(COPY) Kinesiology - PSK4U1 Exam Review
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
141 Terms
Kinesiology
the scientific study of human body movement
anatomical position
In an upright standing position, face and feet pointing forward, arms at the side, forearm fully supinated (palms facing forward)
general rule of plane and axis
axis of rotation is perpendicular to the plane of movement
anterior
front surface of body
posterior
back surface of body
superior
refers to structures being closer to top of the body (excludes arms & legs)
inferior
refers to structures being closer to the lower part of the body (excludes arms & legs)
medial
towards the midline (body position)
lateral
away from the midline (body position)
proximal
towards the upper segments of a limb (arms and legs)
distal
towards the lower segments of a limb (arms and legs)
flexion
decrease the angle between two bones (sagittal plane)
Extension
increasing the angle between two bones (sagittal plane)
Abduction
moving away from midline (movement)
Adduction
moving towards midline (movement)
circumduction
circular motion
Depression
movement in an inferior direction
Elevation
movement in a superior direction
External rotation
rotating outwardly away from the midline
Internal rotation
rotating inwardly towards the midline
supination
lateral rotation of the forearm and hand (palms up)
pronation
medial rotation of the forearm and hand (palms down)
dorsiflexion
pointing the foot upward
plantar flexion
point the foot downward
inversion
standing on outer edge of foot (rotating medially)
eversion
standing on inner edge of foot (rotating laterally)
skeletal system
internal framework of the human body
femur
longest bone in the skeletal system
stirrup
located in ear; smallest bone in body
structural support
one of the functions of skeletal system; supports tissues and muscles
protection
one of the functions of skeletal system; protects organs and fragile body parts (like the skull protecting the brain)
growth centre for cells
a function of the skeletal system; RBC and platelets are made in bones
reservoir of minerals
a function of skeletal system; regulates calcium and phosphorus in body
movement
a function of skeletal system; muscles attach to bones by tendons, and bones aid with movement
axial skeleton
one division of skeletal system that consists of vertebral column, skull, and rib cage
appendicular skeleton
one division of skeletal system that consists of all moveable limbs and supporting structures
long bone
type of bone found in arms and legs; like femur
flat bone
flat and thin bone to often protect vital organs from injury; like parietal bone
irregular bone
odd-looking bones; like vertebrae
sesamoid bone
unusual bone that is small, flat and wrapped within tendons to move over bony surfaces; patella
short bone
width and length are equal; wrist or ankle
fibrous joint
lacks synovial cavity; bones are held very closely together by fibrous connective tissue; allows little to no movement
cartilaginous joint
lacks synovial cavity; bones are tightly connected by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage; little to no movement
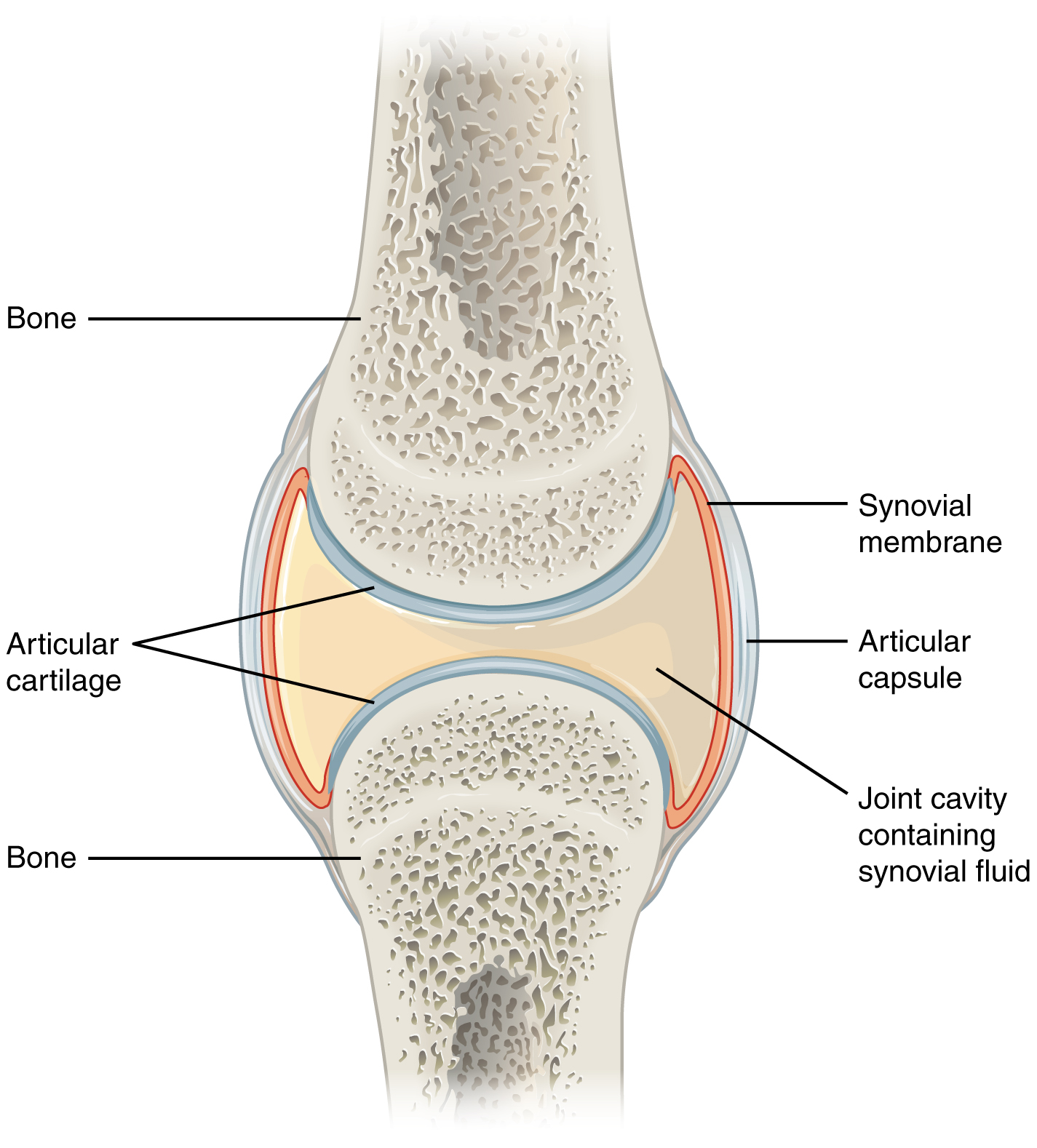
synovial cavity
space between segments of bones filled with synovial fluid; cushions the ends of bones and reduces friction when you move your joints
synovial joint
has synovial cavity between articulating bones; bones at joints are covered by articular cartilage; this cartilage reduces friction to absorb shock and help with movement
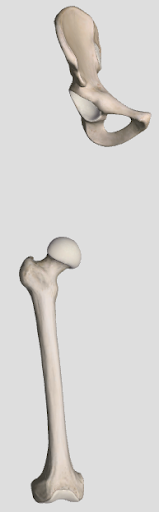
ball and socket joint
“ball“ at one end fits into the “socket“, most maneuverable along movement in 3 axes (ex. hip)
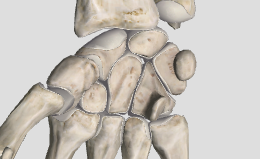
gilding joints
connects flat or slightly curved bone surfaces to glide against one another (ex. the hand carpals)
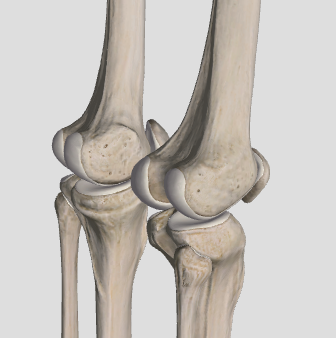
hinge joint
convex portion fitting into a concave portion of another (ex. ulna and humerus)
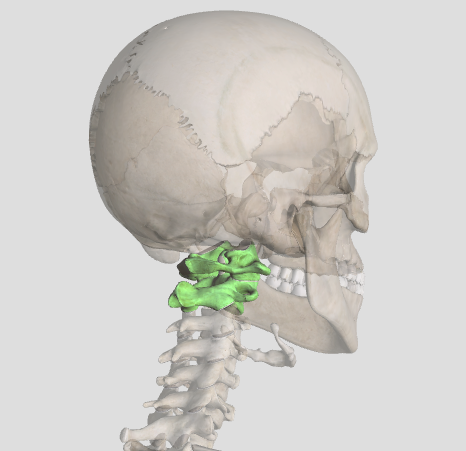
pivot joint
rotation in one plane; rounded point of one bone fits into a groove of another (vertebrae joints)
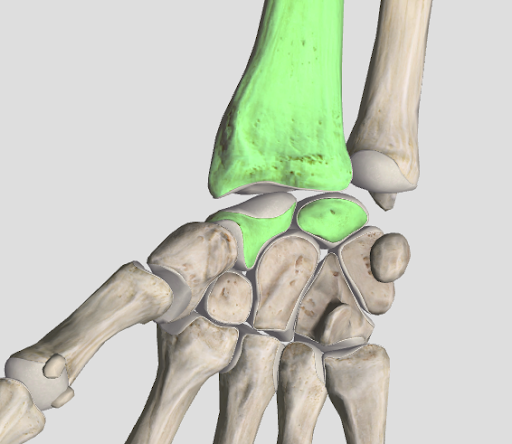
ellipsoid joint
movement in two planes; oval shaped end fits into similarly oval shaped hollow (ex. wrist)
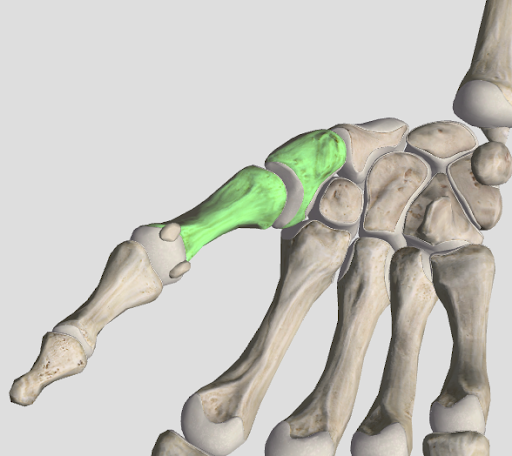
saddle joint
two plant movement (ex. flexion-extension) but no rotation like a ball-and-socket joint (ex. the thumb)
simple fracture
no separation of the bone but a crack is detectable (ex. hairline fracture)
compound fracture
when the bone breaks into separate pieces, but still organized (transverse fracture)
comminuted fracture
broken ends of bone have been shattered into many pieces
stress fracture
muscles become fatigued to absorb shock, and overstressed muscle transfers impact to the bone; causes a tiny crack (most common fracture, like wearing footwear with improper cushioning)
osteroporosis
a disease that deteriorates bone tissue and results in low bone bass; caused from drugs, alcohol, smoking, physical inactivity, and lack of vitamin D or calcium
muscular system
system of tendons, ligaments, and muscles that provides form, support, and stability to a body, thus giving humans the ability to move
smooth muscle
involuntary, dense muscle sheets that surround internal organs, and contract slower but for longer
cardiac muscle
involuntary muscle because it is controlled by autonomic nervous system; has a striped appearance and is only found in the heart to pump blood
skeletal muscle
voluntary muscles that are striated with alternating dark and light patterns; all attached to bones, and make up 30-40% of human body weight
tendons
tissue that attaches muscle to bone
ligaments
attach one or more bones together; significantly less rigid than bones (bone to bone)
sprain
when a ligament is overstretched
first degree sprain
treated easily since few ligament fibers are stretched; minimal swelling and some pain
second degree sprain
partially torn ligaments; maybe bruising; swelling and pain is considerably more
third degree sprain
entire ligament torn; surgery is required to reattach ligament to bone
separation
ligaments are disrupted, causing a tear, and bones may separate; can be caused from a fall or collision
dislocation
bone is displaced from the joint
tendonitis
inflammation of a tendon caused by irritation due to prolonged or abnormal use
arthritis
loss of cartilage at joints causing painful swelling of the joint (ex. rheumatoid arthritis or gout)
joints
point of intersection; where bones come together
action of the muscle
ex. flexor carpi ulnaris (flexion)
direction of the fibres
ex. rectus abdominis (rectus)
location of muscle
ex. tibialis anterior (anterior)
number of division/heads
ex. biceps brachii (2 heads)
shape of muscle
ex. deltoid (resembles the Greek letter delta)
muscle point of attachment
ex. sternocleidomastoid (sternum, mastoid process)
origin
point where the muscle attaches to the more stationary of the bones of the axial skeleton
insertion
point where the muscle attaches to the bone that is moved the most
function
the effect it has on the joint; the movement
isotonic contractions
same tension muscle contraction that changes length and causes movement of a body part; speed varies
concentric contraction
type of isotonic contraction; muscle shortens when contracting; most common in daily and sporting activities; consistent
eccentric contraction
type of isotonic contraction; muscle lengthens when contracting; less common and involves deceleration of a movement
isometric contraction
same distance or not moving contraction; there is no change in length
isokinetic contractions
form of muscle contraction in that the muscle changes in length during the contraction, and produce movement of a constant speed; very rare
cardiovascular system
blood flow system in human body that delivers oxygen and nutrients, removes CO2 and waste, maintains thermoregulation, and prevents infection
respiratory system
air and breathing system that delivers oxygen to body, removes CO2, and regulates blood pH levels
blood circulation
path of blood that goes between heart and lungs to deal with gas exchange, and then distribute blood flow to the rest of the body
arteries
thick vessels that carry blood away from the heart
arterioles
surrounded by rings of smooth muscle to control blood flow
capillaries
smallest, thinnest blood vessel; diffusion (gas and nutrient exchange) occurs here
venules
blood vessels that link blood from capillaries to veins, leading back to the heart
veins
when approaching heart, they have one-way valves so that blood doesn’t go backwards
skeletal muscle pump
contractions from one-way valves in veins makes pressure that moves blood to the heart
thoracic pump
every breathe fluctuates pressure in chest cavities, which affects pressure in veins; pressure of veins in abdominal cavity and thoracic cavity moves blood
nervous system pump
nervous system sends signal to constrict veins (venoconstriction), moving blood to heart
energy system
the specific mechanisms and reactions in which energy is produced and used by your body (ex. the fuel to use a car)
nutrients
chemical substances obtained from food and used by the body for various processes
carbohydrates
most abundant organic substances in nature, and are essential for human and animal life (ex. sugars and starches)
glucose
monomer (or base form) of carbohydrates and main substrate for cellular respiration; stored within skeletal muscles and within the liver as glycogen