Session 4 : The effectiveness of international law in domestic legal systems: focus on core UN Human Rights Treaties
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what are ‘core’ UN human rights treaties ?
Viljoen and Murray 2022
UN human rights treaties that provide for self- standing, separate supervisory bodies composed of independent experts
Core UN human rights treaty bodies
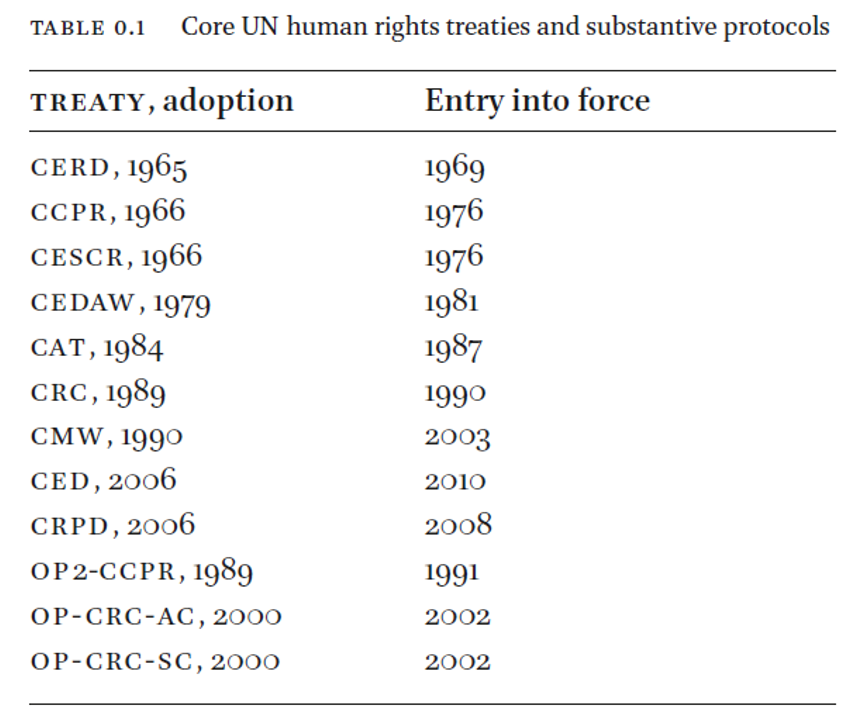
3 new Treaties

Devp of the system
states have signed the treaties but not all of them have ratified the protocols giving jurisdiction to treaty bodies
Defining and Measuring ‘Impact’
Impact = overall domestic effect, influence or repercussions of the 9 core UN HR treaties + findings and recommendations when they find a violation
Defining and Measuring ‘Impact’
direct impact
observable change in the conduct of those the treaty directly target
Defining and Measuring ‘Impact’
Indirect impact
affects a much broader range of stakeholders
Defining and Measuring ‘Impact’
material impact
entails tangible effects that in some way are attributable to the UN treaty system
Ex : adoption of laws
Defining and Measuring ‘Impact’
symbolic impact
Effet on ideas, understanding and narrative framing
Enhanced compliance/impact thanks to treaty bodies?

Legal effects and State compliance through implementation measures

Legal effects: the debate over the direct effect of international law
Jurisdiction of the Courts of Danzig = states can conclude a treaty that created individual rights that should be enforceable in domestic courts
Van Gend en Loos [1963] = direct effect of EU law – required by EU law itself
But no direct effect of EFTA or EEA treaties ! CJEU: Draft agreement between the European Community, on the one hand, and the countries of the European Free Trade Association, on the other, relating to the creation of the European Economic Area, Opinion 1/91 [1991] ECR 1–6079
Direct effect’ of international law outside the EU: some instances across the globe (international law used as direct basis for a decision in an individual case) but in very heterogeneous conceptions and practices
Main forms of direct effect in international law

What about primacy?

Effects and Impacts of core UN human rights treaties in Spain

Effects and Impacts of core UN human rights treaties in Spain
Angela Gonzalez Careno 2018
1 case changed Spain’s views : after a decision from the CEDAW, an individual came in front of the Court of Spain who refused to give them reparation because the CEDAW recommendations were not binding : Spain’s SC overruled the decision and affirmed that Spain was bound by the CEDAW Committee and had to award reparation
Effects and Impacts of core UN human rights treaties in Spain
Angela Gonzalez Careno 2018 suite
Backtrack 2020 : reverses the position, this time concerning the views of the UN Human Rights Committee in a case concerning the right to an appeal in criminal matters (Art. 14(5) of the ICCPR, Case 1381/2005, views of 2007); according to this decision, only judgments of the ECtHR are binding
Effects and Impacts of core UN human rights treaties in Spain
Ruben Calleja
Back to the 2018 position : application of the Convention on the rights of the people with disabilities and awarded compensation
Why ?
Effects and Impacts of core human rights treaties in Finland
fragmented structures + ressources channeled
no coordination
compliance deficit
more focused on the ECHR
better compliance with the CRC and the CRPD w/ national structures monitaring
CEDAW stands out as the UN treaty having received the least serious attention and the weakest institutional back- up at the national level in Finland.
importance of civil society : submission of a new monitoring work
implementation characterized with a certain selectivity
incoherence between external and internal human rights policies
marginal role of education regarding aspects of international law and human rights at the university level, including in law schools
The UN Convention on the Rights of the Child

Status of the UN CRC

Key features of the CRC

Key features of the CRC : 3 pillars
Provision
Participation
Protection
Key features of the CRC : 4 general ppl

Non discrimination (Article 2)
Open list
Broad provision
Best Interests (Article 3.1)
“Shall be a primary consideration”
What does it mean ? : interpreted by the UN Committee
A substantive right - requiring consideration of the child’s interests over and above other factors whenever a decision is made concerning the child, even if there are other compelling interests at stake.
An interpretative legal principle - interpretation shall be afforded which most effectively serves the child’s best interests should be chosen; and
A procedural right - any decision which affects a child must be arrived at by a process which includes an evaluation of the possible impact on the child.
Right to be heard (Article 12)
Right to express freely their own views : they should be part of the proceedings (directly, by representatives, by authorities)

Hearing of the Child - compare
Before the right to express their view they have a right to be informed with the ECECR
How to enforce the right of the child to be heard ?

General comment on art.12
starting point of an intense exchange
ongoing process
Child protection: Article 19 CRC
Requires protection even from the parents : obligation on the State
Effects and Impacts of the CRC: Direct applicability?
French courts position
Belgian courts position
No direct effet of art. 3.1 at first but recognized in 2005
No direct effect at all
The Committee on the Rights of the Child

Example of an individual communication procedure: 136/2021 Camila v Peru
13 yo victim of rape + no access to legal or therapeutic abortion
prosecuted for self abortion
decision : lack of info, lack of access to abortion, no right to life or devp, no care for mental health
revictimization : violation off the right to privacy, discrimination,
Conclusions

