HIV PPQ
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
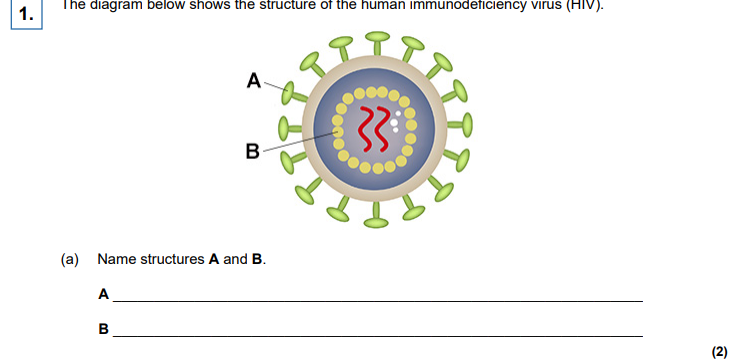
(a) 1. A = Attachment protein; Accept gp41 /gp140 /gp120/CD4/ glycoprotein Accept antigen Ignore receptor protein 2. B = Capsid OR Capsomere OR Protein;
(b) Describe how HIV is replicated.
1. Attachment proteins attach to receptors on helper T cell/lymphocyte; 2. Nucleic acid/RNA enters cell; 3. Reverse transcriptase converts RNA to DNA; 4. Viral protein/capsid/enzymes produced; 5. Virus (particles) assembled and released (from cell);
Describe how the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is replicated once inside helper T cells (TH cells).
1. RNA converted into DNA using reverse transcriptase;
Reject ‘messenger’ or ‘m’ before RNA
2. DNA incorporated/inserted into (helper T cell) DNA/chromosome/genome/nucleus;
3. DNA transcribed into (HIV m)RNA;
Accept descriptions of transcription
4. (HIV mRNA) translated into (new) HIV/viral proteins (for assembly into
viral particles);

(b) Use the information given to evaluate the use of BSCT to treat HIV infections.
(b) For 1. (There appears to be) no virus/ HIV(-1)/RNA/DNA, so could be a cure/effective; Max 4 for reasons for or against Ignore virus is killed
2. No CCR5/receptor, so not get HIV(-1) in the future OR No CCR5/receptor, so nothing for HIV(-1) to bind to; Reject less CCR5/less HIV(-1) bind
3. Only one transplant/BSCT needed (shown by patient Q)
4. Would not need (daily) ART (16 months after BSCT); Against
5. Don’t know if chemotherapy/radiotherapy is needed OR Do not know if BSCT alone would be effective; OR Do not know which treatment is having the effect OR Could be due to chemotherapy/radiotherapy; Accept: chemotherapy/radiotherapy is toxic/harmful/has side-effects
6. Only for HIV-1; Accept: Might not work in other types of HIV
7. Don’t know if it would work in all people OR Only worked/tried in 2 cases;
8. Might not be long term OR Only 18 months;
9. HIV-1 may mutate and be able to bind to a different receptor (on TH cells);
10. Might be a lack of (suitable stem cell/BSCT) donors; Accept stem cells/BSCT (might be) rejected
.Explain how HIV affects the production of antibodies when AIDS develops in a person.
(a) 1. Less/no antibody produced; 2. (Because HIV) destroys helper T cells; Accept ‘reduces number’ for ‘destroys’ 3. (So) few/no B cells activated / stimulated OR (So) few/no B cells undergo mitosis/differentiate/form plasma cells;
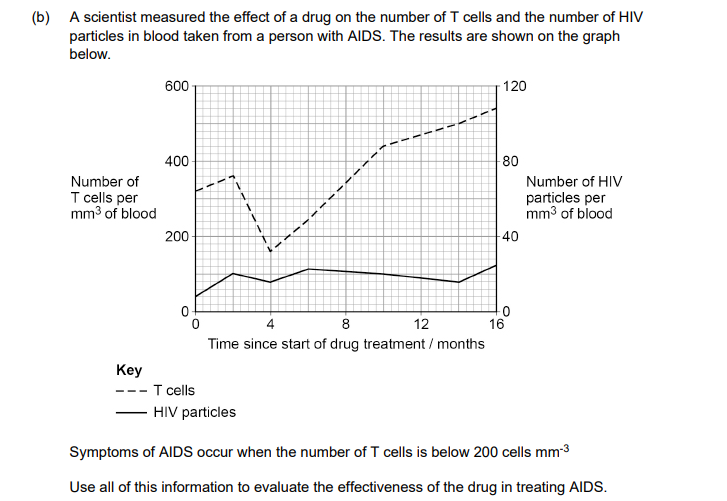
Not effective in treating AIDS because
1. Number of T cells < 200 at 4 months; Max 4 if not one of 9. or 10. Accept 3.5 - 5 months Reject day/week only once
2. (So) drug is not effective OR AIDS symptoms occur;
3. Does not remove (all) HIV (particles) OR Number of HIV (fairly) constant/stable OR (Slight) increase in HIV (over 16 months);
4. No stats test;
5. Only shows (results over) 16 months;
6. Only one person;
7. Unknown side effects (of drug);
8. No control group;
Effective in treating AIDS because
9. Number of T cells > 200 after 5months OR Number of T cells increasing after 4 months; Reject day/week only once Accept any month after 5 months OR ‘in the long term’
10. So drug is effective OR AIDS symptoms relieved/remove
(a) Describe the structure of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
(a) Accept a labelled diagram. 1. RNA (as genetic material); Reject nucleus/DNA/plasmids. 2. Reverse transcriptase; 3. (Protein) capsomeres/capsid; Reject capsule. 4. (Phospho)lipid (viral) envelope OR Envelope made of membrane; Reject if HIV has a cell membrane or a cell wall. 5. Attachment proteins; Accept gp41 and/or gp 120.

Use the data in the table above and your knowledge of the immune response to suggest why HIV controllers do not develop symptoms of AIDS.
(c) 1. (All) have more T helper/CD4 cells; Accept higher proportion of T helper/CD4 to virus particles. Statement must be comparative. 2. Lower viral load to infect/destroy helper T/CD4 cells; For ‘infect’ accept ‘HIV does not reproduce in’. Statement must be comparative. 3. (So more/continued) activation of B cells/cytotoxic T cells/phagocytes; Accept ‘stimulation’ for ‘activation’. 4. (With B cells more/continued) production of plasma cells/antibodies OR (With cytotoxic T cells more/continued) ability to kill virus infected cells; Ignore reference to B cells acting as phagocytes/antigen-presenting cells. 5. (More able to) destroy other microbes/pathogens OR (More able to) destroy mutated/cancer cells;

1. Person (infected with HIV) has HIV DNA (in their DNA); 2. New HIV (particles) still made; 3. (AZT) inhibits reverse transcriptase; 4. (AZT) stops these (new HIV particles) from forming new HIV DNA; OR Slows / stops replication of HIV; 5. Stops destruction of more / newly infected T cells; 6. So immune system continues to work (and AIDS does not develop); 4. Context is important 4. Allow slows / stops (re)production of HIV 4. Reject (AZT) prevents DNA replication
Suggest and explain two advantages of using HAART (lines 7–9).
1. Slows / stops the development of AIDS; 2. Because HIV resistant to AZT is damaged / destroyed / prevented from replicating (by other drugs); OR 3. AZT continues to work as a drug; 4. Because HAART prevents the spread of AZT-resistant HIV to rest of the human population; OR 5. No new HIV particles made; 6. Because HAART might interfere with viral protein synthesis;
Suggest why high doses of AZT lead to muscle wastage (lines 10–11).
1. (Fewer mitochondria so) less (aerobic) respiration; 2. (Muscles receive) less ATP (so waste);
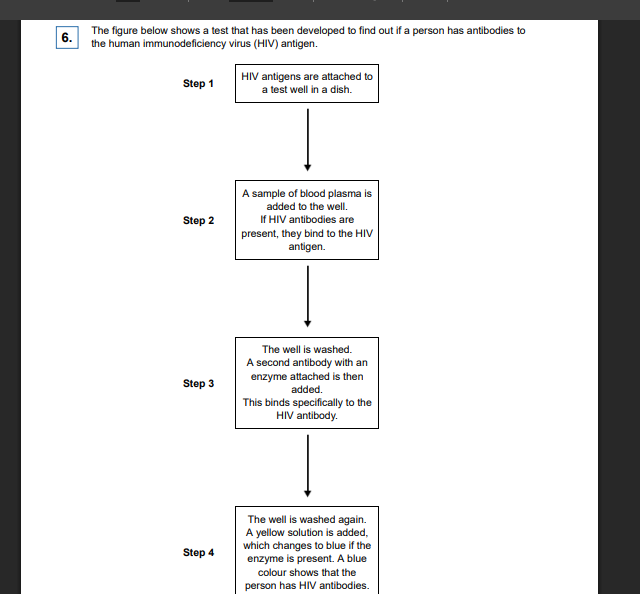
This test only detects the presence of HIV antibodies. Give two reasons why it cannot be used to find out if a person has AIDS.
(a) (To diagnose AIDS, need to look for / at) 1. (AIDS-related) symptoms; 2. Number of helper T cells. Neutral: ‘only detects HIV antibodies’ as given in the question stem
The solution will remain yellow if a person is not infected with HIV. Explain why
1. HIV antibody is not present; Accept HIV antibodies will not bind (to antigen) 2. (So) second antibody / enzyme will not bind / is not present.
A mother who was infected with HIV gave birth to a baby. The baby tested positive using this test. This does not prove the baby is infected with HIV. Explain why
1. Children receive (HIV) antibodies from their mothers / maternal antibodies; 2. (So) solution will always turn blue / will always test positive (before 18 months)
A control well is set up every time this test is used. This is treated in exactly the same way as the test wells, except that blood plasma is replaced by a salt solution. Use information from the figure above to suggest two purposes of the control well.
(Shows that) 1. Only the enzyme / nothing else is causing a colour change; 2. Washing is effective / all unbound antibody is washed away.