26.4 carboxylic acid derivatives
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
naming esters
remove the -oic acid suffix from the parent carboxylic acid and replace it with -oate
the alkyl chain attached to the oxygen atom of the COO group is then added as the first word in the name
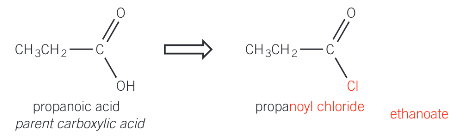
naming acyl chlorides
remove the -oic acid suffix from the parent carboxylic acid and replace with -oyl chloride
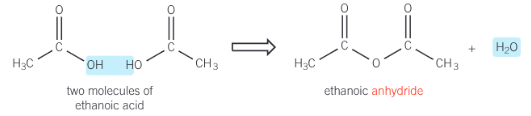
what is an acid anhydrides
it is formed by the removal of water from 2 carboxylic acid molecules as shown in the formation of ethanoic anhydride
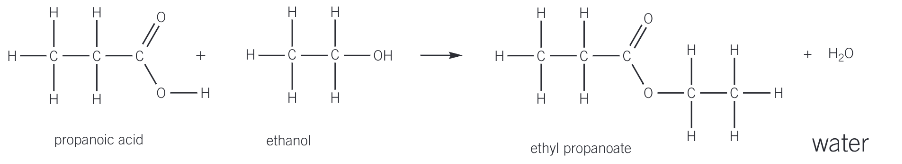
esterification
the reaction of an alcohol with a carboylic acid to form an ester
an alcohol is warmed with a small amount of concentrated sulphuric acid, which acts as a catalyst
acid hydrolysis of esters
the ester is heated under reflux with dilute aqueous acid
the ester is broken down by water, with the acid acting as a catalyst
the products of acid hydrolysis are a carboxylic acid and an alcohol
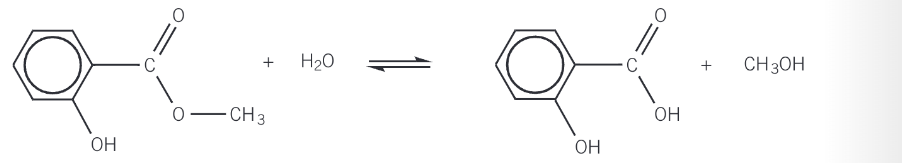
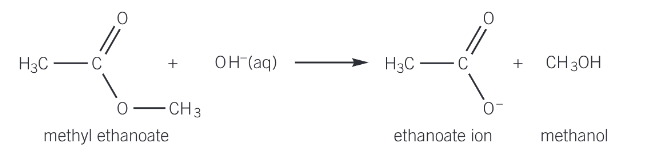
alkaline hydrolysis
is also known as sapification and is reversible
the ester is heated under reflux with aqueous hydroxide ions
preparation of acyl chlorides
can be prepared directly from their parent carboxylic acid by reaction with thionyl chloride, SOCl2
the other products of this reaction, SO2 and HCl are evolved as gases, leaving just the acyl chloride. The reaction should be carried out in a fume cupboard as the products are harmful
they are very reactive and can easily be converted into carboxylic acid derivatives, such as esters and amides with good yields
acyl chlorides react with nucleophiles by losing the chloride ion while retaining the C=O double bond
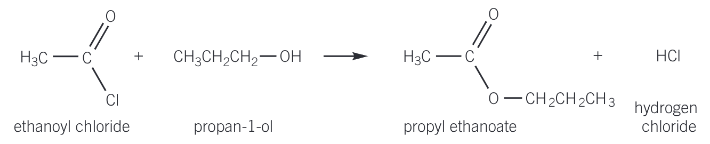
reaction of acyl chlorides to form esters
acyl chlorides react with alcohols to form esters
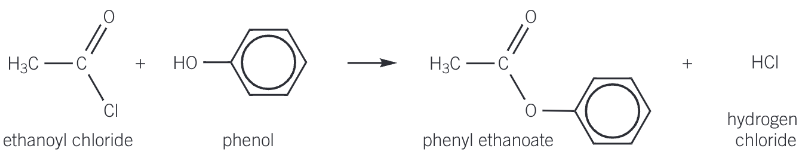
reaction of acyl chlorides with phenols to form esters
carboxylic acids are not reactive enough to form esters with phenols
acyl chlorides and acid anhydrides are both more reactive than carboxylic acids and react with phenols to produce phenyl esters
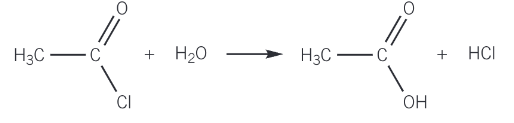
reaction of acyl chlorides with water
a violent reaction takes place with the evolution of dense steamy hydrgoen chloride fumes
a carboxylic acid is formed
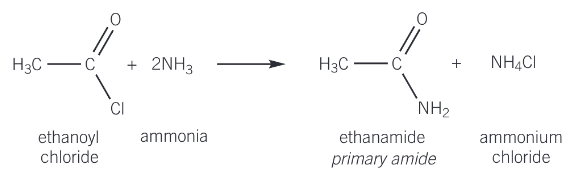
reaction of acyl chlorides with ammonia
ammonia and amines can act as nucleophiles by donating the lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom to an electron-deficient species
their reaction forms a primary amide (the nitrogen atom is attached to one carbon atom
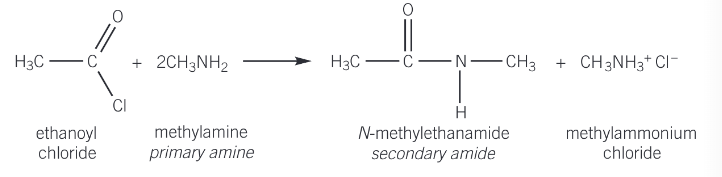
reaction of acyl chlorides with primary amines
a primary amine reacts with an acyl chloride in the same way as ammonia to form a secondary amide (the nitrogen atom is attached to two carbon atoms)