Era 1, 1200 - 1450 CE: Islam + The Fall of the Abbasid Caliphate (Quizlet #5)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1. Era 1 Overview, 1200 CE to 1450 CE
-Era 1 from 1200 - 1450 CE saw a rise in several important Land-Based Empires, as well as a huge increase in trade and travel;
-CRITICAL ERA 1 EMPIRES TO KNOW:
-Song Dynasty in China/East Asia
-Mayans, Incans, and Aztecs in the Americas
-The disintegration [falling apart] of the Abbasid Caliphate into several smaller Turkic empires in the Middle East/South Asia
-The Islamic Delhi Sultanate in South Asia
-Great Zimbabwe in Africa
-Feudalism and decentralization (no empire) in Western Europe
-The Mongol Empire in Asia/Middle East; they come in at the end and knock many empires down!
TRADE also massive. BIG FOUR ERA 1TRADE NETWORKS TO KNOW:
-Silk Roads in Eurasia/Middle East-Trans-Saharan Routes in Africa-Indian Ocean Basin trade
-Mediterranean Sea Trade
RELIGION also huge, with the spread of Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism
-The Black Plague, Marco Polo, Ibn Battuta, also major terms!
![<p>-Era 1 from 1200 - 1450 CE saw a rise in several important Land-Based Empires, as well as a huge increase in trade and travel;</p><p>-CRITICAL ERA 1 EMPIRES TO KNOW:</p><p>-Song Dynasty in China/East Asia</p><p>-Mayans, Incans, and Aztecs in the Americas</p><p>-The disintegration [falling apart] of the Abbasid Caliphate into several smaller Turkic empires in the Middle East/South Asia</p><p>-The Islamic Delhi Sultanate in South Asia</p><p>-Great Zimbabwe in Africa</p><p>-Feudalism and decentralization (no empire) in Western Europe</p><p>-The Mongol Empire in Asia/Middle East; they come in at the end and knock many empires down!</p><p>TRADE also massive. BIG FOUR ERA 1TRADE NETWORKS TO KNOW:</p><p>-Silk Roads in Eurasia/Middle East-Trans-Saharan Routes in Africa-Indian Ocean Basin trade</p><p>-Mediterranean Sea Trade</p><p>RELIGION also huge, with the spread of Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism</p><p>-The Black Plague, Marco Polo, Ibn Battuta, also major terms!</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d77d1d43-64a9-4c08-81bd-12f5829c9cf0.png)
2. Islam
-Major world religion started around 630 CE
-Started by the prophet Muhammad
-God is Allah; this is a monotheistic religion that demands the worship of the one true god, Allah.
-Combined parts of Judaism, Christianity, and Zoroastrianism, all of which influenced this religion
-Holy city of Mecca; believers are encouraged to make a pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in their lifetime, ideally every year
-Centers around the Five Pillars of Islam, which are the five central beliefs of Islam
-the Qur'an is the holy text of Islam and lays out the rules and laws of Islam, including sharia law (the law that Islamic codes follow)
-"jihad"--can be the struggle within a person, or the struggle against the enemies of Islam
-some branches of Islam encouraged members to fight holy wars to spread Islam. Through holy wars, Islam spread rapidly throughout the Middle East and North Africa
-Through holy war, trade with merchants, and through Islamic missionaries like the Sufi mystics, Islam continued to spread throughout Eurasia. Islam took over Spain for a time, and reached into India (South Asia), SE Asia, and far into Sub-Saharan and East Africa

3. The Five Pillars of Islam
-These are five rules or routines that every Muslim must follow. These are critical behaviors that everyone needs to do!
1--Allah is the only god and Muhammad is his prophet
2--Must pray to Allah five times a day, facing Mecca
3--Give money to charity (2.5% of wages each year)
4--Fast (don't eat) during day time in month of Ramadan
5--Must go to Mecca at least once in your lifetime. Ideally every year

4. Muhammad (570 CE - 632 CE)
-Founding prophet of Islam
-Made a famous journey to Mecca, known as the "Hijra." Mecca is now the holy city of Islam. The five pillars of Islam require every Muslim to visit there once
-____________________ CE , DATE REQUIRED IN ANSWER
-Successfully established Islam as a prophet and missionary and spread it throughout the Middle East/Arabia
-Is named in the first pillar of Islam as the prophet of God, Allah
-Muslims believe that Allah sent revelations to Muhammad, and those were written down in the Qur'an. These rules are set down for Muslims to follow
(Dates are before 1200 CE, but he is still important context)
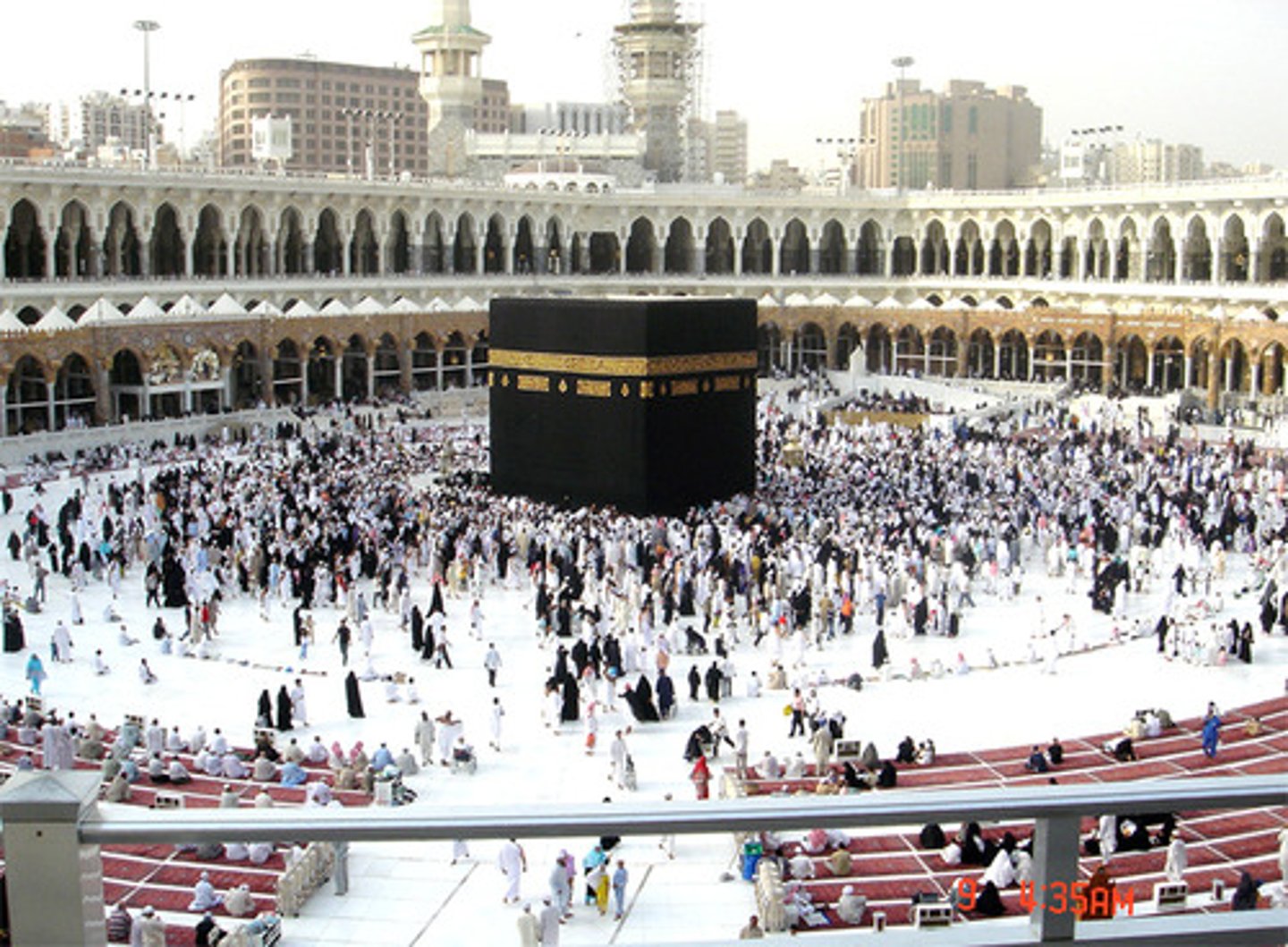

5. The Qur'an
-the most important book in Islam, containing all of Muhammad's revelations [ideas shown to him] and understandings of Allah
-Foundational text of Islam
-Lays out the five pillars of Islam, which are the foundational behavior that every Muslim must observe
-Contains influences from Judaism, Christianity, and Zoroastrianism, all of which heavily influenced Islam
-lays out the rules of Islam, known as "sharia law." These laws form the basis for how the Caliphates and many Islamic states were governed
-Muslims believe that Allah sent revelations [ideas] to Muhammad over the course of 23 years, and these revelations were written down in the Qur'an. Allah sent the messages to Muhammad through the Archangel Gabriel.
![<p>-the most important book in Islam, containing all of Muhammad's revelations [ideas shown to him] and understandings of Allah</p><p>-Foundational text of Islam</p><p>-Lays out the five pillars of Islam, which are the foundational behavior that every Muslim must observe</p><p>-Contains influences from Judaism, Christianity, and Zoroastrianism, all of which heavily influenced Islam</p><p>-lays out the rules of Islam, known as "sharia law." These laws form the basis for how the Caliphates and many Islamic states were governed</p><p>-Muslims believe that Allah sent revelations [ideas] to Muhammad over the course of 23 years, and these revelations were written down in the Qur'an. Allah sent the messages to Muhammad through the Archangel Gabriel.</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/ac6d5b37-6eaa-40eb-9193-9afeec092807.jpg)
6. Jihad
-There are two meanings of the term
- One, the struggle or fight against the enemies of Islam.
- Two, the spiritual struggle within oneself against sin.
-Followers of Islam must take up the sword to protect Muslims from those who threaten Islam
-also means to struggle to spread Islam
-In some historical cases, referred to a holy war to defend Islam or spread Islam
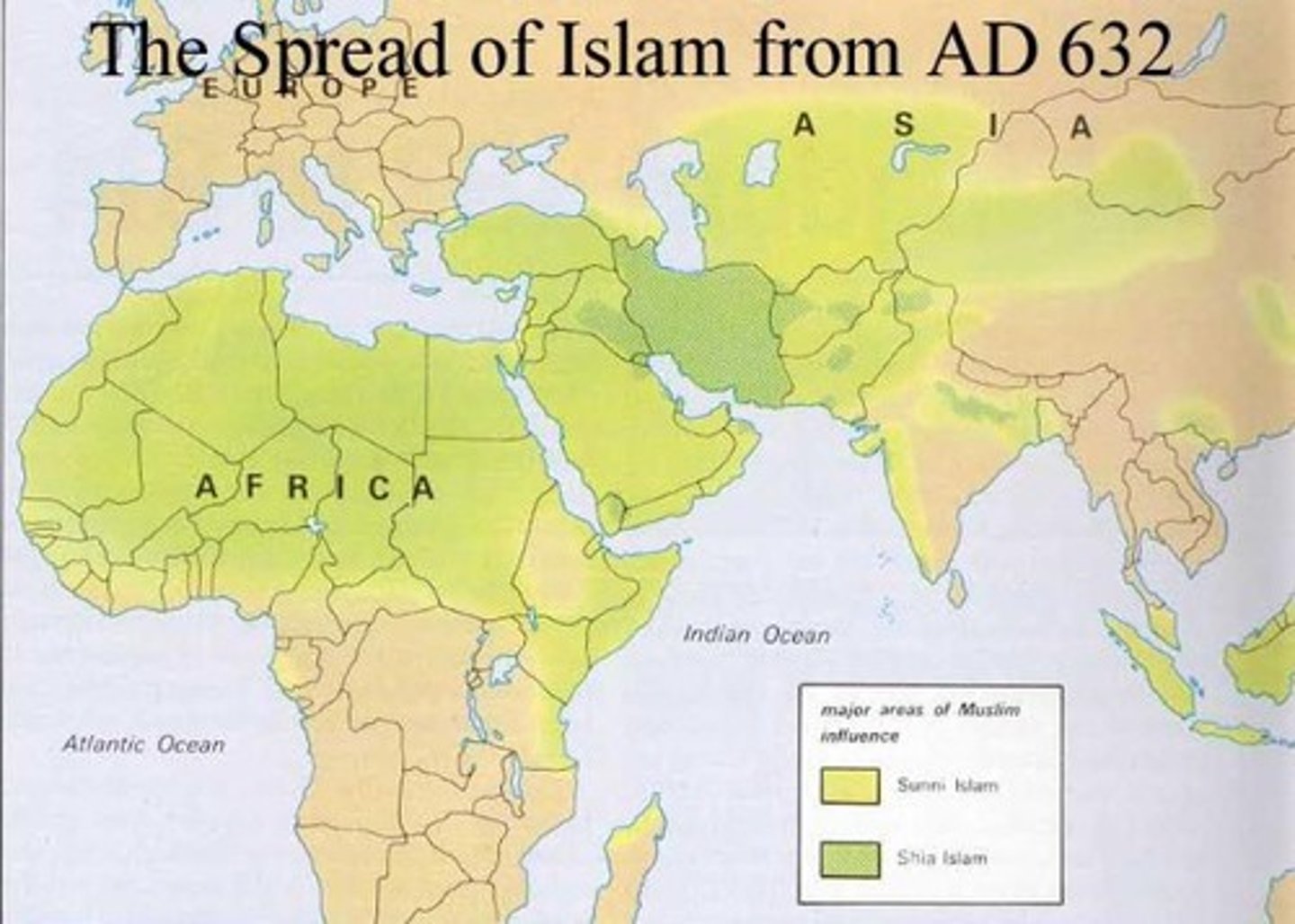
7. Mecca
-Located in Saudi Arabia in the Middle East
-The Holy City of Islam
-Every Muslim required to go to Mecca and make a pilgrimage there once in lifetime as part of the five pillars of Islam, encouraged to go there more often
-Became famous because Muhammad made one of his big early journeys to this city
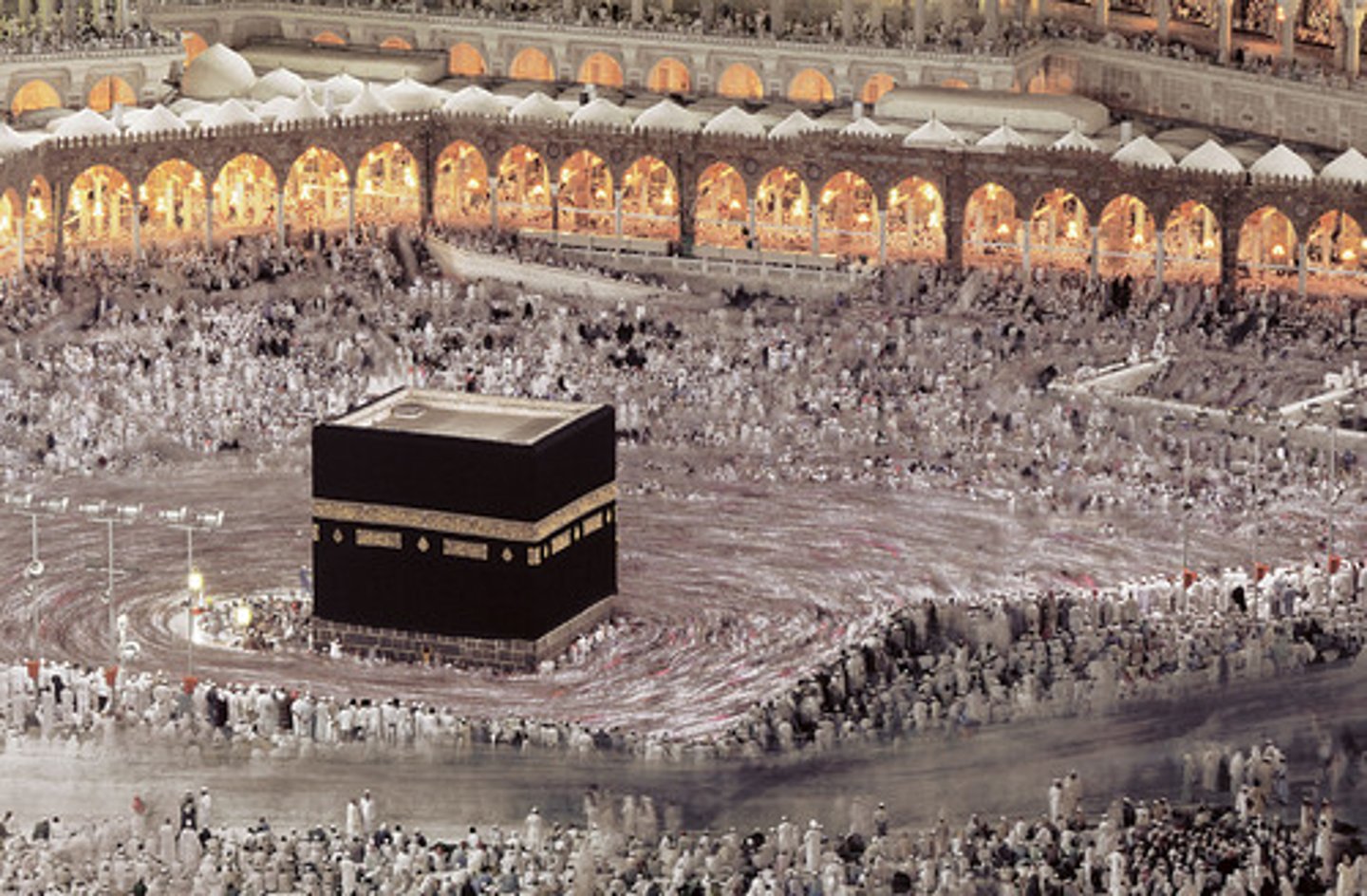

8. Sharia Law
-Islamic Law that governs the way people should live
-Through this law, Islam became more than a religion; in Islamic states, the laws, the society, are all governed by Islam
-In the Caliphates, like the Abbasid Caliphate, ____________________ law was used to govern cities and states
-It covers many areas of life and law, including crime, sexuality and adultery, hygiene, diet, and prayer
-________________ law is seen as the word of God, as recorded in the Qur'an. Remember, the Qur'an is the direct word of god, as told to Muhammad by the archangel Gabriel
-________________ law became more than just a religious set of rules; it became the social, economic, and political laws that governed cities and states in Dar al-Islam

9. Dar al-Islam
-This is a term that refers to all of the places in the world where Islam is the dominant religion
-Literally means "House of Islam"
-Major Islamic areas that are included in this term are:
-North Africa and the Middle East
-East Africa
-Sub-Saharan Africa--cities at the end of the Trans-Saharan caravan routes
-SE Asia and some parts of India (although Hinduism and Buddhism still more popular here).
-As Islam spreads through North Africa and Middle East, this main area becomes known as __________________________
10. Judaism, Christianity, and Zoroastrianism
-Islam combined parts of these three faiths in order to create one religion
-Islam had parts of all three of these faiths in it and was influenced by these faiths
-These were all older religions than Islam

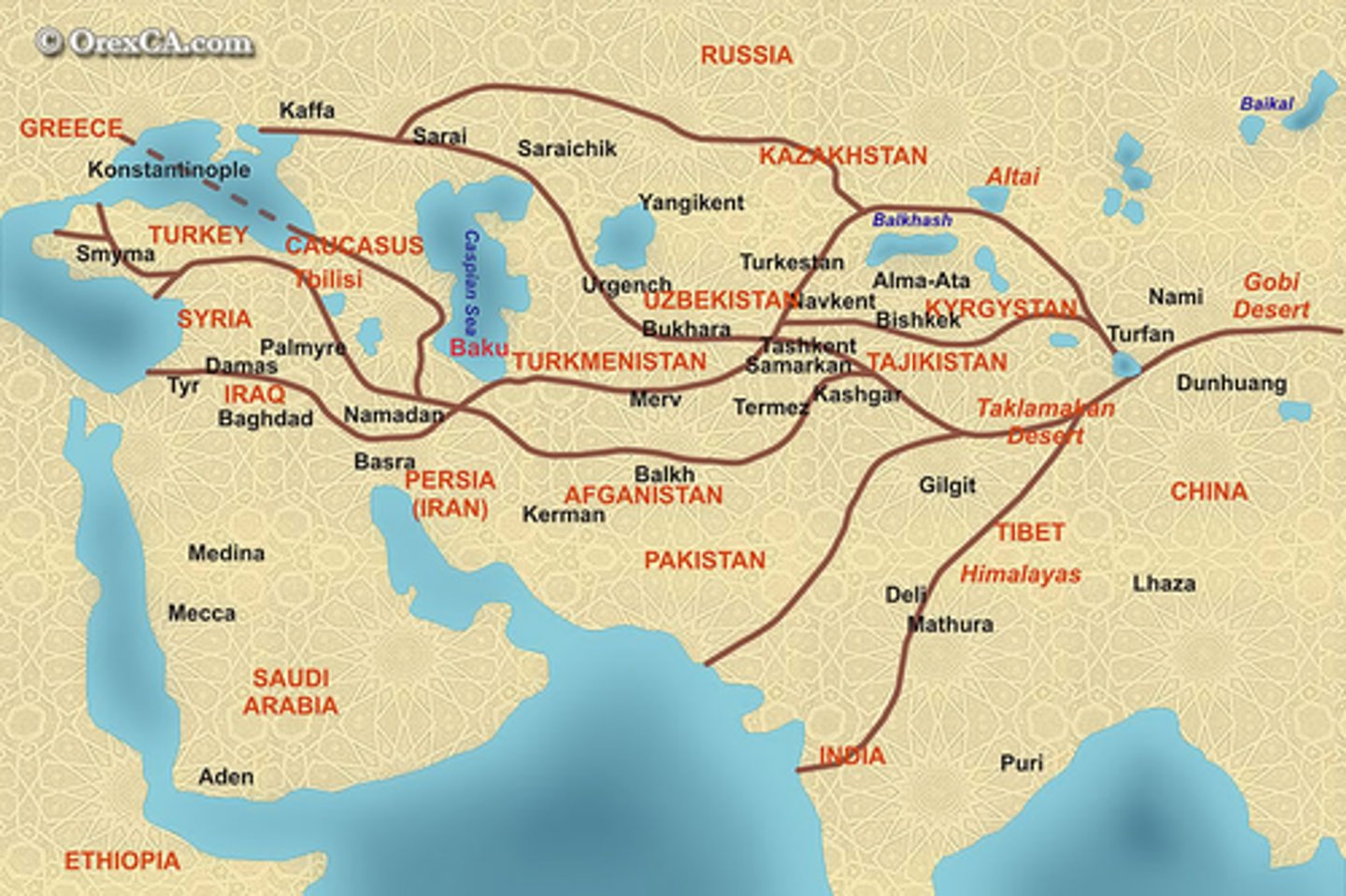
11. The Spread of Islam: Trade, Warfare, and Missionaries
-Islam, like other major religions, spread through three major ways: trade, warfare, and diffusion through missionaries
-Islam expanded rapidly through trade as merchants brought the faith along the Trans-Saharan caravan routes and along the Silk Roads to SE Asia and India; merchants also spread Islam throughout the Middle East and North Africa
-Motivated by "jihad," Islamic people also used their military power to conquer nearby countries and turn them Islamic (note: answer is NOT "jihad")
-Islam also expanded rapidly due to Islamic missionaries spreading the word; types of missionaries include the Sufi Mystics
-Islam spread to North Africa, the Middle East, South Asia (India), SE Asia and even to parts Europe
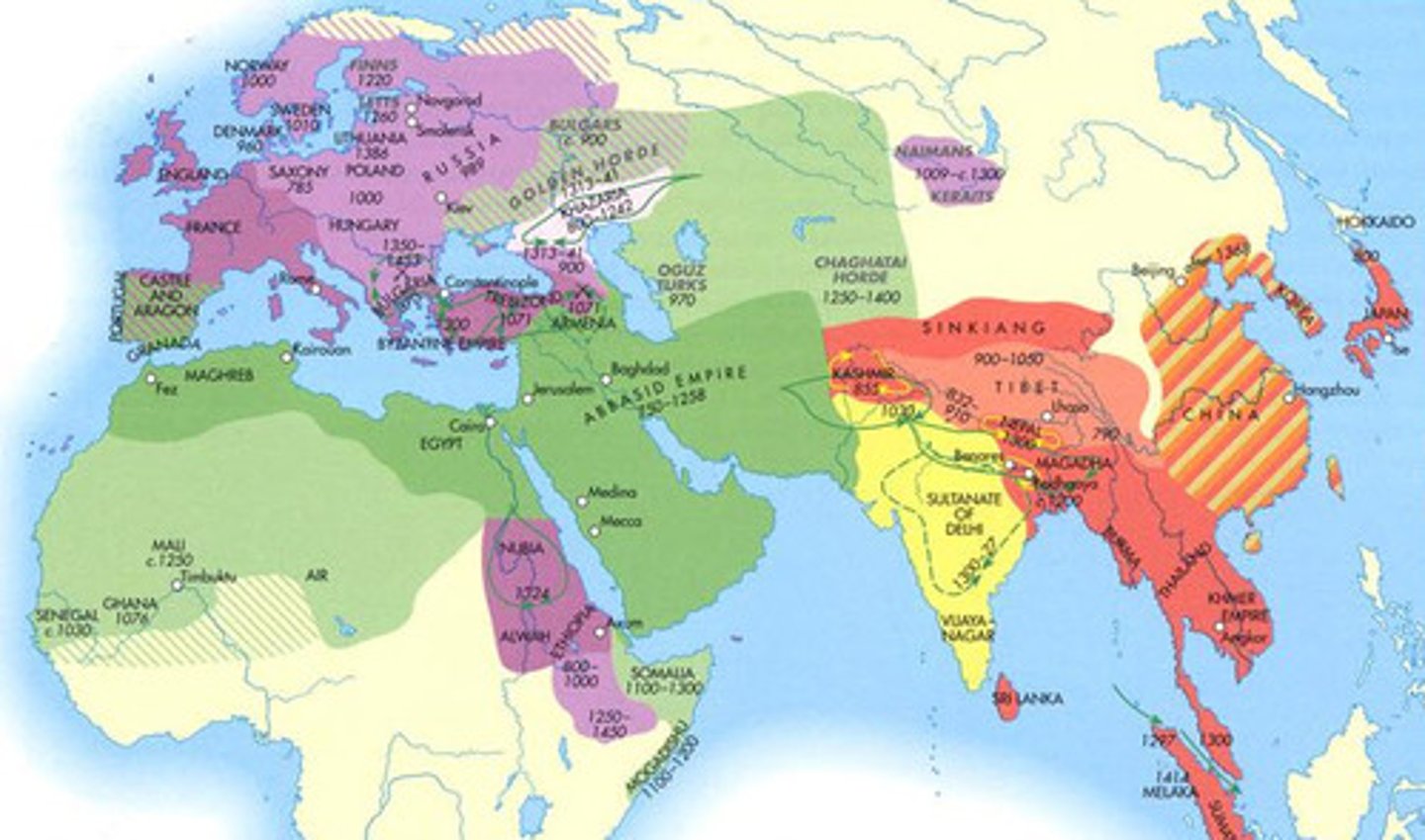
12. Egypt, Arabia, and Persia as part of Dar Al-Islam
-Three areas where Islam spread to through military expansion
-Jihad or religious war was waged in these areas and they became Islamic
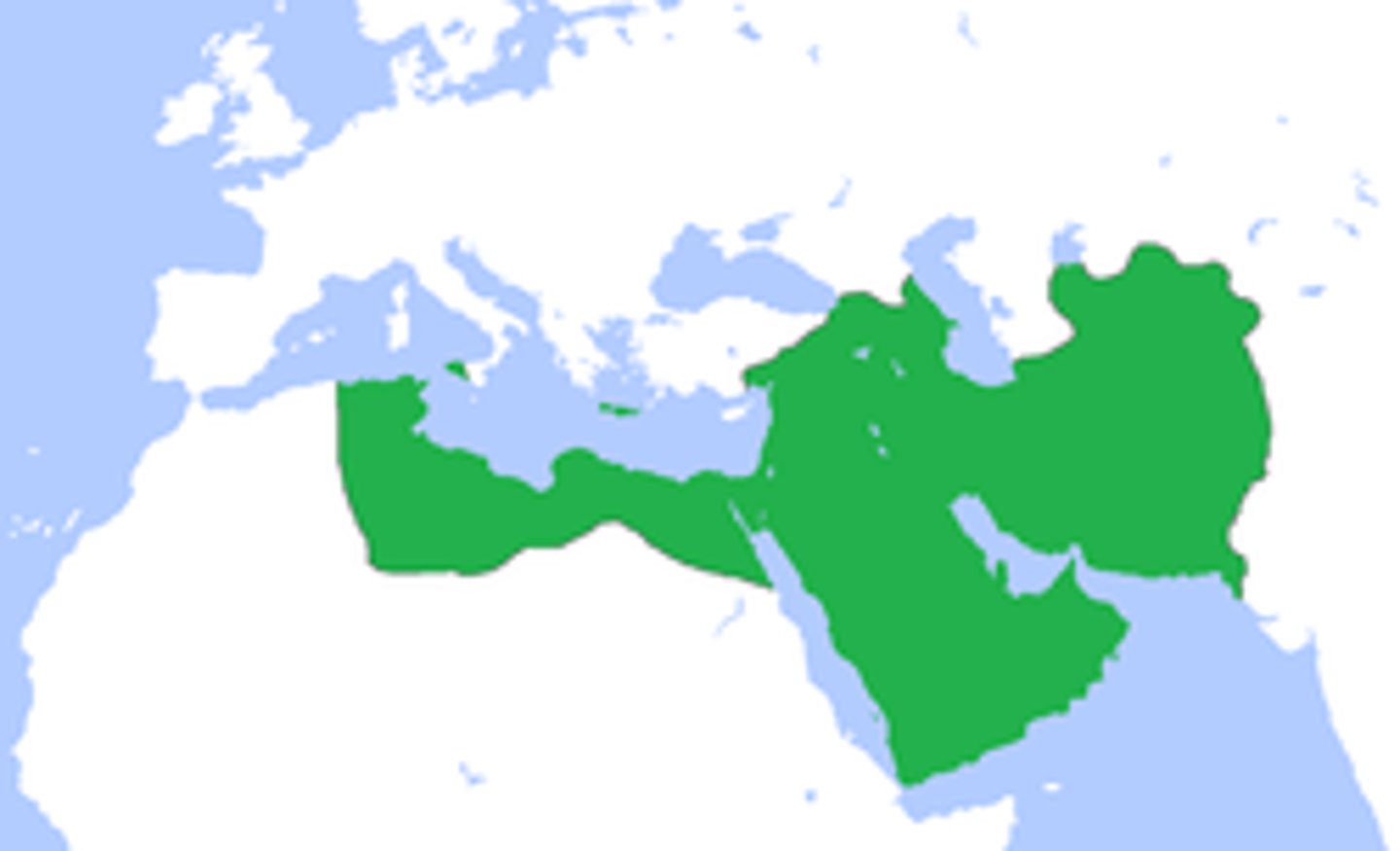
13. Caliph + Caliphate
-When Mohammed died, the Islamic Community had to choose who would rule after him
-A Caliph is the leader or leader of the Islamic Community, chosen by the community
-It's similar to a King, but some Muslims believe he should be elected to the position, while some believe he should be chosen by God/religious leaders
-So a Caliph is a political structure that is kind of similar to a King, but even more powerful, because he is a political and religious leader. Kind of like the King and the Pope combined.
- A Caliphate is an Islamic kingdom or empire; ruled by a person who has been chosen to be Muhammad's successor, known as Caliph
-This was a slightly new type of government in the 700 CEs; it's like an empire, but the ruler is a religious and political figure; almost like the Pope and King combined
-The ruler has ultimate authority as both a political and religious figure
-The most significant caliphate you need to know is the Abbasid Caliphate (fell to the Mongols in 1258 CE)

14. jizya
-Muslim caliphates often placed a tax on non-Muslims living in the Caliphate, such as Jews and Christians
-This was unpopular and led to resistance against the Abbasids
-the Big Three Islamic Empires in Era 2, 1450 - 1750 CE, The Mughal Dynasty in India, Ottoman Empire in the Middle East, and Safavid Empire in the Middle East would also use this tax on Jews and Christians

15. The Abbasid Caliphate (750 CE - 1250 CE)
-major Islamic kingdom/ Empire
-Started by Abu al-Abbas
-Not an empire based on conquering; relied on Islamic missionaries to spread Islam and expand "Dar al-Islam" (the House of Islam)
-The dominant Islamic empire in the Middle East from 750 - 1250 CE. Really really effective government structure and administration; capital city at Baghdad, where everything was organized
-Instead of trying to conquer, the Abbasids wanted to organize the places they ruled. They were strongly influenced by the Persian Achaemenids in the way thy ran the government; they used regional governors,
-"Qadis" (judges) and "Ulama" (religious scholars) were government officials that helped every town follow the rules of Islam
-Declined with the Invasion of the Mongols
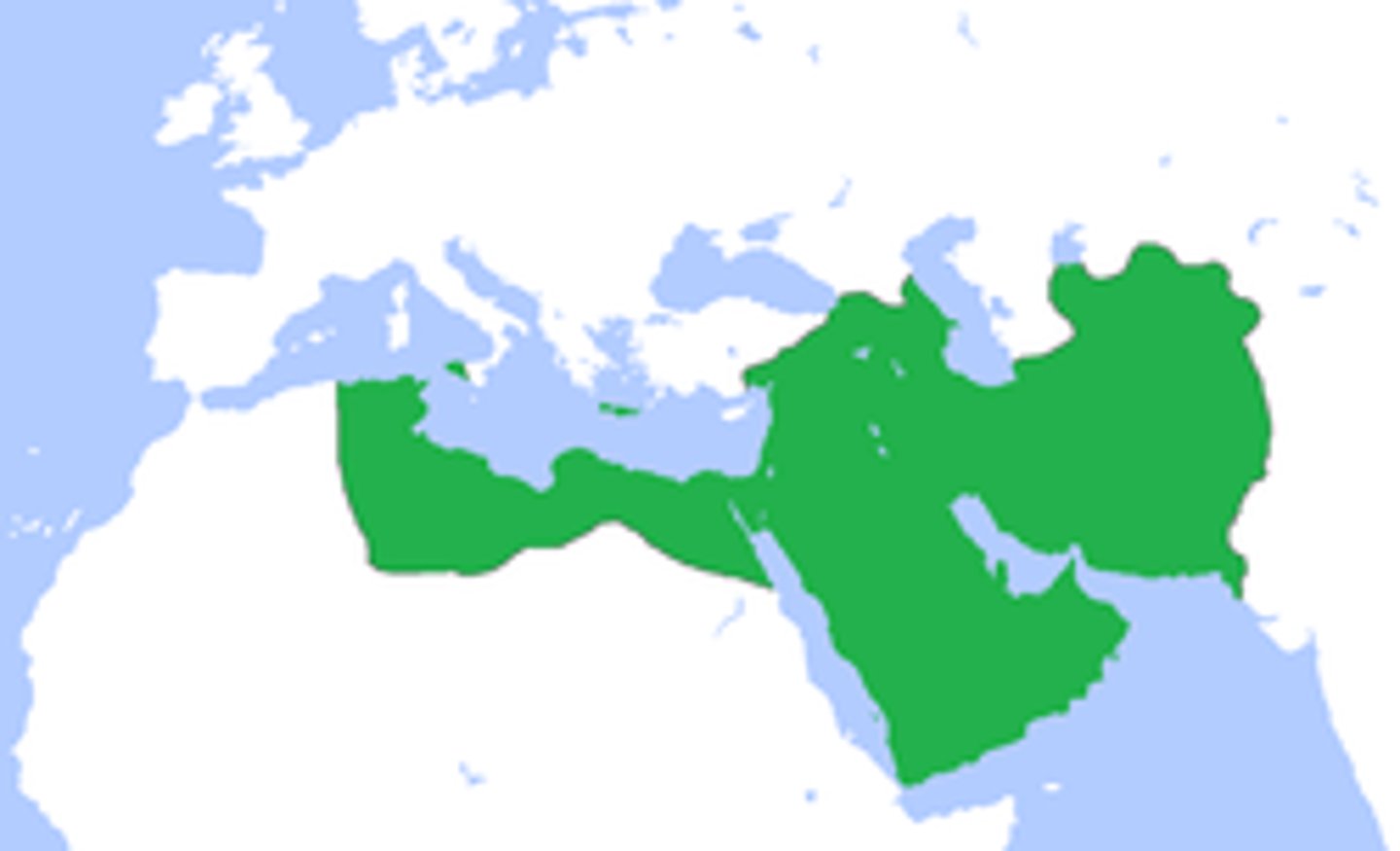
16. The Abbasid Caliphate's Political Organization--influenced by Persian Achaemenids
-This caliphate had an excellent political organization
-They were strongly influenced by the ancient Persian Achaemenids
-Capital city at Baghdad; all rulings came from the city
-Political history and knowledge was gathered at the House of Wisdom, the grand library in Baghdad
-The Caliphate was divided into provinces with regional governors (like the Achaemenid Satrapies)
-The governors collected taxes and reported to the Caliph in Baghdad
-"Qadis" (judges) and "Ulama" (religious scholars) were government officials that helped every town follow sharia law, the rules of Islam

17. Qadi and Ulama
-These were Islamic terms for "Judges" and "religious scholars"
-They were government officials during the Abbasid dynasty. They helped run towns and make sure that everyone was following Sharia law, the rules of Islam
-Ibn Battuta, the famous world traveler, was an Islamic __________ (judge) who traveled the world helping to interpret and run sharia law

18. Baghdad
-Capital City of the Abbasid Caliphate
-Massive trading city, became very wealthy from Silk Roads and all the taxes coming in from the outer realms of the Abbasid Caliphate
-Active trade in this city with the Song Dynasty in China, where silk, spices, and porcelain would arrive
-Large population with hundreds of thousands of people
-Included the House of Wisdom, one of the grandest libraries in the world that contained all of the knowledge of mathematics, geography, history, and literature that the Abbasids had gathered from Dar Al-Islam
-Central city where the Abbasids ran their really well organized government from; influenced by the Persian Achaemenids, they divided the empire up into provinces; the governor of each province reported back to the Caliph at Baghdad
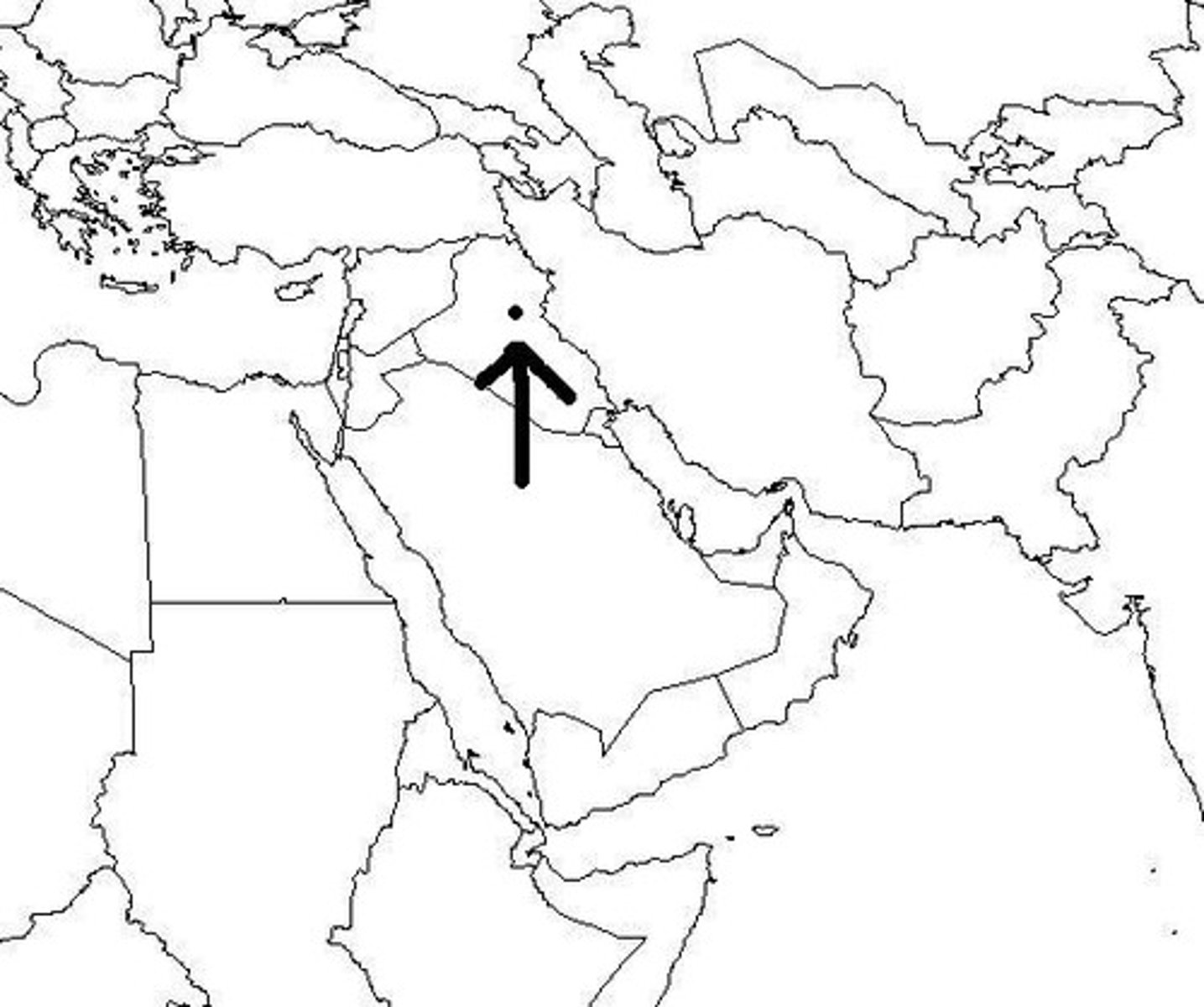
19. The House of Wisdom in Baghdad
-located in the capital city of Baghdad, one of the grandest libraries in the world that contained all of the intellectual and historical knowledge gathered by the Abbasids
-Included translations of Greek, Roman, and Indian classics into Arabic
-Included Arabic learnings on Mathematics, Geography, Sailing, Religion, and other topics
-Was much more than just a library, as it was a center for scientists and researchers to work. Work there was part of the modern foundation for chemistry and astronomy (study of the stars and universe)
-Also a center for mathematicians, who helped create the foundations of Algebra
-Was destroyed by the Mongols in 1258 CE when the Caliph Al-Musta'sim refused to surrender to the Mongols. Supposedly, the books from Baghdad's libraries were thrown into the Tigris River in such quantities that the river ran black with the ink from the books

20. The Sack of Baghdad and the Abbasid Fall (1258 CE)
-After the death of Harun Al-Rashid, the Abbasids began to decline
-His sons fought Civil Wars for power, and there were constant arguments over who should be the next Caliph
-The governors of the different areas were supposed to support the Caliphate. But instead, they started to take power for themselves.
-Peasant uprisings and Rebellions weakened the empire
-The last straw was the invasion of the Mongols in 1258 CE. The Mongols besieged [surrounded] Baghdad and ordered it to surrender; the Caliph Al-Musta'sim refused the Mongol offer of surrender
-within 12 days the Mongols had taken the city and proceeded to destroy the city and massacre the people, committing numerous atrocities (the black tent had gone up...). They destroyed the House of Wisdom
-This was the end of the Abbasid Caliphate, which was then turned into a Mongol Khanate, the Ilkhanate of Persia
![<p>-After the death of Harun Al-Rashid, the Abbasids began to decline</p><p>-His sons fought Civil Wars for power, and there were constant arguments over who should be the next Caliph</p><p>-The governors of the different areas were supposed to support the Caliphate. But instead, they started to take power for themselves.</p><p>-Peasant uprisings and Rebellions weakened the empire</p><p>-The last straw was the invasion of the Mongols in 1258 CE. The Mongols besieged [surrounded] Baghdad and ordered it to surrender; the Caliph Al-Musta'sim refused the Mongol offer of surrender</p><p>-within 12 days the Mongols had taken the city and proceeded to destroy the city and massacre the people, committing numerous atrocities (the black tent had gone up...). They destroyed the House of Wisdom</p><p>-This was the end of the Abbasid Caliphate, which was then turned into a Mongol Khanate, the Ilkhanate of Persia</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/22cfca98-94f8-429d-b241-d4a3246f5c88.jpg)
21. Invasion of the Mongols in 1258 CE DATES REQUIRED
-This was the last event that brought down the Abbasid Caliphate
-Included the Sack of Baghdad and the destruction of the House of Wisdome
-this is the same way so many empires fall!!!!!
DATES REQUIRED FOR FULL CREDIT

22. Indian Influence on Islam
-This society was also widely admired by the Muslims for their achievements in math and science
-In particular, they admired their alphabet and adopted their letters and numbers to help with record keeping
-They also admired their mathematics, which allowed them to start doing astronomy (study of the stars) and they also started using their medical findings
-Many of these things had been discovered during the Gupta Dynasty
-By borrowing from other cultures, Islamic societies like the Abbasid Caliphate became advanced technologically and culturally and rose to great power
-Arabic and Islamic philosophers would help translate Indian works at the House of Wisdom, the grand library in Baghdad, where much of the knowledge would be gathered and stored. They would make their own critiques of Indian works, and add to their work, particularly in the field of mathematics

23. Greek Influence on Islam
-Muslims widely admired these people and borrowed much of the scientific and medical writings from ___________
-They particularly tried to learn from the __________ philosophers Aristotle and Plato
-_______________ mathematics and science influenced Muslims and inspired them to find their own powerful mathematical and scientific discoveries
-By borrowing from other cultures, Islamic societies like the Abbasid Caliphate became advanced technologically and culturally and rose to great power
-Arabic and Islamic philosophers would help translate Greek works at the House of Wisdom, the grand library in Baghdad, where much of the knowledge would be gathered and stored. Arabic/Islamic philosophers would add their own ideas to Greek philosophy

24. "The Arabian Nights" Book
-Persia is basically the territory around modern day Iran and Afghanistan. Ancient Persian culture influenced Islam and the Abbasid Caliphate in lots of different ways
-Persian influence also affected Islamic literature. Islamic literature was written in Persian; the most famous collection of stories was known as ______________________
-The stories in this book presented popular tales of romance, adventure, and daring set in the court of the wealthy Abbasid Caliph, Harun Al-Rashid
-You can still read the stories today, they are famous and fun! The movie "Aladdin" is loosely based off one of the most famous stories

25. Islamic Agriculture --Sugarcane, Rice, and Cotton
-Travel through Dar al-Islam helped spread new ideas for farming
-the use of irrigation, fertilization, and crop rotation spread, and people even started to make books on how to be productive farmers
-all of this led to massive increases in food production, which in turn led to urbanization, the growth of cities like Baghdad (in modern day Iraq) and Cairo (in Egypt)
-As Muslim travelers travelled through Dar al-Islam, there was a lot of DIFFUSION (passing goods and ideas along)
-These were the three most important crops that spread through Dar al-Islam during Era 1, 1200 - 1450 CE.
-These crops led to higher population and nutrition, as well as providing valuable trade goods to go into the four major trade zones: the Trans-Saharan Caravan routes, trade in the Mediterranean Sea, Indian Ocean Basin , and Silk Roads
-One of these crops led to a huge increase in textiles, which became a really important industry in Dar al-Islam
-These goods originated in Asia; they spread West from India into the Islamic Caliphates

26. Effects of Agricultural Diffusion in Dar al-Islam
-As Muslim travelers travelled through Dar al-Islam, there was a lot of DIFFUSION (passing goods and ideas along)
-Crops moved west from Asia and India into the Middle East/North Africa. They had several key effects:
-Population increase (from Rice, spinach, etc)
-Increased cities as population grew. Baghdad and Cairo, in Egypt, are two of the most important cities whose populations grew enormously. This is called URBANIZATION (cities growing)
-They provided valuable trade goods to go into the four major trade zones: the Trans-Saharan Caravan routes, trade in the Mediterranean Sea, Indian Ocean Basin , and Silk Roads
-Cotton led to a huge increase in textiles, which became a really important industry in Dar al-Islam
27.Women in the Qur'an
-initially, the Qur'an helped this group of people and provided women with specific rights and honors
-Female infanticide (killing baby girls) was illegal and women were upheld as honored individuals
-Muhammad himself known for his kindness and generosity towards wives
-However, women also strictly controlled and guarded by male guardians (fathers, brothers, husbands); some intense forms of patriarchy [male domination]
-As time progressed, the patriarchal controls on women increased as Qadis (judges) and the people who interpreted Sharia law used sharia law to control the rights of women and give them less and less freedoms
![<p>-initially, the Qur'an helped this group of people and provided women with specific rights and honors</p><p>-Female infanticide (killing baby girls) was illegal and women were upheld as honored individuals</p><p>-Muhammad himself known for his kindness and generosity towards wives</p><p>-However, women also strictly controlled and guarded by male guardians (fathers, brothers, husbands); some intense forms of patriarchy [male domination]</p><p>-As time progressed, the patriarchal controls on women increased as Qadis (judges) and the people who interpreted Sharia law used sharia law to control the rights of women and give them less and less freedoms</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b5920877-b9af-489a-b15e-ba70ef8211fd.jpg)
28. Veiling of Women
-Some Islamic societies became strongly patriarchal [male domination]; fathers, brothers, and husbands guarded and controlled young women
-Even before Islam, there had been a tradition of upper class women in Persia and Mesopotamia veiling themselves to hide some of their features from lower class men
-as Islam spread into Persia and Mesopotamia, upper class women began adopting this old Mesopotamian tradition of wearing veils to hide their features from men
-increasingly became identified with Islamic dress and control over women; over time, this helped increase patriarchal male control over women
![<p>-Some Islamic societies became strongly patriarchal [male domination]; fathers, brothers, and husbands guarded and controlled young women</p><p>-Even before Islam, there had been a tradition of upper class women in Persia and Mesopotamia veiling themselves to hide some of their features from lower class men</p><p>-as Islam spread into Persia and Mesopotamia, upper class women began adopting this old Mesopotamian tradition of wearing veils to hide their features from men</p><p>-increasingly became identified with Islamic dress and control over women; over time, this helped increase patriarchal male control over women</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f1d91fb9-1592-44a7-a210-055808a88923.jpg)