micro exam 3- cytokineses in microbes (oct 23 lecture)
1/254
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
255 Terms
what do cytoskeletal systems provide
structural support
trafficking
cytokineses
DNA replication
cell shape
what do bacteria use in the cytoskeleton
Fts Z (tubulin like proteins)
what do euk have in cytoskeleton
microfilaments (actin)
microtubules (tubulin)
intermediate filaments (vimetin, lamin)
what is the only form of cytokineses in bacteria
binary fission
what organisms can use binary fission
protists
archea
bacteria
phases of binary fission
B
C
D
is binary fission present in vertebrates/ multicellular organisms
no
what euk microbes can use binary fission
protists
microalgae
is the process of binary fission conserved across domains
yes
period B
time between cytokineses and initiation of chromosome replication
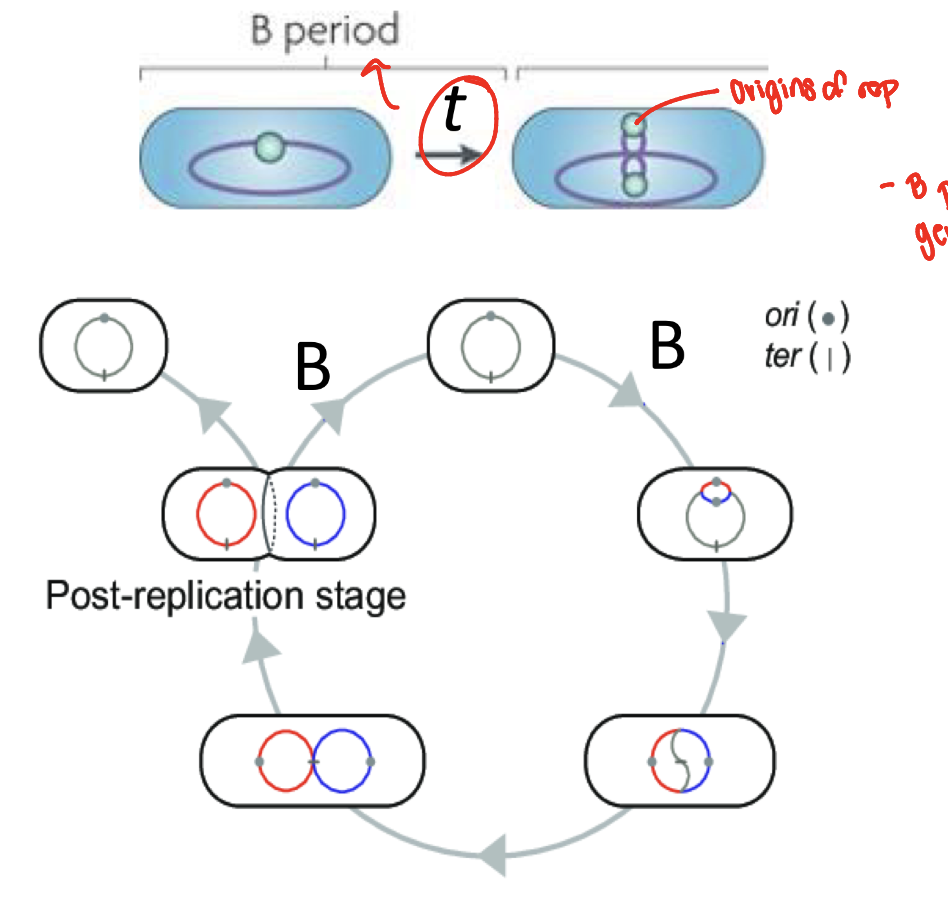
what does the B period determine
generation time in a cell
period C
chromosome replication and vegetation (inc in cellular volume)
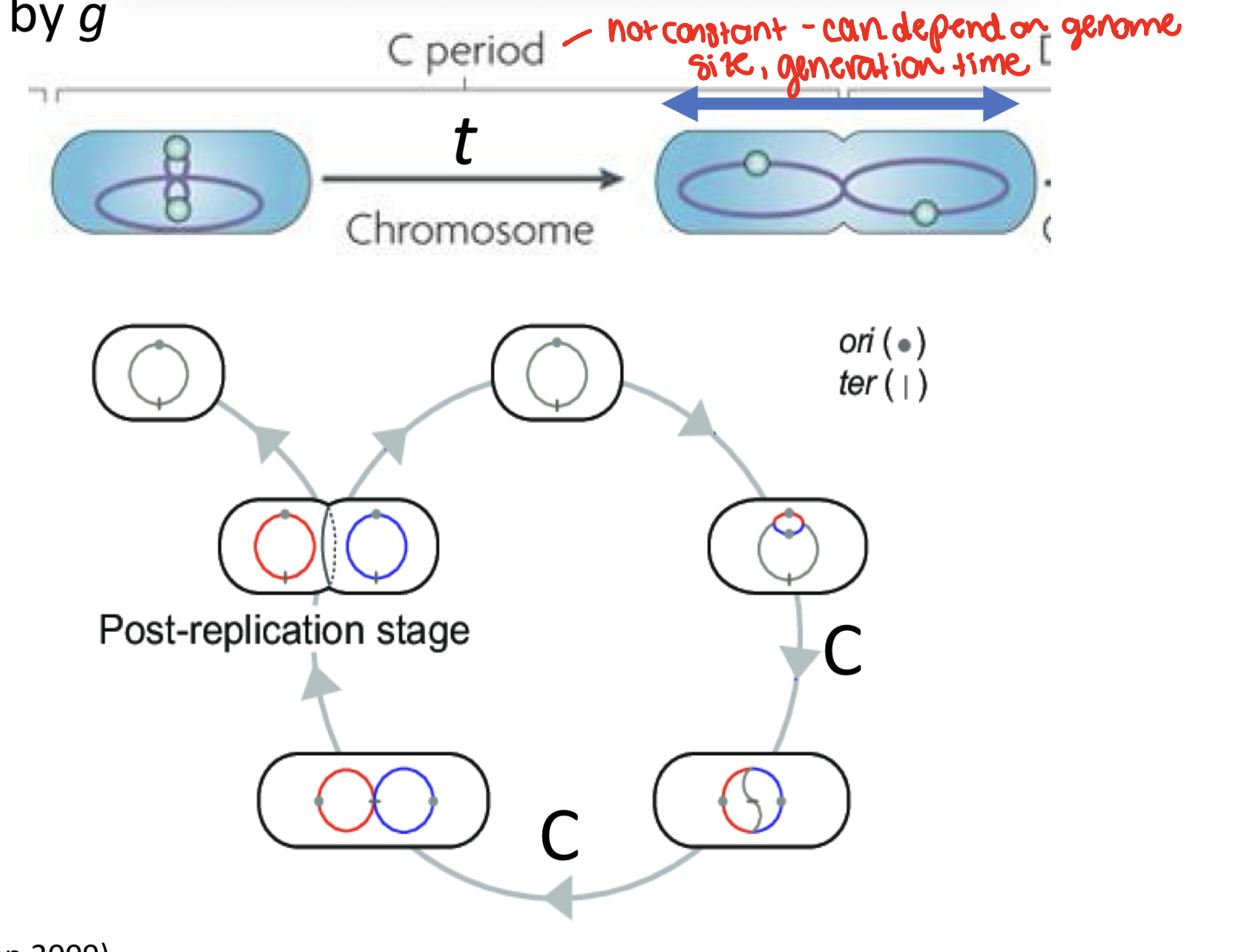
what is vegetation
an increase in cellular volume
what is the length of period C determined by
by generation time
what is generation time dictated by
growth restraints
period D
cytokinesis- chromosome and cellular materials segregate and the cells divide
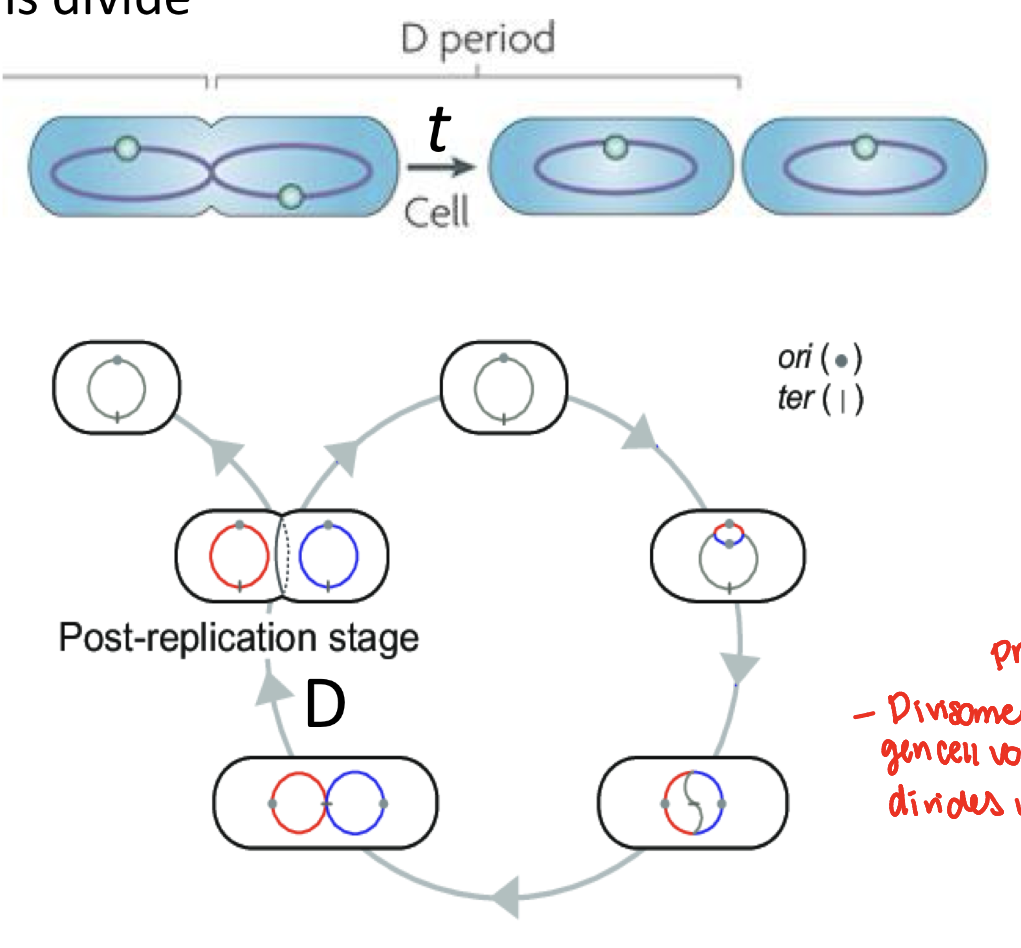
what is the only tubulin like protein in bacteria
Fts Z
what is binary fission initiated by
by FtsZ Z ring (polymer of FtsZ) formation at mid cell
divisome proteins
makes cell walls at the mid-cell (division scaffold)
what is septation
the separating of two cells (cleavage furrow in euk) by constricting the cell envelope, makes two genetically identical daughter cells.
archea tubulin like proteins
CetZ
FtsZ
role of CetZ
in cell shape and motility, only in archea
is FtsZ or CetZ involved in cytokineses
only ftsZ
contractile ring, what is it made of
eukaryotic homolog of a Z ring. made of F actin and myosin II.
abiotic parameters in which most microbes live in
temp: 20C-40C
pH: 6.5-7.5
salt: 0.5%-0.9%
pressure: 1atm - sea level
water activity (Aw): 0.91- 1.0
what is water activity
the amount of water available in a cell or system
how do microbes adapt to harsh environments
cellular differentiation (biofilms and sporulation- spores resilient to abiotic stressors)
extremophilism
where are extremophiles (what domains)
all domains- most common in archea
extremophiles
grow and survive in extreme environments
extremotolerant
survive but do not grow
what are piezophiles (barro)
pressure sensitive
order of piezo extremophiles
piezosensitive → piezophiles → hyperpiezophiles
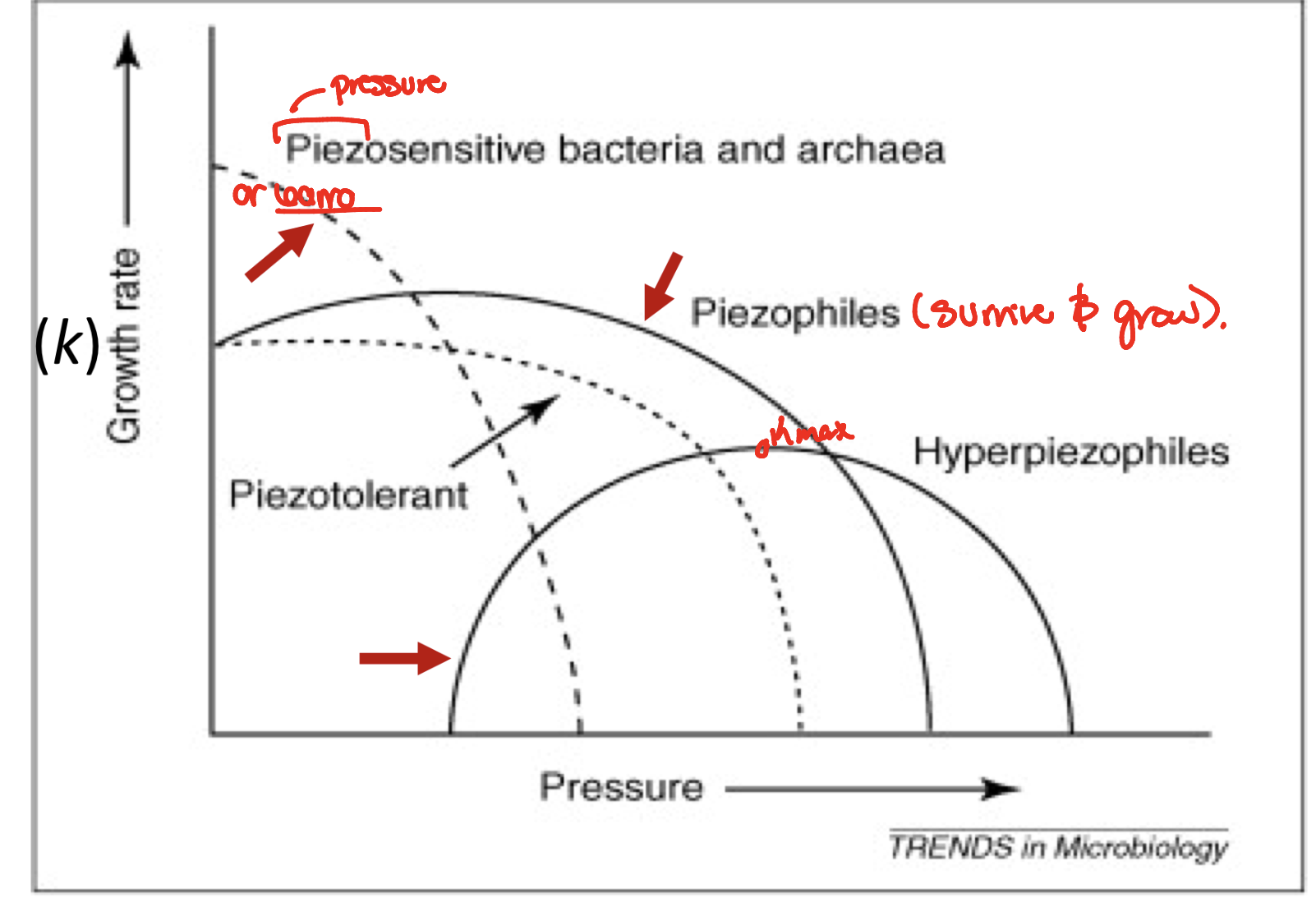
until what pressures can piezophiles grow
1,000 atm (100 Mpa)
what is 1 atm
15 psi
what is 1,000 atm in psi
14,500 psi
hyperpiezophile that requires high pressure to grow
shewanella benthica (bacteria)
psi range of shewella benthica
7000 PSI to grow
Kmax is at 11,000 PSI (80Mpa)
where was shewenalla bethica found
37,000 ft under the ocean surface
how do piezophiles surivive
>90% of benthica membrane fats are unsaturated docosahexanoic acid (DHA)
what does DHA do
increases membrane fluidity under extreme pressure
what does pressure normally do to membranes and how is this combated
it normally turns membranes into solid structures. piezophiles turn all membrane into DHA- which makes the membrane fluid and allows for survival.
what is present in cold loving psychrophiles that allows for surivival
DHA in the membranes
what is the Kmax of psychrophiles plus temp range
less than 10C (-5 to 20C)
mesophiles make up what percent of microbes that are thermally classified and their temp range
more than 90% (15 to 45 C)
thermophiles temp range
40 to 80C
what is the kmax of hyperthermophiles and temp range
more than 90 C (65 to 105C)
what microbe is used to manufacture DHA as an omega fat
crypthecodinium cohnii
when does c.cohnii concentrate DHA
when grown at low temperatures
what is crypthecodinium cohnii
a dinoflagellate. also a psychrophile that produces DHA when grown at low temperatures. (dinoflagellates also responsible for red tide)
what does thermococcus kodakarensis use in extreme environments
changes in protein biochemistry
where was thermococcus kodakarensis found
in a solfatara (volcano)
thermococcus kodakarensis growth time at what temp
less than 60 min at 85 C (also polyploidic)
what does changing the amino acid primary structure of proteins do
its an adaptation that effect structural flexibility
flexibility effect in heat
reduced (membrane wants to be too fluid, to combat this, it is made more rigid)
flexiblity effect in cold
increased (membrane turns more rigid, so DHA combats this by making it flexible)
what do thermophilic proteins have compared to mesophilic proteins
more ion pairs and bonding
compact core containing disulfide bonds/bridges
More H bonds
more rigid
more intra and intermolecular binding
thermococcus aquaticus
thermophilic
from yellowstone
contains taq (thermostable dna poly III)
what is taq useful for
in PCR because it can polymerize dna at high temps (which is needed to seperate the strands)
what did previous PCR rely on
Klenow DNA pol I of E.coli (thermo-sensitive and would break down at high temps- no dna polymerization)
what can adaptations of microbes be used for
for biotechnology
what percent of microbes can replicate in under 10 mins
10%
what is the slowest growing organism on earth
microorganism
how much could a single microbe multiply in 24 hours
1012
how long for a microbe to cover the surface of the earth
5 days
how long for microbe to get to 4000 times the mass of earth
5 days plus 72 hrs (8 days)
how long for fly to replicate
1 day
how long for rat to replicate
30 days
how long for whale to replicate
1 yr
size hypothesis
in macroorganisms, gestation or replication is correlated to size
size hypothesis in microorganisms
explains some part of the constraint but it is more complicated than just size
microbes and food
microbe growth is limited by the availability of nutrients and the type of nutrient because they cannot store it
what is good food
glucose and gluc-malt
what is bad food
maltose
what is maltose
a disaccharide of glucose, which requires maltase for its breakdown.
what are macronutrients used for (the big 6)
to get energy and make biopolymers
big 6 molecules
C
N
Ph
H
O
S
metal macronutrients
Magnesium (mg 2+)
Iron (Fe 2+)
Potassium (K+)
Calcium (Ca 2+)
CIMP (like simp)
what do the metal macronutrients do
make enzyme cofactors and regulatory molecules (cellular function)
what do the big 6 molecules make in order to generate energy and biosynthesis
macromolecules
micronutrients
Cobalt (Co 2+)
Copper (Cu+)
Manganese (Mn 2+)
Molybdenum (Mo 2+)
Nickel (Ni 2+)
Zinc (Zn 2+)
what do micronutrients make
make components of cofactors or enzymes
most limiting nutrient
carbon
how much of biomass does carbon control
50%
what properties of carbon make it important
tetravalency and catenation
what are the two ways carbon is assimilated
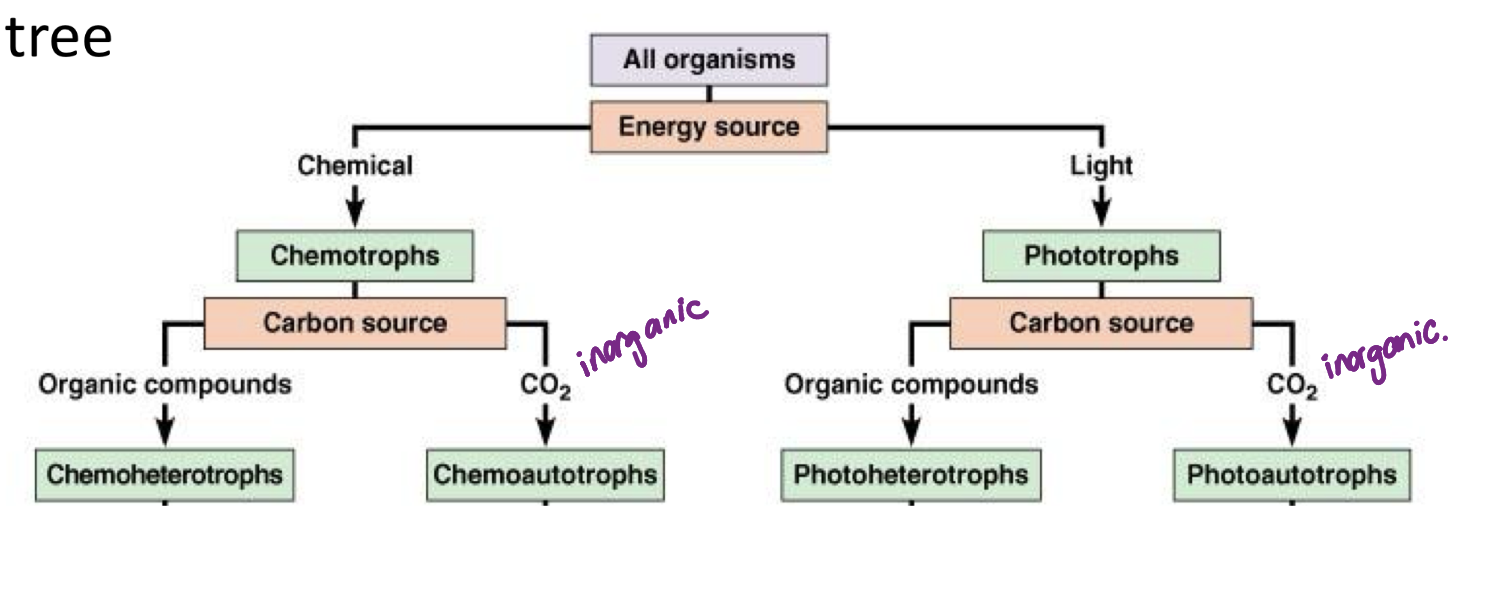
heterotrophy and autotrophy
heterotrophy
acquire carbon from consuming other organisms
heterotrophic diagram
carbohydrates go to the TCA by glycolysis
fats, proteins, nucleic acids go to TCA
this process allows for assimilation and energy
heterotrophy examples
predation
culture
disease
autotroph diagram and what is it
Gets their carbon from CO2
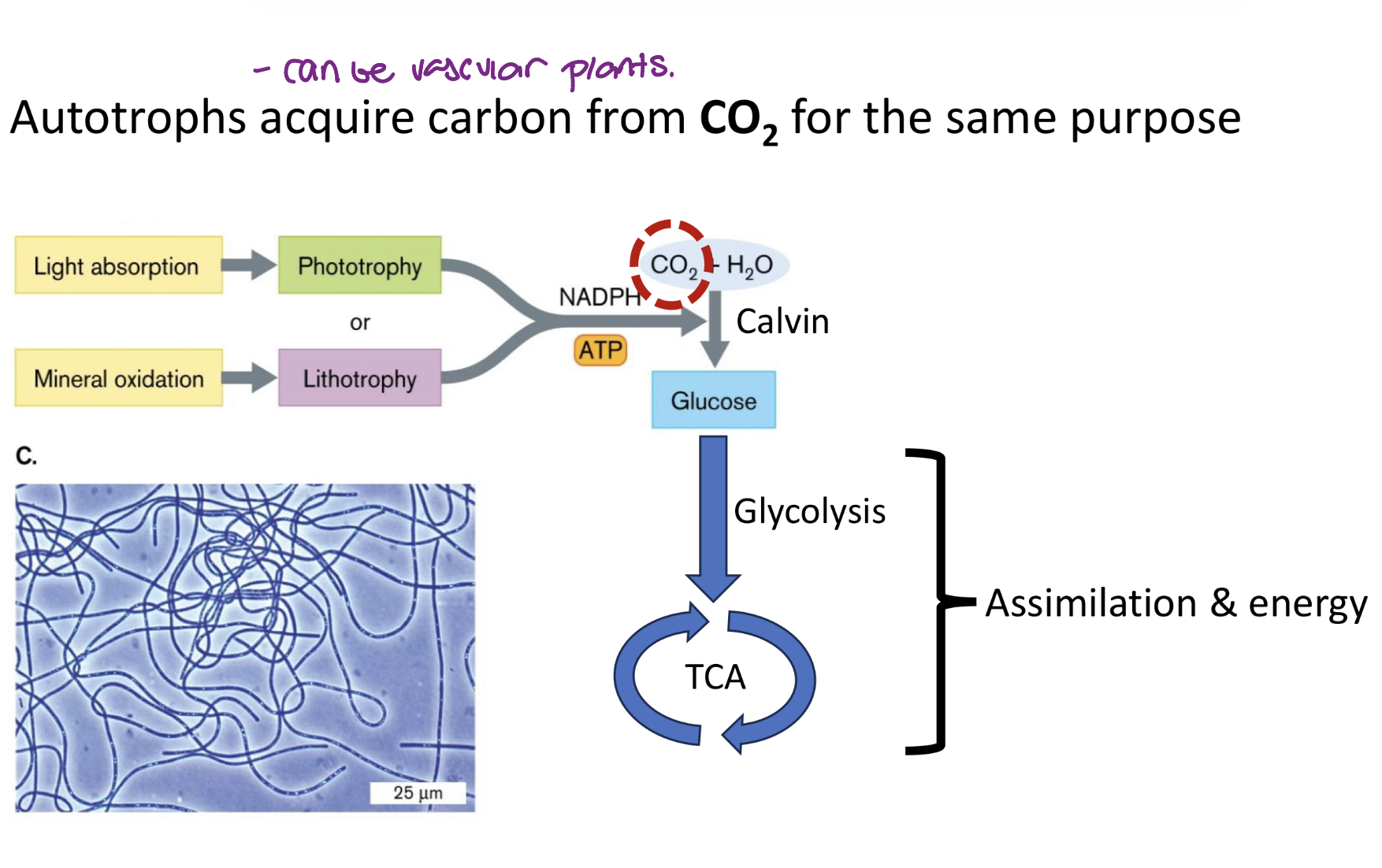
autotrophy examples
photosynthesis and CO2 fixation
autotrophy organisms examples
nostoc spp. (bacteria), look like rods
volvox spp. (eukarya algae), look like balls with clusters of chlorophyll
both have chlorophyll
what does growth require
energy
phototrophic
energy obtained through chemical reactions driven by light absorption
chemotrophic
energy obtained through the rearangement of organic compounds (redox, making/breaking bonds)
decision tree of what type of organism it is
two ways energy can be used
for work or stored
types of work
transport, biosynthesis, motility, metabolism
how can energy be stored
in high energy molecules or membrane potentials (electrochemical gradients)
high energy molecules
ATP
GTP
NADH
NADPH
FADH2
PEP
broken down to access the energy
how is energy accessed from the two forms of storage
their state is changed