Diversity of Protists and Parasitic Organisms
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms

Anabaena
thin, blue-green strands containing specialized cells called heterocysts, capable of nitrogen fixation when nitrogen is limited, and are autotrophic due to chlorophyll and other pigments.
Aeolosoma
tiny segmented worms that feed by suctioning up microscopic organisms.
Aeolosoma
They have bilateral symmetry, segmentation, three tissue layers, and a true body cavity (coelom).
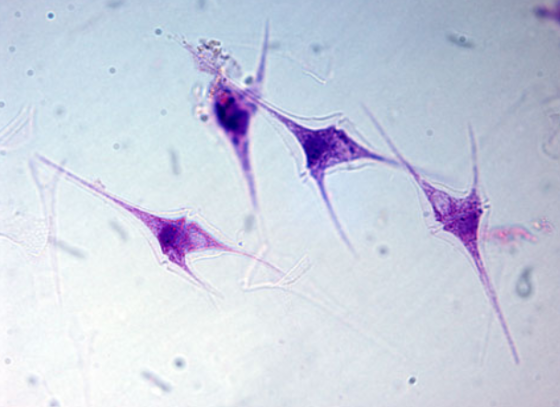
dinoflagellates
mostly marine, some are bioluminescent, characterized by perpendicular grooves and cellulose plates, biflagellated, and can live symbiotically with corals or jellyfish. They are responsible for red tides due to neurotoxins.
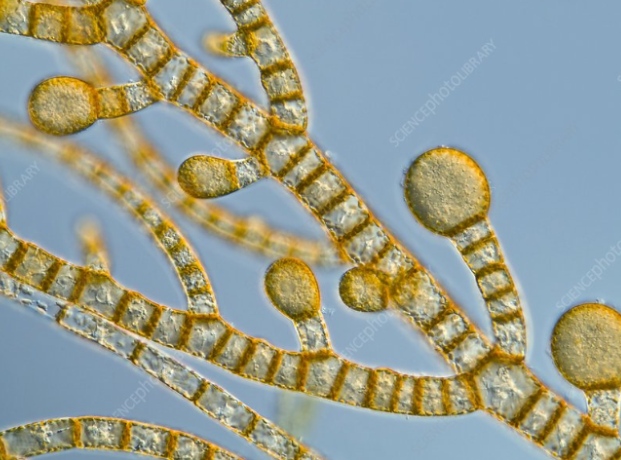
Brown Algae
Brown algae are autotrophic protists with pigments like chlorophyll a and fucoxanthin, ranging from microscopic to giant kelp, using flotation bladders for buoyancy, and are economically important for food and alginates.
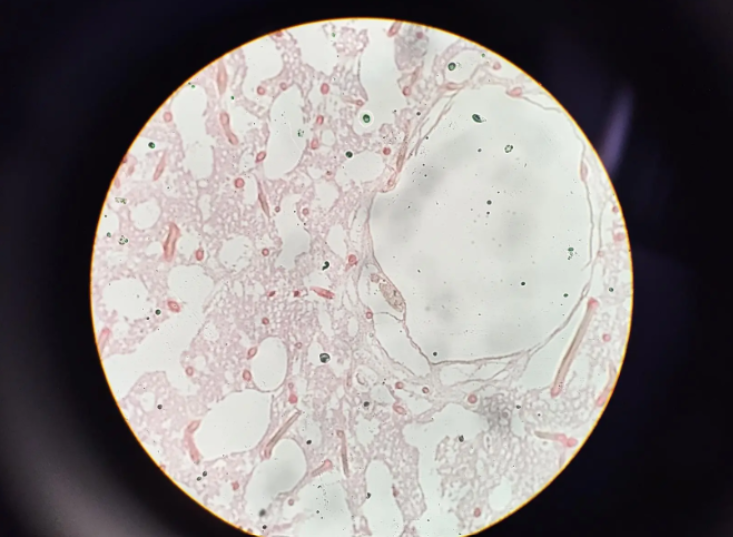
sponges (Phylum Porifera)
aquatic filter-feeding animals that take in water through tiny pores and expel it through larger openings (oscula), phagocytosing particles and bacteria.
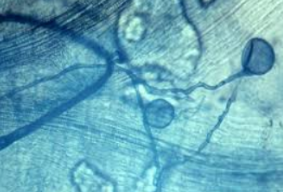
mycorrhizae
mutualistic fungi associated with plant roots that enhance water and nutrient uptake, especially phosphorus, and provide protection against parasitic fungi.
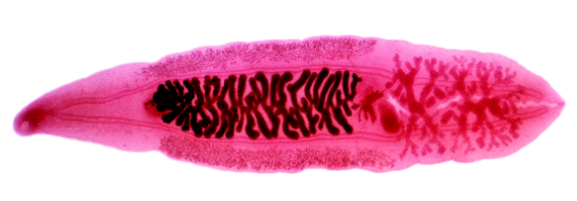
Chinese Liver Fluke (Clonorchis sinensi
hermaphroditic parasite of humans with an oral sucker, ventral sucker, intestines, uterus, and testes, with snails and fish as intermediate hosts.
What is the procedure for blanking a spectrophotometer?
Turn on the machine, select Abs, set the wavelength, insert a blank tube, zero the machine, then insert the sample tube to take a reading.
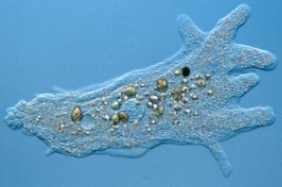
Tubulinids
heterotrophic protozoa that use pseudopodia, with Physarum polycephalum as a sample, now classified as polyphyletic protists.
How do amoebae move and feed?
Amoebae use pseudopods for movement and feeding, found in various aquatic environments and some are human parasites.
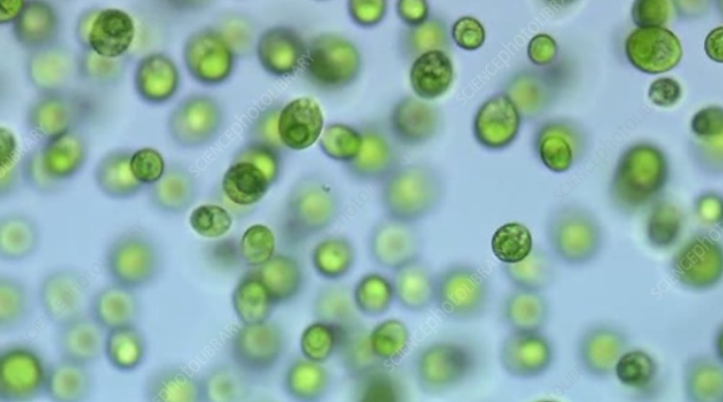
What defines Chlamydomonas?
Chlamydomonas is a single-celled green algae with flagella, moving in circular or spiraling motions, and is autotrophic due to chlorophyll.
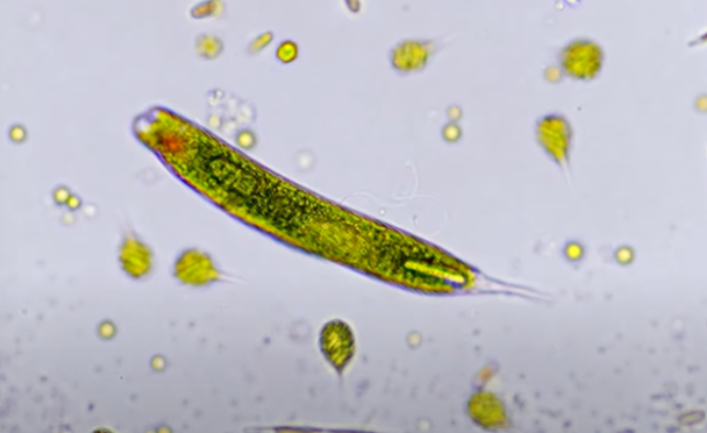
What are the features of Euglenozoans?
Euglenozoans are flagellated protists, many are autotrophic, have eyespots for phototaxis, and exhibit euglenoid movement.
What diseases are caused by Leishmania donovani?
Leishmania donovani causes cutaneous and visceral leishmaniasis, with a life cycle involving vector transmission via sand flies.
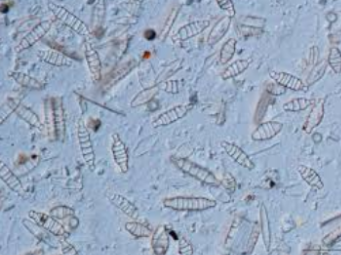
What are diatoms and their ecological role?
Diatoms are autotrophic protists with silica shells, responsible for ~40% of oceanic primary production and play a key role in the carbon cycle.
What are the two main forms of diatoms?
Diatoms have two main forms: pennate (bilateral symmetry) and centric (radial symmetry).
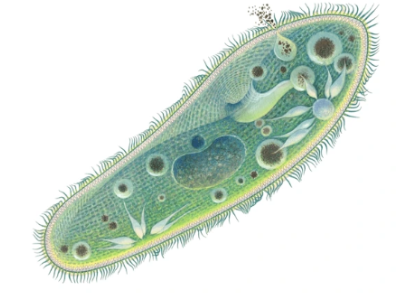
What are the characteristics of ciliates?
Ciliates are heterotrophic protists using cilia for movement and feeding, with samples like Paramecium that exhibit avoidance behavior and have both macronucleus and micronucleus.

What is the body structure of flatworms (Phylum Platyhelminthes)?
Flatworms have bilateral symmetry, three tissue layers, and are acoelomates (lack a true body cavity).
What is the significance of contractile vacuoles in ciliates?
Contractile vacuoles in ciliates regulate water balance within the cell.
How do brown algae adapt to intertidal zones?
Brown algae produce a viscous gel to retain water in intertidal zones and have thin blades for nutrient diffusion.
What is the ecological importance of red tides caused by dinoflagellates?
Red tides are harmful due to the neurotoxins produced by certain dinoflagellates, affecting marine life and human health.
What is the significance of the eyespot in Euglena?
The eyespot in Euglena aids in phototaxis, allowing the organism to move towards light.