7.1 - Chromosomes, Sex
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What are the layers of sexual identity? (4)
chromosomal, gonadol, anatomical, psychological
Sexual reproduction involves creating new individuals _______ distinct from parents.
genetically
Organisms produce special reproductive cells called ______.
gametes
What’s unique about gametes though in comparison to other chromosomes?
contains half the usual genetic material
humans have __ pairs of chromosomes
23
They have __ pairs of autosomes
22
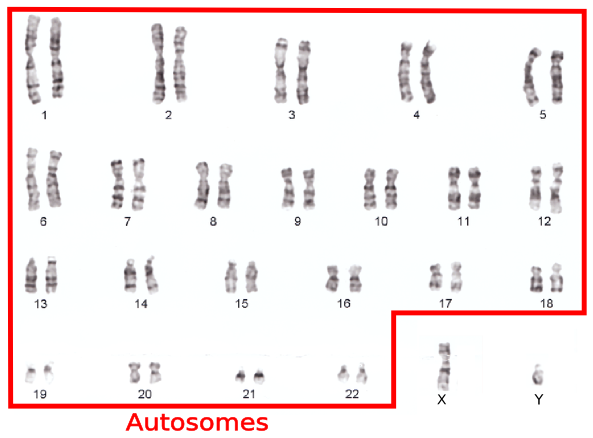
The autosomes are ________ and direct _____ ________.
homologous; human biochemistry
humans have one pair of ____ chromosomes
sex
Of the sex chromosomes; there is ALWAYS one ___ chromosome.
X
Female chromosomes:
XX
Male chromosome:
XY
The Y chromosome carries about how many genes?
70
What is the most important gene on the Y chromosome?
SRY gene
SRY gene produces →
testes determining factor (TDF)
Around week 3 of embryonic development, what event occurs?
X-inactivation
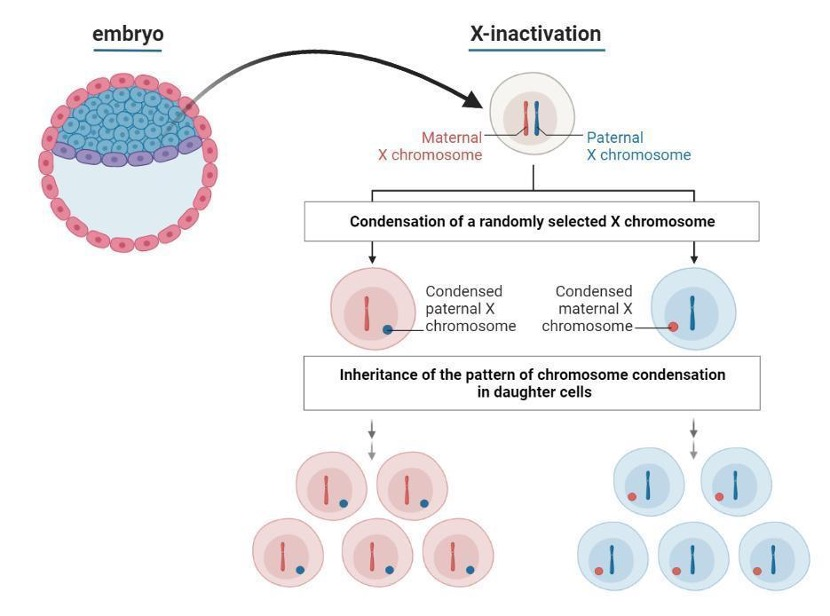
What occurs to the chromosomes during X-Inactivation?
all but one X chromosome in each cell condenses
Why does X-inactivation occur? (note: mostly happens to females, males X only kinda silenced)
to prevent gene overdosage from the X chromosome
Trisomies are when →
there are 3 copies of a chromosome rather than 2
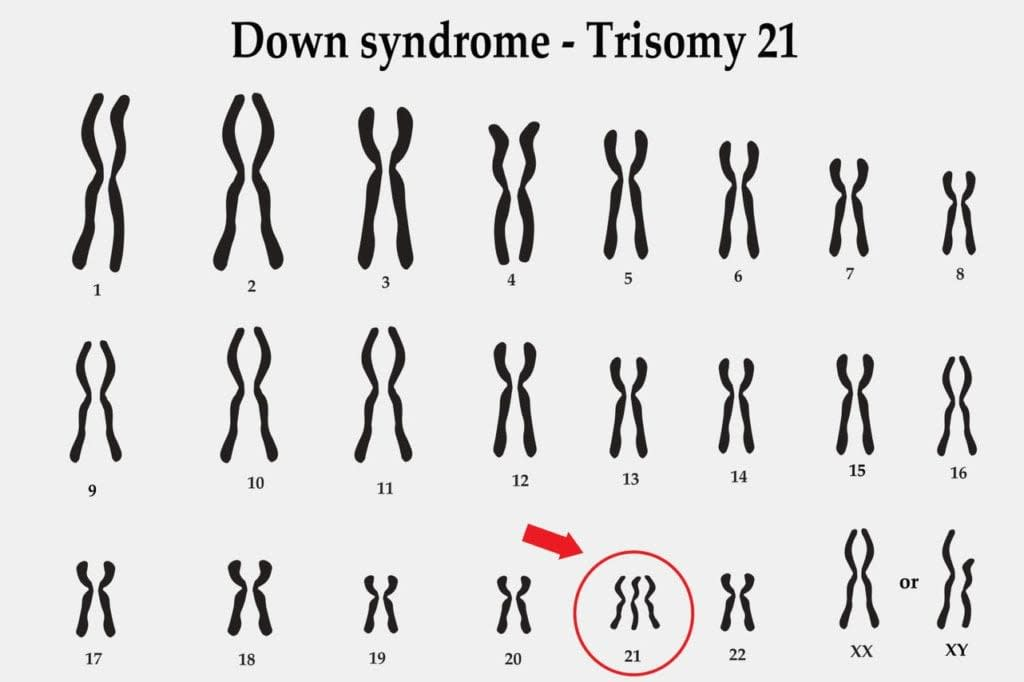
Most trisomies are fatal, except if on chromosome ___. That person will have _____ ______.
21; down syndrome
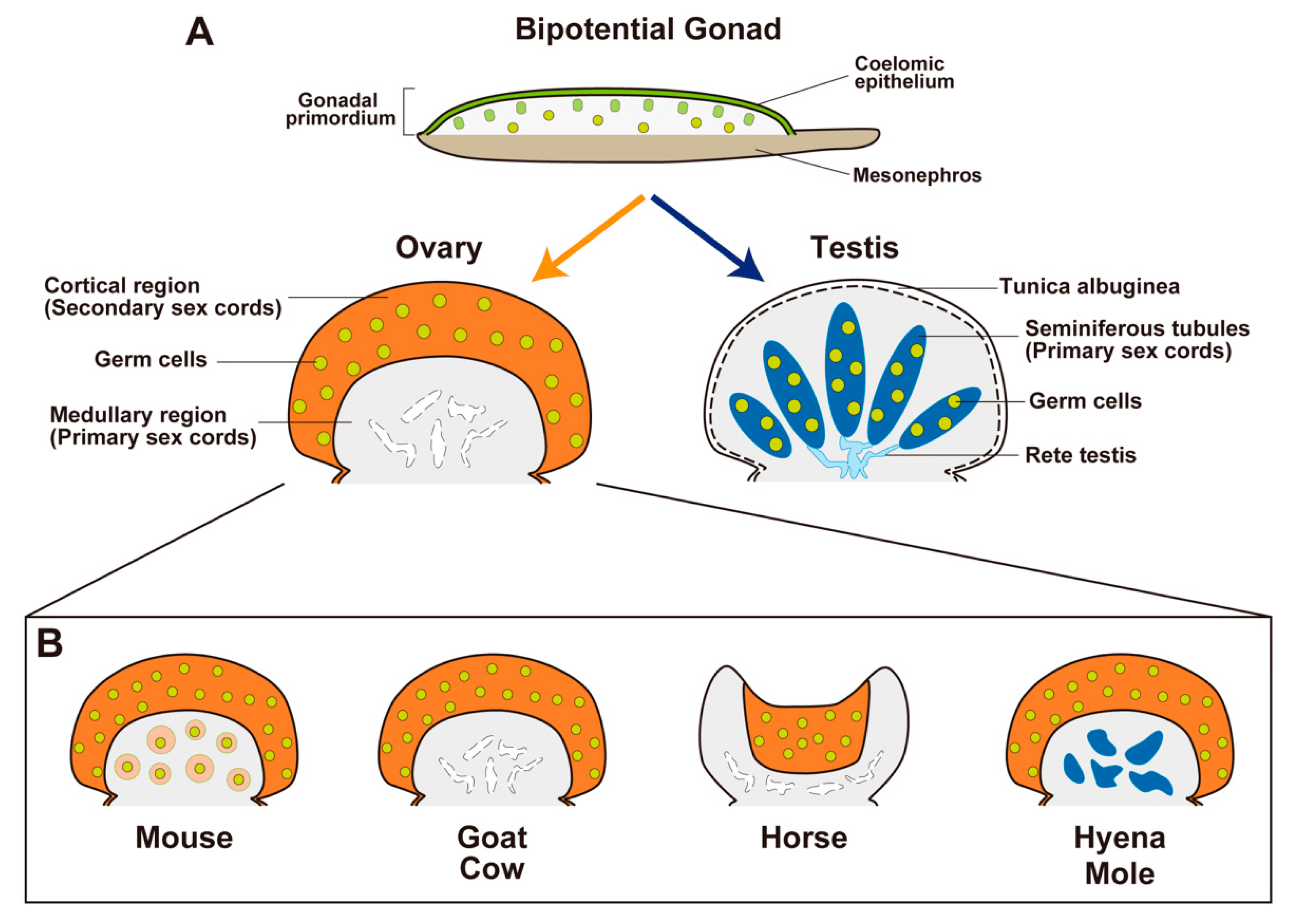
Embryos begin/start with what type of gonads?
bipotential gonads
By week ___-__, the gonads differentiate.
6-8
The gonads differentiate into XX →
ovaries
Gonad differentiation for XY → ____ _____ ____→ _____
SRY produces TDF → testes
Anatomical differentiations begin around ___-__ weeks.
8-12
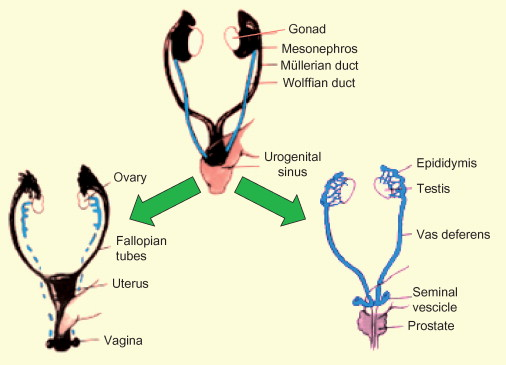
Internally, all embryos begin with how many sets of ducts?
2
What is the name of the 2 internal sets of ducts?
mullerian and wolffion ducts
In XX chromosomes, the Mullerion ducts become → (3 organ structures)
uterus, fallopian tube, upper 1/3 of vagina
In XX chromosomes, the Wolffion ducts become →
degenerated (become tiny vestigial structure)
In XY chromosomes, testes produce _______. (hormone)
testosterone
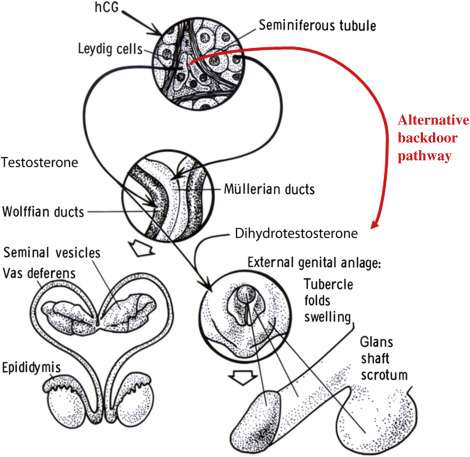
In XY chromosomes, the Wolffion ducts become → (3 structures)
epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vessicles
In XY the mullerian ducts →
degenerate (anti-mullerian)
External Anatomy:
By __ weeks, embryos have ______ ______.
8; ambigous genitalia
What are the external ambigious genitalia of the embryos? (not specific yet, 3)
genital tubercle, labioscrotol swellings, urethral folds
For XX, the genital tubercule turns into the →
clitoris
For XX the labioscrotal swellings turn into →
labia major
For XX, the urethral folds turn into → (2)
lower 2/3 of vagina, labia minora
For XY genital tubercule turns into →
head (glands) of penis
For XY labioscrotol swellings turn into →
scrotum swellings
For XY urethral folds turn into →
shaft of penis
XY produces testes which produce testosterone, but testosterone must be converted into _________.
dihydrotestosterone (DHT; more potent version)
What enzyme convertes testosterone → dihydrotestosterone?
5-alpha reductase
Define Aneuploidies?
chromosomal abnormalities (defined by atypical number of chromosomes → leads to genetic disorders)
Turner Syndrome has what chromosome pair?
XO (only one X chromosome, not 2)
1 in every _____ people have Turner Syndrome?
2000
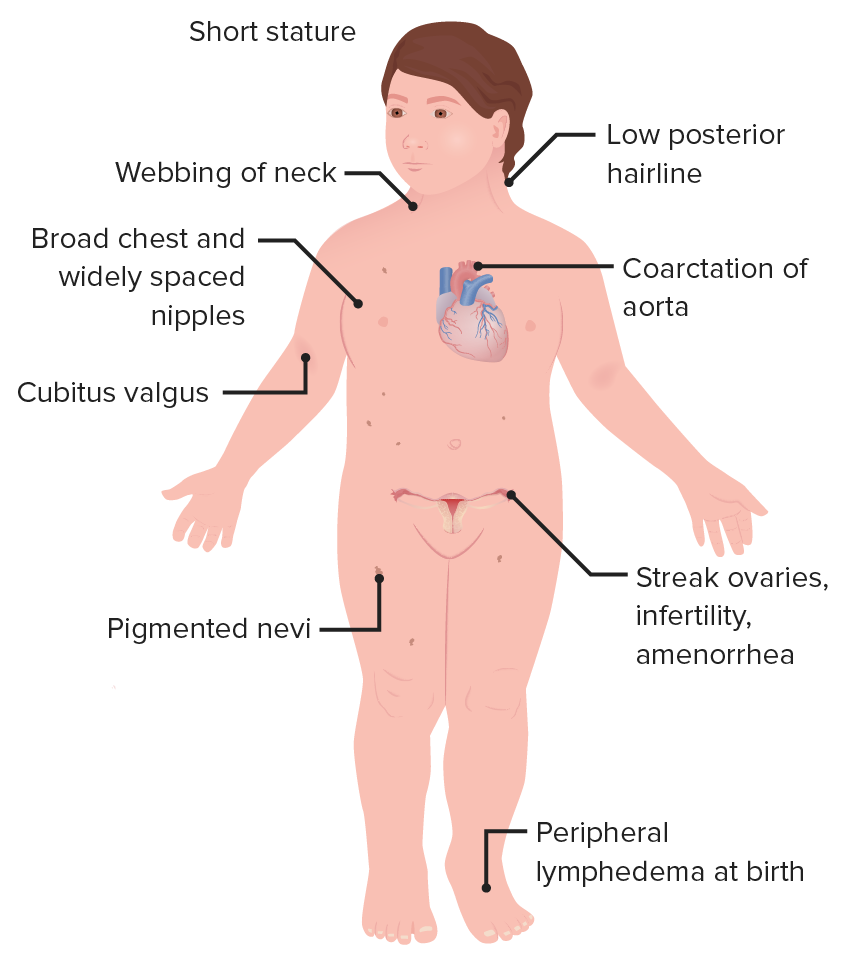
Turner Syndrome is characterized by: (6)
short, webbed neck, has ovaries & typical female anatomy, few secondary sex characteristics, usually infertile
Klinefelter syndrome has what chromosomal trisomy?
XXY (extra X chromosome)
1 in every ______ people have Klinefelter Syndrome.
1000
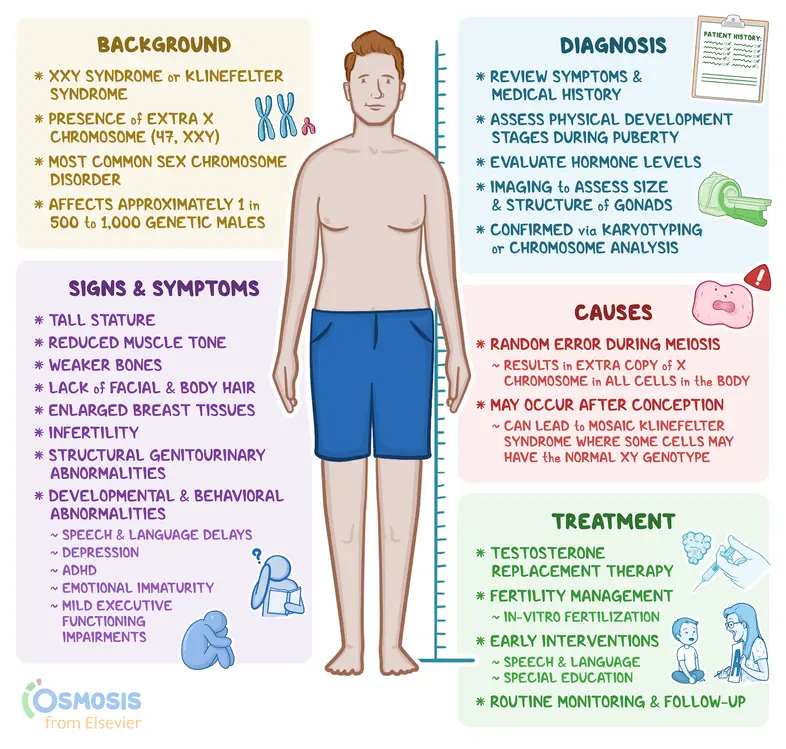
Klinefelter syndrome is characterized by: (9)
male anatomy, masculine identity, tall height, small testes, little body hair, less muscle, some breast/hip development, some signs of infertility
Triple X Syndrome involves what trisomy?
XXX
1 in _____ people have triple X syndrome.
1000
Are there any clear symptoms of XXX?
no
XYY is seen 1 in every _____ people. No clear signs also (even less than XXX)
1000
So name all the chromosomal Aneuploidies that were just mentioned (just chromosomal pairings) → (4)
XO, XXY, XXX, XYY
Other atypical patterns involve XX with ____ gene.
SRY
XX with SRY gene become an XX male → They get ______ gender identities, typically smaller/lighter, usually infertile.
masculine
XY with non-functional SRY leads to what syndrome?
Swyer Syndrome
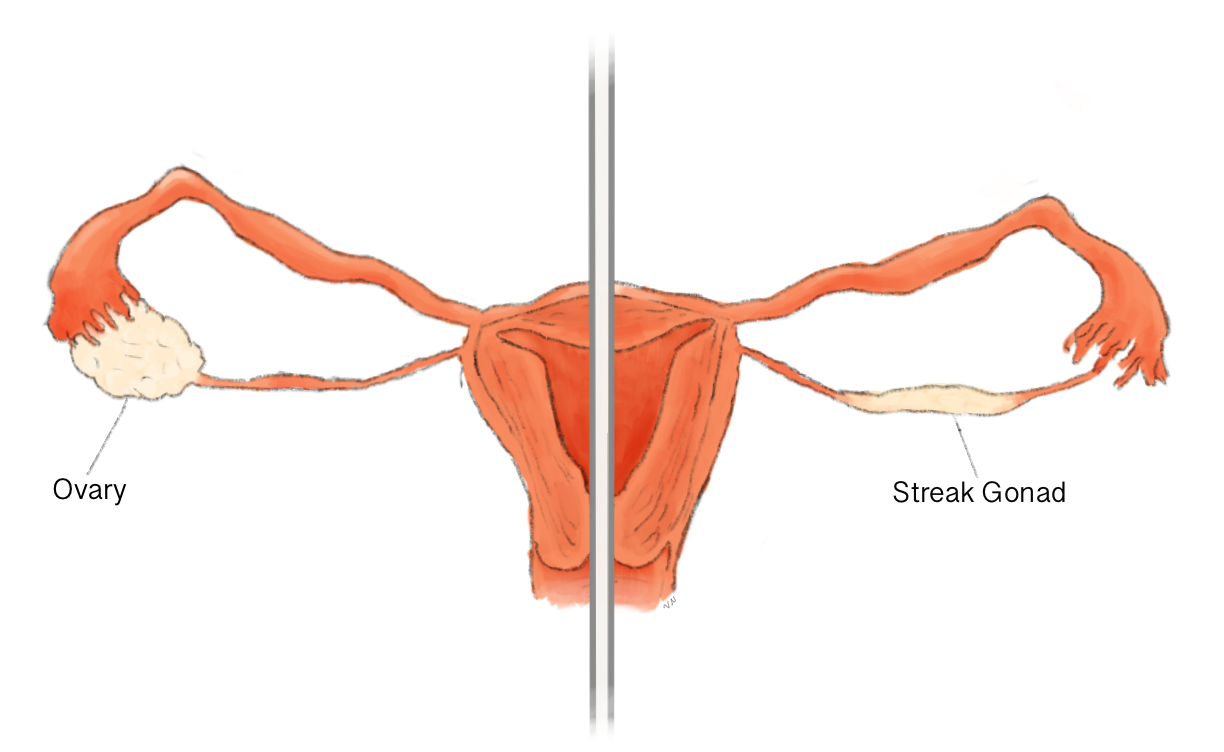
What type of gonads to those with Swyer Syndrome get?
streak gonads
People with Swyer Syndrome are almost always _____.
infertile
Do people with XY w/ nonfunctional SRY develop secondary sex characteristics? (without the help of supplementary hormones)
no
What type of anatomy do people with Swyer Syndrome get?
female anatomy
Androgen Insensitivity is when (AIS) →
testosterone receptor is nonfunctional/partially functional
Complete Androgen Insensitivity (CAIS) for XY causes → (2 characteristics)
internal testes
external female genitals
What do people sexually identify theirselves as with CAIS?
female
People with CAIS is typically unrecognizable at ____.
birth
Partial Androgen Insensitivity (PAIS) leads to →
ambiguous external genitalia (partial androgen response)
What occurs with Congenital adrenal hyperplasia?
adrenal cortex doesn’t produce cortisol
Does Congenital adrenal hyperplasia affect XX or XY?
XX
For XX, an overproduction of ACTH causes the adrenal cortex to be _________ so it will produce _______ (hormone).
overstimulated; testosterone
The adrenal cortex producing more testosterone in a XX person causes the genitals to be _____.
ambigious
5-alpha reductase deficiency shows up in ___ people.
XY
So, the XY folks can produce testosterone, but since they have 5-alpha reductase deficiency, they can’t convert to ________.
dihydrotestosterone
People with 5-alpha reductase deficiency may be assigned _____ at birth, but once puberty occurs, they get a surge of _______.
female; testosterone
This surge of testosterone that occurs for the ppl with 5-alpha reductase deficiency at puberty causes development of their _____ ______ more.
male genitals
So for ppl with 5-alpha reductase deficiency; the “large clitoris” developes into →
small penis
People with XY 5-alpha reductase deficiency typically have a strong _____ identity.
masculine