Chemistry of Life - Pt. 1
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
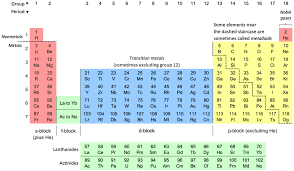
element
matter in its simplest form (sodium, potassium, etc.)
SPONCH - Elements of life
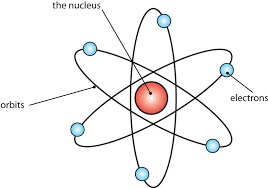
atom
the smallest unit of an element, consisting of protons, neutrons, and electrons, which defines the chemical properties of that element.
made of subatomic particles
Bohr model
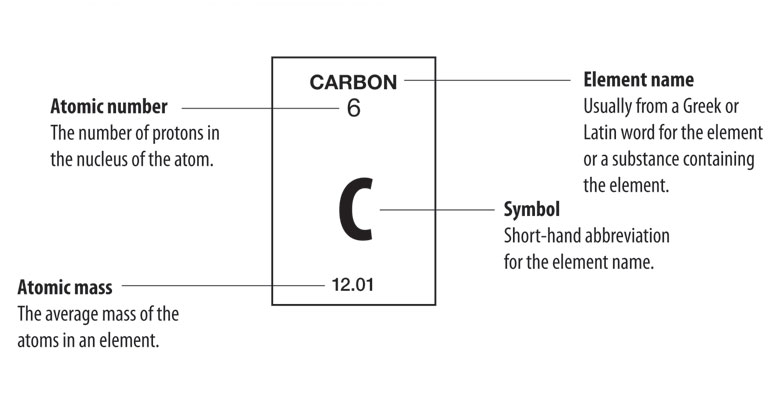
Atomic number = how many protons
Mass number = neutrons + protons
Atomic mass = average weight of atoms, USUALLY DECIMALS
Ion
an atom with a charge (positive/negative)
cations
positively charged ions formed when an atom loses one or more electrons/has more protons than electrons.
anions
negatively charged ions formed when an atom gains one or more electrons/has more electrons than protons.
compounds
molecules that have more than one type of atom bonded together. They can be either ionic or covalent.
variations in carbon skeleton
length
branching
double bonds
rings
isomers
same molecular formula but different structures
structural, geometric, enantiomers
structural: differ in covalent arrangement
geometric: spatial arrangement (cis cis trans trans)
enantiomers: mirror images (left and right hand)
covalent bonds
sharing of electrons to bond
non-polar covalent - electrons shared equally (hydrogen molecule)
polar covalent - not shared equally, results in a negative and positive side (water molecule)
ionic bonds
bonding from attractive forces (negative & positive)
between cations and anions
organic compounds vs inorganic
organic - found in all living organisms, typically have carbon and hydrogen
inorganic - do not consist mainly of carbon and hydrogen; often derived from non-living sources.
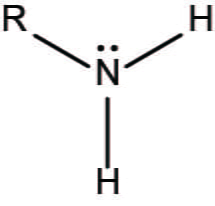
amino group
NH2 attached. Forms amino acids. Other compounds containing amino groups called amines.
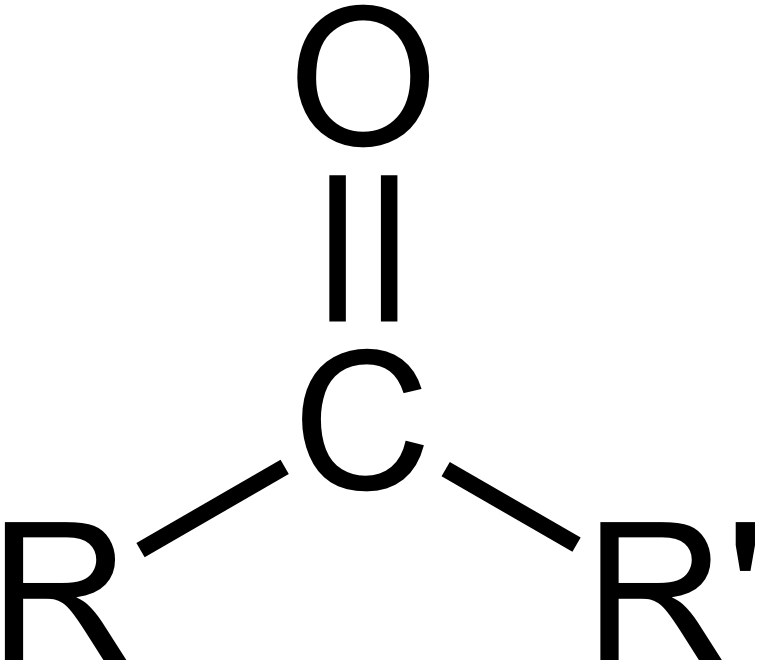
carbonyl
Carbon double bonded to oxygen. Middle is ketone, aldehyde is all de way at de end
Makes a compound hydrophilic and polar
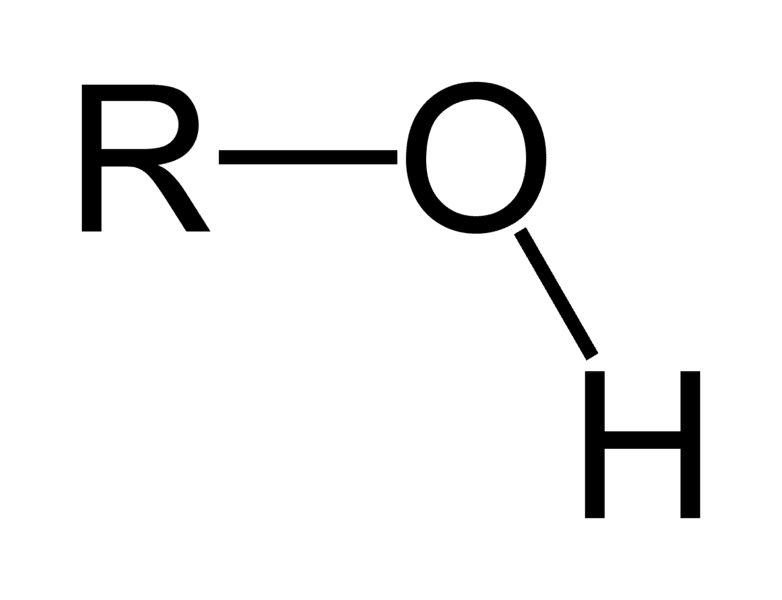
hydroxyl
Oxygen and hydrogen
present in alcohols
hydrophilic and polar
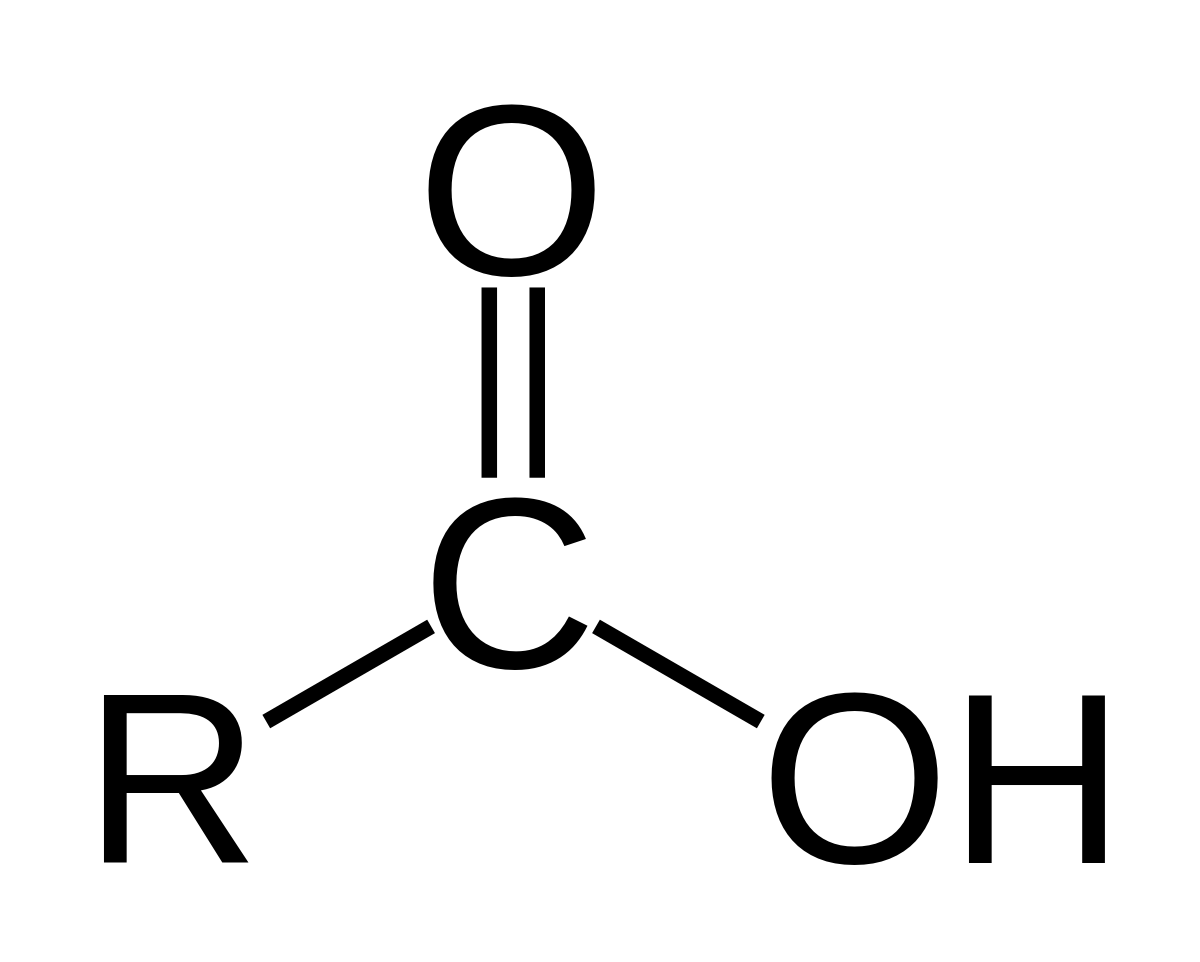
carboxyl
carbonyl + hydroxyl
acids - donate protons to other compounds (carboxylic acids)
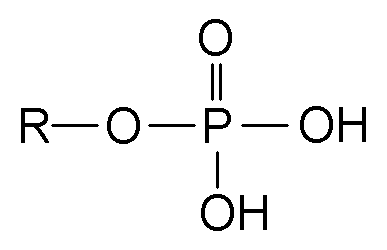
phosphate group
ATP, ADP, GTP
Acidic
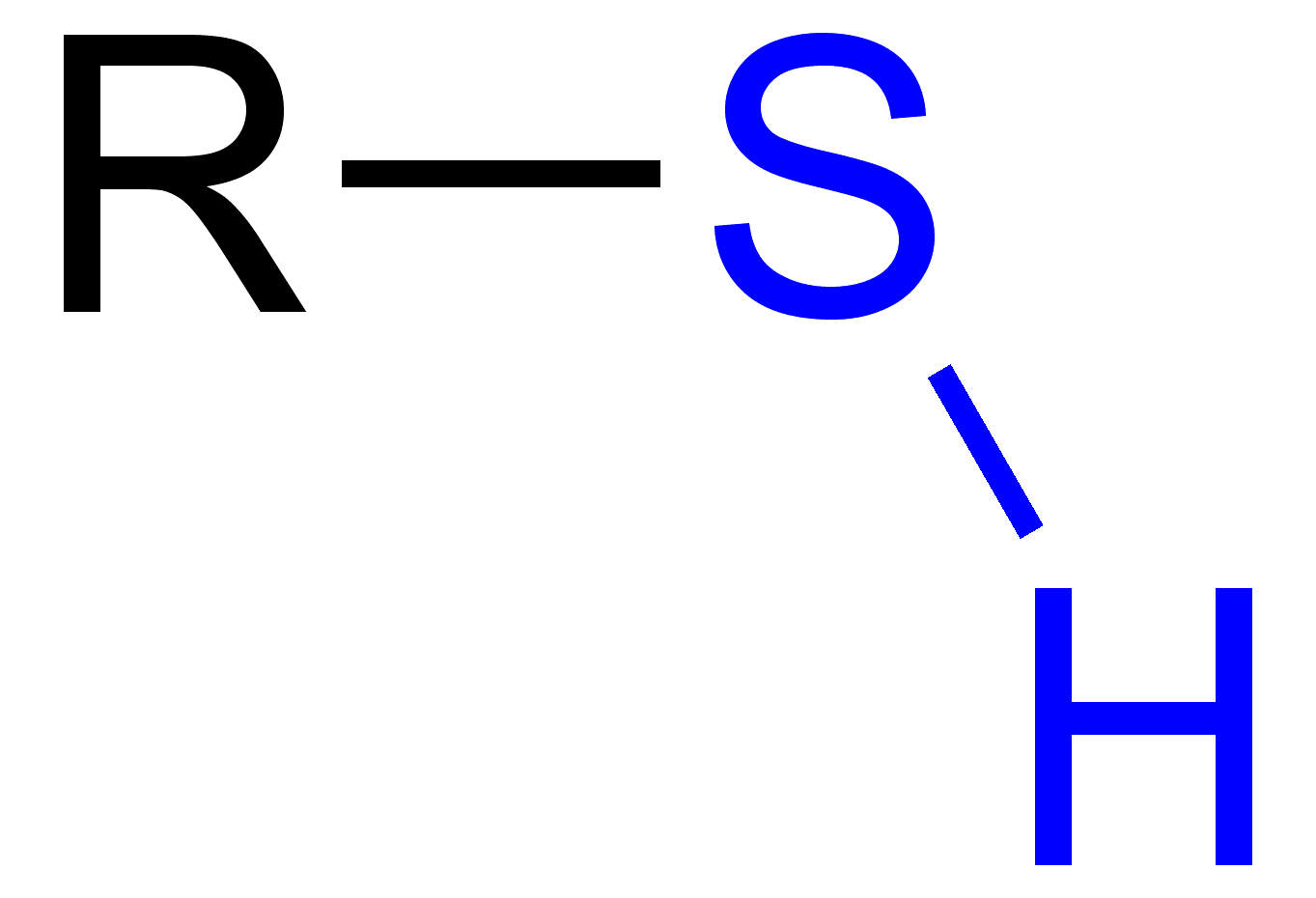
sulfhydryl group
Important in structure & stability of proteins
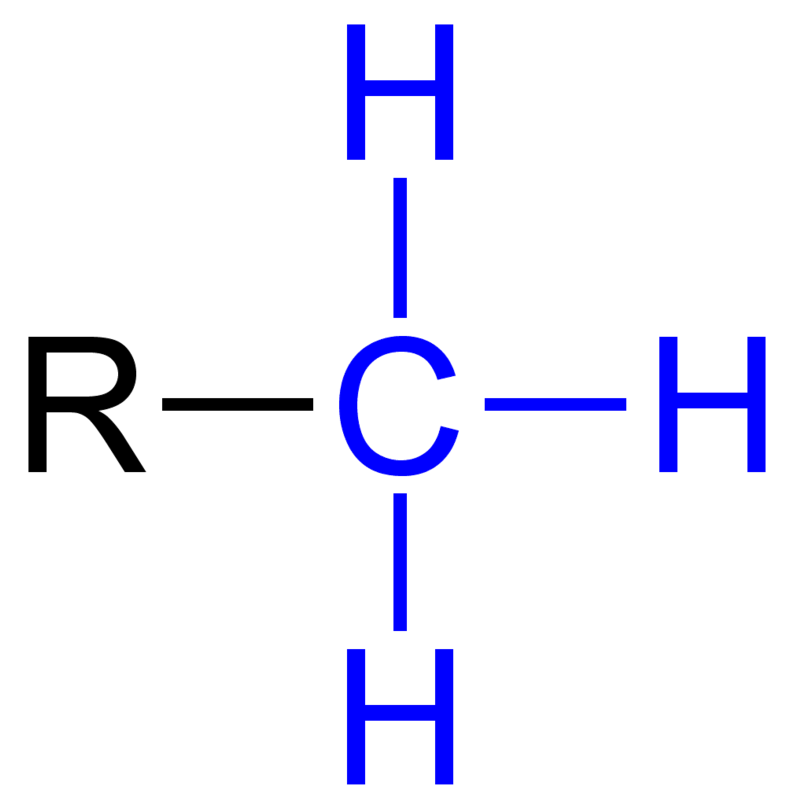
methyl groups
only non polar functional group
CH3
stops reactions
polar vs non polar
polar are hydrophilic (love)
non polar are hydrophobic, neutral bc shared equally (fear)
hydrogen bonding
Attractive force between a positive hydrogen atom and electronegative atom, essential for water properties and protein structure.
Van der Waals Interactions
“hot spots” created from movement of electrons in constant motion
cohesion vs adhesion
cohesion: water molecules sticking to themselves
adhesion: water molecules sticking to other substance (hydrogen bonds)
capillary action: water moving up plants
Evaporative cooling
“hot” molecules leave as a gas, “cool” molecules stay liquid
surface of object is cooler after evaporation
takes a lot of energy to change temp. of water
sweat lowers body temp.
“heat bank” - absorb and release large amounts of heat
Surface Tension
caused by cohesion
how difficult to break or stretch surface of liquid, water fairly great
ex: water strider
universal solvent
water dissolves more substances than any other solvent
colloid - suspension of particles in liquid
ice
solid water less dense than liquid, so ice floats
Macromolecules
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucelic acids
made up of polymers which are made up of monomers (joined by covalent bonds)
dehydration synthesis
forms macromolecules
releases water molecule to the reaction
making from the polymers’ structure (H+ + OH)
hydrolisis
break down macromolecues
addition of water to the reaction
consumption from the polymers' structure. (H+ + OH)
acids vs bases
acids to the left of pH (0-7), more H+, donates
bases to the right of pH (7-14) accepts protons