Nasal Cavity (4/24)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
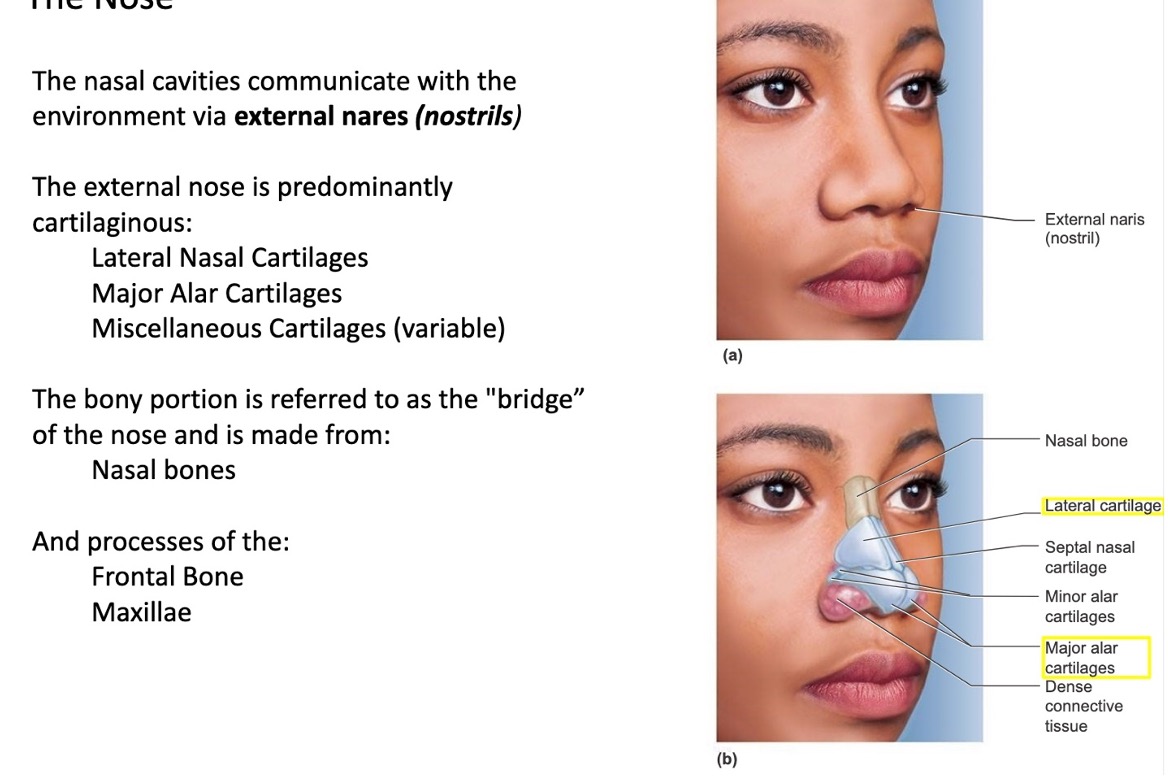
via what structures do the nasal cavities communicate with the environment?
external nares (nostrils)
the external nose is predominantly cartilaginous. it is composed of what cartilages?
lateral nasal cartilages
major alar cartilages
miscellaneous cartilages (variable)
*don’t have to memorize cartilages, just know that most of the external nose is cartilaginous
what is the bony portion of the nose called?
the “bridge” of the nose
what bony structures make up the bridge of the nose?
nasal bones
processes of the frontal bone and maxillae
(not a Q) nose
*if you “break your nose” it’ll be pretty high up, where bone is
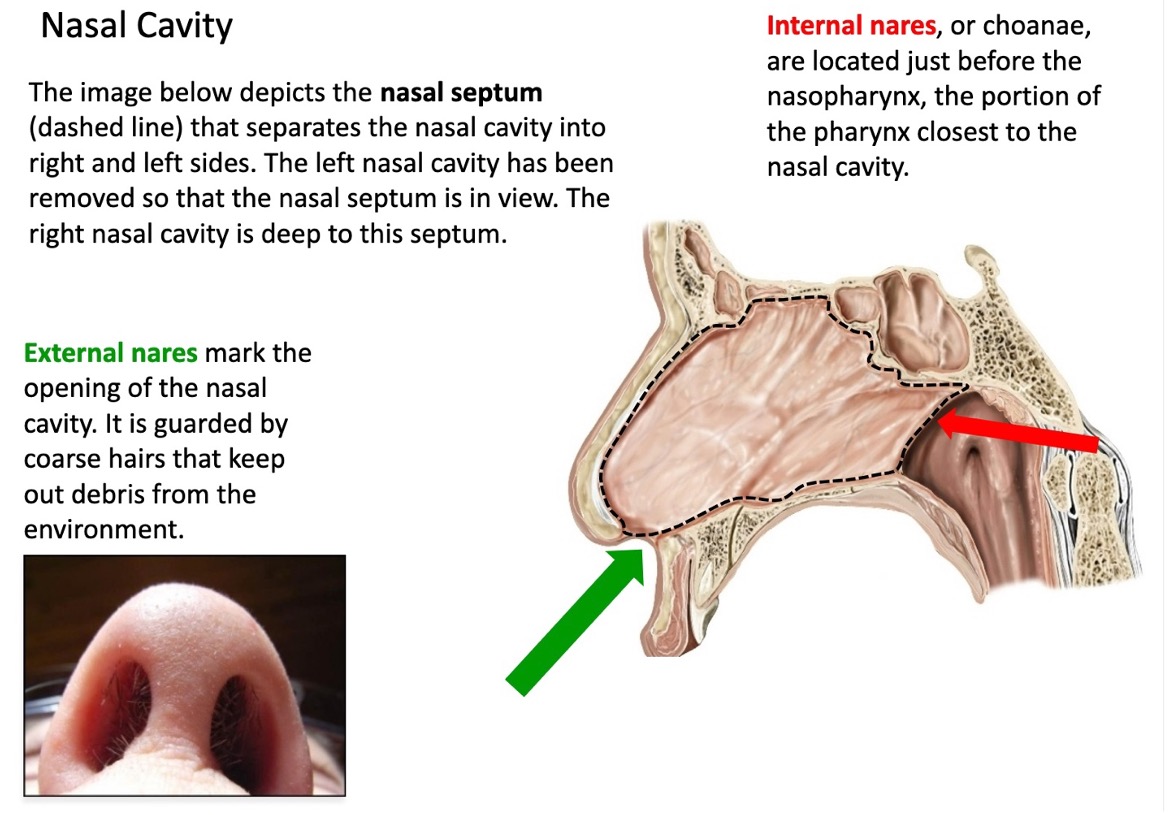
what structure separates the nasal cavity into R/L sides?
nasal septum
what structures mark the opening of the nasal cavity?
external nares
what guards the external nares?
coarse hairs that keep out debris from the environment
what is another name for internal nares?
choanae
internal nares are located just before what portion of the pharynx?
nasopharynx
(not a Q) nasal cavity
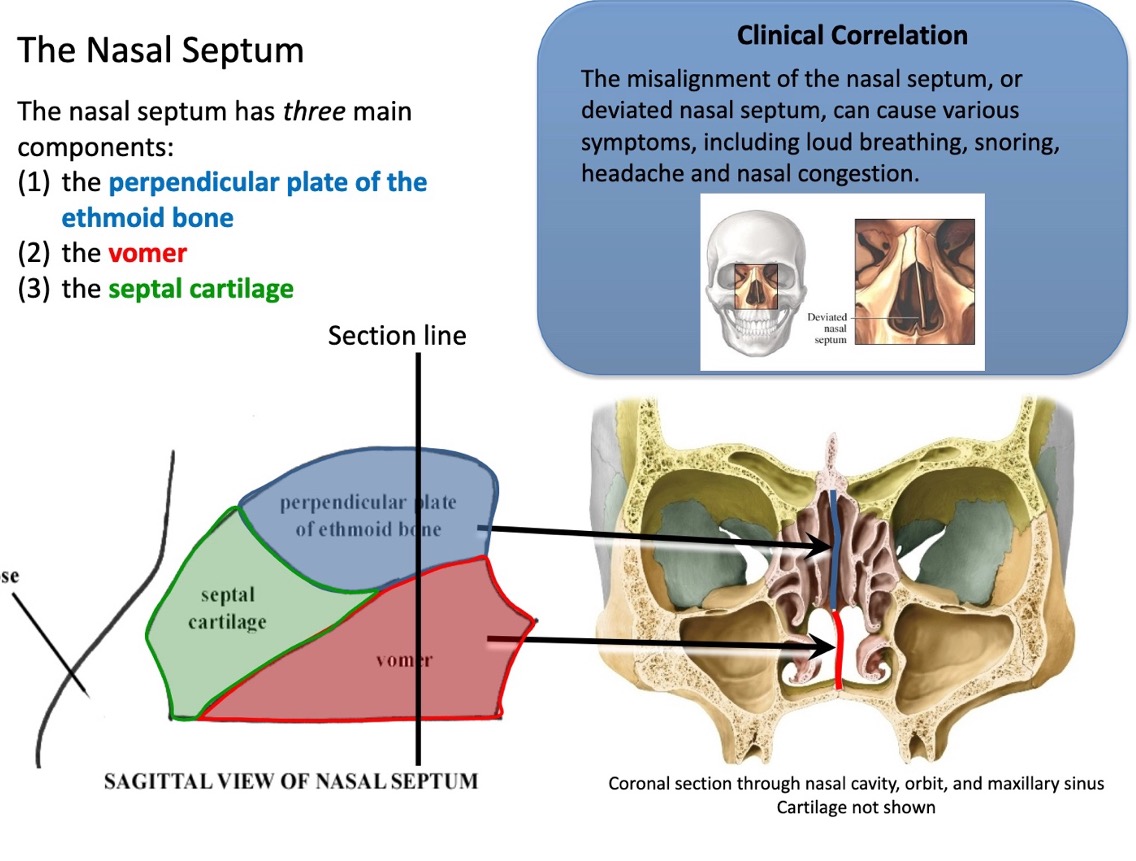
name the 3 main components of the nasal septum
perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone
vomer
septal cartilage
what symptoms can misalignment of the nasal septum (deviation of the nasal septum) cause?
loud breathing
snoring
headache
nasal congestion
(not a Q) nasal septum
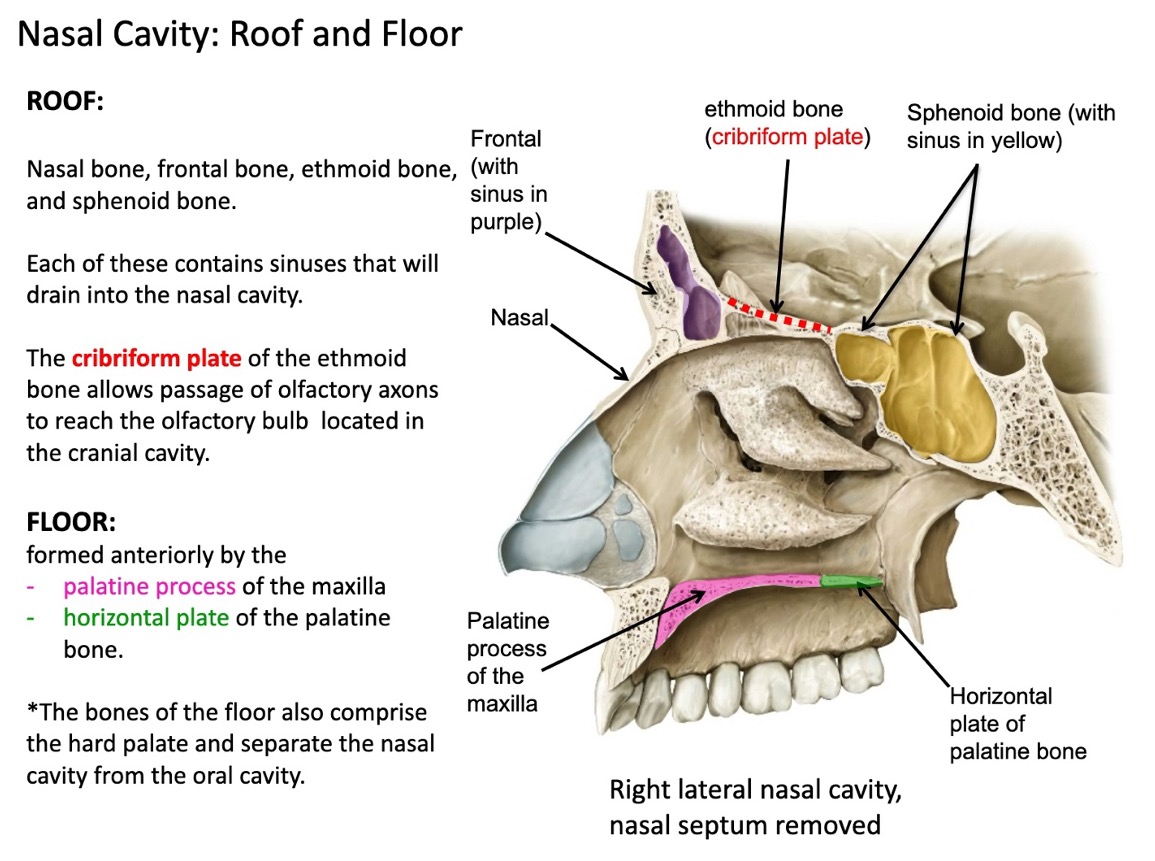
what forms the roof of the nasal cavity?
nasal bone
frontal bone
ethmoid bone
sphenoid bone
true or false: each of the bones that form the roof of the nasal cavity contains sinuses that will drain into the nasal cavity
true
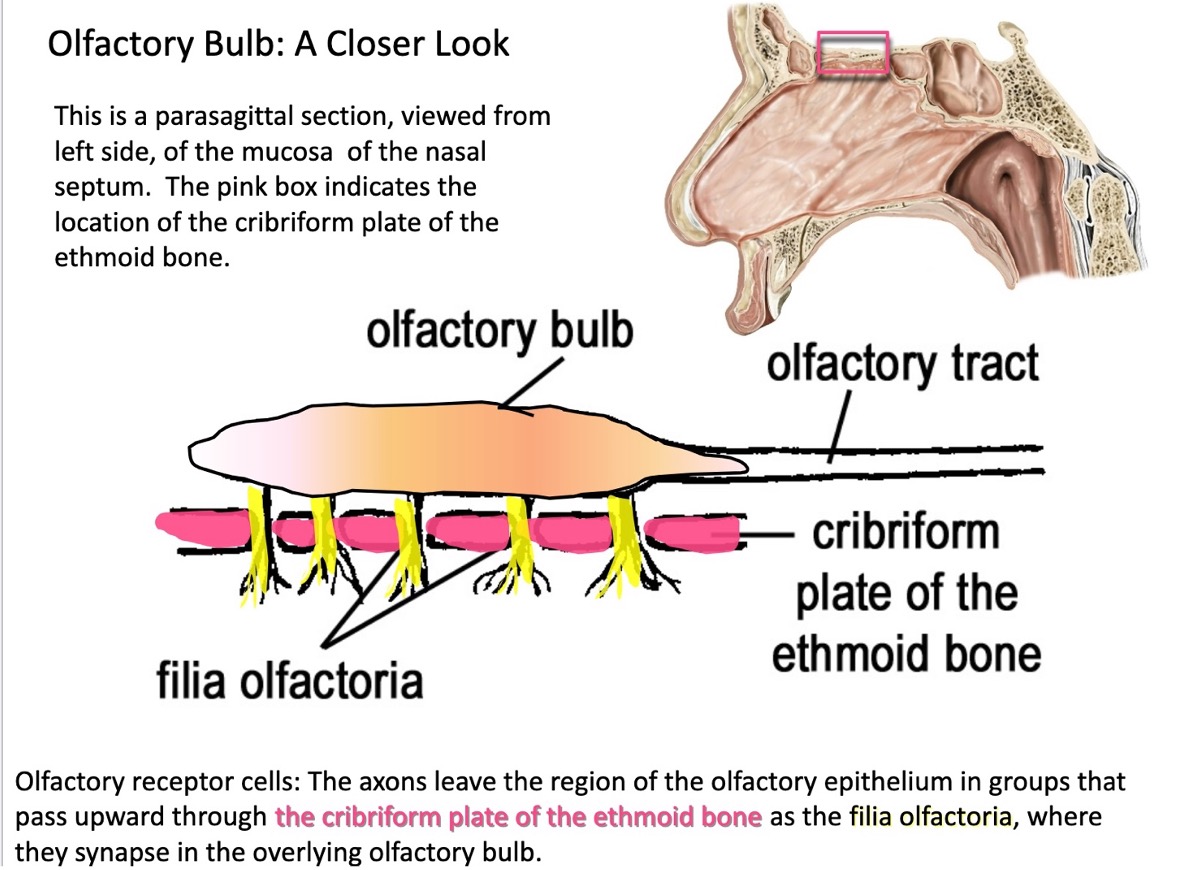
what structure allows passage of olfactory axons to reach the olfactory bulb located in the cranial cavity
the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone
what forms the floor of the nasal cavity?
formed anteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of the palatine bone
(hard palate is floor of nasal cavity)
true or false: the bones of the floor of the nasal cavity also comprise the soft palate and separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity
partially true
the bones of the floor also comprise the hard palate and separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity
(not a Q) nasal cavity roof and floor
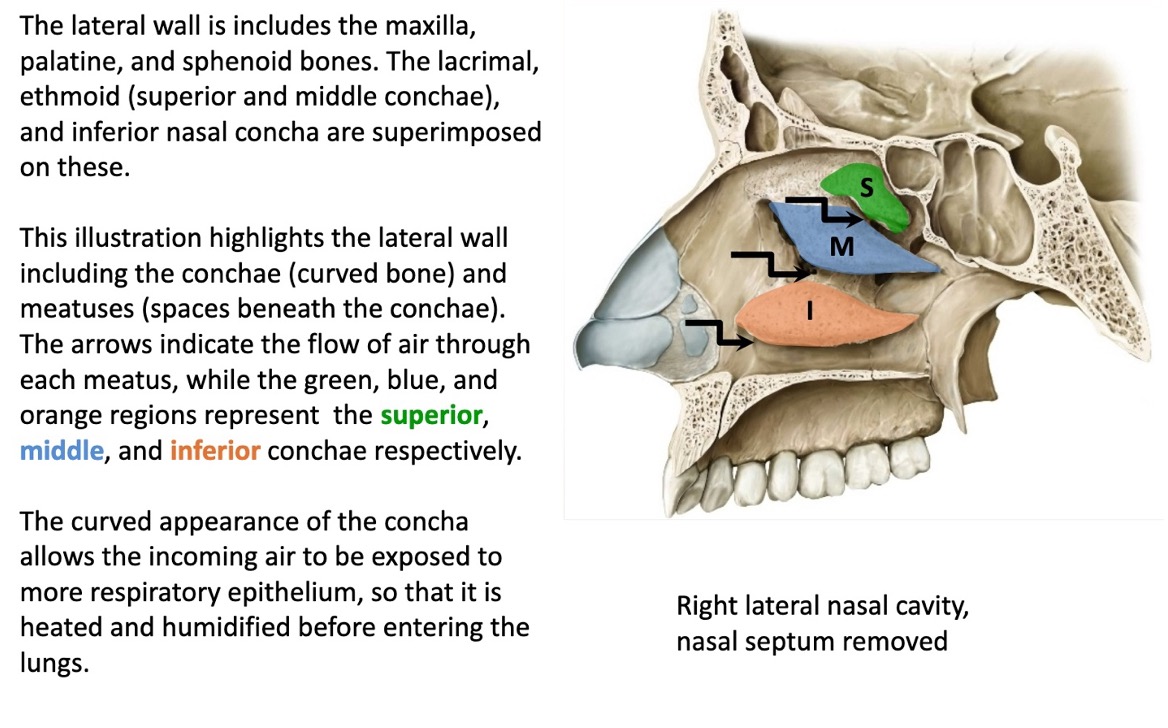
the lateral wall of the nasal cavity includes what bones?
maxilla, palatine and sphenoid bones
what structures are superimposed on the bony lateral walls of the nasal cavity?
lacrimal, ethmoid (superior and middle conchae), and inferior nasal concha
what is the function of the curved appearance of the conchae?
allows the incoming air to be exposed to more respiratory epithelium, so that it is heated and humidified before entering the lungs
also helps trap more pathogens in inhaled air
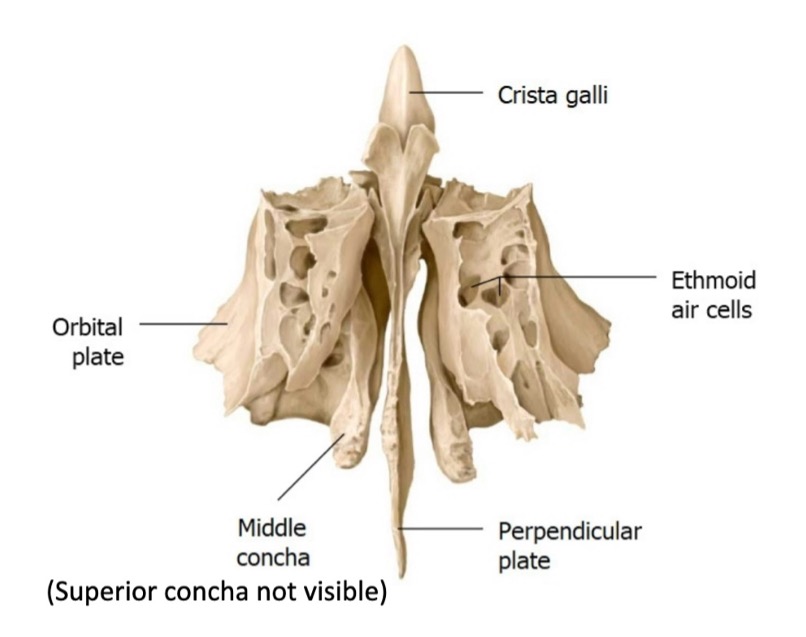
which conchae come from the ethmoid bone?
superior and middle conchae come from the ethmoid bone
the inferior concha is its own bone
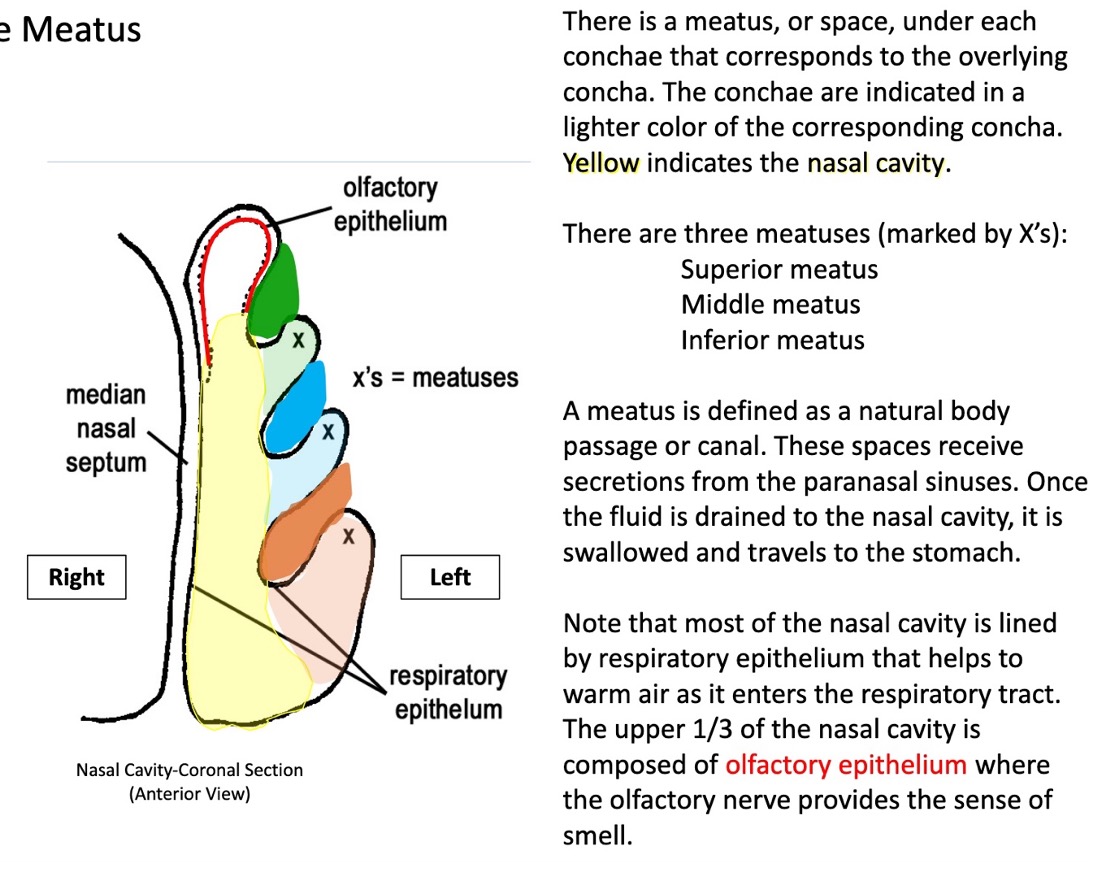
what is the definition of a meatus?
a natural body passage or canal
what are the spaces between conchae called?
superior, middle, and inferior meatus
(not a Q) nasal cavity lateral wall
the nasal meatuses receive secretions from what structures?
they receive secretions from the paranasal sinuses
(once the fluid is drained to the nasal cavity, it is swallowed and travels to the stomach)
what is most of the nasal cavity lined with?
respiratory epithelium
(this helps to warm air as it enters the respiratory tract)
what is the upper 1/3 of the nasal cavity composed of?
olfactory epithelium
(this is where the olfactory nerve provides the sense of smell)
(not a Q) the meatus
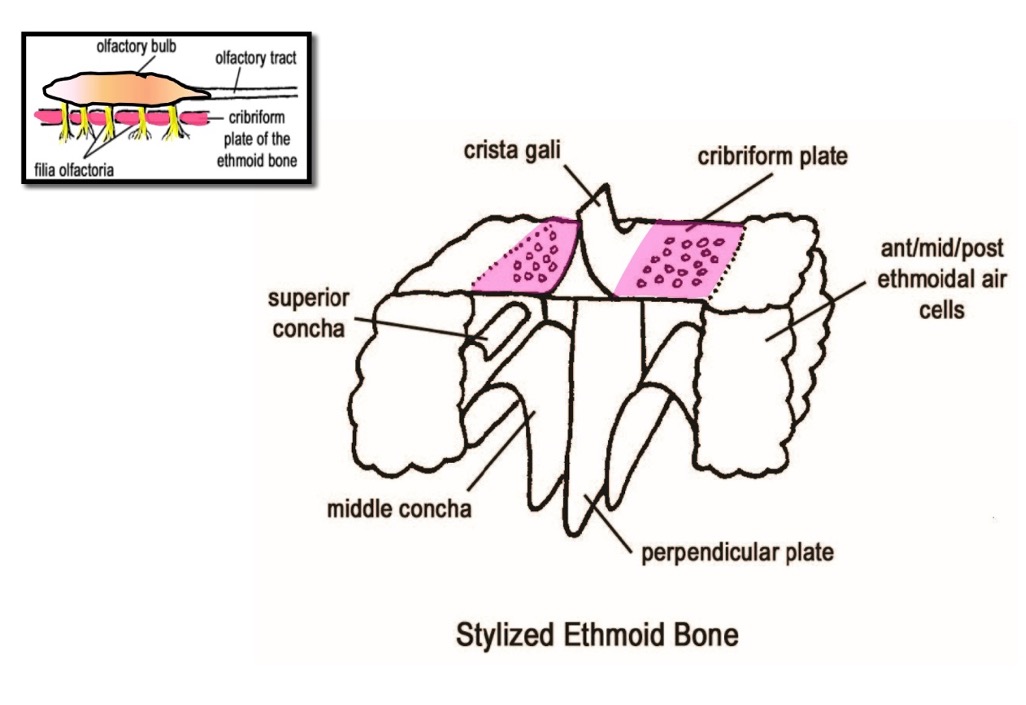
the axons of olfactory receptor cells leave the region of the olfactory epithelium in groups that pass upward through the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone—what are these groups called?
filia olfactoria
where do the axons of olfactory receptor cells synpase?
in the overlying olfactory bulb
(not a Q) olfactory bulb
(not a Q) features of the ethmoid bone
(not a Q) features of the ethmoid bone
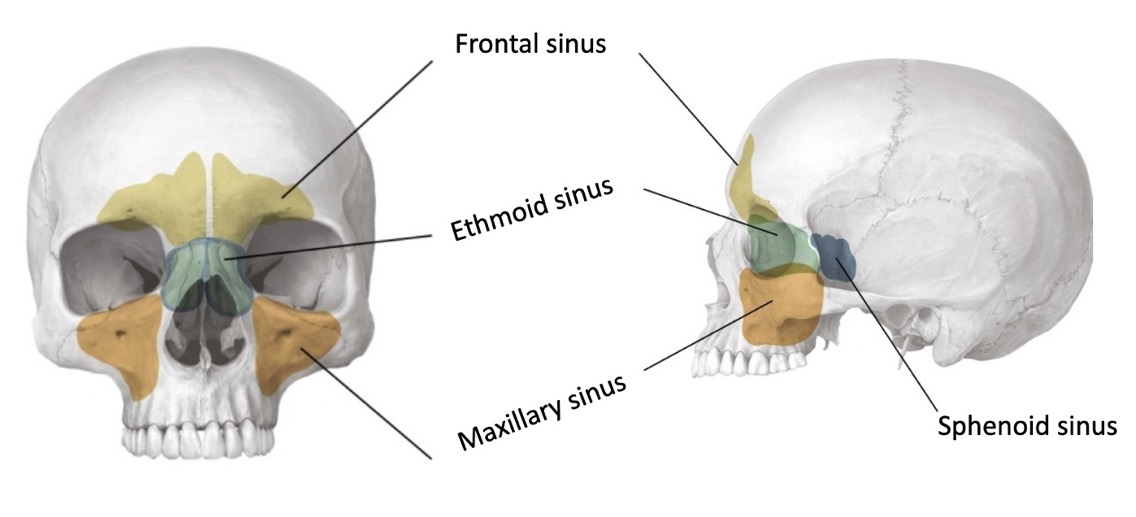
the paranasal sinuses are developed as extensions of what space?
the nasal cavity
what space do the paranasal sinuses drain back to?
the nasal cavity
what is each paranasal sinus named for?
the bone in which it is found
true or false: the paranasal sinuses lighten the skull
true
true or false: the paranasal sinuses are involved in resonation of voice
true
V₂ runs through which sinus?
maxillary sinus
(not a Q) paranasal sinuses
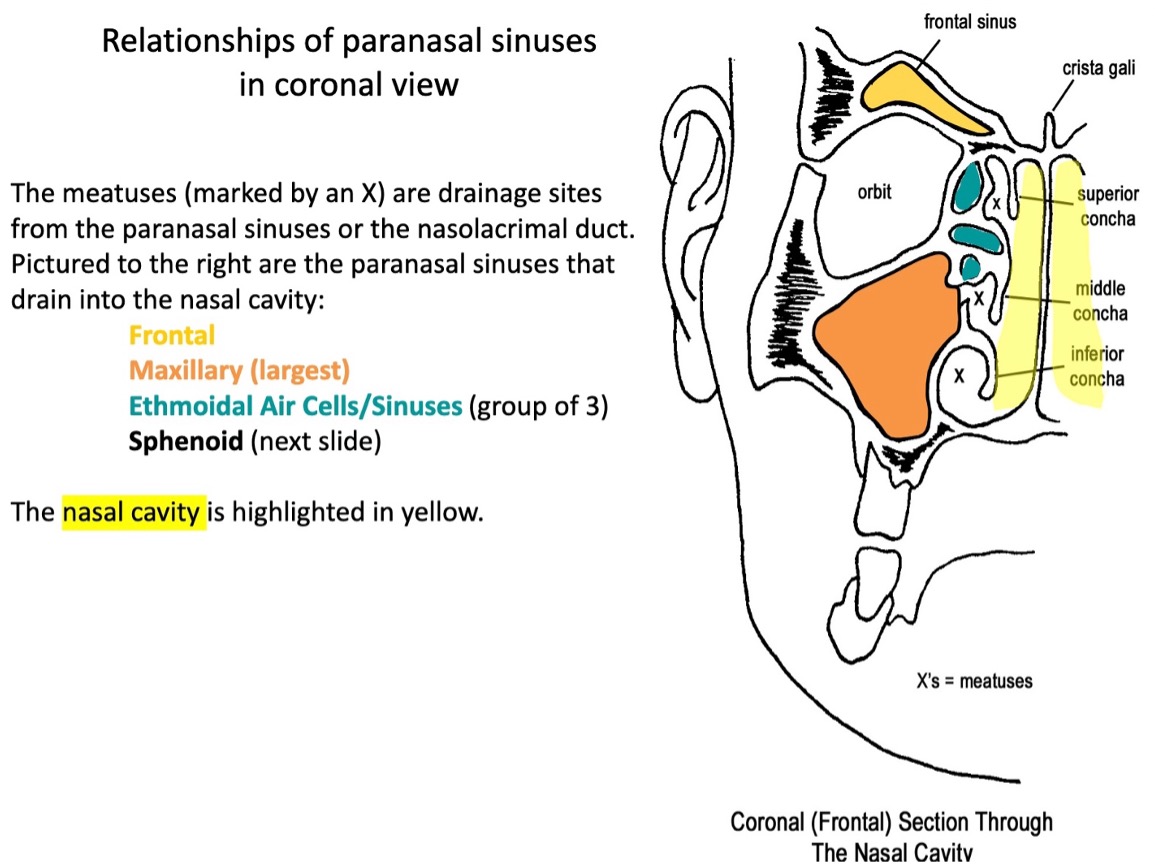
(not a Q) relationships of paranasal sinuses in coronal view
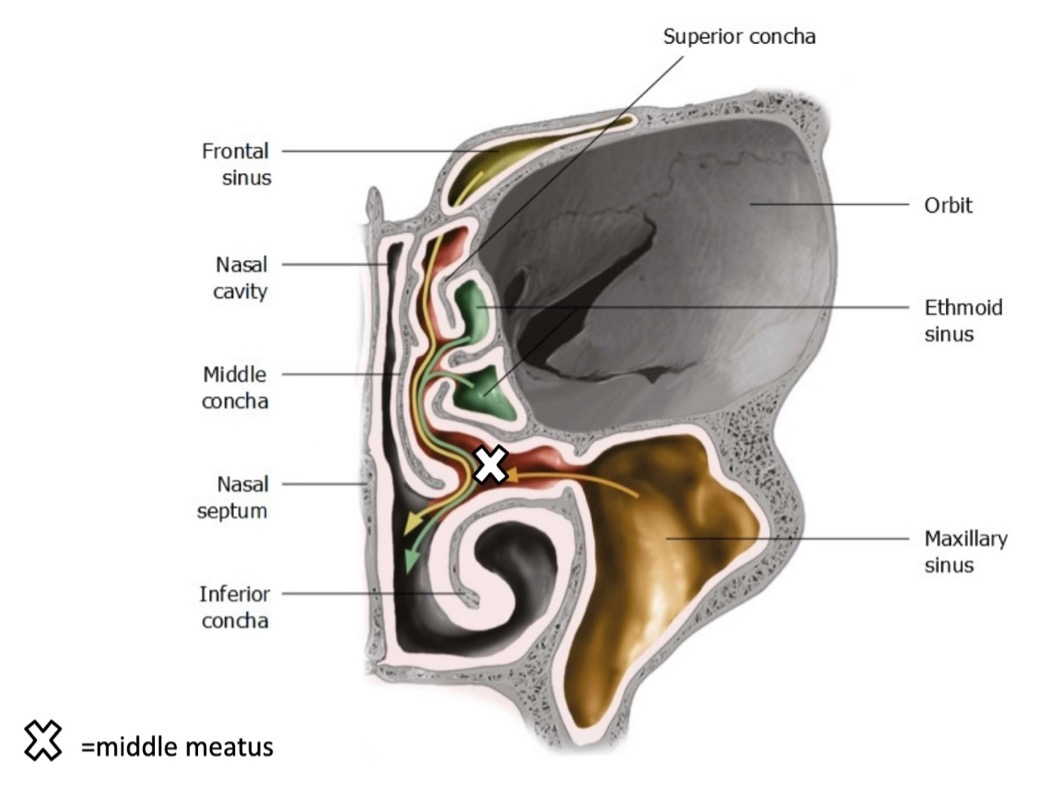
the sphenoid sinus drains to where?
sphenoethmoid recess
the posterior ethmoid air cells drain to where?
superior meatus
the anterior ethmoid air cells, maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, and middle ethmoid air cells drain to where?
middle meatus
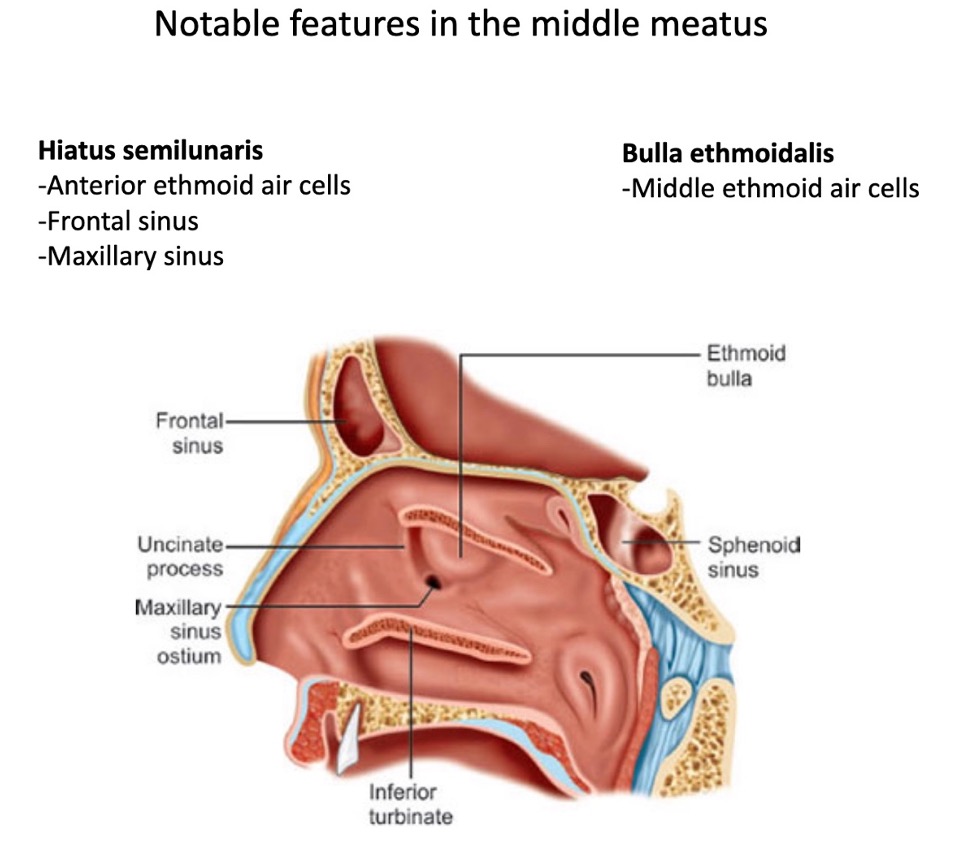
what structures make up hiatus semilunaris?
anterior ethmoid air cells
maxillary sinus
frontal sinus
what is another name for the middle ethmoid air cells?
bulla ethmoidalis
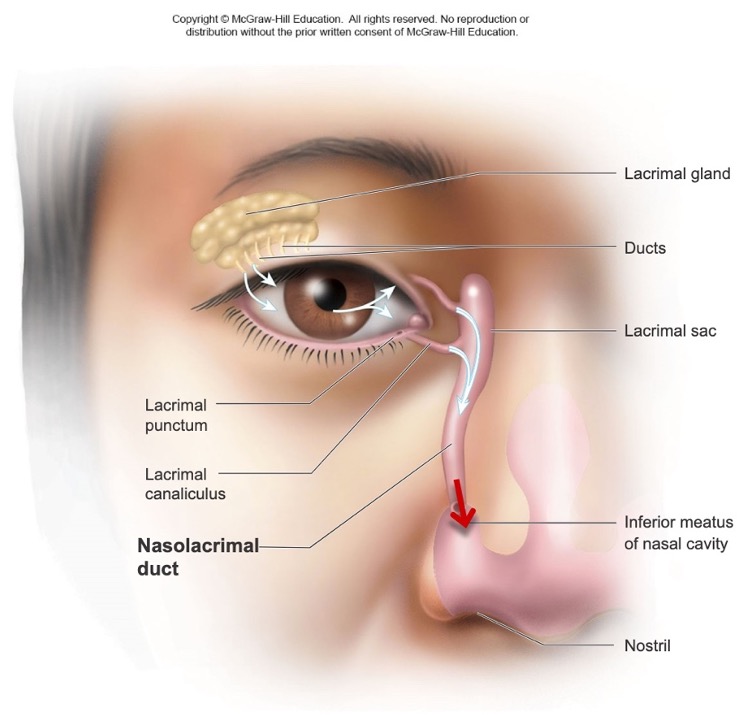
what does the nasolacrimal duct drain to?
inferior meatus
is the nasolacrimal duct a sinus?
no
(not a Q) drainage pattern of sinuses
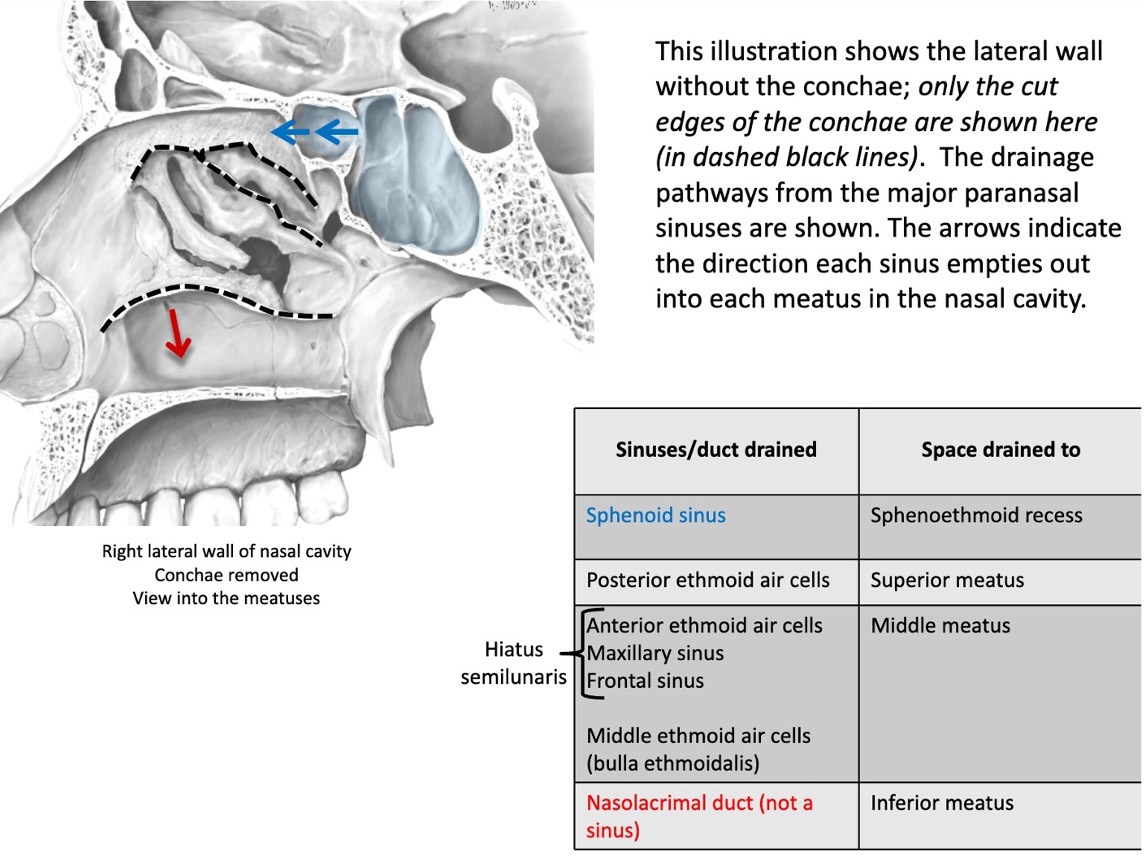
(not a Q) nasal cavity cross section
(not a Q) notable features in the middle meatus
what is another name for the nasolacrimal duct?
tear duct
the nasolacrimal duct collects tears from the eye and drains them where?
into the inferior meatus in the nasal cavity
is the nasolacrimal duct considered a paranasal sinus?
no, but it still drains to the nasal cavity
which drainage pathway is the source of a runny nose when crying or suffering from allergies?
nasolacrimal duct
(not a Q) nasolacrimal duct
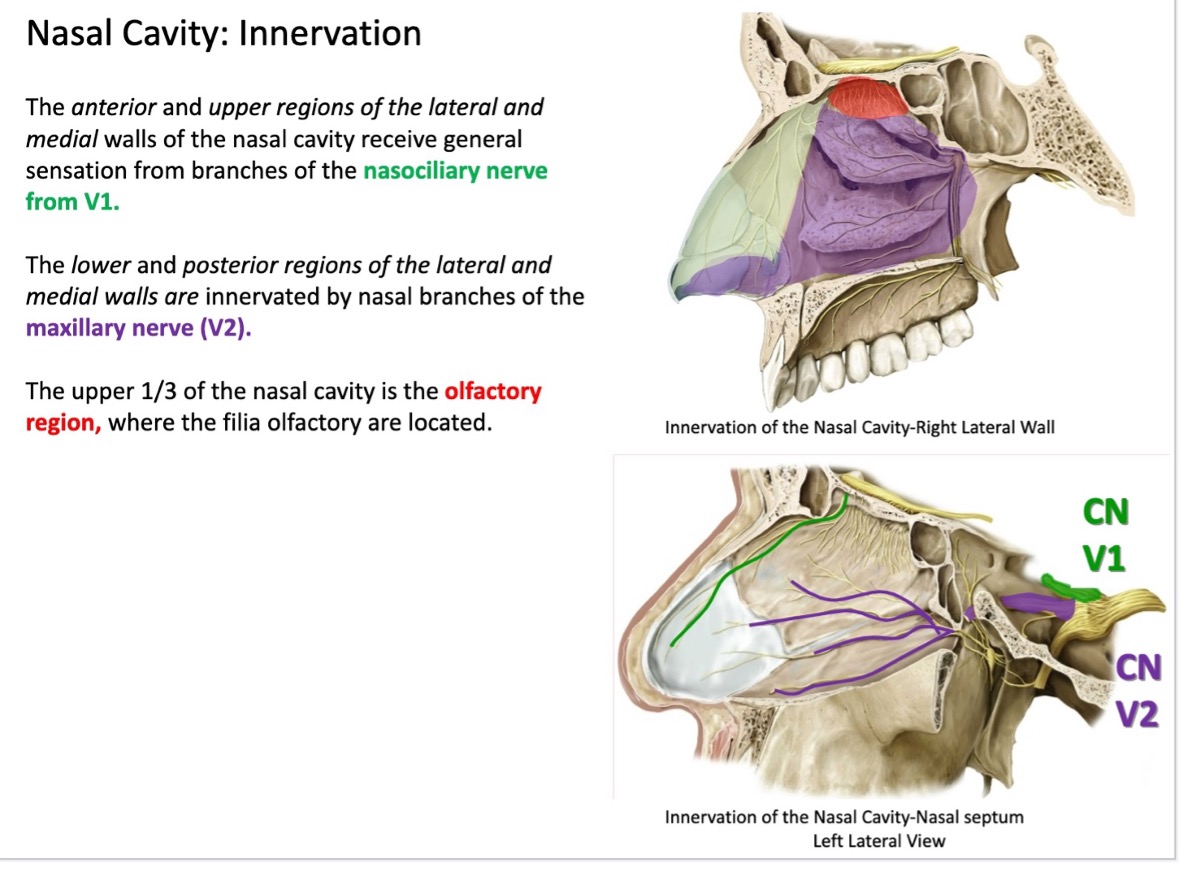
what provides sensory innervation to the anterior and upper regions of the lateral and medial walls of the nasal cavity?
nasociliary nerve (from V₁)
what provides sensory innervation to the lower and posterior regions of the lateral and medial walls of the nasal cavity?
nasal branches of the maxillary nerve (V₂)
(not a Q) nasal cavity innervation
(not a Q) blood supply of the nasal cavity
*just understand that the blood supply to the nose is vast
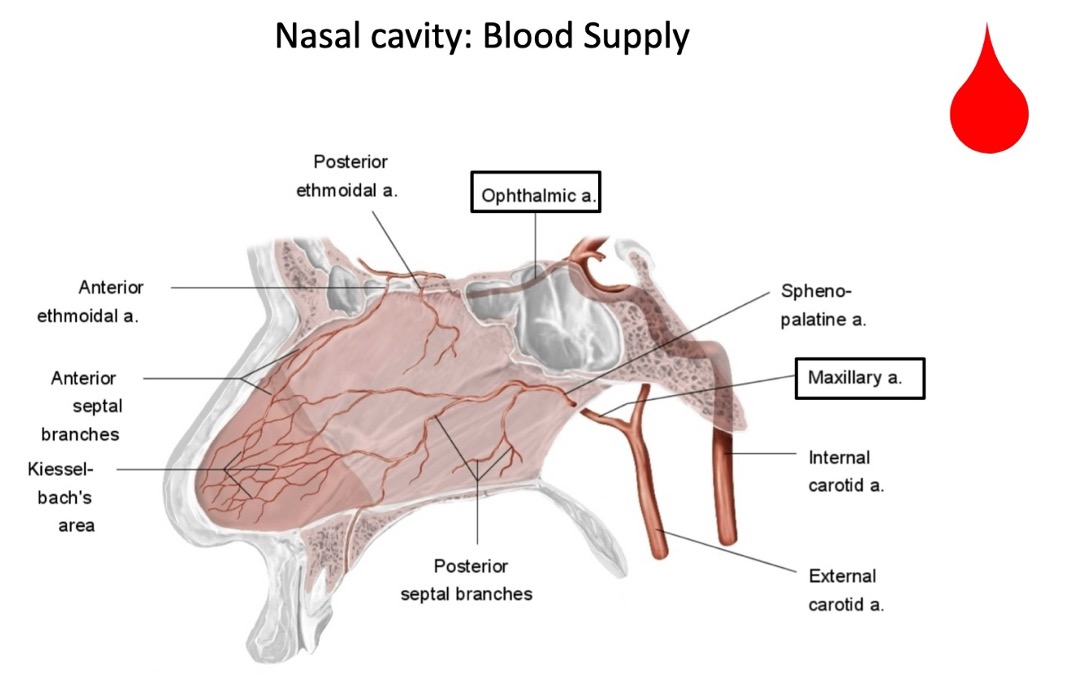
what arteries provide most of the blood supply of the nasal cavity?
maxillary artery (from external carotid artery)
ophthalmic artery (from ICA)