science notes chapter 13 - electrical systems
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
ammeter
measures the current flowing through an electric component
to be connected in series
voltmeter
measures the potential difference across an electrical component
to be connected in parallel
current
the rate of flow of electric charge
SI unit for current
ampere A
resistance
a measure of how much the component opposes the flow of electric current
fixed resistor
connected in a circuit to provide a constant resistance, which limits the current so that components do not overheat or get damaged.
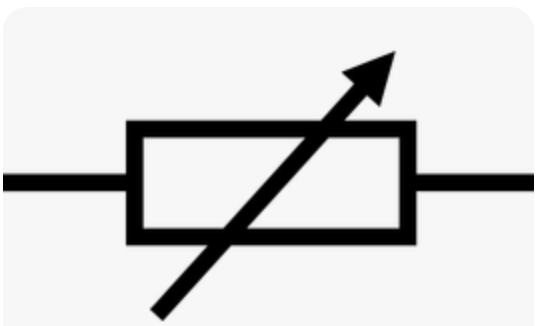
variable resistor
connected to the circuit to enable us to change resistance this will change the current flowing through
symbol for fixed resistor

symbol for variable resistor
si unit for potential difference
voltage v
formula for total resistance in series
R1 + R2 + R3….
formula for total resistance in parallel
(R1 + R2 +R3…) to the power of negative 1
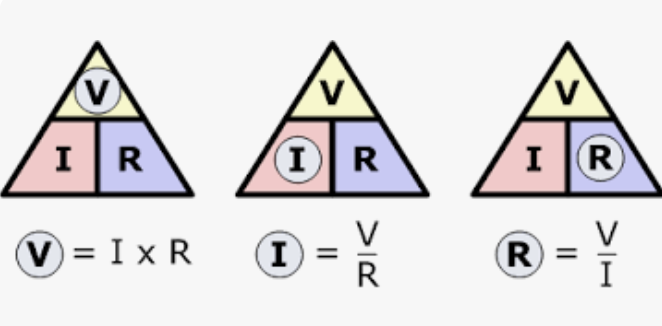
formula for electricity
SI unit for resistance
Ohm
live wire
The live wire carries the current from the power supply (mains) into the electrical appliance
neutral wire
connects the appliances back to the source in order to close the circuit for the object to work
earth wire
a safety feature that is usually connected to the metal casing of appliances. it helps prevent electric shock by diverting current into the ground when the live wire touches the metal casing
fuse
safety device added to an electrical circuit to prevent excessive current flow . it will blow up when the operating current exceeds its current rating
symbol for fuse

features of series circuit
current flowing through each resistor is the same as total resistance
potential across each resistor added up is the total emf of cell
lightbulbs in series
removing one lightbulb will result to other lightbulbs not lighting up due to an open circuit
features of parallel circuits
current in each resistor adds up to total current
potential difference is constant for all resistors in the circuit
effect of adding more lightbulbs in parallel
each lightbulb will still remain the same brightness
removing one lightbulb in parallel
other bulbs remain lit
SI unit for power
watt w
power
the rate of energy converted into other forms
formula for electrical energy consumption (energy)
power x time
si unit for electrical energy consumption
kWh
formula for cost
energy x cost per kWh