respiratory system
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
define association (in terms of haemoglobin)
the combining of oxygen with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin.
define dissociation (in terms of haemoglobin)
the release of oxygen from haemoglobin.
define oxyhaemoglobin (in terms of haemoglobin)
a bright red substance formed by the combination of haemoglobin with oxygen, present in oxygenated blood.
define haemoglobin
a red protein responsible for transporting oxygen in the blood of vertebrates. Its molecule comprises four subunits, each containing an iron atom bound to a haem group.
define saturation (in terms of haemoglobin)
the extent to which haemoglobin in the blood is bound with oxygen
define external respiration
the process of exchanging gases between the alveoli in the lungs and the blood
define internal respiration
the exchange of gases, between the body's tissue cells and the blood
define partial pressure
the pressure exerted by an individual gas held in a mixture of gas.
define diffusion
the movement of gases across a membrane down a gradient from an area of high pressure (or conc) to an area of low pressure (or conc)
define diffusion gradient
the difference in areas of pressure (or conc) from one side of a membrane to the other.
define pulmonary ventilation
the inspiration and expiration of air from the atmosphere behind us.
define gaseous exchange
the extraction of oxygen from the air into the blood stream and then into the muscle tissues
define breathing frequency
the number of breaths taken per minute.
what percent of blood is plasma and what percent is blood cells?
blood consists of:
55% plasma
45% blood cells
what percent of blood combines with haemoglobin to produce oxyhaemoglobin and what happens to the rest?
97% combines with haemoglobin to produce oxyhaemoglobin (HbO2)
the other 3% is dissolved within the blood plasma
how is carbon dioxide transported in the blood?
70% dissolved in water and carried as carbonic acid
23% combines with haemoglobin to create carbaminohaemoglobin
7% dissolved in blood plasma
define tidal volume
Tidal volume is the volume of air inhaled or exhaled in one normal breath.
define minute ventilation
Minute ventilation is the total volume of air inhaled or exhaled per minute.
resting and maximal value for breathing frequency
resting = 12 - 16
maximal = 40 +
resting and maximal for tidal volume
resting = 0.5 litres
maximal = 3-5 litres
resting and maximal for minute ventilation
resting = 6-8 litres
maximal = 200+ litres
how does external respiration work at rest?
Occurs in the alveoli of the lungs
O₂ diffuses from alveoli → capillary blood
High O₂ in alveoli, low O₂ in blood
CO₂ diffuses from capillary blood → alveoli
High CO₂ in blood, low CO₂ in alveoli
Diffusion gradients are moderate
Meets low oxygen demand at rest
how does external respiration work during exercise?
Breathing rate and depth increase
O₂ diffuses from alveoli → blood at a faster rate
Steeper gradient due to ↓blood O₂
CO₂ diffuses from blood → alveoli at a faster rate
Steeper gradient due to ↑blood CO₂
Ensures sufficient oxygen supply to working muscles
how does internal respiration work during rest?
Occurs at muscle capillaries
O₂ diffuses from blood → muscle cells
High O₂ in blood, low O₂ in muscles
CO₂ diffuses from muscle cells → blood
High CO₂ in muscles, low CO₂ in blood
Diffusion gradients are small
Matches low metabolic demand
how does internal respiration work during exercise?
Muscles increase aerobic respiration
O₂ diffuses rapidly from blood → muscles
Very steep gradient due to ↓muscle O₂
CO₂ diffuses rapidly from muscles → blood
Very steep gradient due to ↑muscle CO₂
Increased temperature and CO₂ maintain steep gradients
Supports increased energy production
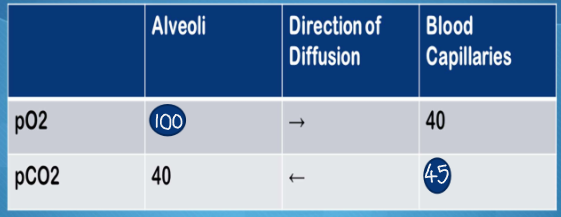
what are the partial pressures at external respiration at rest?
PO2 in alveoli = 100
PO2 in blood capillaries = 40
so diffusion of O2 goes from alveoli to blood capillaries
PCO2 in alveoli = 40
PCO2 in blood capillaries = 45
so diffusion of CO2 goes from blood capillaries to alveoli
what are the partial pressures at internal respiration at rest?
PO2 in muscle cell = 40
PO2 in blood capillaries = 100
so diffusion of O2 goes from blood capillaries to muscle cell
PCO2 in muscle cell = 45
PCO2 in blood capillaries = 40
so diffusion of CO2 goes from muscle cell to blood capillaries
what are the partial pressures at internal respiration during exercise?
PO2 in muscle cell = 5
PO2 in blood capillaries = 100
so diffusion of O2 goes from blood capillaries to muscle cell
PCO2 in muscle cell = 80
PCO2 in blood capillaries = 40
so diffusion of CO2 goes from muscle cell to blood capillaries