M1: L3: Animal Characteristics and Development
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
When did the most recent common ancestor of all living things first formed?
about 3.5 BYA
When did the two other kingdom (eukarya and archaea) formed?
about 3 BYA
When did animals first formed?
about 700 MYA
What are the characteristics of animals?
1) multicellular eukaryotes
2) heterotrophic
3) sexually reproducing
4) highly mobile (in at least 1 stage of life)
5) have tissues
a) muscle
b) nerve
heterotrophic means eating other organisms
T/F - Muscle and nerve tissues is not unique to animals.
false
define tissues.
specialized cells that func tgt
T/F - Sponges do have tissues.
false
T/F - Cnidarians are triploblastic.
false - they’re diploblastic
how many tissues do other animals have besides the sponges and cnidarians?
triploblastic
What are the 3 tissue layers? What do they give rise to?
ectoderm becomes the outer covering (epidermis)
endoderm becomes the digestive tract
mesoderm becomes the muscle and most of the other organs
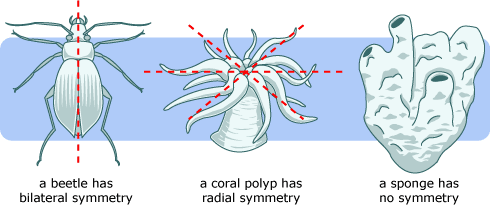
define bilateral symmetry.
cut in only ONE DIRECTION in the middle of any organism and it gives mirror images
What are the stages of animal development?
zygote —> cleavage: 2 cells —> 4 cells —> 8 cells —> morula —> blastula —> gastrulation: gastrula
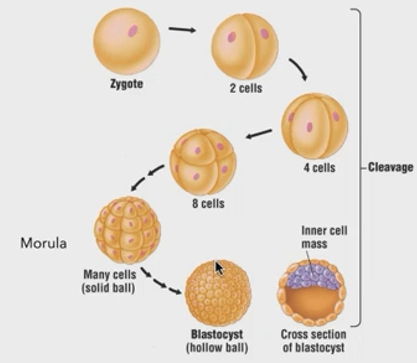
define morula.
solid ball of cleaved cells
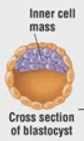
define blastula (blastocyst).
outside: cleaved cells
inside: inner mass of cells or blastocoel
define cleavage.
1) a form of mitosis where identical copies of cells are made
2) volume of the cells do not change either
define blastocoel.
empty space inside the blastula (blastocyst)
define gastrulation.
the formation of a gut
grastrula means belly
What are parts of the gastrula?
1) blastopore
2) archenteron
3) endoderm
4) blastocoel
5) ectoderm
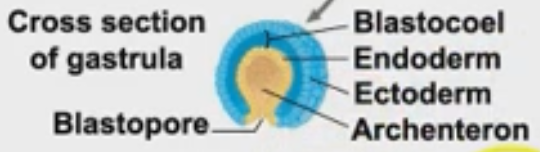
define blastopore.
the opening of the gastrula
define archenteron.
the tunnel inside the gastrula
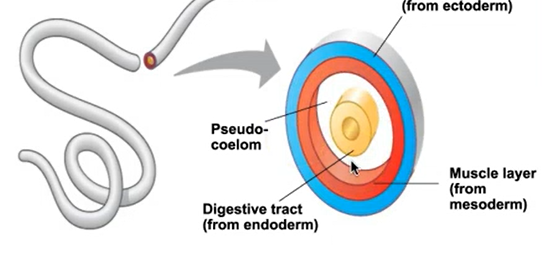
what are the 3 types of tripoblastic animals?
acoelomate, coelomate, and pseudocoelomate (or hemocoelmate)
define acoelmate
tissue-filled region completely filled by the mesoderm
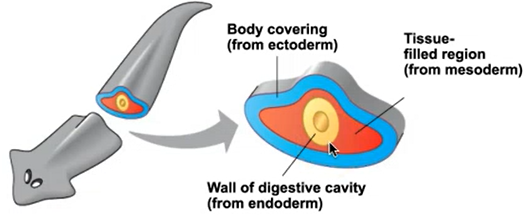
define coelomate.
true body cavities completely lined by the mesoderm
define coelom.
an empty cavity that suspends (holds) internal organs
define pseudocoelomate (hemocoel).
animals that have a fluid-filled cavity which is not completely lined by the mesoderm
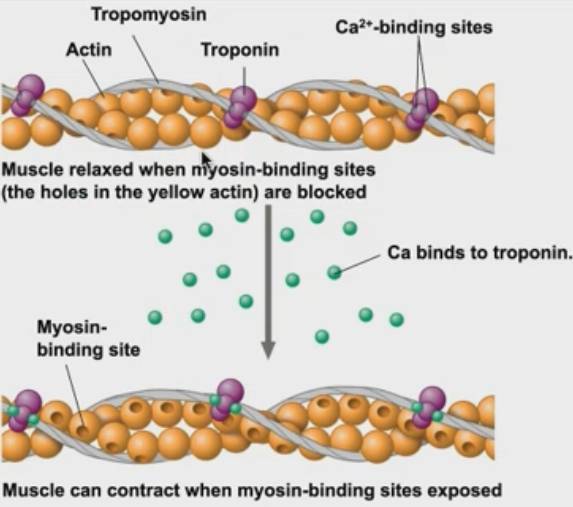
What makes up the muscle?
a bundle of muscle fibers —> made of a single muscle fiber —> (made of a single cell with multiple nuclei) —> surrounded with p.m —> made of myofilaments
define sacromere.
a contractible, functional unit of muscle cells
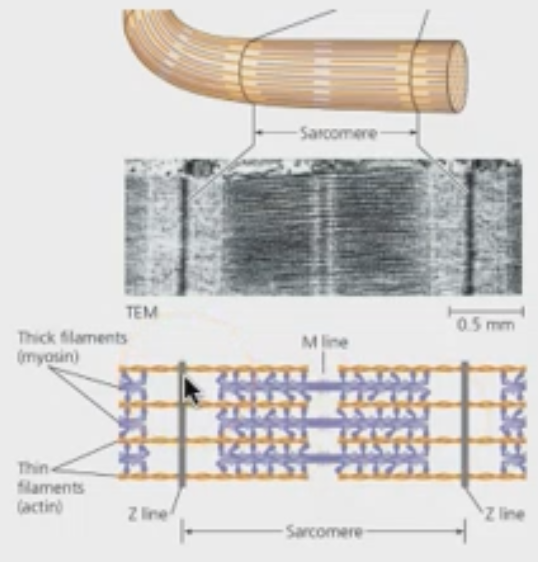
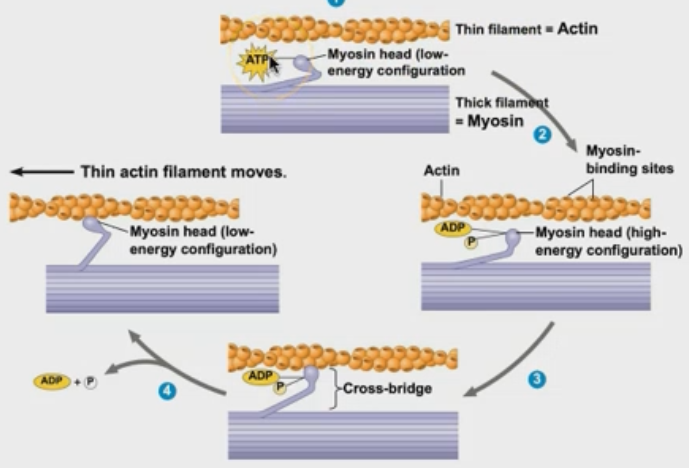
What are the two types of muscle filments?
thin filament made of actin
thick filament made of myosin
Rank the stages of muscle contraction from the shortest sacromere to the longest sacromere.
1) fully contracted muscle
2) contracting muscle
3) relaxed muscle
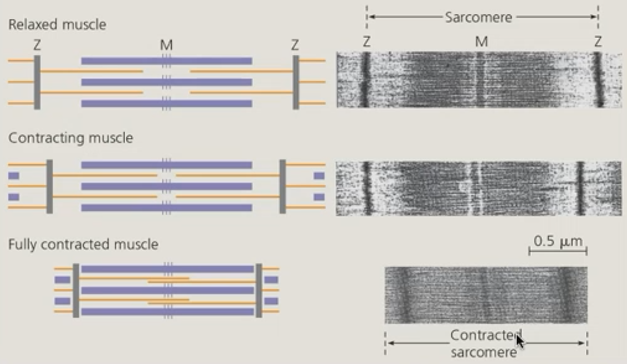
T/F - When muscle contracts, the sarcomere elongates.
false - it shortens
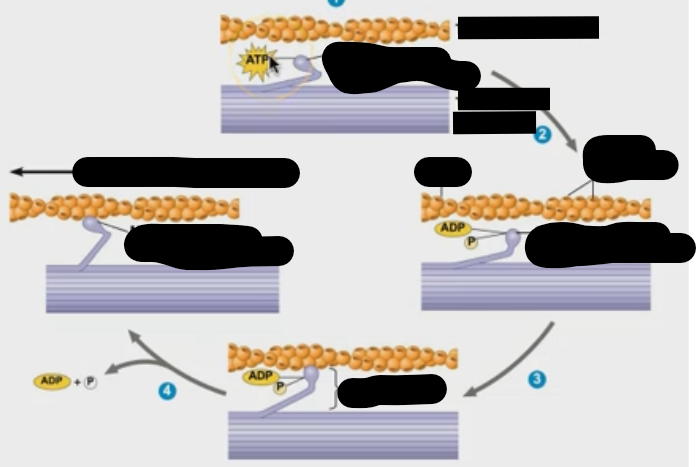
How do muscles contract?
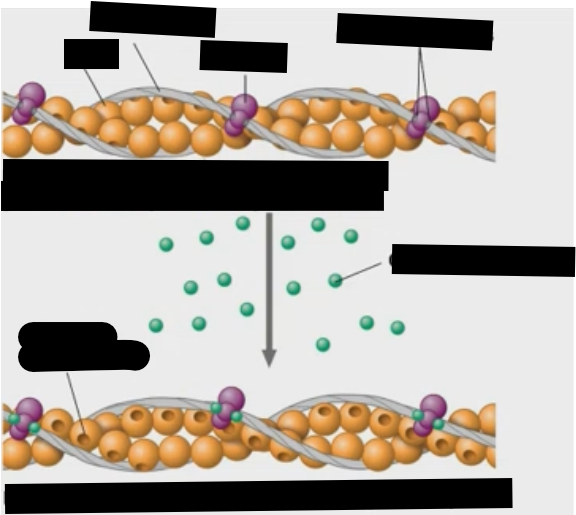
How does a neuron tell a muscle to move?
What are the 3 types of muscles?
1) smooth
2) skeletal
3) cardiac
What are the func.s of the skeletal (striated) muscle?
1) voluntary
2) attaches to the skeleton
3) used for movement
voluntary means the brain can control the movement of muscles
What are the func.s of the cardiac muscle?
1) has striations, but not as pronounced
2) involuntary
3) ONLY found in the heart
What are the func.s of the smooth muscle?
1) slower, but more sustained
2) involuntary
3) lining of the digest tract, bld vessels, urinary tract, etc.
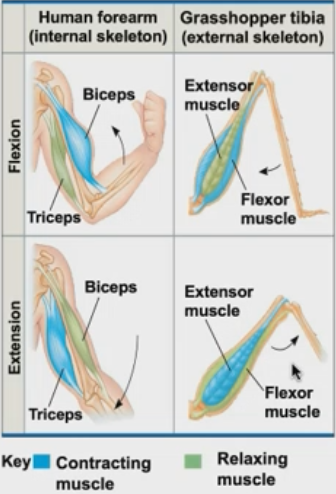
Give an example of how skeletal muscle moves.
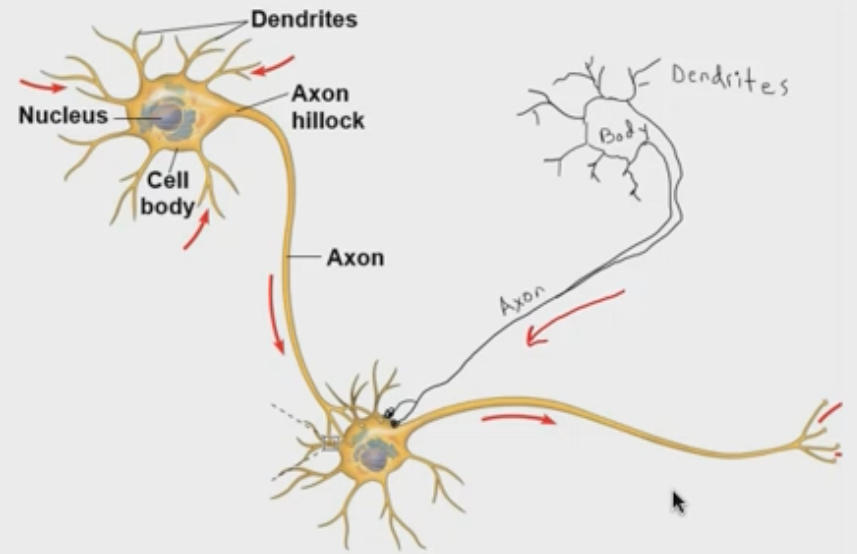
What is the func of a dendrite?
receive signals from other neurons
func of axon
deliver signals to other neurons
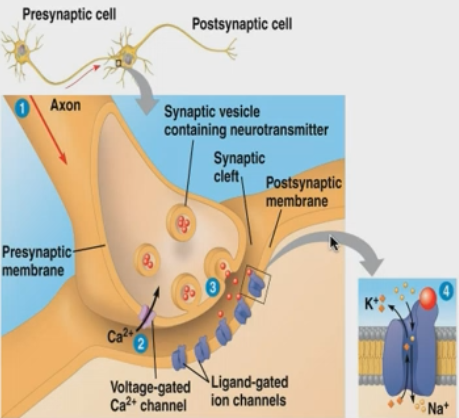
func of synapse
neuron to neuron communication
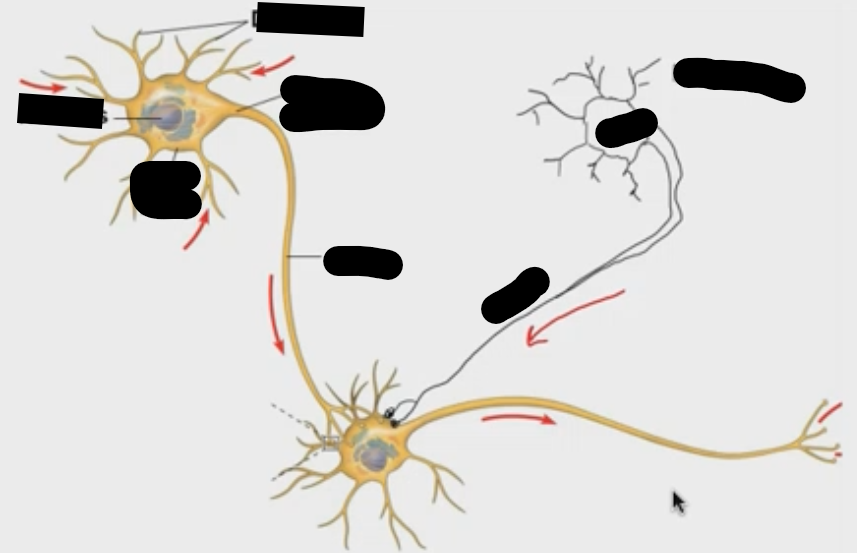
What is the structure of a neuron?
1) synapse
a) presynaptic cells
b) postsynaptic cells
What is the resting potential of a neuron?
diff in charge across the plasma membrane of a neuron
inside cell/neuron: more neg ions
outside cell/neuron: more positive ions
at ~ 90 mV
what maintains the resting potential of a neuron?
Na+/K+ pump —> slow process by ACTIVE transport
3 Na+ out of the cell and 2 K+ inside the cell
Ion channels (open pores) —> fast process by PASSIVE transport
more K+ channels, so the K+ molecules rapidly diffuse out
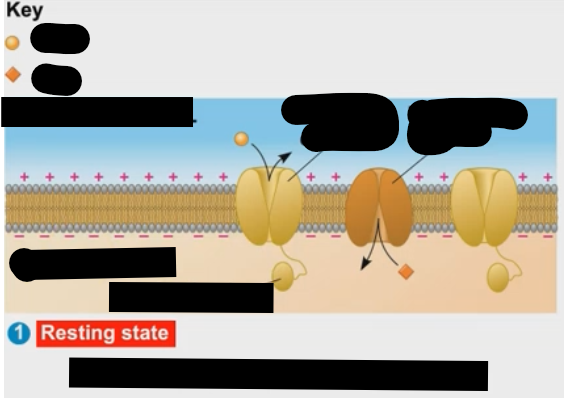
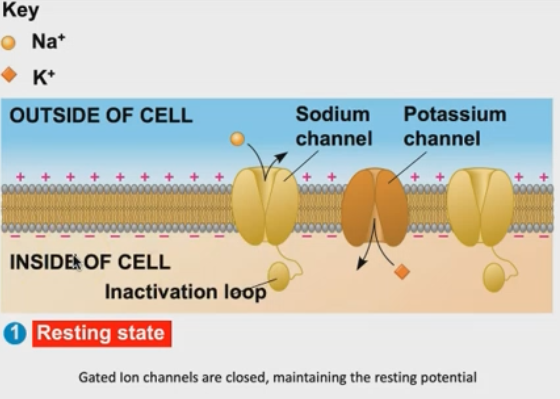
What is happening at the resting state of the neuron?
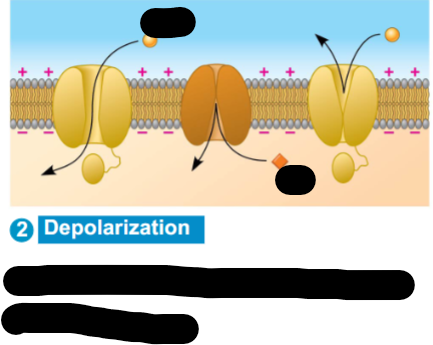
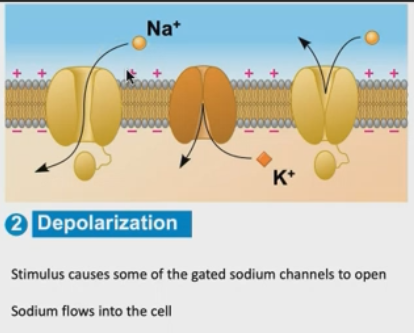
What is happening at the depolarization stage?
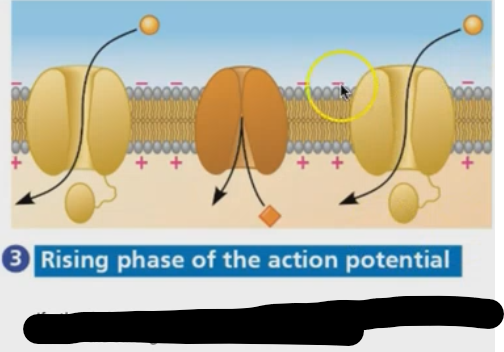
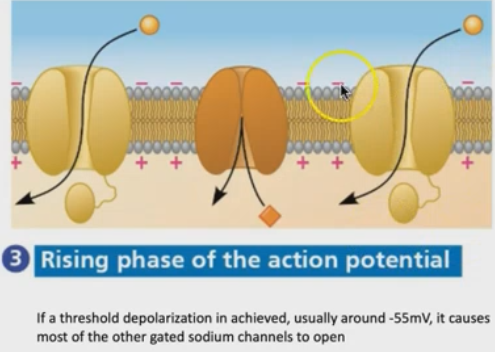
What is happening at the rising phase of the action potential?
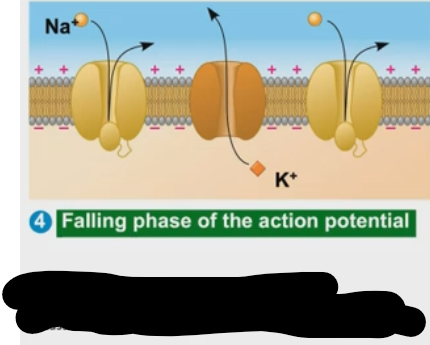
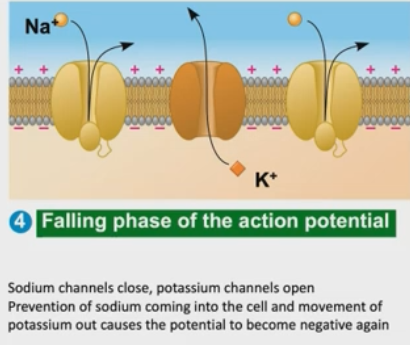
What is happening at the falling phase of the action potential?
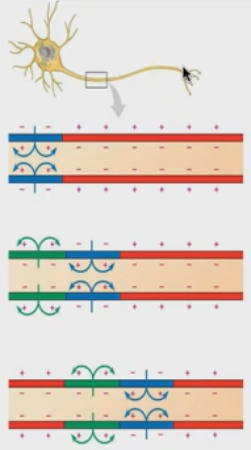
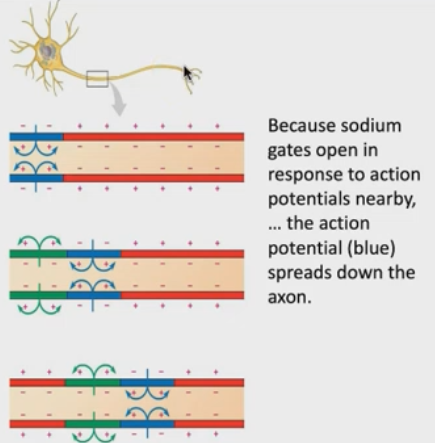
How does the action potential spead down the axon?
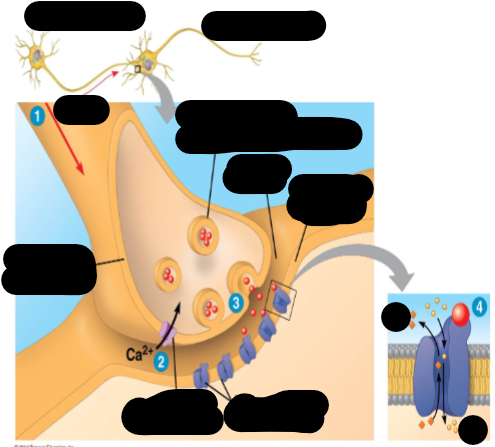
How do neurons communicate with each other?
1) action potential moves down the acon
2) voltage-gated channels open and allows the flow of calcium in
3) synaptic vesicle binds with membrane, releasing neurotransmitter
4) neurotransmitters bind with the ligand-gated ion channels, triggering an action potential in postsynaptic cell