Clinical Chemistry Lecture 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
CLIA
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Act
CAP
College of American Pathologists
Borosilicate
Pyrex (volumetric), glassware
Corex
6x stronger than borosilicate, glassware
Low actinic
Amber or red for light-sensitive materials, glassware
Polypropylene
Plastic pipette tips, some specimen & test tubes (plasticware)
Polyethylene
Test tubes, bottles, graduated tubes, disposable transfer pipettes - binds or absorbs dyes, stains & some proteins (plasticware)
Polycarbonate
Graduated cylinders & flasks (plasticware)
Polystyrene
Rigid & clear, will splinter, capped graduated tubes and test tubes (plasticware)
Teflon
Chemically inert, wide temp range, used for stirring bars, tubing, bottle cap liners (plasticware)
Centrifuge
A rapidly rotating device to separate materials within a sample
Relative centrifugal force
Force * gravity
RPM
Revolutions per minute
RCF
1.1118×10-5 * r * rpm2 (r is rotor radius in centimeters)
TD
To deliver
TC
To contain (Sahli)
TD/Blowout
To deliver/blowout
Reverse osmosis
Water forced through a semi-permeable membrane, serves as a molecular filter
Distillation
Water is vaporized and then condensed
Deionization
Ion-exchange filters remove ions using anion or cation exchange resin
Molarity
Moles of solute per liter of solution; used to calculate the concentration of a solution Molecular weight * molarity = g/l
Normality
Gram equivalents of solute per liter of solution
Percent solutions:
# parts of solute per 100 parts of solution
Dilution
Mixing parts of the solute with parts of solvent
½ dilution
(1:1) 1ml serum + 1ml water = 2ml dilution
1/3 dilution
(1:2) 1ml serum + 2ml water = 3ml dilution
1/10 dilution
(1:9) 1ml serum + 9ml water = 10ml dilution
Electromagnetic Radiation
The wavelengths of light on the visible and invisible spectrum
Spectrophotometry
Used to detect colored reactions via the intensity of the color, or the appearance or disappearance of color
Light reflection
The reason to see colors on an object
Creatinine
The measurement for absorbance is 500nm, which is in the blue-green region, reflects red.
A = abc = ebc
A = absorbance
a = absoptivity (extinction coefficient e)
b = path length of cell (cm)
c = concentration
Beer-Lambert Law
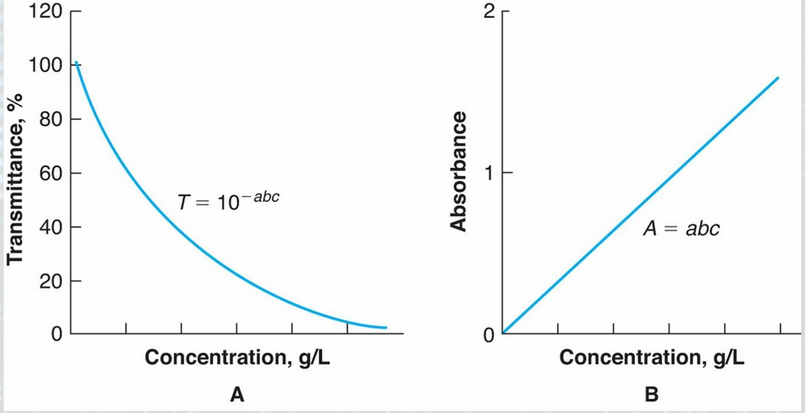
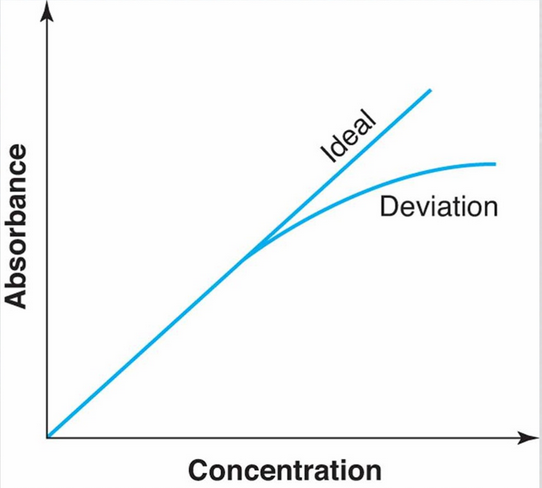
Beer-Lambert Law: Measurement Range
Spectrophotometers
A machine that measures light at a selected wavelength/spectrum
Photometers
A machine that measures light without specifying wavelength
Chromogen
An added chemical to a sample to help change the color
light
Wavelength selector
Sample holder/cuvette
Photodetector
The basic components of a spectrophotomer
Tungsten or Tungsten halogen
EMS Lamps
Deuterium
UV Radiation lamps
Monochromator
A component that selects the wavelength of light in a narrow band
Prism
A monochromator that uses refraction to create visible light
Cuvette
A component that holds the sample when reading
Photodetector
A component that converts light into electrical signals
<1%
The maximum amount of stray light allowed in a spectrophotomer
Reflectometer
A photometer that measures the amount of light reflected by a liquid sample dispensed on a non-polished surface (such as urine dipstick and dry chemistry slides)
Refractometry
Based on the refraction of light as it passes through a medium, such as glass or water.
Fluorometry
Involves exciting compounds with EMR (high energy, short wavelength) and detecting emitted EMR (lower energy, longer wavelength).
Chemiluminescence
A type of luminometry where Light that is produced from a chemical or electrochemical reaction (produces light without heat)
Electrochemiluminescence
A type of luminometry that uses an electrode, and can be detected with photomultiplier tube
Nephelometry
Measurement of light scattered by a particulate solution (Ag-Aby)
Turbidimetry
Measurement of reduction in light transmission caused by particle formation
Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS)
Primarily used for metals; absorbs EMR unique to that metal, detector picks up unabsorbed monochromatic EMR
Potentiometry
The measurement of electrical potential (voltage) between two electrodes in an electrolyte solution
Potentiometry ion selective electrodes
Membrane based electrodes that only allow specific ions to pass and be measured
pH electrodes
Glass electrodes that measure hydrogen ion activity
PCO2 electrodes
A pH electrode with sodium bicarb at the reference electrode
Direct ISE
Use undiluted samples, sensitive to free ions; doesnt detect bound ions; not affected by high protein or high lipids
Indirect ISE
Use diluted samples (chem analyzers), interfered by high protein and/or lipids; will underestimate the electrolyte concentration
Conductometry
Measures electrolytic conductivity; current is proportional to amount of ions; electrical conductance can be used to assess water purity (high reading = more ions/ low reading = pure)
Coulometry
Based on amperometry
Chromatography
Separation techniques; separates individual compounds from a mixture based on physical and chemical interactions of those compounds in the sample
Retention Time
Related to strength of interaction with stationary phase
Resolution
The ability in chromatography to separate two or more analytes in a sample
Short Retention TIme
A compound that favors the mobile phase; exits the stationary phase the quickest
Ion-exchange chromatography
Uses an ion-exchange mechanism to separate analytes based on their charge; uses a charged stationary phase, like an ion-exchange resin column
Partition/Liquid Chromatography
Based on the differential distribution of solutes between two immiscible (doesn’t mix) liquids which act as the stationary phase and the mobile phase
Adsorption Chromatography
Uses electrostatic hydrogen bonding to separate compounds by adsorption and desorption of solutes at the surface of a solid particle
Affinity Chromatography
Liquid technique that uses biological interactions like the binding of enzymes with substrates, ligands with receptors, or antigens with antibodies
Size-Exclusion Chromatography
Gel or filter pores sort molecules by size
Planar chromatography
Solid phase is a plane (flat) like paper or a layer of media, ex: thin layer chromatography
Column chromatography
Stationary phase is coated onto support particles that are packed into a tube or capillary; ex: ion-exchange chromatography
Gas chromatography
Uses a gas mobile phase (carrier gas) and a column stationary phase; solutes separate based on vapor pressure differences (volatility)
Liquid Chromatography
Uses a liquid mobile phase with very small stationary phase particles and pressure
Mass spectrometry
Used to identify unknown compounds, determine concentration of known substances, study molecular structure of organic and inorganic material
Ionization source
A device that ionizes the target molecule then separates and measures the mass of the molecule and its fragments
Electron impact ionization
Uses a beam of electrons to fragment the molecules in the sample
Matrix-assisted Laser Desrption/Ionization
Soft ionization that does not produce fragments; uses UV laser and a matrix in which the sample is embedded; used in bacterial identification
Inductively Coupled Plasma
An inert gas (argon) is inductively heated via current through a surrounding electromagnetic coil to form a plasma. The sample (typically in liquid form) is inserted, aerosolized, and digested in the plasma into ion fragments
Electrospray ionization
Ion source of choice for LC-MS; applies a high voltage to a liquid to produce an aerosol
Quadrupole mass spectrometer
Filters sample ions based on their m/z ratio; their detection is determined by the stability of their trajectory in an oscillating electrical field
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer
m/z ration is determined by a time measurement in an electrical field of known strength and a known length of detector
Tandem Mass Spectrometer (MS/MS)
Two MS end to end; the first MS selects the parent ions by m/z, the the collision cell fragments the parent ions, then the second MS acquire the mass of the fragment ions
Electrophoresis
Separation of charged compounds in a liquid medium under the influence of an electrical field
Zone electrophoresis
Uses agarose gel to separate by charge
Isoelectric focusing electrophoresis
Uses a polyacrylamide gel with a pH gradient that immobilizes proteins at their neutral pH
Capillary electrophoresis
Uses a narrow bore, fused silica capillaries to separate large and small molecules and uses high electric field strengths. Separates on charge, size, and hydrophobicity
Blotting techniques
separation of DNA and DNA fragments by agarose gel electrophoresis, then blotted on nitrocellulose paper and detected with a hybridized nucleic acid probe
Osmolality
Osmotic pressure governs movement across membranes
Osmometry
The measurement of osmolality of a solution (serum or urine)
Freezing-point osmometer
Sample is supercooled; temperature is then rised back to the freezing point, which causes crystallization)