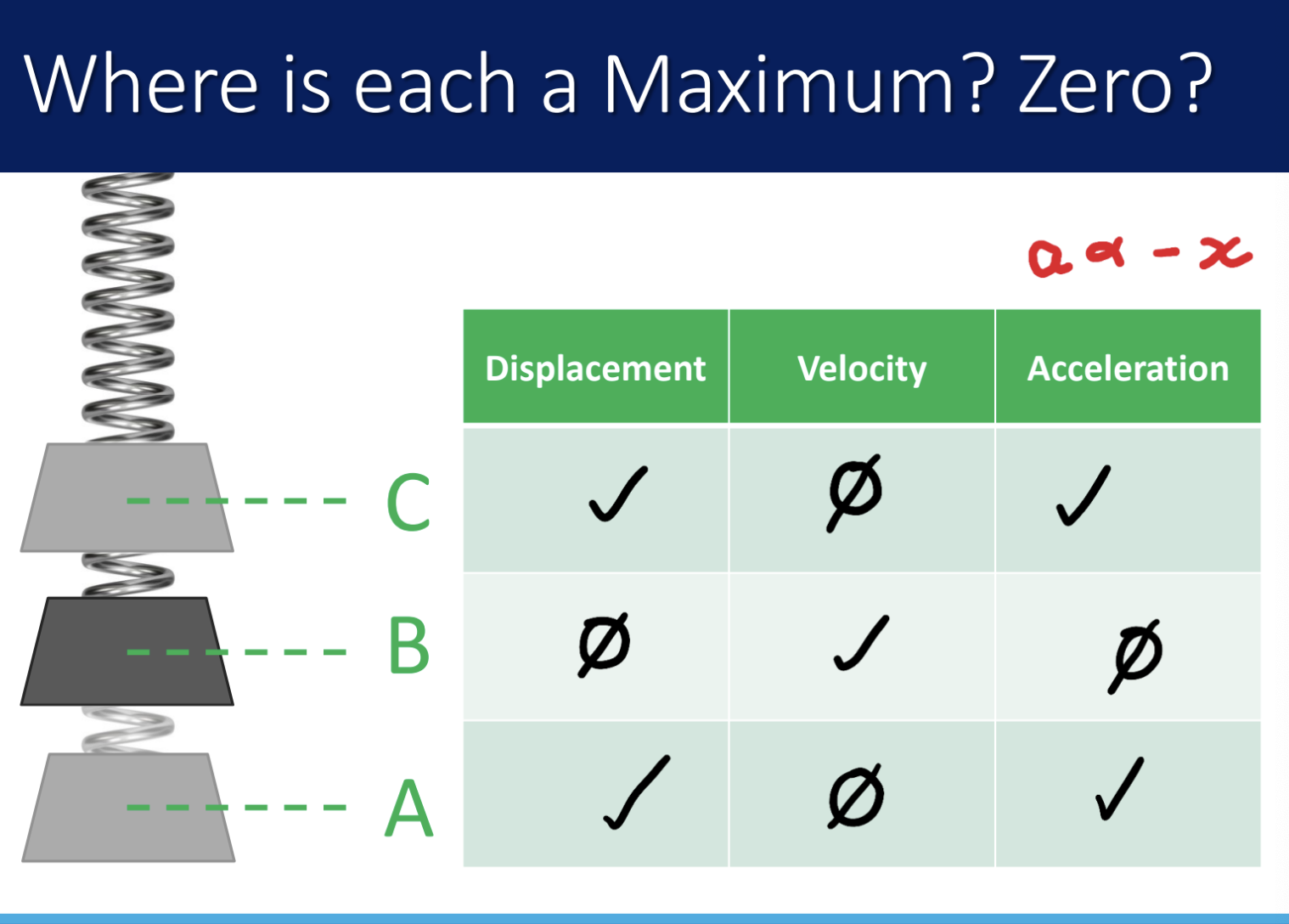
what is the period of a x-t graph vs a PE-t graph?
x-t graph:
period is from one position to its return
like an actual cycle
PE-t graph:
1 period = 2 cycles on PE -t graph
KE: 0 → max → 0 → max→ 0
PE: max → 0 → max → 0
what is k and its units
k = spring constant, how stiff the spring is (N/m)