Endocrine Disruptors
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are some examples of endocrine disruptors?
Bisphenol A (BPA)- plastics, Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCB), Phthalate (furniture, clothing, flame retardant), Diethylstilbesterol (DES)- synthetic estrogen, Phytoestrogens (like soy), Pesticides (like DDT)
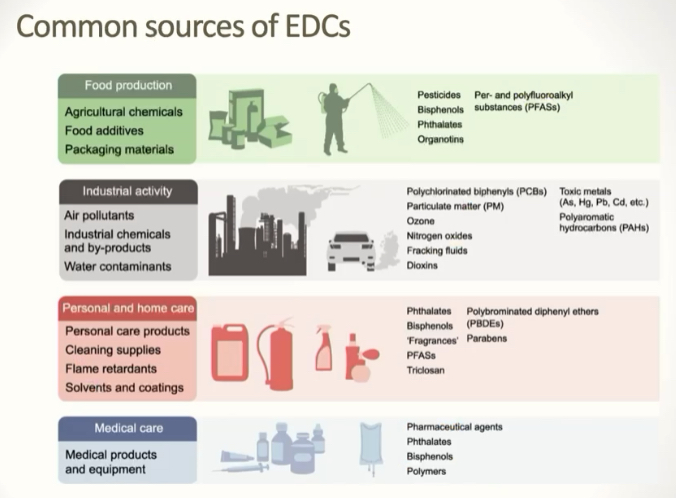
Where are EDCs found?
water, food, clothing, cosmetics, everywhere…
What is an endocrine disruptor?
a chemical that, when absorbed into they body, either mimics or blocks hormones and disrupts the body’s normal functions
No longer just synthetic, can be natural
How do endocrine disruptors work?
Basic hormone action, normal hormone
Hormone mimic (agonist)
Hormone blocker (antagonist): prevents endogenous hormone action
Why may exposure to EDCs be bad and which specific exposure periods would be more detrimental?
hormones act on behavior
Puberty or pregnancy or in utero
Gene expression and transcription
Accumulation/generational exposure
Feedback systems
Why are EDCs so bad?
endocrine disruptors and target hormone systems
They don’t kill cells or attack DNA
Hormone-disrupting chemicals can cause deficits in individuals without making them sick
These impairments can have serious consequences over a lifetime and for a society
Even small amounts at the right time can have permanent effects
There are more than 85,000 man-made chemicals used for industrial purposes (>350,000 in existence)
Exposure is nearly impossible to avoid: air, food, water, clothing, furniture, etc
Describe the “biggest human experiment ever.”
doctors prescribed DES to almost 5 million pregnant women for decades as a way to decrease miscarriages and produce “bigger and stronger babies”
It was later found to cause reproductive tract deformities, infertility, and uterine and vaginal cancer in female offspring
More recently, reproductive issues have been found in males (e.g. sperm issues)
How have EDCs altered fertility in humans?
volume of ejaculation decreased by 20% in the last 50 years
Decreased sperm counts — from 113 million in 1940 to 66 million in 1990
Decreased sperm motility
Altered sperm morphology
Reduced testicular mass
Correlation with maternal endocrine disruptor stores and testicular cancer
Describe the changes in sex ratio in the Canadian community.
35% boys and 65% girls
Sex ratio was stable and normal until 1993 when it began to drop
Starting in 1999 for 5 years, fewer than 35% of live births were boys compared to the expected of just over 50%
Why did it take so long for the dangers of EDCs to be realized?
EDCs interfere with endocrine action by targeting hormone systems
They don’t kill cells or attack DNA
Hormone-disrupting chemicals can cause deficits in individuals without making them sick
The long latency between exposure and onset of sickness or development of disease makes it difficult to draw associates
Reading Questions

Describe the evidence seen in Herring gulls.
Animals were nesting in female-female pairs
Most birds are biparental but males weren’t helping
Increased rates of pre-hatching deaths
The offspring born to those females demonstrated hermaphroditic characteristics and grotesque deformities
Effects linked to DDT and could be mimicked with treatment with estrogen
Describe the evidence seen in bald eagles.
Dramatic decrease in newly-hatched eaglets
Abnormally thin eggshells
2/3 of the adult birds appeared indifferent to their normal courtship and nesting behaviors
Reproductive failure: 80% of the males were sterile
Birds usually put a lot of effort into mating, eagles stopped
Describe the evidence seen in alligators.
In some lakes in Florida, up to 90% of the eggs laid are hatched
At lake apopka, the hatching barely reached 18%
Half of those born died within 10 days
Of those that made it, males had abnormally small penises and decreased T levels (T and DHT critical for external genetalia)
The effects were linked to increased levels of DDT and dicofol (lake contamination)
Why are PCBs still a problem?
still out there
Chemically stable and resist degradation
Can move easily around the world
Humans are most often exposed via consumption
They’re lipophilic, so they accumulate in the fat of animals and magnify in the food chain
What is at particular risk to PCBs?
Infants who can be exposed to the contaminant both in utero and via lactation during critical periods of development
Communities in western Michigan that rely largely upon Great Lakes whitefish
Individuals exposed occupationally (e.g. firefighters covered in flame retardant)
*What are the effects of PCBs in humans?
thyroid problems (e.g. disrupted metabolism)
Decreased vigor/muscle weakness
Sensory neuropathy (numbness, areflexia)
Delayed cognitive development
ADHD/inability to concentrate
Retarded growth
Reproductive abnormalities—abnormal sexual development, altered fertility
Compromised immune system function
What are some effects of PCBs on animals in the lab?
altered sexual behavior and partner preference
Changes in brain chemistry (DA and 5-HT)
Increased hyperactivity
Altered response to stress
Decreased fertility
What is the traditional experimental paradigm in rodents for EDC exposure?
methods: give through ingestion (mimics human exposure) or injection (control amount)
Offspring exposed in utero, then measure effect
How is a rodent mother’s care altered with gestational PCB treatment?
maternal behavior in rodents is driven by hormones
progesterone is high throughout pregnancy, then slowly drops near the end when estradiol and prolactin increase sharply
Dams were treated with PCB 77 on gestation days (GD) 6-18
Offspring development and MB were examined
Various measures were altered: pup weight gain, pup survival, time on the nest, pup-directed licking and grooming, high crouch nursing
Why does the traditional experimental paradigm need to be reconsidered?
Virgin females hate offspring
Scientists need to be sure that the effect they’re attributing to the contaminant are due to the contaminant, and not indirect effects on behavior
Changes care based on offspring
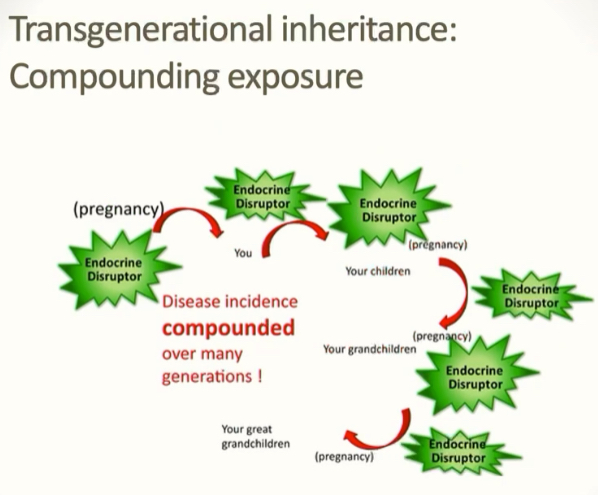
What is transgenerational inheritance?
From exposure in one generation: exposure to an ED during pregnancy leads to effects that are transmitted across generations resulting in toxicity that continues (and may be exacerbated) across generations
Disease incidence is compounded over many generations
Are we safe if PCBs have been banned?
in all of the Great Lakes, old contaminants like DDT are declining but are being replaced by new ones, such as flame retardants
How can we defend ourselves?
Action is required on several fronts to minimize exposure to current contaminants and eliminate new sources
Scientific research, chemical and manufacturing redesign, new government policies, individual efforts
Know your water
Choose your food intelligently
Avoid animal fat and fatty fish, choose organic produce, avoid microwaving food in plastic or with plastic wrap
What WAS (and no longer is…) being done?
EPA developed an Endocrine Disruptor Screening Program in 1996 to evaluate substance for their potential to affect the endocrine system of humans and wildlife
developing high through-put methods for evaluating the 87,000 chemicals that are produced today
2-tiered screening process
Tier 1: identify the chemicals that have the potential to interact with the endocrine system
Tier 2: determine the endocrine-related effects caused by each endocrine disruptor