Radiographic Selection Criteria
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Oral Radiography
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
what is radiographic selection criteria?
was developed to assist a dentit’s judgment in making informed decisions about the need for diagnostic imaging, consideration of the patient’s medical and dental histories and assessment of the patient’s signs, symptoms and susceptibility to environmental factors that may impact oral health.
What is child with primary dentition or mixed dentition?
a child with primary dentition is when they have all baby teeth, a child with mixed dentition means they have a mix of baby teeth and adult teeth
whats an adolescent with permanent dentition?
a teenager your young adult with most or all of their permanent teeth
whats an adult that dentate or partially dentate?
an adult that has all of their natural teeth, partially is an adult that has most of their natural teeth
whats an edentulous adult?
an adult that’s missing all of their natural teeth
what is the warranty for radiographic imaging for a NEW PATIENT child with primary dentition?
if there is no presence of disease and proximal contacts are open radiographic imaging may not be necessary
once the proximal contacts are closed, radiographic bitewing imaging for caries assessment is warranted. A selected periapical or anterior occlusal radiographic examination may be indicated to evaluate tooth development, dentoalveolar trauma, or suspected pathoses. Periapical and bitewing radiographic imaging may be necessary to assess pulpal pathosis in primary molars.
What is pulpal pathosis?
a diseased or damaged state of the dental pulp, the nerve-rich inner part of a tooth, typically caused by inflammation
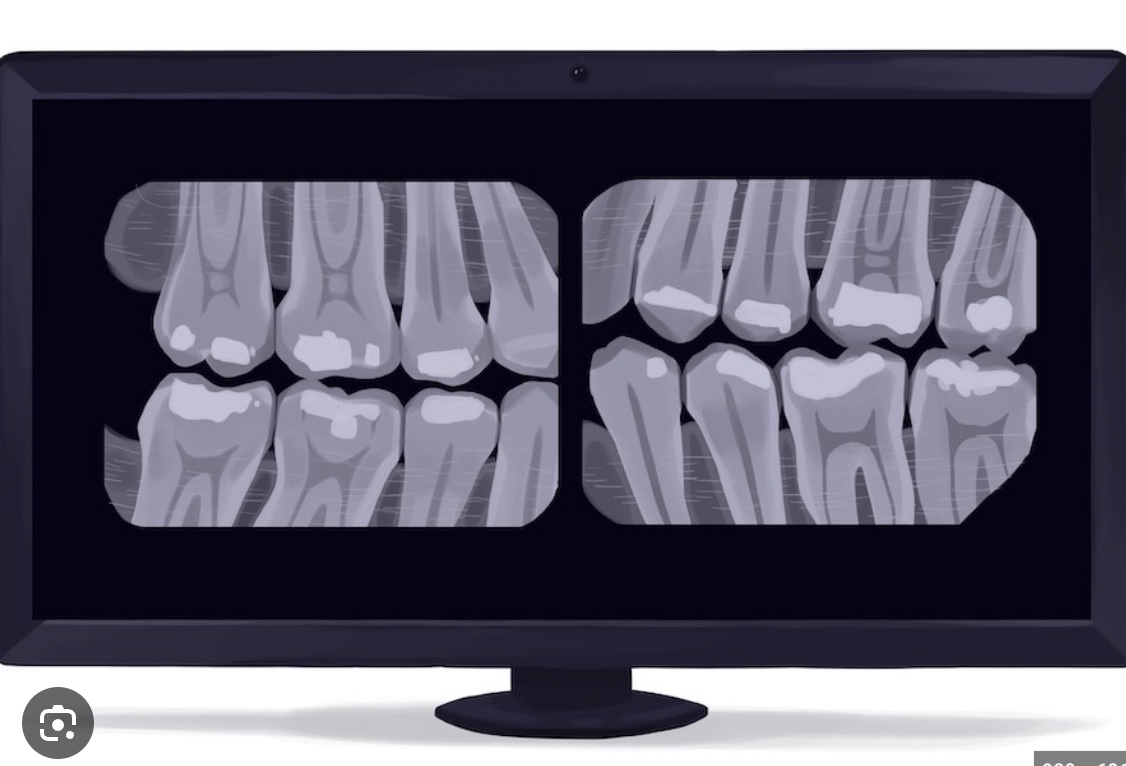
what are bitewing xrays?
show the crowns of the back teeth and bone levels to detect decay between teeth, these xrays are intraoral
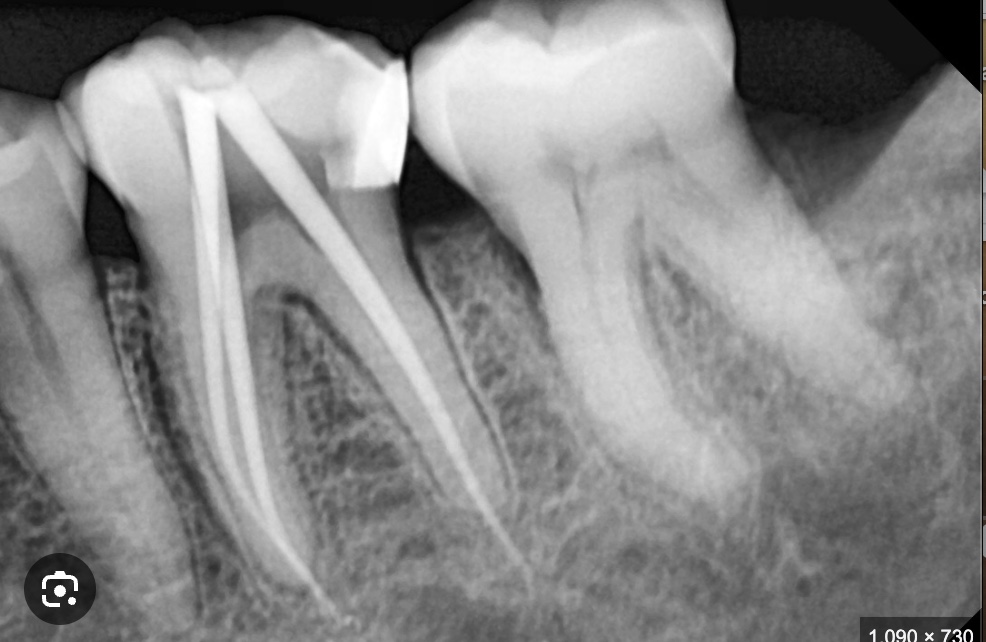
what is periapical xrays
show the entire tooth from crown to root tip and the bone around it, allowing dentists to diagnose issues like abscesses or bone loss at the root's end. these selective images and are used to hyperfocus on a few teeth these xrays are intraoral
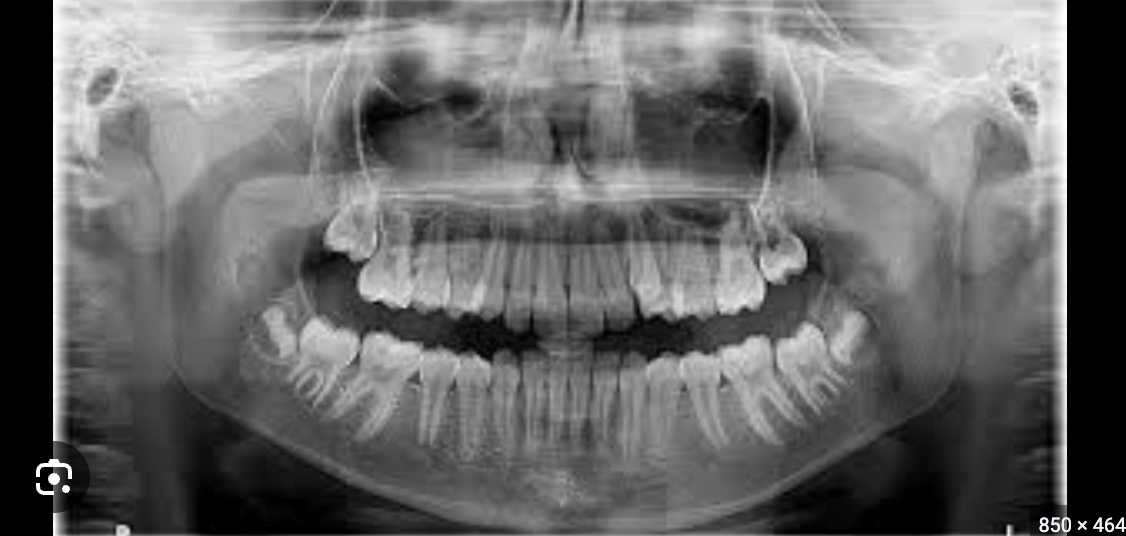
what are panoramic xrays aka orthopantomogram?
a type of dental X-ray that provides a wide, panoramic view of the entire upper and lower jaw, provide a wide-angle, top-down or bottom-up view of a dental arch, showing the full layout of teeth in either the upper or lower jaw. They are used to detect issues like extra teeth, impacted teeth, cysts, tumors, or jaw fractures, and to monitor the development and placement of teeth, especially in children. these xrays are extraoral
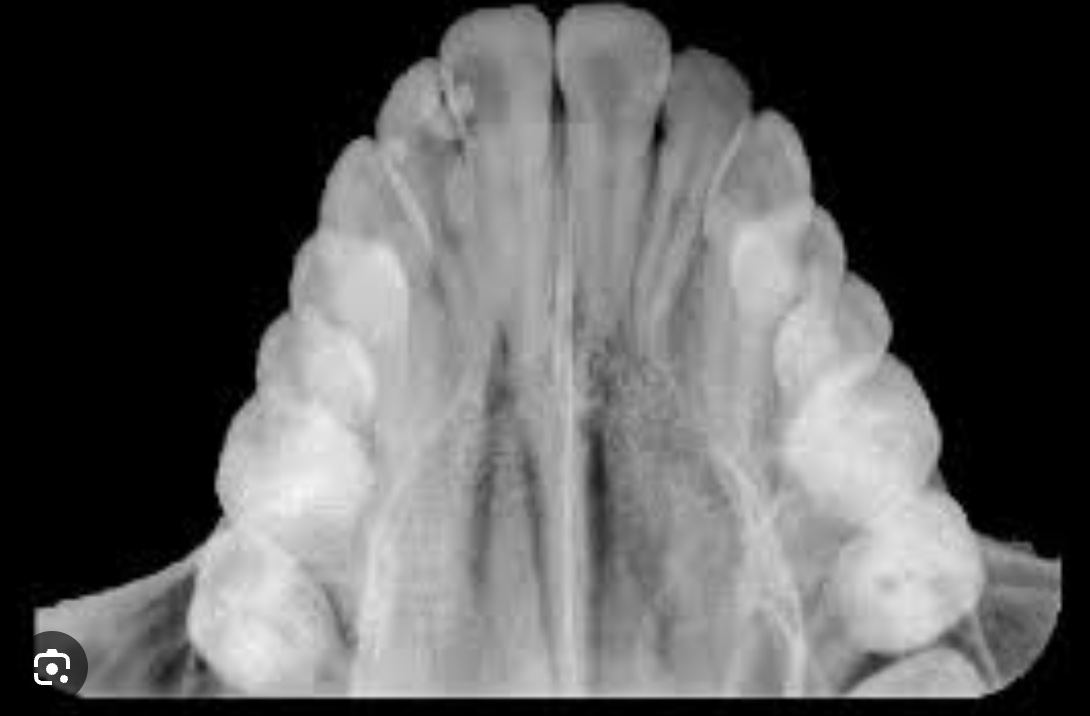
what are occlusal xrays?
provide a wide-angle, top-down or bottom-up view of a dental arch, showing the full layout of teeth in either the upper or lower jaw. They are used to detect issues like extra teeth, impacted teeth, cysts, tumors, or jaw fractures, and to monitor the development and placement of teeth, especially in children.
what is the warranty for radiographic imaging for a NEW PATIENT child with mixed/transitional dentition?
at this stage the concern for caries come in with closing proximal contacts as well as the likelihood of caries varies for children of different incomes, races, ethnicities at this age group and because of this bitewings are indicated. although atypical if clinical proof of periodontal disease is present selected periapicals and bitewings indicated to check the extent or periodontitis and alveolar bone involvement, full mouth survey if indicated
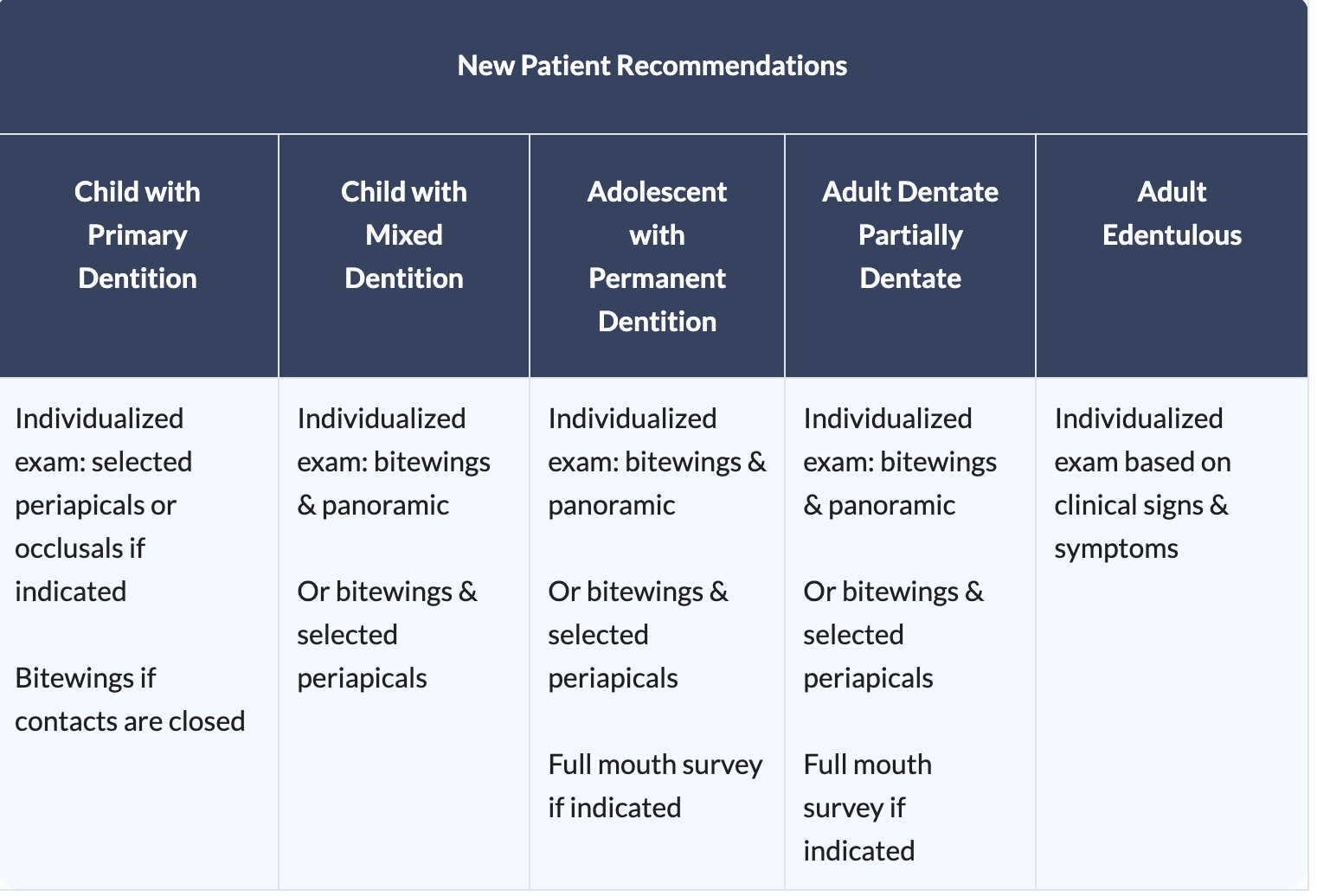
what is the warranty for radiographic imaging for a NEW PATIENT adolescent with permanent before the eruption of 3rd molars dentition?
variations in diet and dental hygiene habits are common at this age, these factors can also impact periodontal health. so periapicals and bitewings may be warranted. if there is evidence of generalized oral disease a full mouth survey is preferred. panoramic imaging is also beneficial for the monitoring of tooth development especially of the third molars. occlusal and periapical imaging can determine the position of a supernumerary or unerupted tooth, full mouth survey if indicated
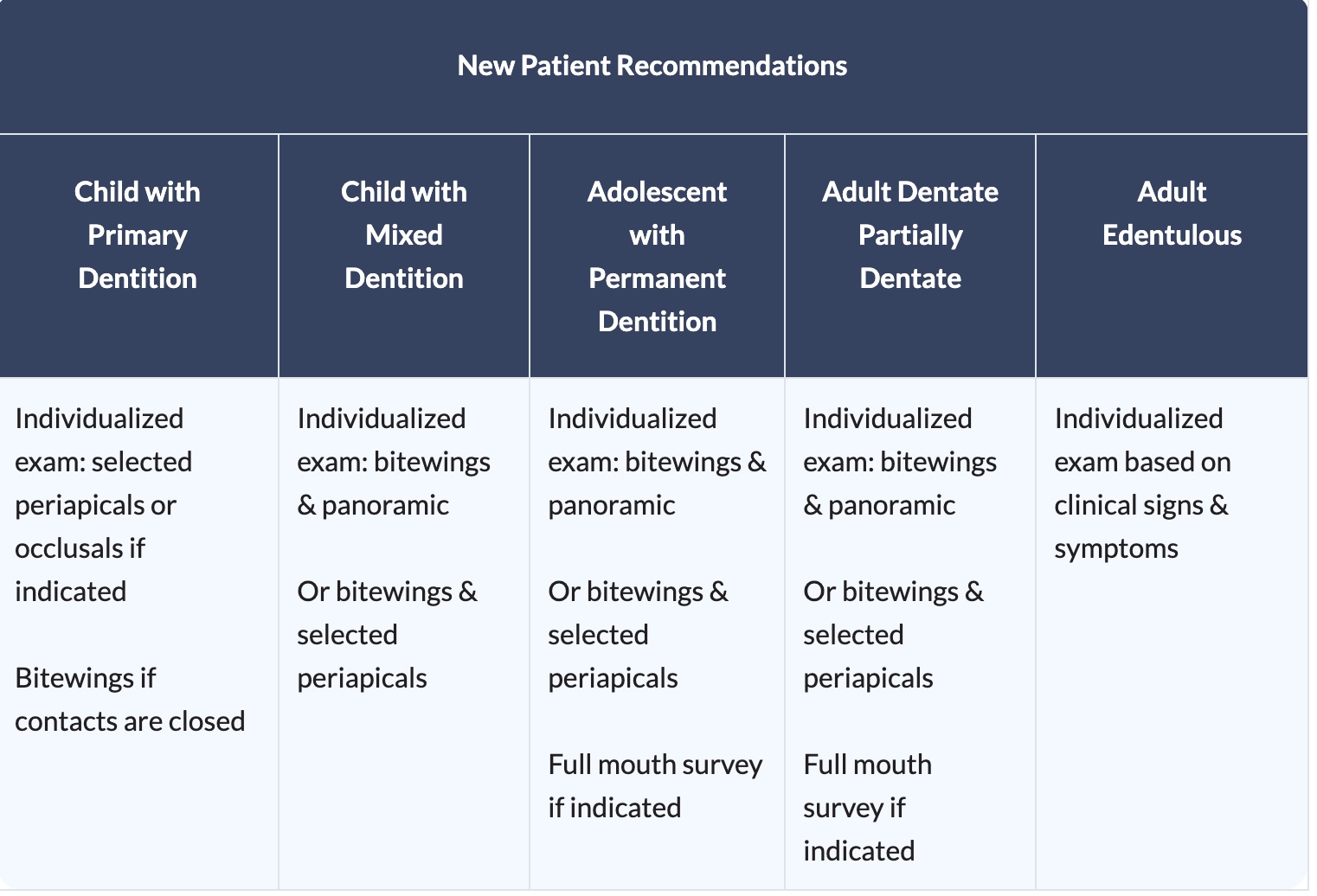
what is the warranty for radiographic imaging for an adult dentate patient?
caries risks and risk factors change over time so posterior bitewings are warranted. periodontitis and caries increase with age so if patient has previous experience with periodontitis then intraoral imaging may be necessary to monitor and assess. panoramic imaging with posterior bitewings may be useful if periapical pathosis, unerupted teeth are suspected, partially erupted teeth are visible, carious lesions are present, or clinical facial swelling. if patient presents with clinical evidence of generalized oral disease or a history of extensive dental treatment, a full mouth survey is preferred
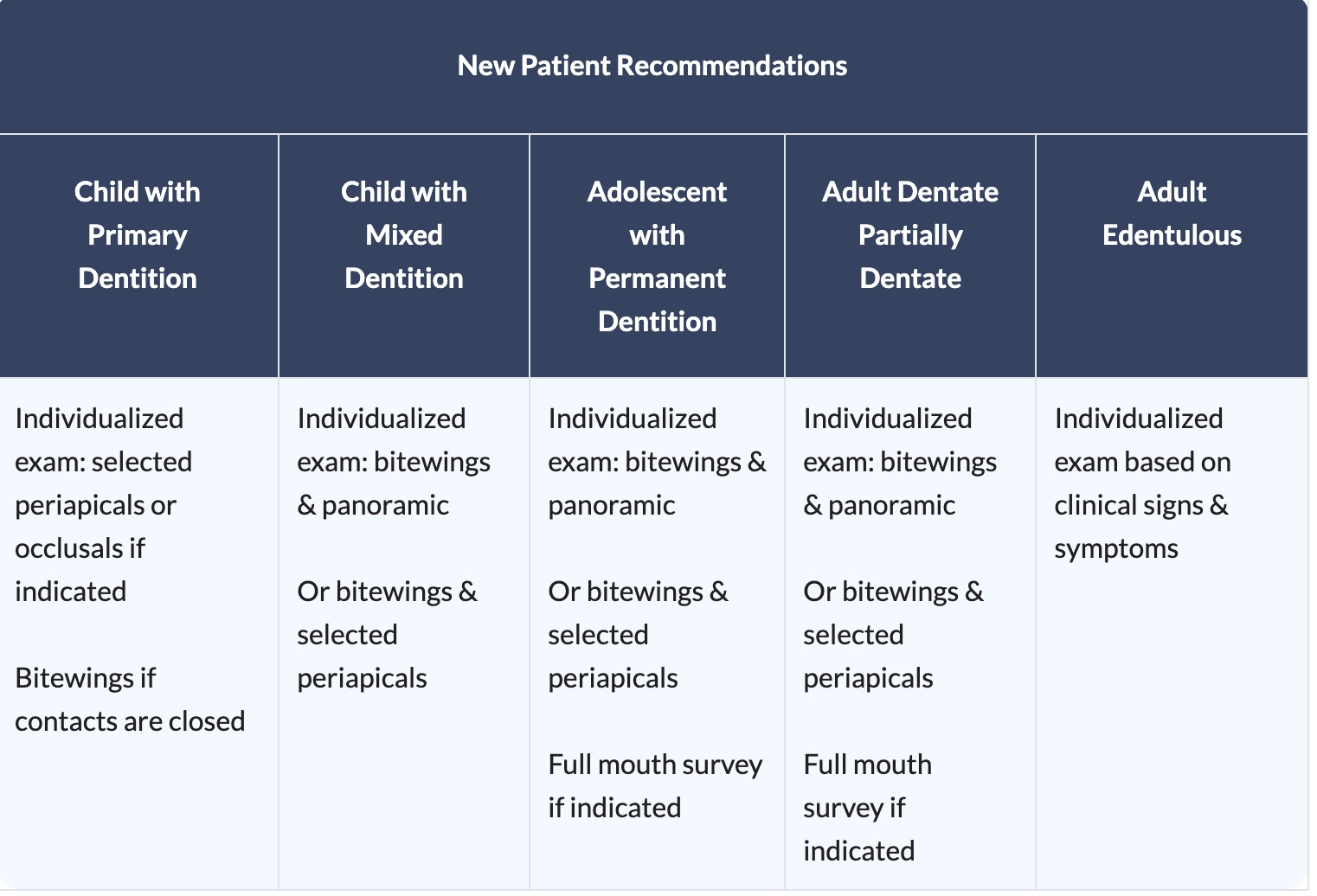
what is the warranty for radiographic imaging for an adult edentulous patient?
unless the patient is there for oral prosthetic treatment, several studies which focused on treatment outcomes indicated that there is little evidence to warrant screening radiographic imaging, if they are looking for oral prosthetic treatment then radiogrpahic imaging is appropriate. radiographic imaging may consist of these possible surveys: full mouth periapical images or a combination of panoramic, occlusal or other extraoral imaging.
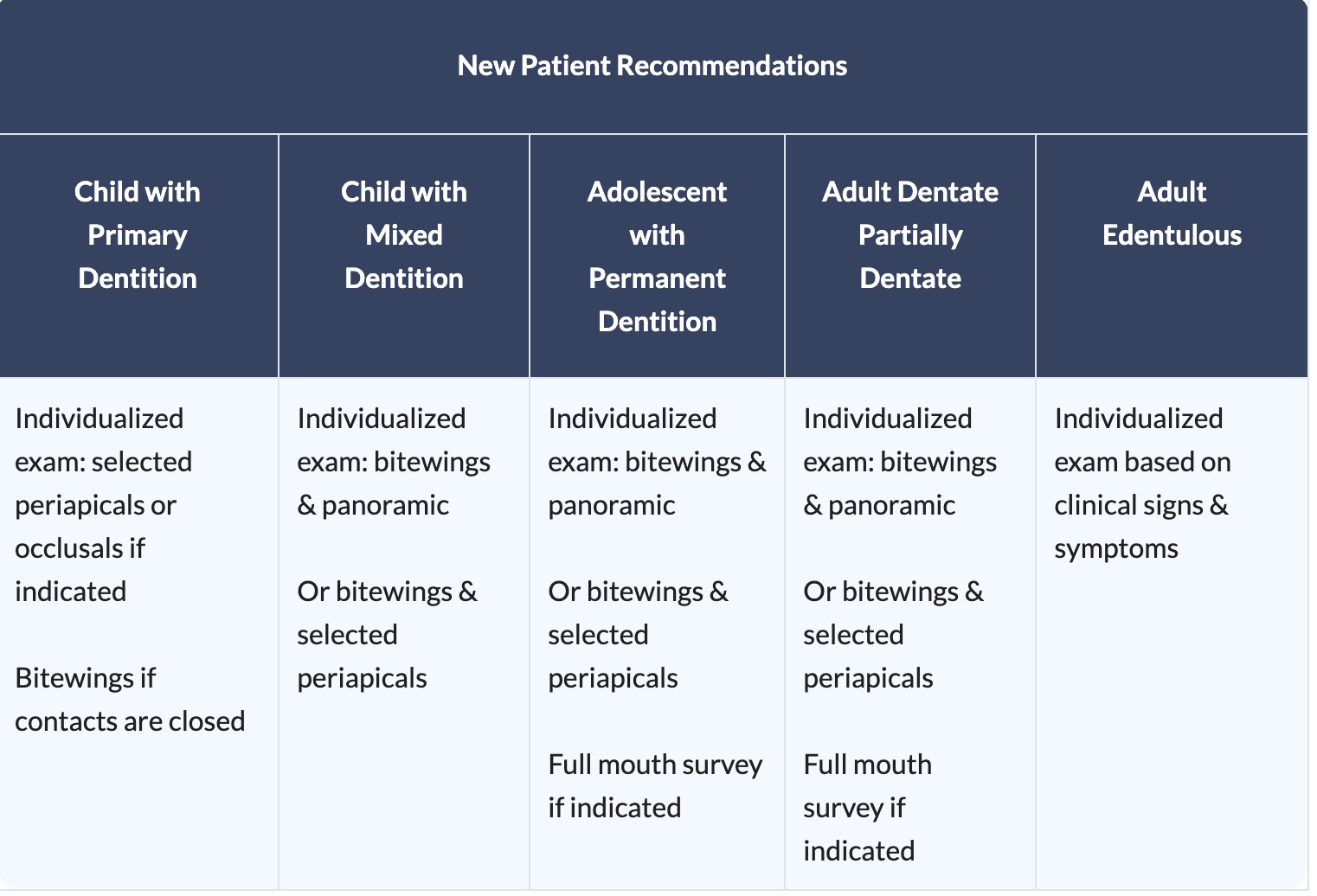
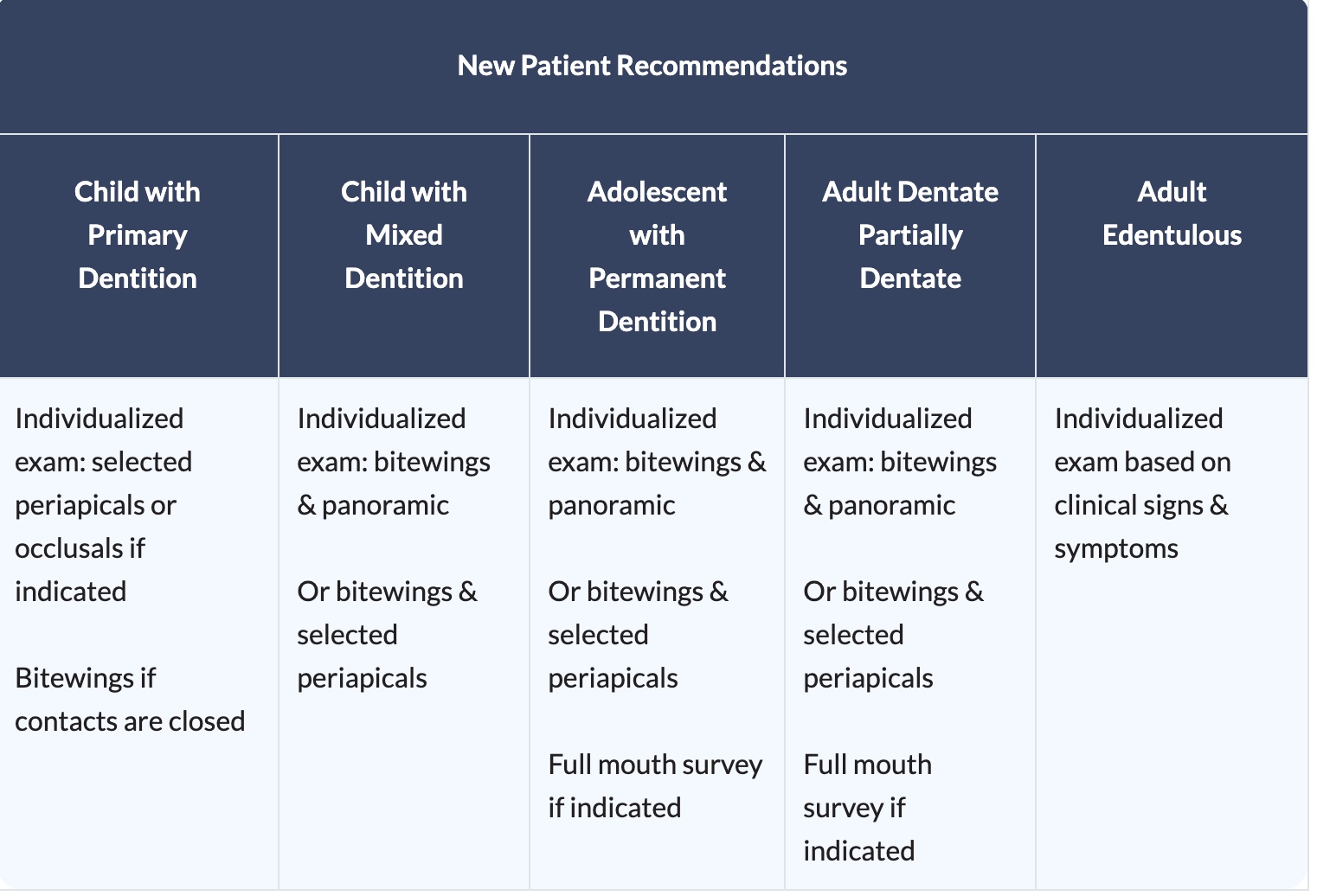
What are the radiographic imaging recommendations recall patients with CARIES AND/OR RISK for kids with primary dentition to ednetulous adults?
kids primary dentition, kids mixed dentition, and adolescents with permanant dentition all require Bitewings at 6 to12 month intervals if contacts are closed
adult dentates require Bitewings at 6 to18 month intervals
edentulous adults are not applicable without presence of disease
What are the radiographic imaging recommendations recall patients WITHOUT CARIES AND/OR RISK for kids with primary dentition to ednetulous adults?
kids primary dentition and kids mixed dentition Bitewings at 12 to 24 month intervals if contacts are closed
adolescents with permanent dentition Bitewings at 18 to 36 month intervals
adult dentate patients Bitewings at 24 to 36 month intervals
edentulous adults are not applicable without presence of disease
What are the radiographic imaging recommendations recall patients with periodontitis and/or risk for kids with primary dentition to ednetulous adults?
child with primary, child with mixed, adolescent with permanent, adult dentate all require clinical judgment for need & type of images, may include selected periapicals and/or bitewings as indicated. this is because every person and their progression of the disease is different
edentulous adults are not applicable
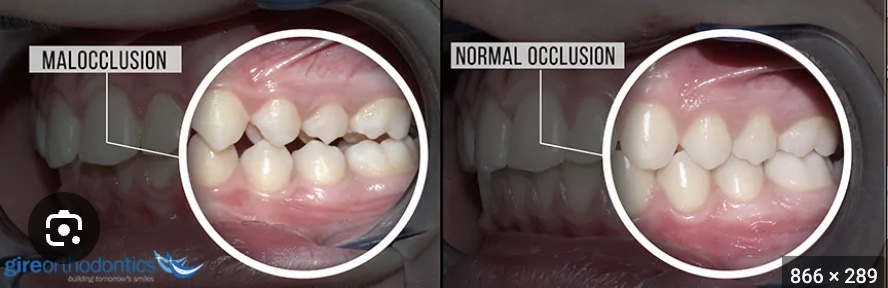
define malocclusion
a dental condition where the teeth are misaligned or do not meet properly
What are the radiographic imaging recommendations new/recall patients to Monitor Growth and Development or to Assess Dental or Skeletal Relationships for kids with primary dentition to ednetulous adults?
kids with primary and mixed dentition are required clinical judgment for need & type of images for assessment type
adolescent with permanent dentition are required clinical judgment for need & type of images for assessment type as well as panoramic or periapicals for 3rd molars
for adult dentates and edentulous adults they are usually not indicated
what is cephalometric imaging?
a specialized side-view X-ray of the skull used in orthodontics and oral surgery to provide detailed views of the teeth, jawbones, and soft tissues. It allows for precise measurements of the jaw's position and relationship to the skull, helping orthodontists plan treatments for "bad bites" (malocclusions), assess facial growth, and evaluate conditions like sleep apnea. it is extraoral imaging
what is dentofacial growth?
refers to the biological process of jaw and facial bone development that occurs primarily in children and adolescents, influencing the growth of the teeth, facial structure, and overall alignment of the jaws.
how can third molar evaluation be accomplished radiographically and at what stage?
at adolescent with permanent dentition and with periapical or panoramic imaging
what are other circumstances that would require radiographic imaging to be prescribed and how would that be judged for each age group?
examples include, but are not limited to, implantology, restorative and/or endodontic treatment, dental or craniofacial anomalies/pathoses, treated periodontal disease and caries remineralization. from kids with primaries to edentulous adults clinical judgment for need & type of images for assessment or monitoring
what is marginal gingivitis?
is an inflammation of the gums (gingiva) that primarily affects the area where the gums meet the teeth
When diagnosing a patient what are the 4 questions to ask yourself?
What positive historical findings were reported? What are the clinical signs & symptoms presented in this case? What are the risk factors for caries? Given the guidelines for a new child patient with a transitional dentition, what radiographic examination is recommended?
what are the methods for limiting patient radiation exposure?
Limit the number of acquired images to the minimum necessary, Use the fastest receptor compatible with the diagnostic task, Use receptor holders designed to align the collimated beam for intraoral imaging, Collimate the beam to the size of the receptor when possible, Use protective aprons and thyroid collars as appropriate, Use proper receptor exposure and processing (when applicable) techniques