Weathering
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

22 Terms
Two types of weathering
1. Physical (Mechanical)
2. Chemical
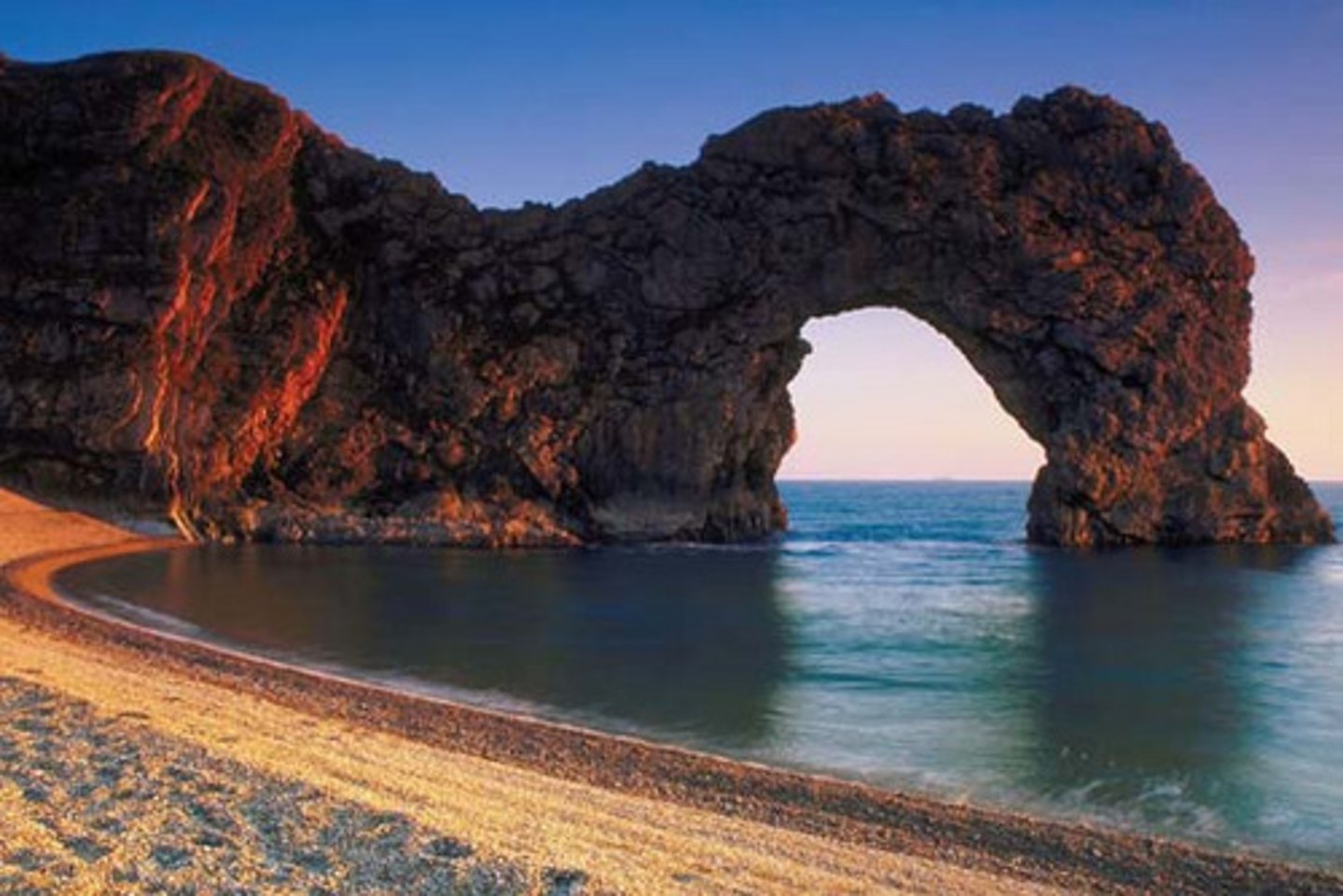

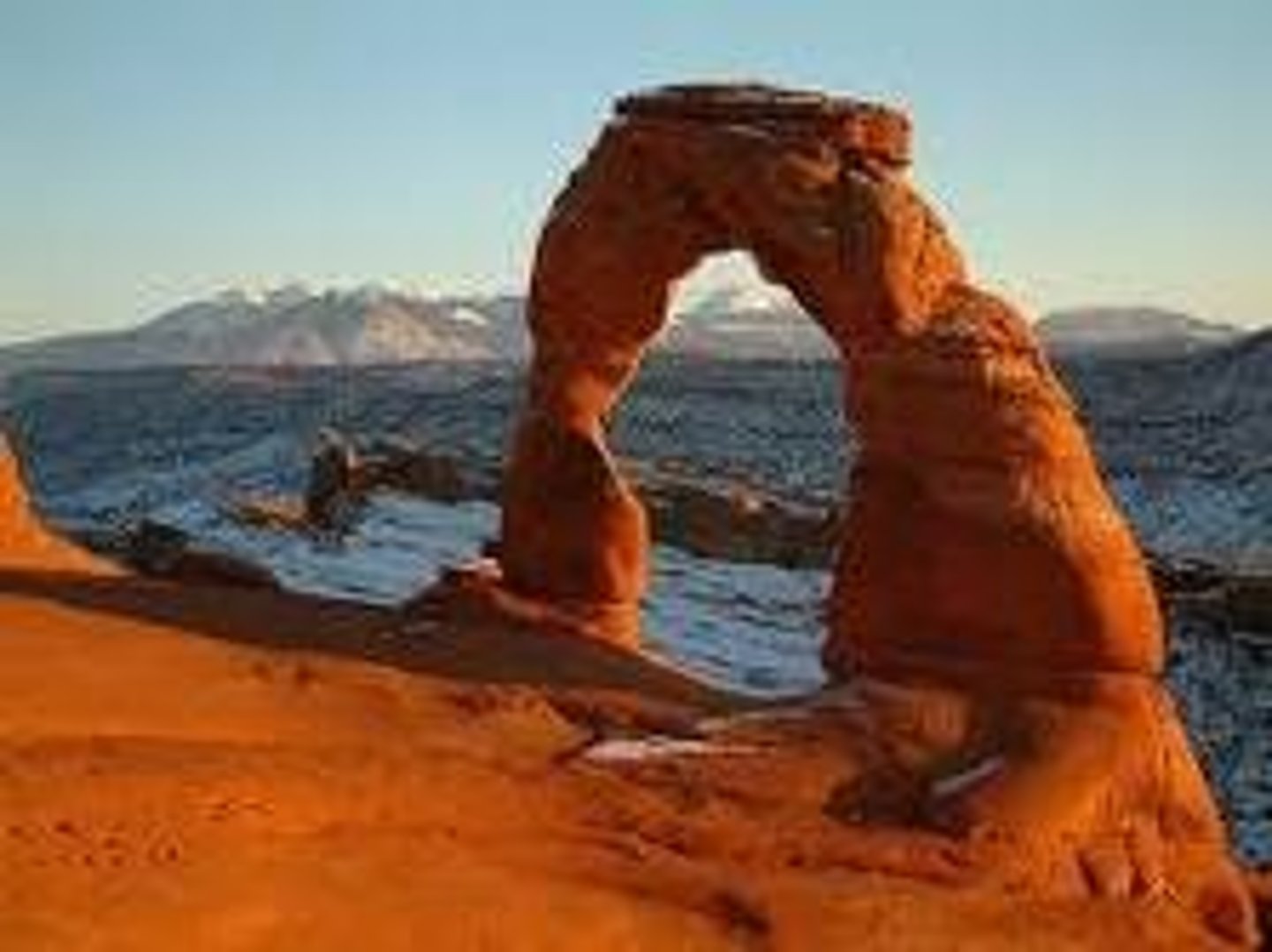
Physical Weathering
rocks broken down into smaller pieces by external conditions (not changing the material)

Chemical Weathering
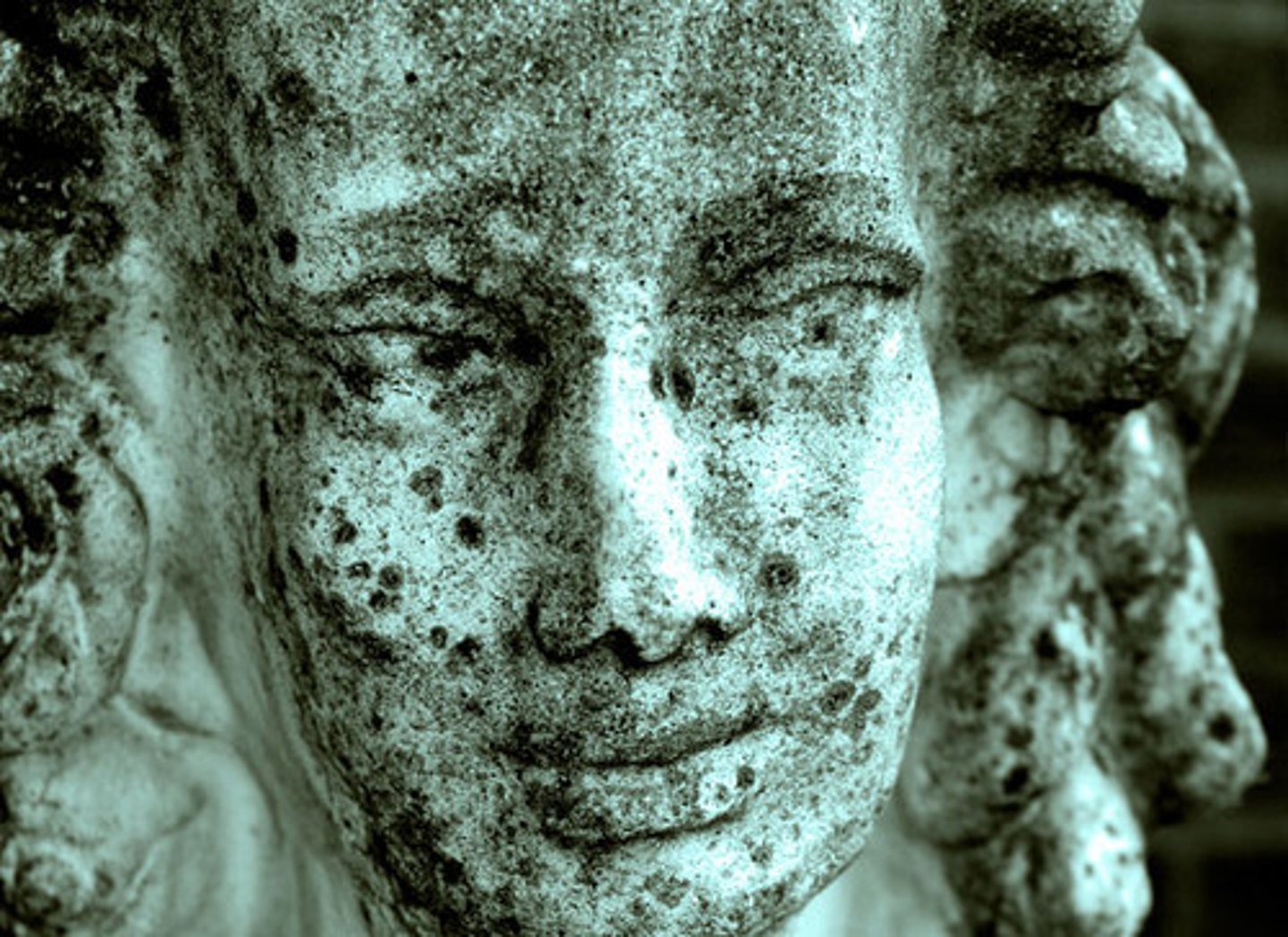
rocks broken down through chemical changes (changing the material)

Abrasion
scrapping of rock surfaces by hitting other rocks/sand (mechanical weathering)
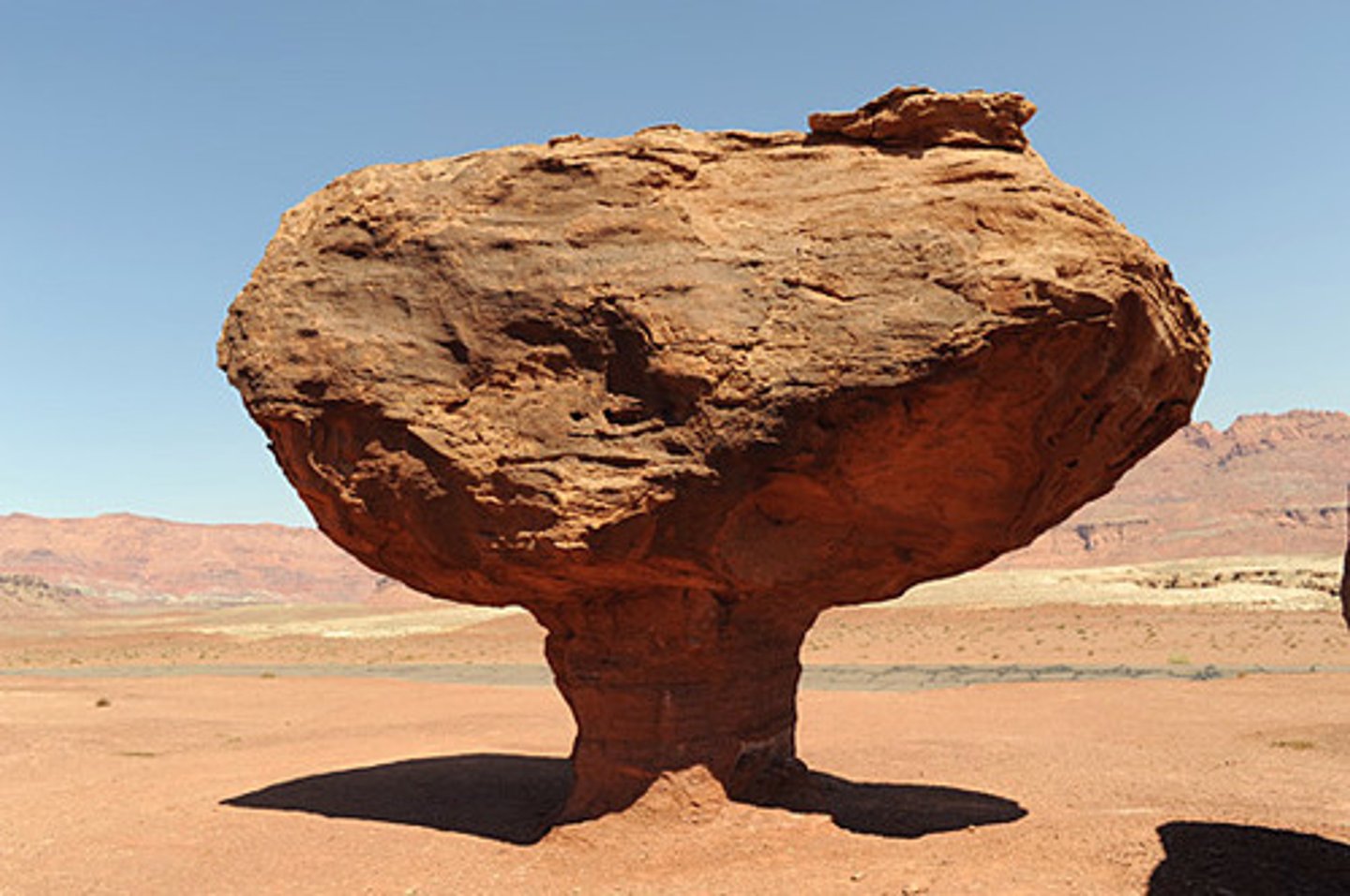

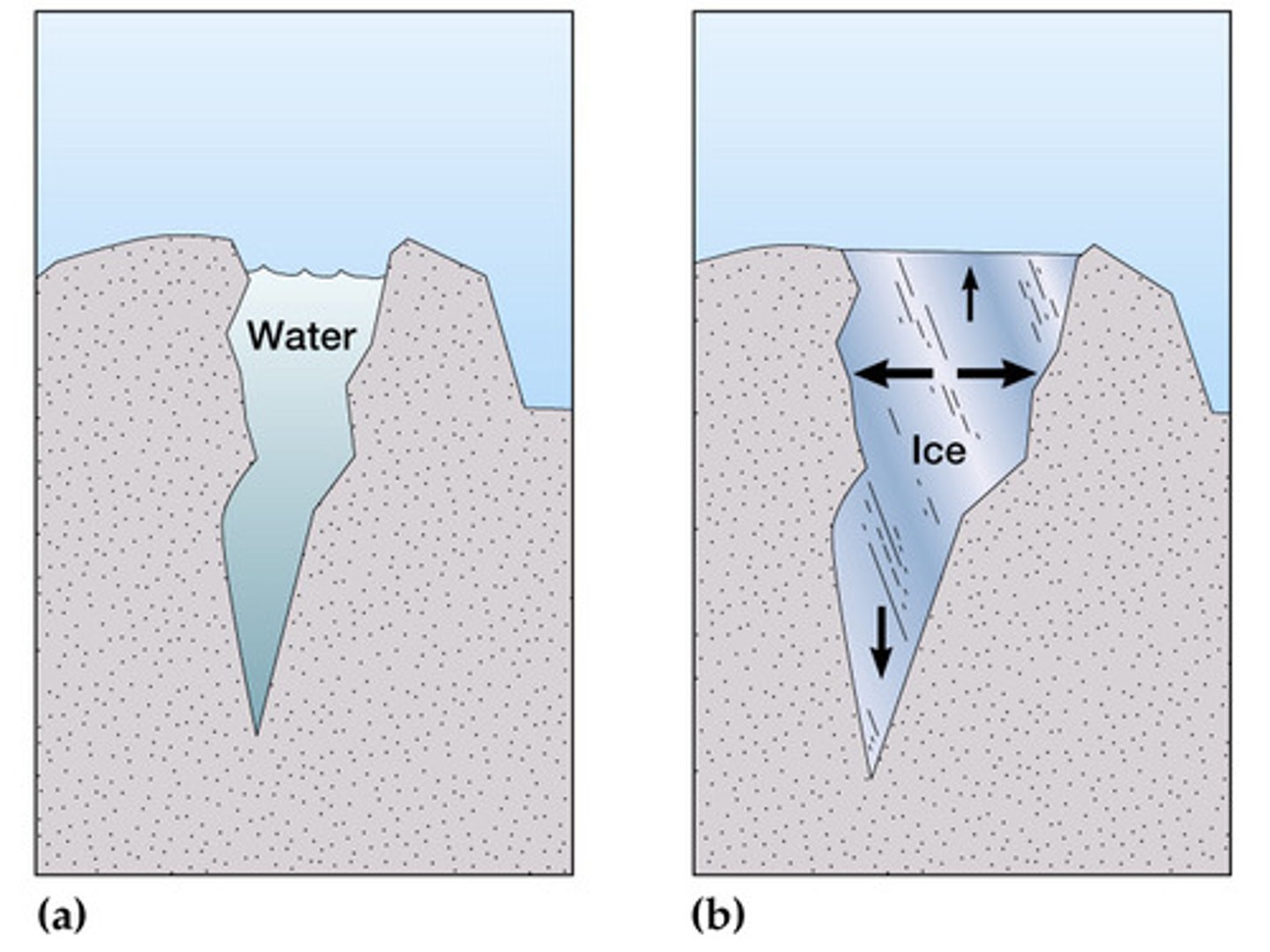
Ice wedging (frost action)
water gets into cracks and freezes causing the cracks to get bigger (mechanical weathering)
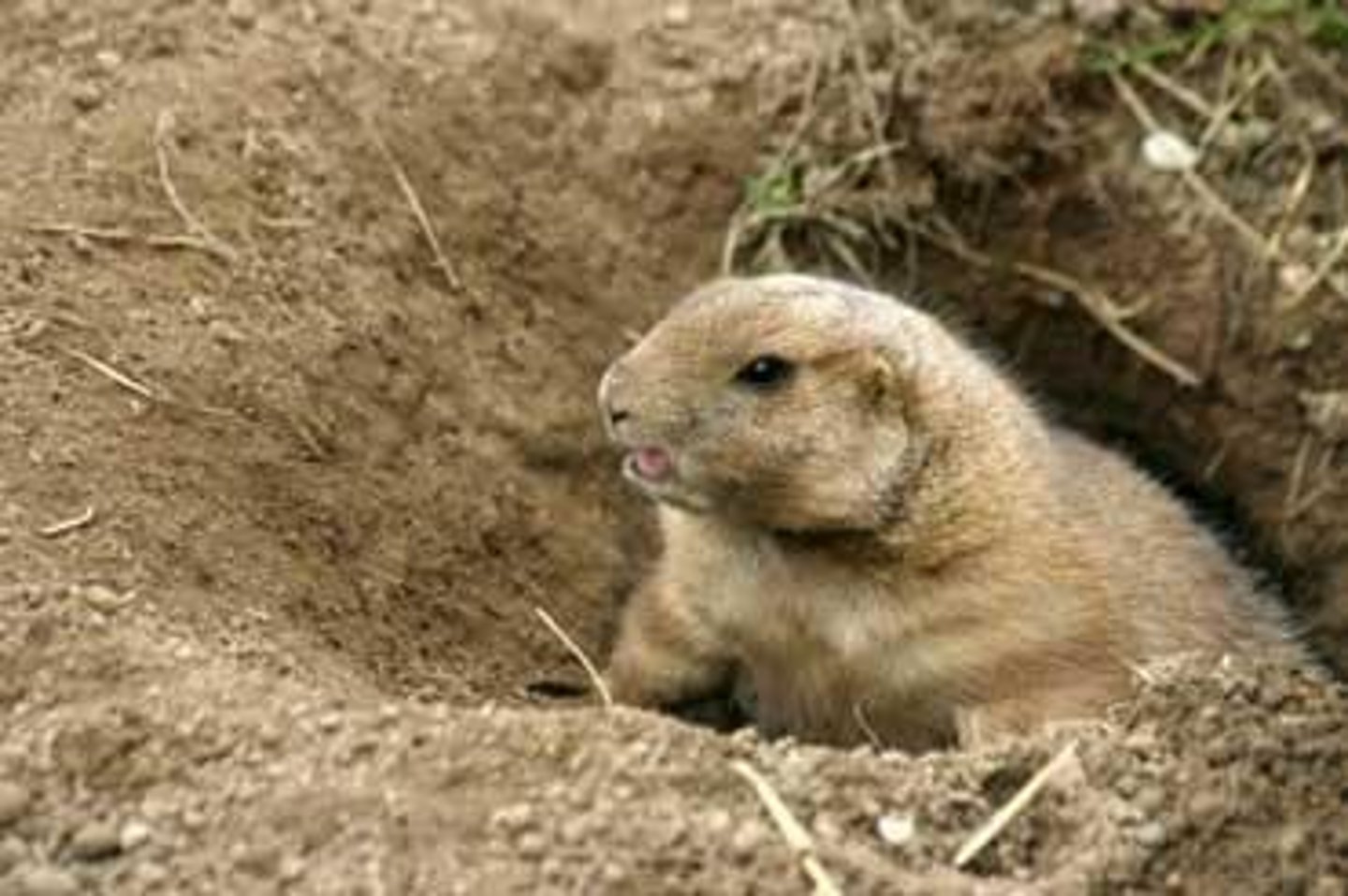
animal action
animals burrow and dig moving sediments (mechanical weathering)

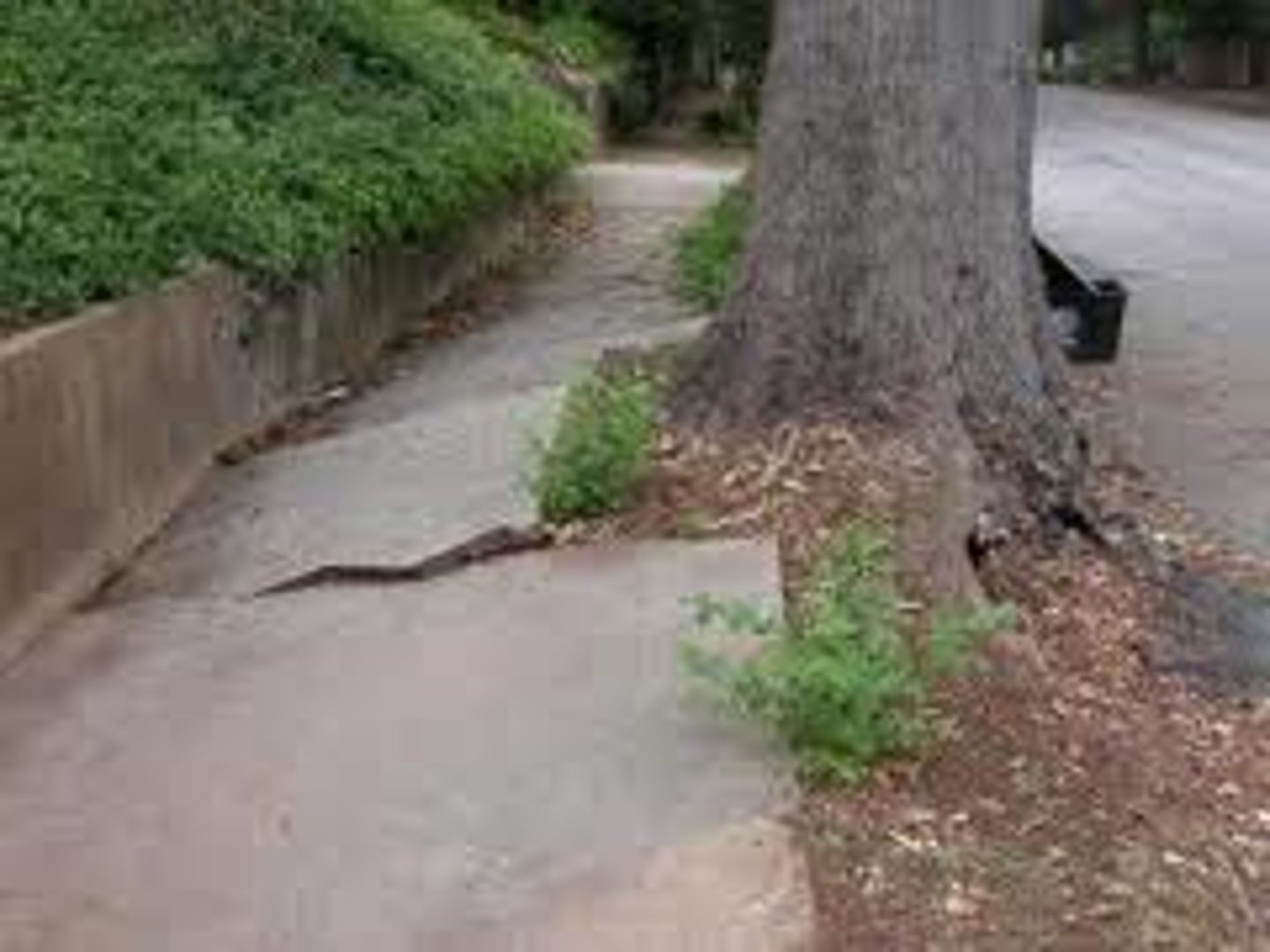
root wedging
rocks are broken due to plants as they grow through cracks (mechanical weathering)

exfoliation (pressure release)
sheets of rocks breaking off due to release of pressure (mechanical weathering)
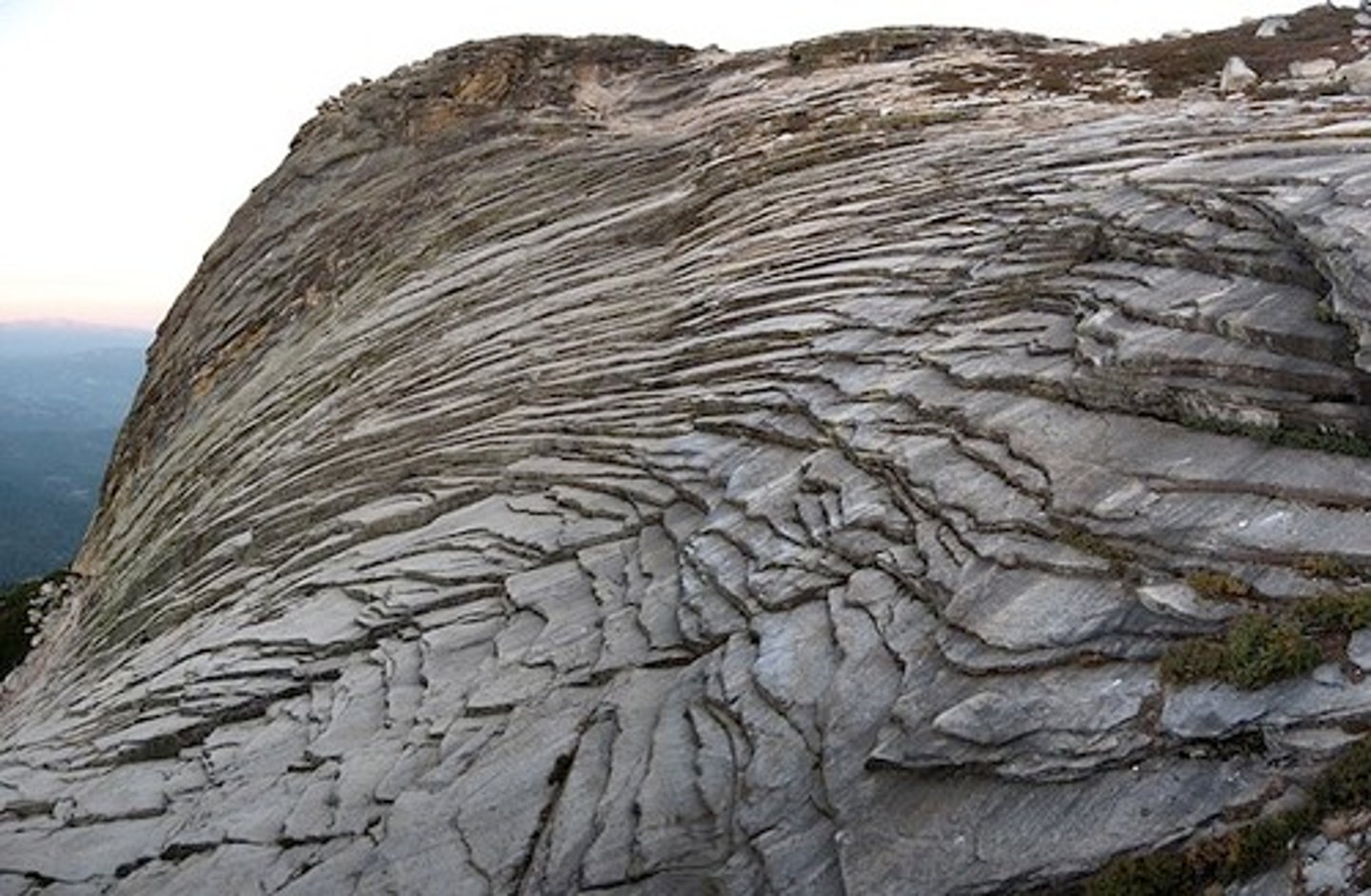

Hydrolysis
water weathers rock by dissolving it (chemical weathering), dissolve minerals and chemically alters them
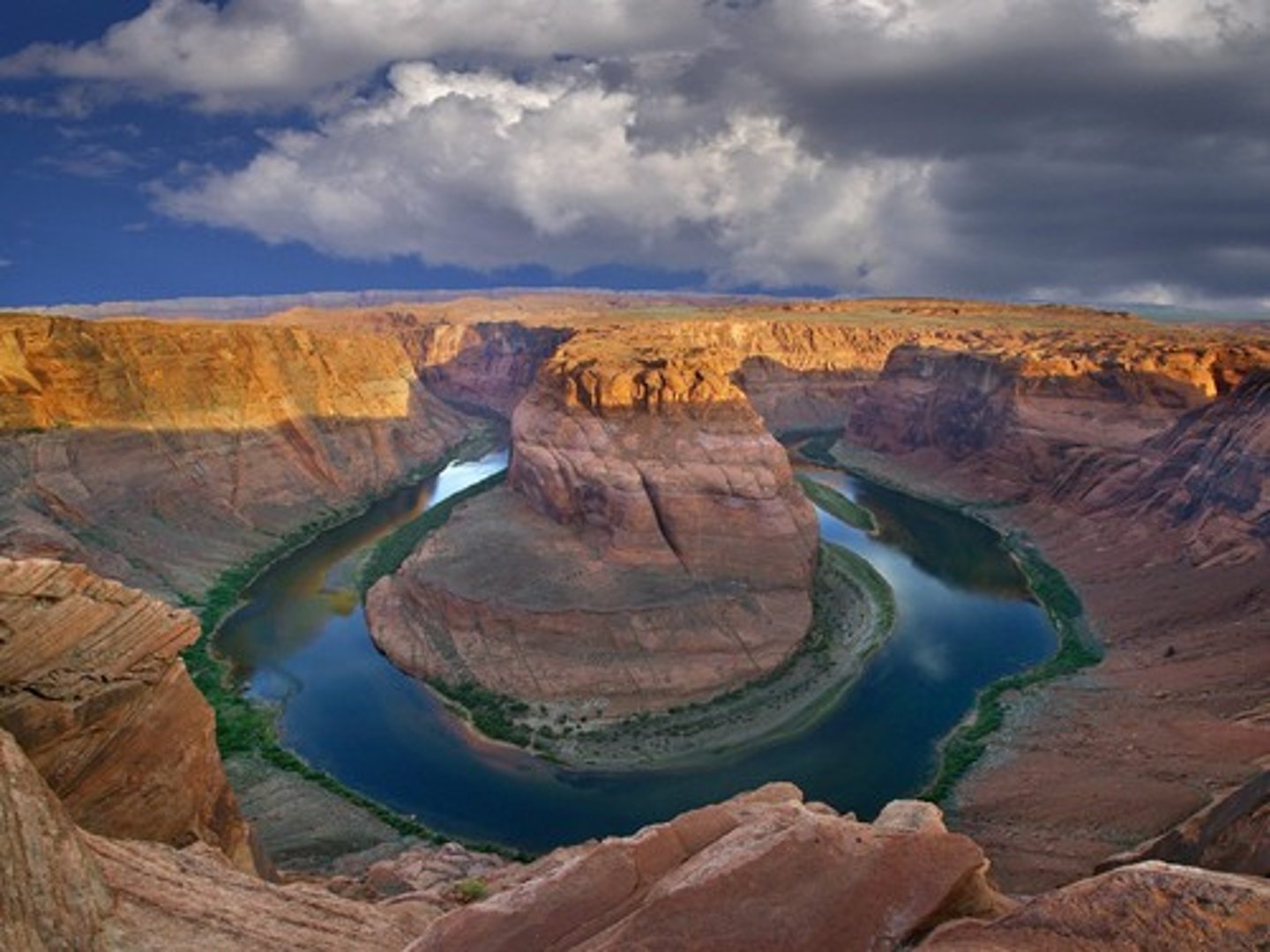

oxidation
oxygen combines with minerals that have iron causing "rusting" (chemical weathering)

acid rain
gases react chemically with water forming acids such as like sulfuric acid and nitric acid from burning fossil fuels (chemical weathering)

Warm and Wet Climate
This climate would have more chemical weathering

Cool and Wet Climate
this climate would have more physical weathering (ice wedging)

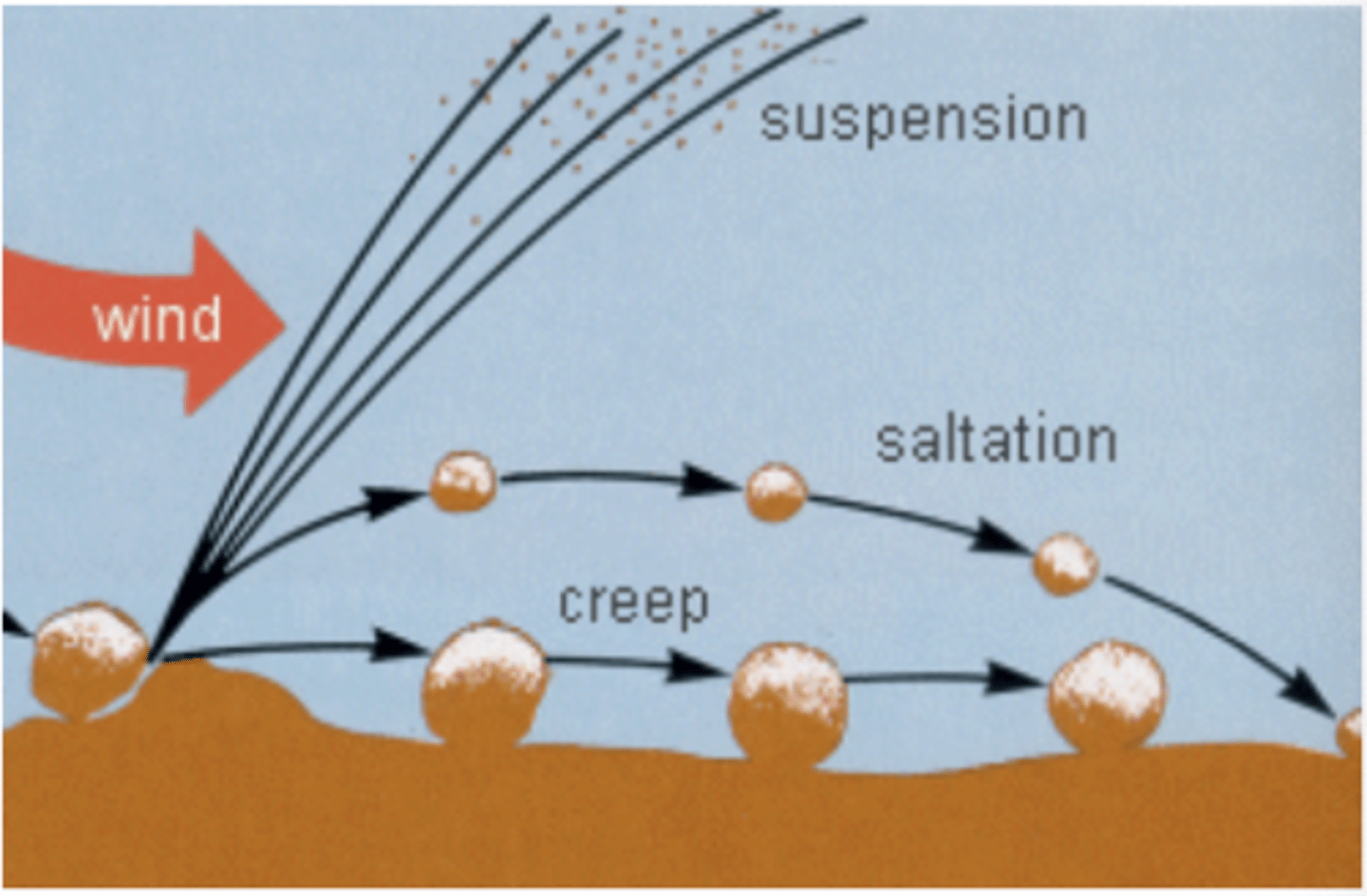
Agent Wind
this agent can create sorted sediments. Sediments undergo abrasion.
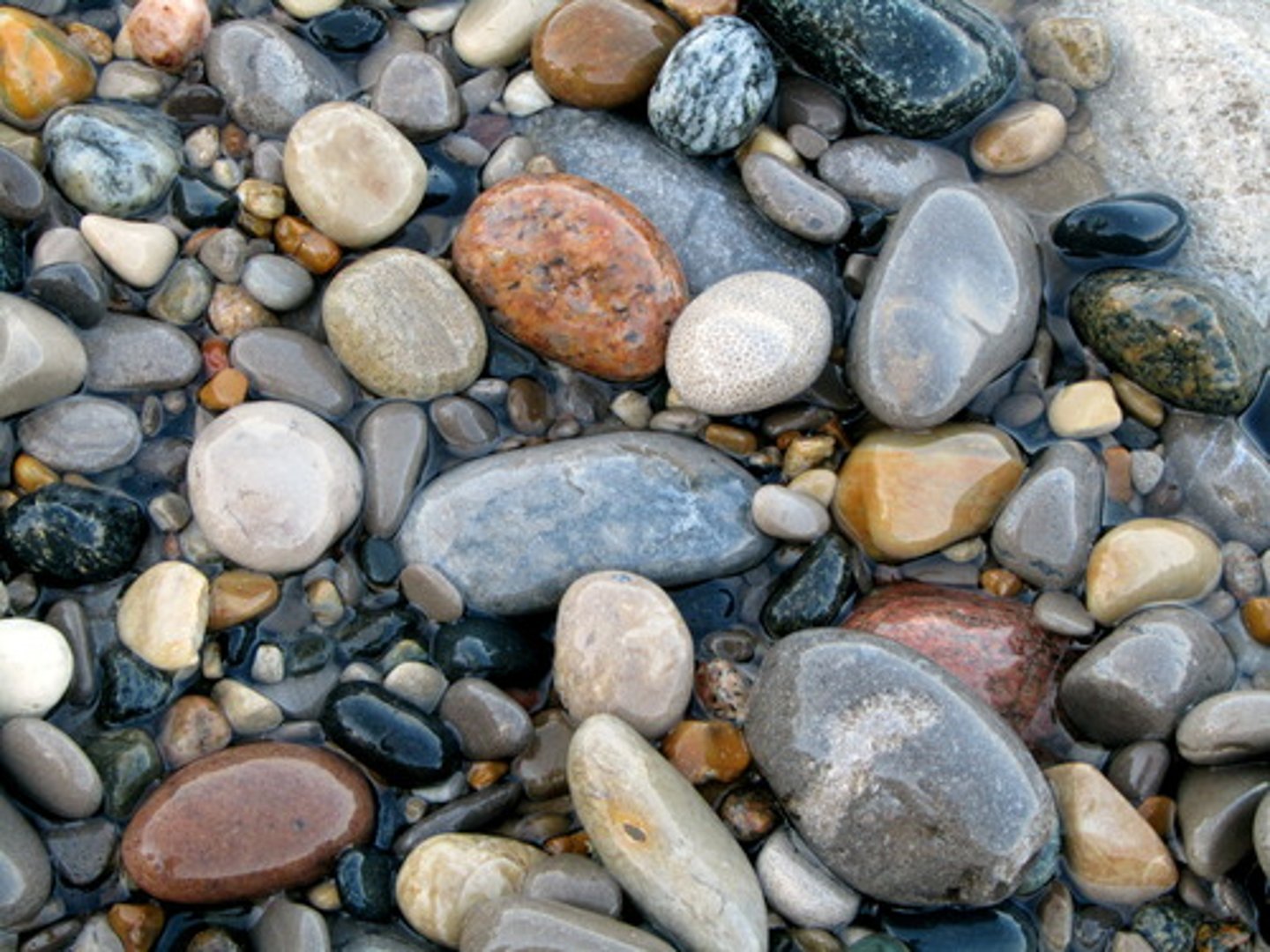
Agent Water
this agent can create sorted, rounded rocks. Sediments undergo abrasion.

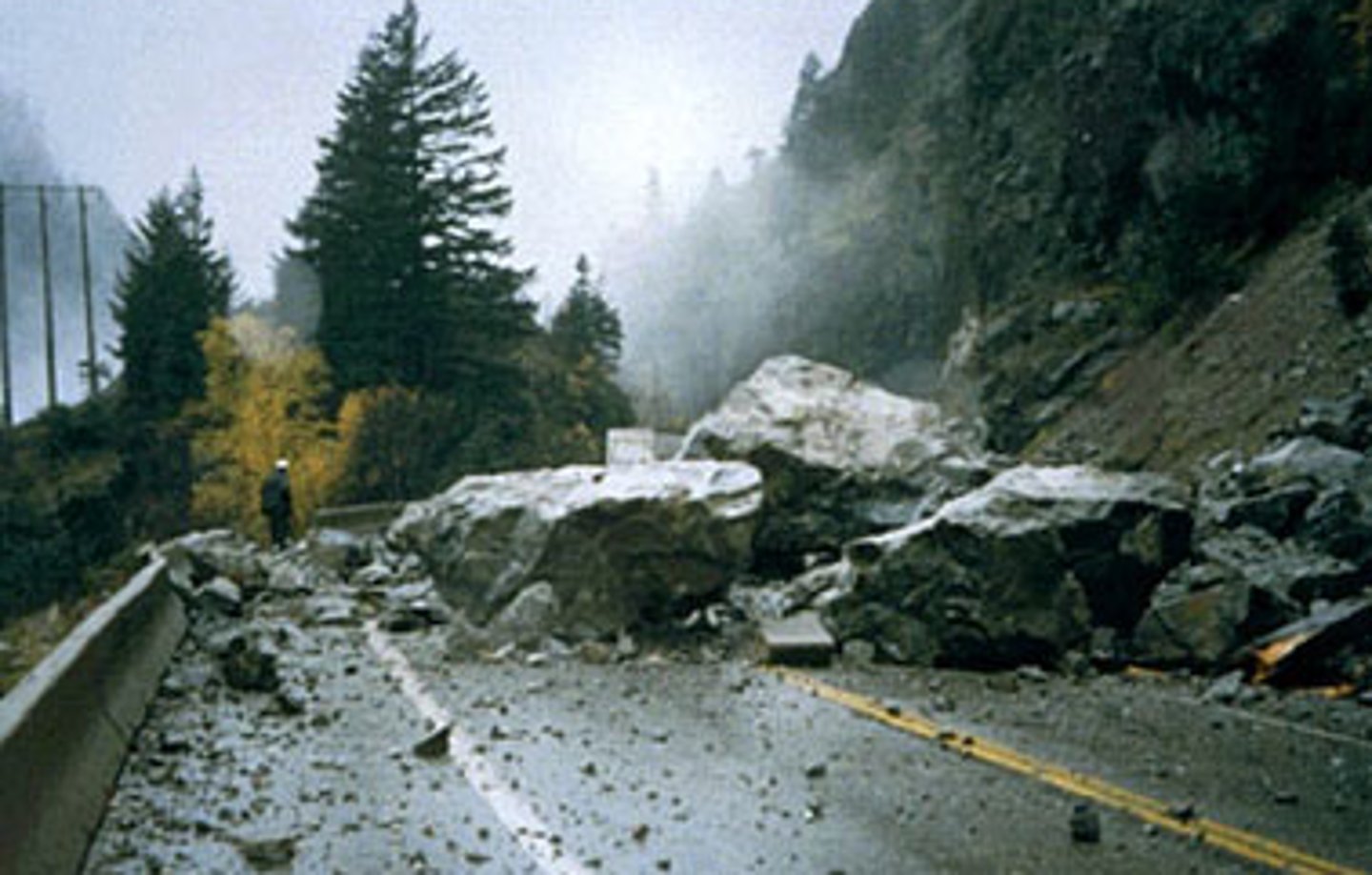
Agent Gravity
this agent creates piles of unsorted, jagged rocks on the bottom of mountains and cliffs

Erosion
The process by which wind and water transports soil and sediment from one location to another

Weathering rate
The weathering rate is the rate in which a rock breaks down. Dependent on climate and rock type

Surface area and weathering
-Physical weathering increases surface area
-Chemical weathering rates are directly proportional to surface area
-Therefor physical weathering increasing chemical weathering rates

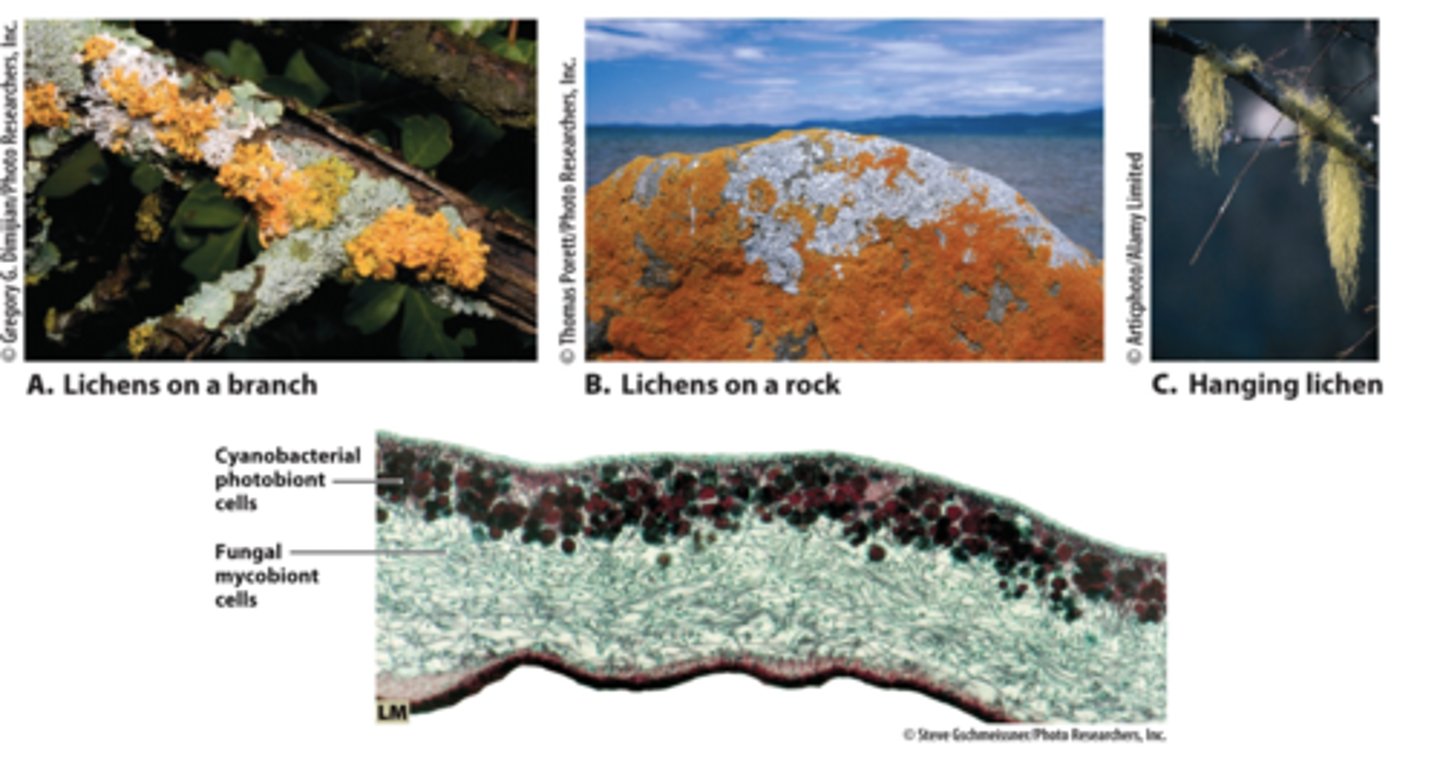
Lichens are
symbiotic association of algae and fungi
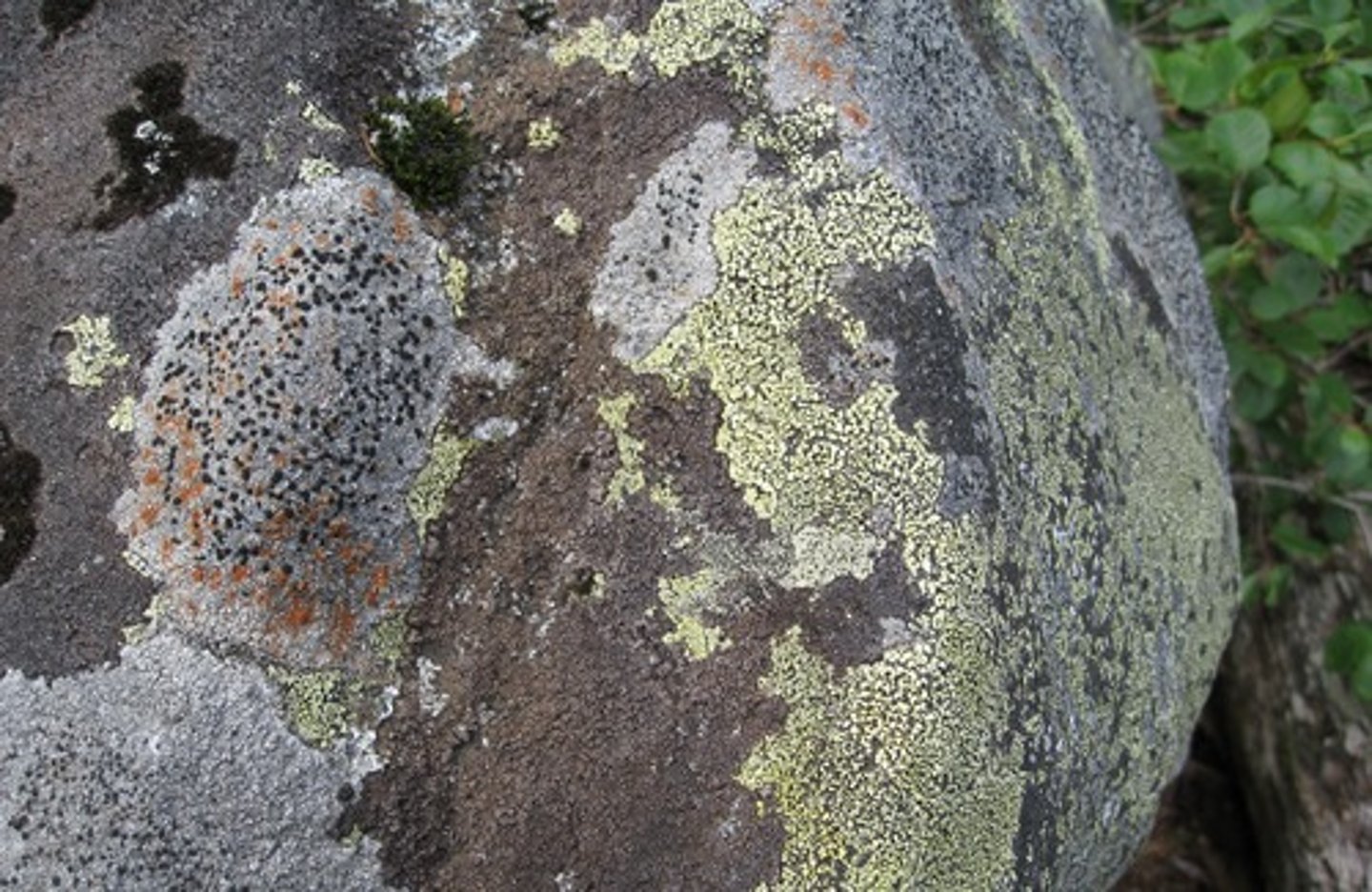

Lichens produce
a weak acid that breaks down all sorts of things including rocks
Carbonic acid/carbonation
a very weak acid formed in solution when carbon dioxide dissolves in water.
