Security+ Review
1/700
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
701 Terms
Security Controls Categories
Technical/Logical, Managerial/Administrative, Operational, Physical
Technical Security Controls (AKA = ?)
AKA = Logical Security Controls
Hardware and Software mechanisms executed by COMPUTER SYSTEMS used to protect systems and data
Ex: Firewalls, IDS's, Encryption
Managerial Security Controls (AKA = ?)
AKA = Administative Controls
Administrative controls focused on REDUCING RISK OF SECURITY INCIDENTS and related to the OVERSIGHT OF A SYSTEM. Documented in WRITTEN POLICIES
Ex: Organizational security policies, Standard Operating Procedures, Risk Assessments, Security Awareness Training
Operational Security Controls
Focused on the DAY-TO-DAY PROCEDURES of an organization. Controls for the HUMAN ELEMENT. Used to ensure EQUIPMENT CONTINUES TO WORK as specified. Primarily IMPLEMENTED AND EXECUTED BY PEOPLE
Ex: Awareness Programs, Configuration Management, System Backups, Patch Management
Physical Security Controls
Security controls designed to DETER, DETECT, AND PREVENT UNAUTHORIZED ACCESS. Measures taken to protect the physical hardware and facilities
Ex: Lighting, locks, fences, badge readers, security guards
Security Control Functions
Preventative, Deterrent, Detective, Corrective, Compensating, Directive
Preventative Security Control Function
Blocking access to a resource
Ex: Encryption, Firewalls, Anti-virus Software
Deterrent Security Control Function
Discourages an intrusion attempt but does not directly block access
Ex: Warning Signs, Lighting, Fencing/Bollards
Detective Security Control Function
Identify and log intrusion attempts
Ex: Log Monitoring, Security Audits, CCTV, IDS, Vulnerability Scanning
Corrective Security Control Function
Apply new controls after an intrusion attempt has been detected
Ex: Recovering data from backups, applying software updates and patches, IRPs, DRPs
Compensating Security Control Function
Using temporary means to prevent exploitation of a weakness because existing controls are not sufficient
Ex: Backup Power Systems
NOT Compensating: MFA, App Sandboxing, Network Segmentation
Directive Security Control Function
Directing a subject towards security compliance through POLICIES AND PROCEDURES
Ex: IRP, AUP
NOT Directive: MFA, IDS, IPS
CIA Triad (AKA = ?)
Definition of Each?
AKA AIC Triad
Used to describe the BASIC PRINCIPLES OF INFORMATION SECURITY
Confidentiality: Ensuring information is accessible only to those authorized to access it. Ex: Encryption, Access Controls, Data Classification
Integrity: Ensuring information is accurate and complete and has not been altered in an unauthorized manner. Ex: Hashing, Digital Signatures, Certificates, Non-Repudiation
Availability: Ensuring information and systems are available to authorized users when they are needed. Ex: Redundancy, Backups, Load Balancing/Failover
Non-Repudiation
Ensures that someone cannot deny the validity of their actions/communications by providing proof of the origin and integrity of the data sent by the Sender. The Sender cannot deny sending the info and the Receiver cannot deny receiving it
Proof of Origin
Methods?
Ensures the authenticity of the Sender of a message. Methods include Digital Signatures, PKI, and Certificates
AAA Framework
Definition of Each?
Authentication, Authorization, Accounting
Authentication: Verifying the identity of a user/device/entity BEFORE granting access to a NETWORK/SYSTEM. Ex: Passwords, Biometrics, Tokens
Authorization: Determining what resources or services an AUTHENTICATED USER is allowed to access AND what actions they are permitted to perform. Ex: Access Control Models (DAC, MAC, RBAC, ABAC), Access Control Lists
Accounting: TRACKING AND LOGGING user activities, resource usage, and actions taken within a system
Gap Analysis
What are the Steps?
Assessment of the differences between where we are and where we want to be
Steps: Define Objectives, Assess Current State (people and processes), Identify Desired State, Analyze Gaps, Develop Action Plan
Zero Trust
A security framework that operates on the principle of "Never Trust, Always Verify". Assumes that threats can come from BOTH inside AND outside the network. EVERY access request should be verified, authenticated, and authorized regardless of origin
Planes of Operation
Part of the Zero Trust Framework
Splits the Network into functional planes:
Management Plane: Secures administrative access. Techniques include MFA, RBAC, and encryption of administrative traffic
Data Plane: Processes data frames, packet forwarding, and network data. Includes encryption, data integrity checks, firewall rules
Control Plane: Manages the ACTIONS of the Data Plane. Defines policies and rules, determines how packets should be forwarded, and includes route authentication and protocol hardening
Example: Physical Switch. Data Plane involves all of the interfaces used to move data from one part of the network to another. Control Plane involves the configuration of the device
Adaptive Identity
Adjusting access controls and authentication requirements based on the context and risk level associated with a user and access request. Uses Risk Indicators such as relationship to org, physical location, device health, connection type, IP address, etc
Threat Scope Reduction
Decreasing the number of possible entry points of a network
PDAC
Policy-Driven Access Control
Combines Adaptive Identity with a predefined set of rules. Policies define the rules and conditions under which access is granted/denied, and can be dynamic based on Risk Indicators
PEP
Policy Enforcement Point
The MAIN COMPONENT of the DATA PLANE. A point in the network that is responsible for ENFORCING ACCESS CONTROL POLICIES by acting as the gate keeper to a network based on the CONTROL PLANE POLICIES. Can consist of multiple components working together. Enforces decisions made by the PDP
PDP
Policy Decision Point
The MAIN COMPONENT of the CONTROL PLANE. Evaluates access requests against defined security policies and makes AUTHORIZATION DECISIONS, then provides those decisions to the PEP. Consists of 2 parts, the Policy Engine and Policy Administrator.
PE
Policy Engine
Part of the PDP. Decides EACH ACCESS DECISION based on policies and other information
PA
Policy Administrator
Part of the PDP. Tells the PEP the POLICY ENGINE'S DECISION. Also generates ACCESS TOKENS/CREDENTIALS
Honeypots
Types?
A security mechanism designed to ATTRACT AND TRAP ATTACKERS by mimicking a LEGITIMATE TARGET. 2 Types: Low Interaction (limited in functionality) and High Interaction (sims a full-fledged system)
Honeynets
A NETWORK OF HONEYPOTS designed to attract and analyze malicious activity. Emulates a REAL NETWORK ENVIRONMENT
Honeyfiles
Decoy files placed into a network or system that contains FAKE INFORMATION. Often used as BAIT FOR HONEYNETS
Honeytokens
Acts as BAIT for Attackers and is used to TRACK THE ATTACKER. Adds TRACEABLE DATA to a Honeynet. Can be embedded within legit data and apps
Change Management
Need Clear Documentation For?
Process?
The structured approach of PLANNING, IMPLEMENTING, AND MONITORING CHANGES in an organization's IT infrastructure, systems, policies, or processes
Need Clear Documentation For: Frequency, Duration, Installation Process, Fallback Procedures
Process:
Determine SCOPE OF CHANGE
Analyze the RISK ASSOCIATED with the Change
Create a CHANGE PLAN
Get END-USER APPROVAL
Present Proposal to the CHANGE CONTROL BOARD
Have a BACKOUT PLAN if Change Doesn't Work
DOCUMENT THE CHANGE
Change Approval Process
What are the steps?
Process of evaluating, approving, and managing changes
Steps: Change Request Submitted, Initial Assessment, Change Evaluation, Change Approval, Implementation Planning, Testing and Validation, Change Deployment, Post-Implementation Review
Sandbox Testing Environment
A CONTROLLED AND ISOLATED replica of the PROD environment where SOFTWARE, APPS, AND CHANGES can be tested with NO CONNECTION to the actual PROD or the real world
Backout Plan
A SUREFIRE WAY TO REVERT CHANGES that are planned to be made
Allow/Deny List
What does Allow and Deny mean? Examples of Lists?
Security mechanism used to control ACCESS TO RESOURCES, SYSTEMS, OR NETWORKS based on predefined criteria.
ALLOW = NOTHING runs unless approved
DENY = EVERYTHING can run EXCEPT things on the list
Examples: IP Addresses, Applications, User Access Controls
Downtime
Period during which a SYSTEM, APP, SERVICE, OR NETWORK is UNAVAILABLE/NOT OPERATIONAL
PKI
Public Key Infrastructure
A hierarchical system for CREATION, MANAGEMENT, STORAGE, DISTRIBUTION, AND REVOCATION OF DIGITAL CERTIFICATES AND MANAGEMENT OF PUBLIC-KEY ENCRYPTION, ensuring that public keys are associated with their respective owners.
RA
Registration Authority
An entity in the PKI framework that is RESPONSIBLE FOR ACCEPTING REQUESTS FOR DIGITAL CERTIFICATES AND VERIFYING/AUTHENTICATING THE ENTITY REQUEST before a digital certificate is ISSUED. Acts as an INTERMEDIARY between the CA and User
CA
Process?
Certificate Authority
A TRUSTED THIRD PARTY in the PKI framework that is RESPONSIBLE FOR ISSUING, VALIDATING, AND REVOKING DIGITAL CERTIFICATES
Process:
1. Applicant creates THEIR KEY PAIR and SENDS THE PUBLIC KEY TO THE CA to be signed
2. RA VALIDATES THE REQUEST and the CA DIGITALLY SIGNS the Certificate using the CA's PRIVATE KEY and returns it
CRL
Certificate Revocation List
A LIST OF THE DIGITAL CERTIFICATES THAT HAVE BEEN REVOKED BY THE CA. Is a PERIODIC PUBLICATION of the certificates that have been revoked
CSR
Contains What Info?
Certificate Signing Request
A message sent FROM A DIGITAL CERTIFICATE APPLICANT to the CA to APPLY FOR A DIGITAL CERTIFICATE. Contains information that will be included in the certificate, including PUBLIC KEY, APPLICANT NAME, DOMAIN NAME, LOCALITY
OCSP
Online Certificate Status Protocol
A PROTOCOL that enables ON-DEMAND QUERYING of the REVOCATION STATUS OF AN X.509 DIGITAL CERTIFICATE IN REAL-TIME. The FASTEST WAY to check the validity of a DIGITAL CERTIFICATE
DN
Distinguished Name
A UNIQUE IDENTIFIER used in directory services and digital certificates to SPECIFY AN ENTITY'S IDENTITY in a hierarchical structure
PKCS
Famous Standards?
Public Key Cryptographic Standards
A set of STANDARDS developed to facilitate SECURE COMMUNICATION AND DATA EXCHANGE USING PUBLIC KEY CRYPTOGRAPHY. Defines various cryptographic techniques including FORMATS FOR PUBLIC KEYS, PRIVATE KEYS, DIGITAL SIGNATURES, AND DIGITAL CERTIFICATES
Famous Standards:
#1: RSA Encryption Algorithm
#5: Password-based Cryptography
#7: Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS)
#10: Format of CERTIFICATE SIGNING REQUESTS (CSRs)
#11: Specifies CRYPTOKI API for interacting with cryptograhpic tokens
#12: Defines secure and portable file format for STORING AND EXCHANGING PII
#13: Defines standards for Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC)
Symmetric Encryption (AKA = ?)
AKA Secret Key Encryption, Single Key Encryption, Private Key Encryption
Utilizes a SINGLE SHARED SECRET KEY to both ENCRYPT and DECRYPT data. VERY FAST - less overhead than Asymmetric encryption. DOES NOT SCALE WELL
Asymmetric Encryption (AKA = ?)
AKA Public Key Encryption, Two-Key Encryption
Utilizes a PAIR OF MATHEMATICALLY RELATED KEYS, one key (the PUBLIC KEY - so that ANYONE can ENCRYPT DATA) for ENCRYPTION and one key (the PRIVATE KEY - so that ONLY ONE PERSON can DECRYPT DATA) for DECRYPTION.
Key Escrow
A THIRD PARTY managing your PRIVATE KEYS
Database Encryption
Ensures the protection of STORED DATA and TRANSMISSION OF THAT DATA
Transparent Encryption
A method of ENCRYPTING DATA AT THE STORAGE LEVEL and ensuring the data REMAINS ENCRYPTED THROUGHOUT ITS LIFECYCLE within a DB. Involves using a SYMMETRIC KEY to ENCRYPT data before it is written to storage and DECRYPT data when it is requested
Record-Level Encryption
Encrypts INDIVIDUAL COLUMNS and uses SEPARATE SYMMETRIC KEYS for EACH COLUMN
Transport Encryption
Securing data that is TRAVERSING THE NETWORK
VPN
Common Protocols?
Virtual Private Network
Creates a SECURE AND ENCRYPTED CONNECTION that ENCRYPTS ALL DATA TRANSMITTED over the connection. An ENCRYPTED TUNNEL used to establish a secure connection between the USER AND VPN SERVER
Common Protocols: OpenVPN, IPsec, SSL/TLS
IPsec
Internet Protocol Security
A SUITE OF PROTOCOLS AND TECHNOLOGIES designed to ensure SECURE EXCHANGE OF PACKETS AT THE IP LAYER. Provides ENCRYPTION, AUTHENTICATION, AND DATA INTEGRITY for network traffic between 2 systems
AH
Authentication Header
Part of IPsec suite. Provides DATA INTEGRITY, AUTHENTICATION OF SENDER, AND PROTECTION AGAINST REPLAY ATTACKS. Does NOT provide ENCRYPTION
ESP
Encapsulating Security Payload
Part of IPsec suite. Provides CONFIDENTIALITY (ENCRYPTION), INTEGRITY, AND AUTHENTICATION
SAs
Security Associations
Part of IPsec suite. Establishes the PARAMETERS for IPsec connections, such as the ENCRYPTION ALGORITHM AND KEY EXCHANGE MECHANISM
SPD
Security Policy Database
Part of IPsec suite. Defines the SECURITY POLICIES FOR NETWORK TRAFFIC in IPsec. Specifies SECURITY REQUIREMENTS for how DATA PACKETS should be handled
PFS
Perfect Forward Secrecy
A cryptographic feature that ENSURES SECURITY OF ENCRYPTED COMMUNICATION even if the Private Key is COMPROMISED. EACH SESSION HAS ITS OWN KEY, so the compromise of one key DOESN'T AFFECT security of other sessions
Site-to-Site VPN
Connects MULTIPLE NETWORKS securely OVER THE INTERNET
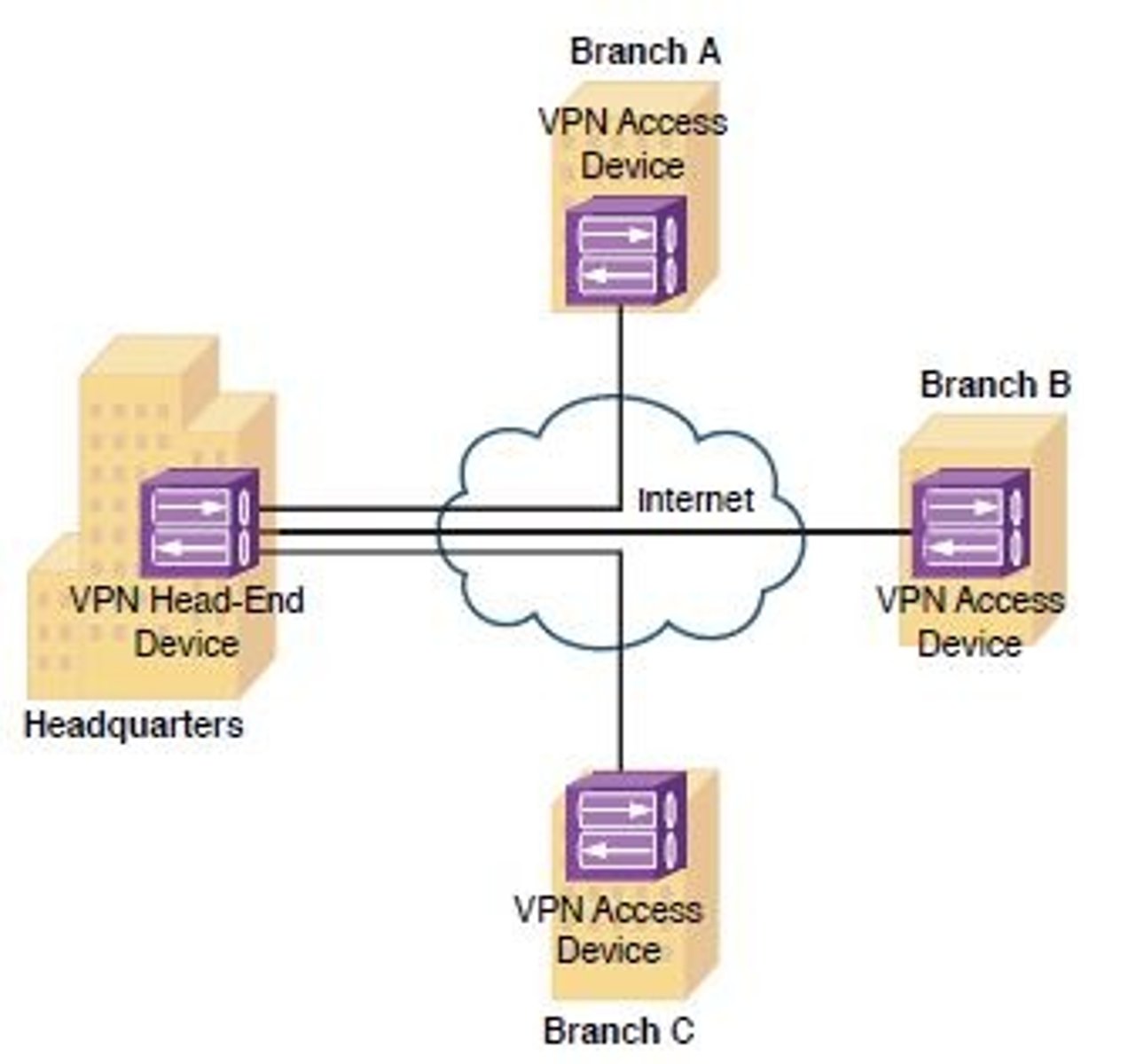
TLS
Transport Layer Security
A CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROTOCOL designed to PROVIDE SECURE COMMUNICATION OVER A COMPUTER NETWORK. REPLACED SSL
SSL
Secure Sockets Layer
A CRYPTOGRAPHIC PROTOCOL designed to provide secure communication OVER A COMPUTER NETWORK. DEPRECATED and REPLACED BY TLS
STARTTLS
A PROTOCOL COMMAND used to UPGRADE AN EXISTING INSECURE CONNECTION to a SECURE CONNECTION USING TLS. Commonly used in EMAIL TRANSMISSION
Key Stretching
A cryptographic technique that ENHANCES SECURITY OF SENSITIVE DATA by REPEATEDLY APPLYING A RESOURCE-INTENSIVE FUNCTION to the input data, thus making a WEAKER KEY STRONGER
Out-of-Band Exchange
Transfer of data/info through a SEPARATE, INDEPENDENT CHANNEL from the MAIN CHANNEL. Used to send SENSITIVE INFO through a path that is NOT SUSCEPTIBLE TO THE SAME VULNERABILITIES AS THE MAIN CHANNEL
In-Band Exchange
How to Deliver a Symmetric Key?
Transfer of data/info through the SAME COMMUNICATION CHANNEL as the MAIN CHANNEL.
Ex: Using ASYMMETRIC ENCRYPTION to deliver a SYMMETRIC KEY.
1. Create symmetric key
2. Use the PUBLIC KEY to encrypt the symmetric key
3. Send the ENCRYPTED SYMMETRIC KEY via In-Band Exchange. The recipient can use the PRIVATE KEY to get the symmetric key
Session Keys
What is the Process?
TEMPORARY encryption keys for SECURING A SINGLE COMMUNICATION SESSION between 2 parties. Generated for EACH SESSION and discarded at the end of the session
Process:
1. Client encrypts a RANDOM SYMMETRIC KEY and the SERVER'S PUBLIC KEY = SESSION KEY. The Client shares it with the Server
2. The Server DECRYPTS the SESSION KEY and uses the Session Key to ENCRYPT THE DATA THE CLIENT REQUESTS
TPM
Trusted Platform Module
An EMBEDDED MICROCONTROLLER used for SECURE BOOT, DISK ENCRYPTION, and SYSTEM INTEGRITY VERIFICATION. Also stores ENCRYPTION KEYS, DIGITAL CERTS, AND OTHER CRITICAL SECURITY INFO
HSM
Hardware Security Module
A DEDICATED HARDWARE DEVICE with ASSOCIATED SOFTWARE/FIRMWARE that PROVIDES A SECURE ENVIRONMENT FOR MANAGING AND PROTECTING CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEYS AND PERFORMING CRYPTOGRAPHIC OPERATIONS
KMS
Key Management System
A framework of POLICIES, PROCEDURES, TECHNOLOGIES used to MANAGE ALL CRYPTOGRAPHIC KEYS from a CENTRALIZED MANAGER throughout their lifecycle, including key GENERATION, DISTRIBUTION, STORAGE, ROTATION, ARCHIVAL, AND DESTRUCTION. Can be an HSM, software-based, or cloud-based
Secure Enclave
A PROTECTED/ISOLATED HARDWARE/SOFTWARE ENVIRONMENT within a computing device where SENSITIVE DATA AND CRYPTOGRAPHIC OPERATIONS CAN BE STORED AND PROCESSED SECURELY. Designed to ensure confidentiality and integrity of code and data EVEN IF THE MAIN OS IS COMPROMISED
Obfuscation
Techniques employed to OBSCURE/HIDE THE TRUE MEANING OF DATA, making it challenging for UNAUTHORIZED parties to DECIPHER/REVERSE-ENGINEER the info.
"Hiding information in plain sight"
Steganography
Concealing information INSIDE A SEEMINGLY INNOCUOUS PIECE OF DATA (images, TCP packets, audio, video)
Tokenization
Replacing SENSITIVE DATA with a NONSENSITIVE EQUIVALENT which HOLDS A REFERENCE TO THE ORIGINAL DATA and enables its processing but has no value if breached
Data Masking
HIDING PART of the ORIGINAL DATA. Protects PII. May STILL BE INTACT IN STORAGE and only be HIDDEN from view
Hashes
Characteristics?
A way to REPRESENT DATA as A FIXED-SIZE OUTPUT
Characteristics:
Can be used as a DIGITAL SIGNATURE.
A ONE-WAY cryptographic function.
Good hashes have HIGH DIFFUSION (SMALL plaintext change = BIG ciphertext change) AND HIGH CONFUSION (deriving the plaintext from the ciphertext is DIFFICULT) rates.
Collisions ARE possible.
Hash Collision
When 2 DISTINCT pieces of data result in the SAME HASH VALUE when using the SAME HASH FUNCTION
Salting
Adding a UNIQUE, RANDOM VALUE to EACH PASSWORD BEFORE it is hashed. Enhances security of Passwords AGAINST RAINBOW TABLES OR BRUTE FORCE
Digital Signature
What is the Process?
A CRYPTOGRAPHIC TECHNIQUE that VERIFIES THE AUTHENTICITY, INTEGRITY, and NON-REPUDIATION of DIGITAL DOCUMENTS/MESSAGES by using a UNIQUE ENCRYPTED IDENTIFIER from the SENDER.
Sender signs with their PRIVATE KEY, Receiver can verify with the SENDER'S PUBLIC KEY. Any change in the message invalidates the signature
Blockchain
An OPEN PUBLIC LEDGER to keep track of transactions
Open Public Ledger
A DISTRIBUTED DATABASE stored across MULTIPLE COMPUTERS IN A P2P NETWORK.
Ex: Blockchain
Digital Certificate
Standard Format?
A DIGITAL DOCUMENT used to VERIFY THE IDENTIFY of an individual, device, service, or organization in online communications. Used to verify the OWNERSHIP OF A PUBLIC KEY
Standard Format: X.509. Contains Serial #, Version, Issuer, Name of Certificate Holder, Public Key
SAN
Subject Alternative Name
An EXTENSION of the X.509 Digital Certificate Format that ALLOWS USERS TO SPECIFY ADDITIONAL HOST NAMES for a SINGLE SSL/TLS CERTIFICATE
OCSP Stapling
The OCSP status is INCLUDED IN THE SSL/TLS HANDSHAKE that is DIGITALLY SIGNED BY THE CA. This enables Clients to QUERY A RESPONDER to determine whether a certificate is STILL VALID
Threat Actor
Entity that is responsible for an event that HAS AN IMPACT ON THE SAFETY OF ANOTHER ENTITY
Threat Actor Attributes
The CHARACTERISTICS of the Attacker
Internal v External
Level of Resources
Level of Sophistication/Capability
Motivations
Threat Actor Types
Nation State
Unskilled Attacker
Hacktivist
Insider Threat
Organized Crime
Shadow IT
Nation State Threat Actor Attributes
External
Massive Resources - can attack constantly
Highest Sophistication
Motivations: Espionage, Political/Philosophical Beliefs, Disruption/Chaos, War
APT
Advanced Persistent Threat
A PROLONGED AND SOPHISTICATED CYBERATTACK often carried out by WELL-FUNDED and ORGANIZED groups. Often, an Intruder will GAIN ACCESS TO A NETWORK and remain UNDETECTED FOR AN EXTENDED PERIOD
Unskilled Attacker Threat Actor Attributes
Internal OR External
Low Resources
Low Sophistication
Motivations: Disruption/Chaos, Financial Gain, Revenge
Hacktivist Threat Actor Attributes
External
Low to Medium Resources
Low to Medium Sophistication
Motivations: Ethical Beliefs, Philosophical/Political Beliefs, Disruption/Chaos
Insider Threat Threat Actor Attributes
Internal
Low to High Resources
Low to High Sophistication
Motivations: Revenge, Financial Gain, Service Disruption
Organized Crime Threat Actor Attributes
External
Medium to High Resources
Medium to High Sophistication
Motivations: Financial Gain, Data Exfil, Extortion
Shadow IT Threat Actor Attributes
Internal
Low to Medium Resources
Low to Medium Sophistication
Motivations: Convenience, Lack of Security Awareness, Meeting Specific Needs
Threat Vector / Attack Vector - Definitions/How Differ?
Threat Vector: A PATH/MEANS by which an Attacker can INTRODUCE/DELIVER a CYBER THREAT to a TARGET SYSTEM (i.e. How the Attacker can exploit a vulnerability or introduce an attack.)
Attack Vector: A PATH/MEANS by which an Attacker can GAIN ACCESS TO A COMPUTER/SERVER in order to DELIVER A PAYLOAD/MALICIOUS OUTCOME (i.e. The ATTACK the Attacker uses.)
Types of Attack Vectors
Message-Based: Email, SMS, Phishing, Social Engineering
Image-Based: An image that can also contain an XML file
File-Based: Executables that can be hidden in other file types (PDF, ZIP/RAR, MS Office)
Voice Call: Vishing, Spam Over IP, War Dialing
Removable Device: USB Devices
Vulnerable Software: Client-based (infected executables) OR Agentless (compromised SOFTWARE on a Server - infects all users)
Unsupported System: Outdated systems that no longer receive patches
Unsecure Network: Wireless (outdated protocols like WEP, WPA, WPA2, WPS or open networks), Wired (unsecure interfaces that don't follow 802.1X)
Open Service Ports: TDP/UDP Ports - each App has its own Port
Default Credentials
Supply Chain: Tampering with the underlying infra/manufacturing process
SVG
Scalable Vector Graphic
An IMAGE-BASED VECTOR. More than just an image - contains an XML FILE THAT ALLOWS YOU TO EMBED OTHER INFO. Can perform HTML INJECTION
Vishing
Phishing OVER THE PHONE
Spam Over IP
Using VOICE OVER IP (VOIP) SYSTEMS to SEND LARGE-SCALE PHONE CALLS
War Dialing
Finding UNPUBLISHED phone numbers that MAY GIVE ATTACKERS ACCESS TO A SYSTEM
Air-Gapped Network
A security measure that involves PHYSICALLY isolating a computer/network from ANY OTHER NETWORK, including the Internet.
The system is NOT connected to any other networks/systems so DATA TRANSFER MUST OCCUR VIA PHYSICAL MEANS.