Intro to Med Medical Records (All of it with a few extra questions and fixes)
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Primary diagnosis is?
What is going on today; with ruled out possibilities
Secondary diagnosis is?
Chronic underlying conditions already diagnosed

Components of Plan
Diagnostic studies, pharmacological treatment, non-pharmacological treatment, patient education, and follow up instructions
SOAP stands for?
Subjective, Objective, assessment, and plan
Introductory statement involves?
Patient name, age, ethnicity, gender, pertinent past medical history, and chief complaint with duration
LNMP means?
Last normal menstrual period
NKDA means?
No known drug allergies
WD means?
Well developed
WN means?
Well nourished
WF means?
White female
WM means
White male
NAD means
No apparent distress
PMHx means?
Past medical history
What’s written when someone has a medication in a SOAP note?
Drug name, strength, dose, route, frequency, and indication
What’s in general statement?
Age, habitus, ethnicity, gender, and distress level
All parts of an objective section of SOAP
Vital signs, general statement, problem specific physical exam, and diagnostic studies
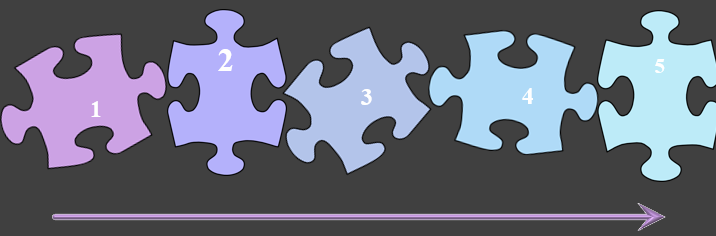
Pieces of diagnostic process
Symptoms, signs, diagnostic tests, diagnosis, and treatment and management

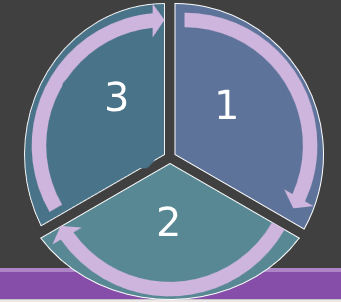
Steps of the diagnostic process
Gather information, analyze the information, and make judgements and decisions
How do you set the stage of an exam
Establish a rapport, properly introduce yourself, and provide the purpose of visit
Steps of subjective exam
Chief complaint, HPI (7 factors), past medical history (allergies and medications), personal and social history, and family history
Chief complaint is?
Main reason for patient’s visit
HPI is?
History of present illness (7 factors)
Name all 7 factors
Setting, chronology, location, quality, quantity, aggravating/alleviating factors, and associated manifestations
The first factor is?
Setting
The second factor is?
Chronology
The third factor is?
Location
The fourth factor is?
Quality
The fifth factor is?
Quantity
The sixth factor is?
Aggravating/Alleviating factors
The seventh factor is?
Associated manifestations
Setting (In HPI) is?
Where the patient’s symptoms started and what they were doing at the time
Chronology (In HPI) is?
The story of the chief complaint and how it has changed and developed
Location (In HPI) is?
Where the patient’s symptoms are located
Quality (In HPI) is?
How the patient describes symptoms
Quantity (In HPI) is?
Numerical value of complaint
Aggravating/Alleviating factors (In HPI) is?
What makes symptoms better or worse
Associated manifestations (In HPI) is?
Other complaints and symptoms patient denies
Name the four physical examinations for normal visit
Inspection, palpation, percussion, and auscultation
In what order do the 4 physical examination go when it is an abdominal examination?
Inspection, auscultation, percussion, and palpation
Objective things are?
What you see, hear, feel, and smell
Subjective things are?
What the patient says
What are the vital signs? (no abbreviations)
Pulse, respiratory rate, temperature, blood pressure, height, weight, body mass index, and pulse oximeter
What are the vital sings? (with abbreviations)
P, R, T, BP, Ht, Wt, BMI, and POx

Why do we order diagnostic testing?
To support, confirm, and rule out
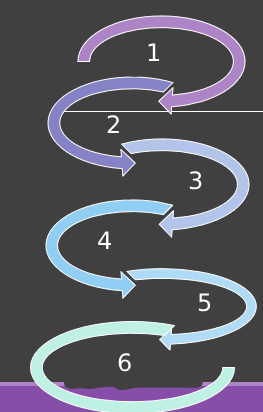
What are the steps of analysis of information
Patient’s history, PE and testing, interpretation, possible causes, further questions, and diagnosis

Assessment is?
What is wrong with the patient
Plan is?
What we are going to do for the patient
Meaning of Rx
Prescription
Meaning of OTC
Over the counter
Top line of a prescription
Drug name and strength
Middle line of a prescription
Sig: Dose, route, frequency, and duration
Bottom line of a prescription
Dispensing quantity
What does 1 kg equal to in pounds
2.2 lbs
What does “AM” mean on a prescription?
Morning
What does “cap” mean on a prescription?
Capsule
What does “gm” mean on a prescription?
Gram
What does “gtts” mean on a prescription?
Drops
What does “IM” mean on a prescription?
Intramuscularly
What does “IV” mean on a prescription?
Intravenously
What does “mcg” mean on a prescription?
Microgram
What does “PM” mean on a prescription?
Afternoon
What does “prn” mean on a prescription?
As needed
What does “QID” mean on a prescription?
Four times a day
What does “Sig:” mean on a prescription?
Label
What does “subcut” mean on a prescription?
Subcutaneously
What does “TBSP” mean on a prescription?
Tablespoon
What does “tsp” mean on a prescription?
Teaspoon
What does “O.S.” mean on a prescription?
Oral suspension
What should be inspected on a medication?
Medical indication, contraindication, precautions, interaction, and adverse reactions
Medical indication for a medicine is?
Reasons to use
Contraindication for a medicine is?
Reasons to avoid
Precautions for a medicine is?
Reasons to avoid or take caution using
Interaction for a medicine is?
How the medication interacts with other drugs
Adverse reactions on a medication is?
Side effects
Tylenol’s generic name
Acetaminophen
Motrin’s generic name
Ibuprofen
Glucophage’s generic name
Metformin
Coumadin’s generic name
Warfarin
Prilosec’s generic name
Omeprazole
Synthroid’s generic name
Levothyroxine
Acetaminophen’s brand name
Tylenol
Ibuprofen’s brand name
Motrin
Metformin’s brand name
Glucophage
Warfarin’s brand name
Coumadin
Omeprazole’s brand name
Prilosec
Levothyroxine’s brand name
Synthroid
Schedule I drugs are?
Most abused
Schedule V drugs are?
Least abused
Name all major forms of administration routes
Oral, inhalation, topical, transdermal, suppository, and parenteral
Name all oral routes
Tablet, capsule, solution, and suspension
Name all inhalation routes
Gas, liquid, and powder
Name all topical routes (all the ones that are labeled topical in slides)
Lotion, gel, cream, ointment, transdermal, and suppository
Name all parenteral routes
Subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous

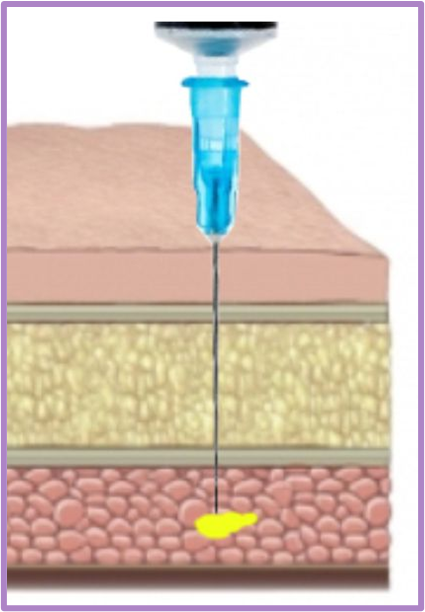
What form of administration is this
Subcutaneous parenteral
What form of administration is this?
Intramuscular parenteral
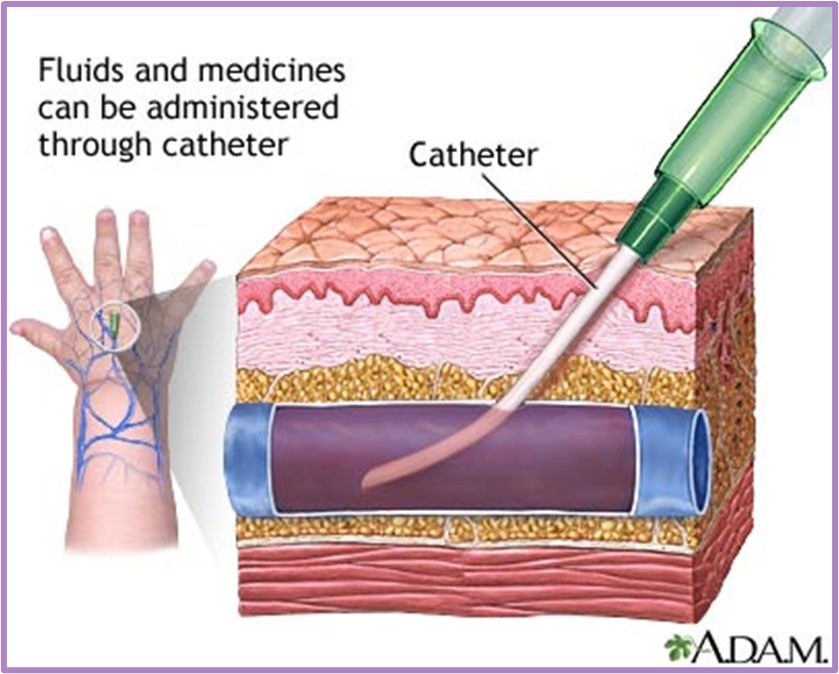
What form of administration is this?
Intravenous parenteral

What form of administration is this?
Oral tablet
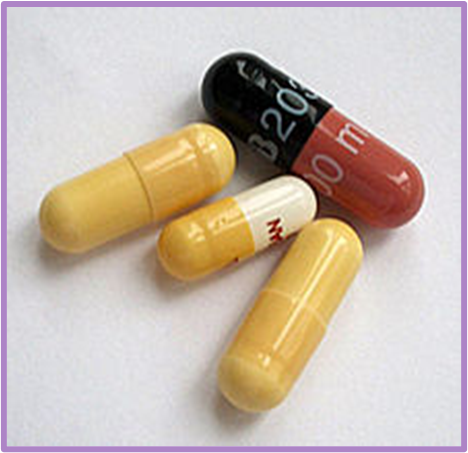
What form of administration is this?
Oral capsule
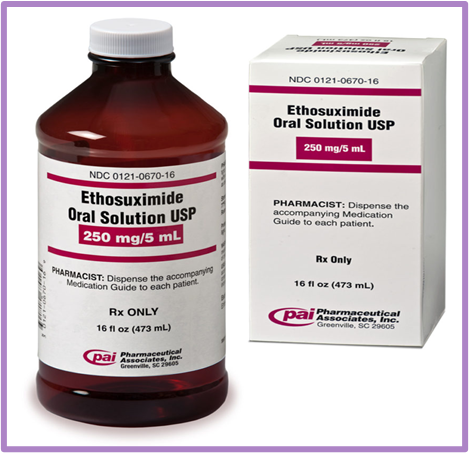
What form of administration is this?
Oral solution

What form of administration is this?
Oral suspension