Comparative Study of C3, C4, and CAM Photosynthesis Pathways
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What are the learning goals of Lesson 10?
To understand different methods plants use to maximize carbon fixation, explain the C4 cycle, describe CAM plants, and compare C3, C4, and CAM metabolic pathways.
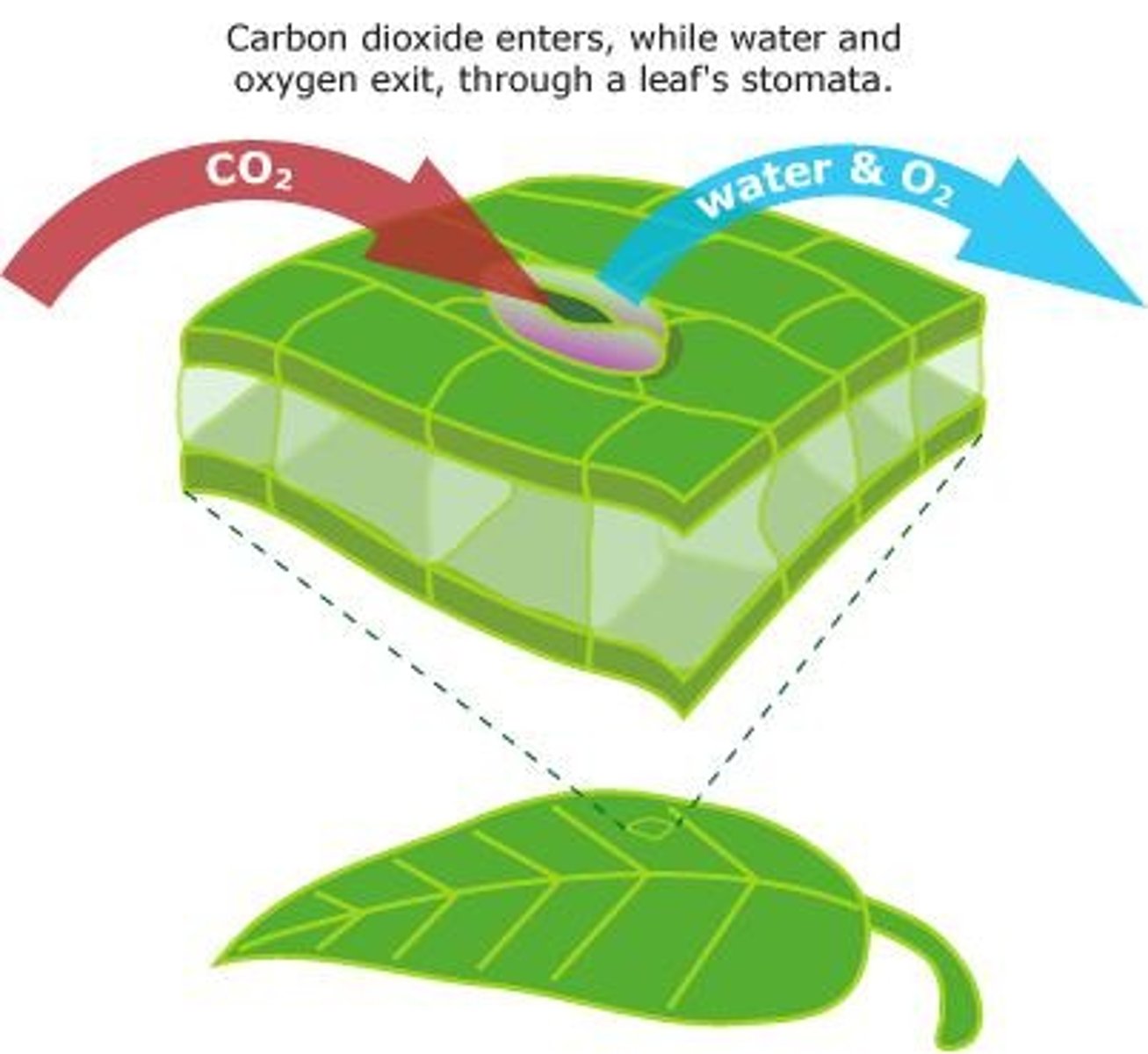
What is the role of stomata in plants?
Stomata are pores on the underside of leaves that can be opened and closed by guard cells, allowing for gas exchange while limiting water loss.
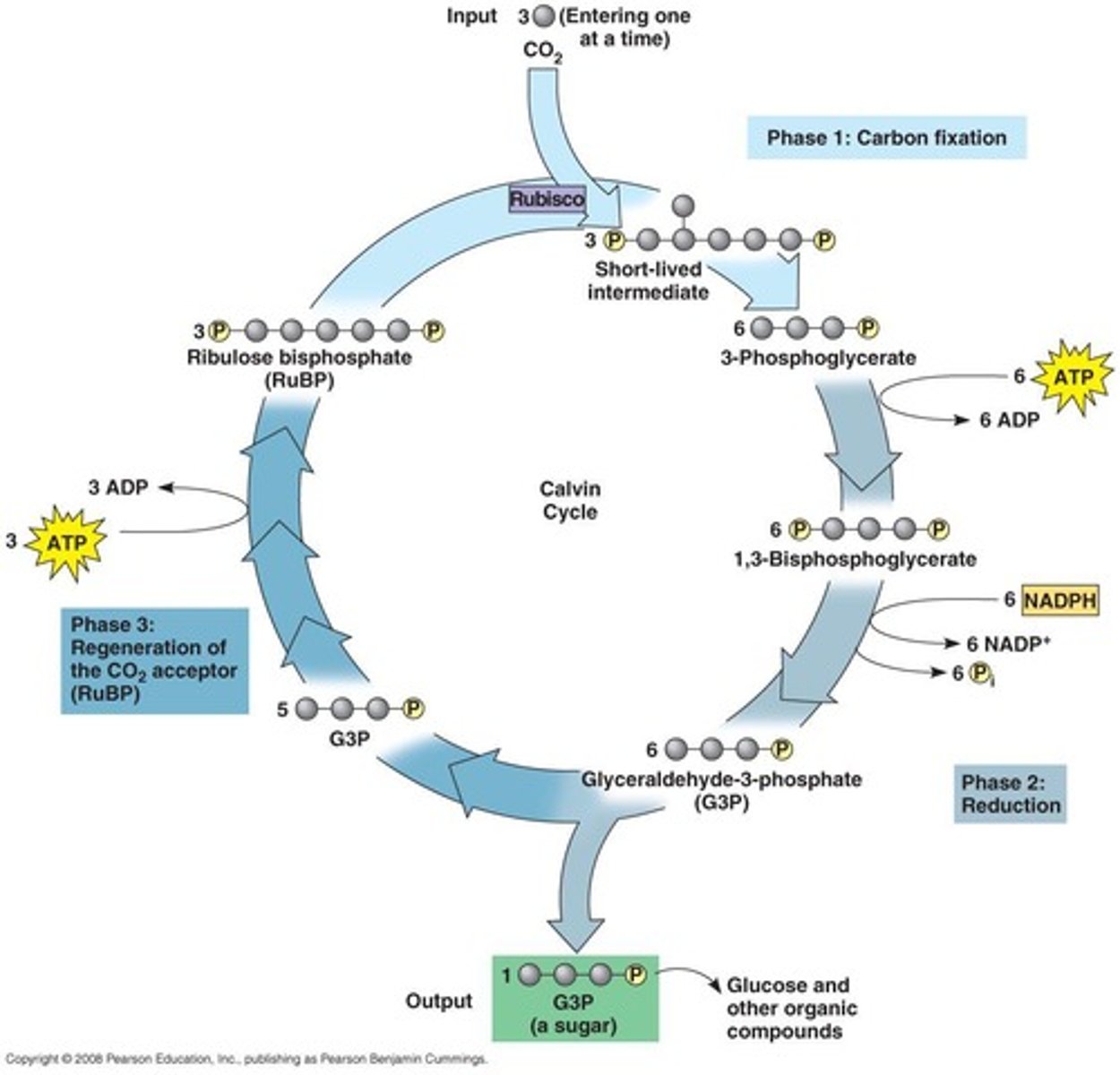
What is the Calvin Cycle?
The Calvin Cycle is a process where CO2 is fixed by RuBP to produce PGA, which is then converted into G3P.
What is Rubisco and its significance?
Rubisco is an enzyme that catalyzes the fixation of CO2 in the Calvin cycle, but it also binds O2, leading to photorespiration.
What is photorespiration?
Photorespiration is a process where Rubisco binds O2 instead of CO2, forming a useless product that must be converted back to CO2.
How does the concentration of O2 and CO2 affect Rubisco's activity?
In atmospheric conditions, Rubisco binds O2 about 25% of the time due to the higher concentration of O2 compared to CO2.
What are C4 plants and how do they differ from C3 plants?
C4 plants perform the Calvin cycle and C4 cycle simultaneously in different locations, using PEP carboxylase to fix CO2 more efficiently.
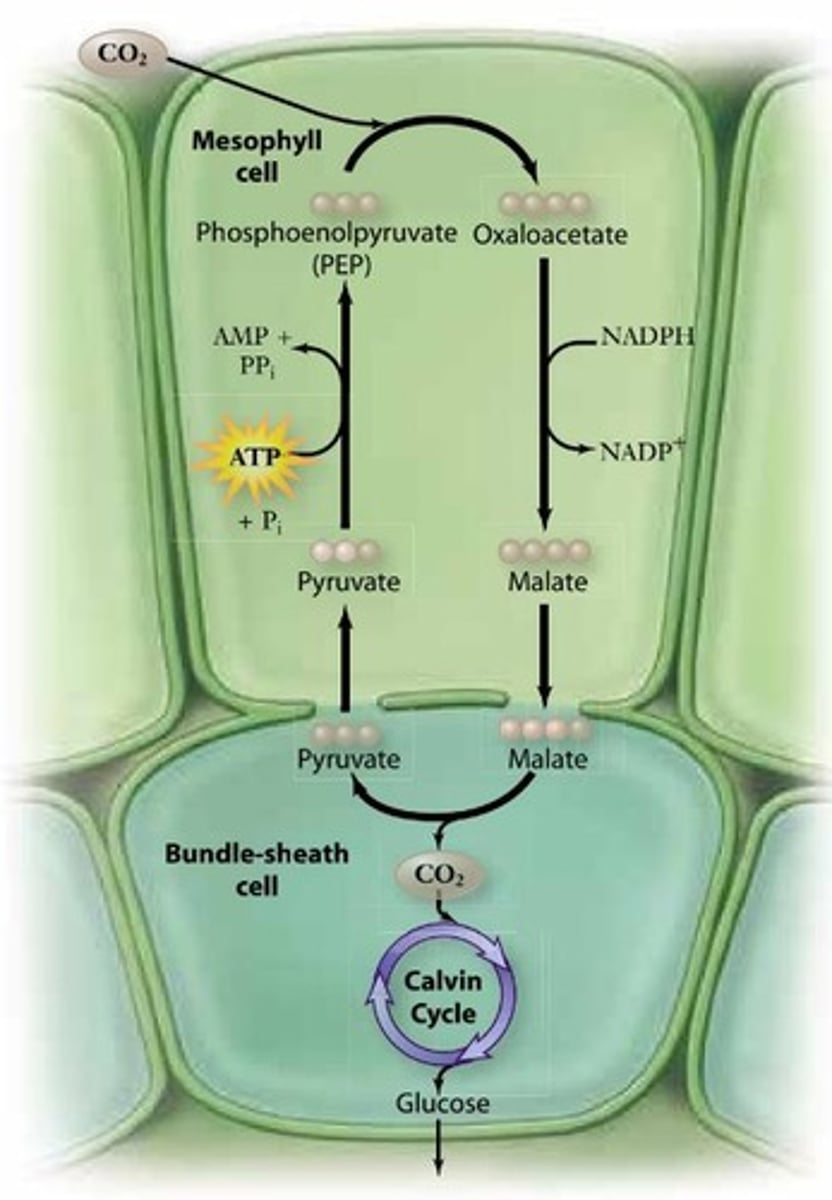
What is the initial step in the C4 cycle?
In the C4 cycle, CO2 reacts with PEP to form oxaloacetate, facilitated by the enzyme PEP carboxylase.
Why is the C4 pathway considered expensive?
The C4 pathway is expensive because it involves double hydrolysis of ATP to AMP.
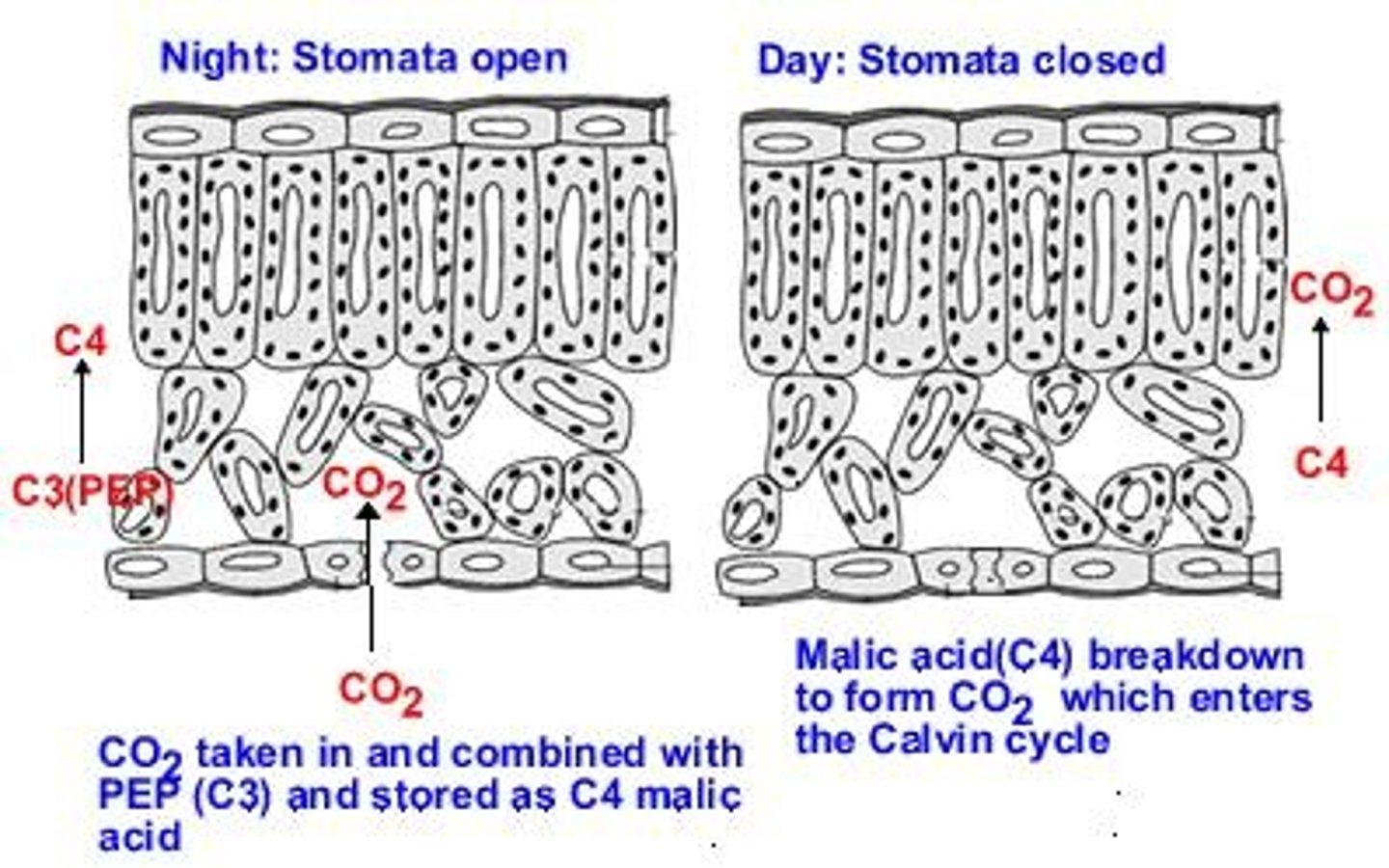
What are CAM plants and how do they function?
CAM plants open their stomata at night to fix carbon using the C4 cycle and perform the Calvin cycle during the day, all in the same cell.
What is the net equation for the Calvin Cycle per molecule of glucose?
6CO2 + 18ATP + 12NADPH + H2O → 2G3P + 16Pi + 18 ADP + 12 NADP+.
What are the three phases of the Calvin Cycle?
The three phases are carbon fixation, reduction reactions, and RuBP regeneration.
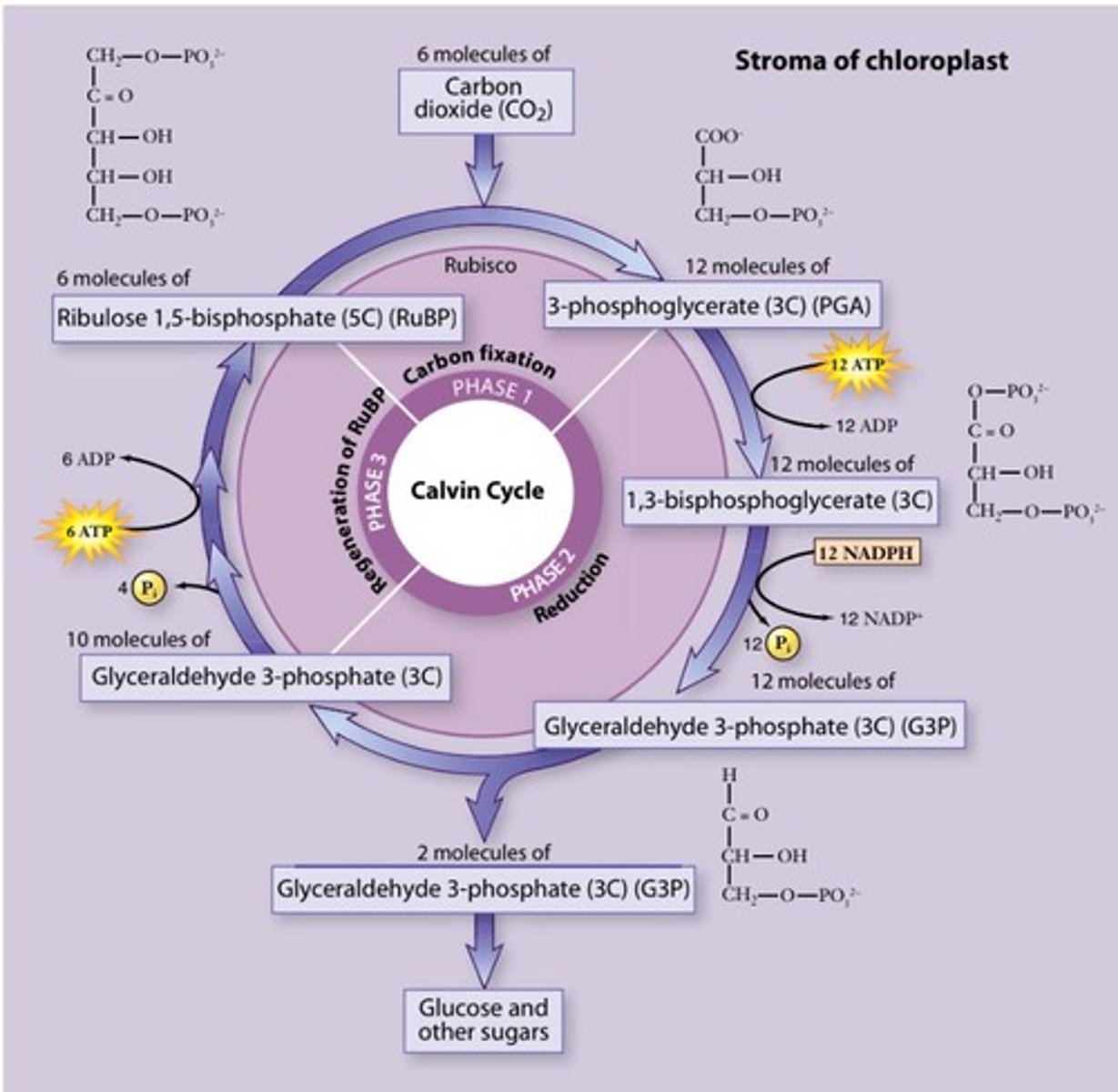
How many times does the Calvin Cycle occur to produce glucose?
The Calvin Cycle occurs six times to produce two G3P molecules, which are used to create glucose.
What happens during the reduction reactions of the Calvin Cycle?
The six 3C PGA molecules are phosphorylated by ATP and reduced by NADPH to form six G3P molecules.
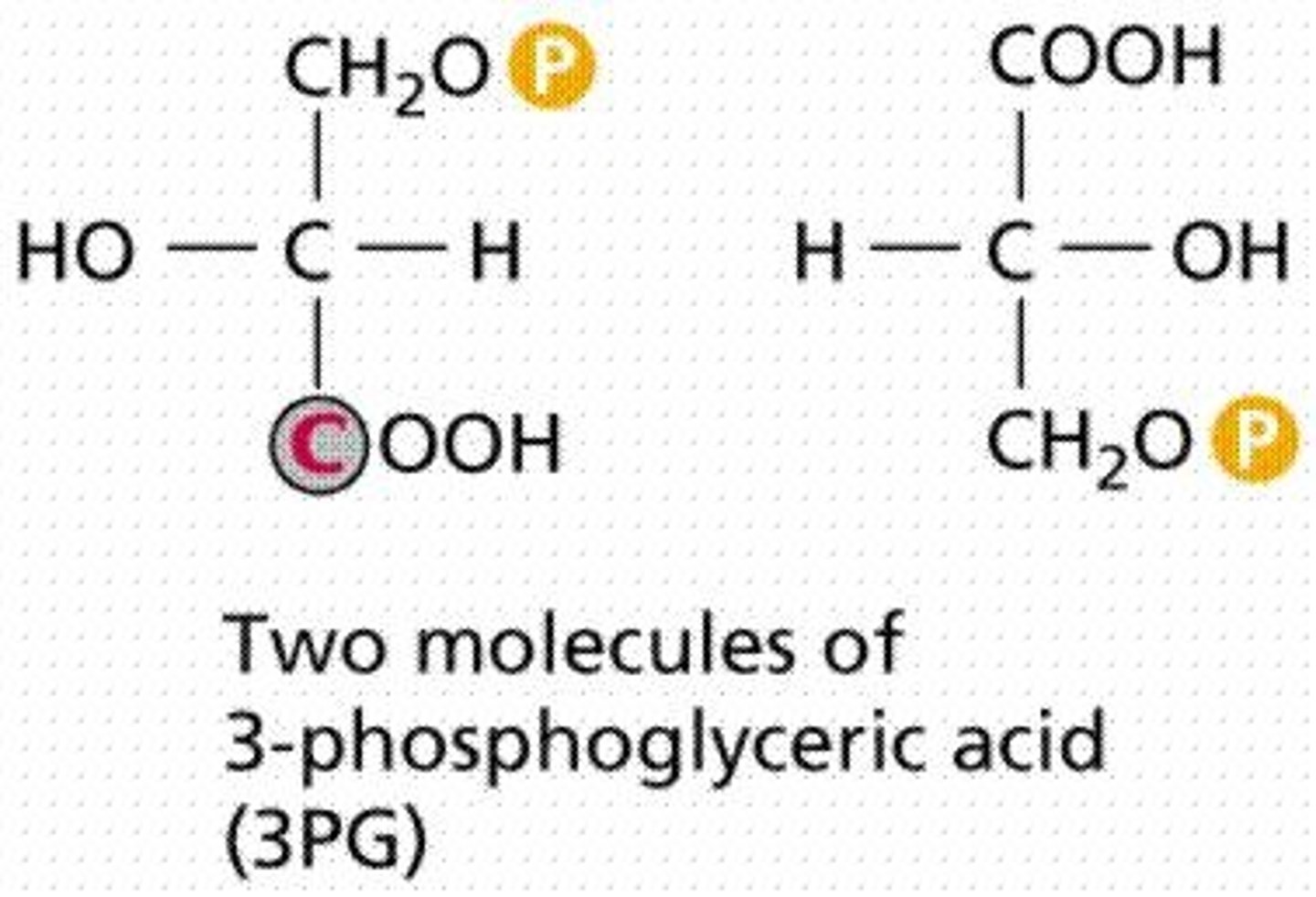
What is the role of G3P in plants?
G3P is used to make other molecules required by plants, mainly carbohydrates.
What adaptations do plants have to limit water loss?
Plants have evolved mechanisms such as closing stomata to limit water loss, which can also reduce gas exchange.
What is the significance of guard cells?
Guard cells regulate the opening and closing of stomata, balancing gas exchange and water conservation.
What type of conditions do C4 plants thrive in?
C4 plants thrive in hot, dry areas, such as corn and sugar cane.
What is the primary product of the Calvin Cycle?
The primary product of the Calvin Cycle is G3P, which can be used to form glucose.
What is the difference between light-dependent and light-independent reactions?
Light-dependent reactions convert light energy into chemical energy, while light-independent reactions (Calvin Cycle) use that energy to form carbohydrates.
What is the role of ATP and NADPH in the Calvin Cycle?
ATP provides energy, and NADPH provides reducing power for the conversion of PGA to G3P in the Calvin Cycle.