MICROBIO LAB FINAL
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1. To achieve safe environments, all labs must include the following
a. Safety equipment
b. Safety practices
c. All of the above
d. None of the above
c. All of the above
2. What is the correct way to clean up a spilled culture in the micro lab classroom?
a. Ask your lab instructor to clean it for you
b. Cover the spill with paper towels and soak with Lysol
c. Dilute with DI water and clean with paper towels
d. None of the above
b. Cover the spill with paper towels and soak with Lysol
3. The act of handwashing is commonly referred to as
a. Cleaning
b. Decluttering
c. Degerming
d. Disinfection
c. Degerming
4. PPE means ______________?
a. Personal Protective Equipment
b. Personal Preparation Experiment
c. People Progress Examination
d. Participant Protective Education
a. Personal Protective Equipment
5. Soaps are considered microbicidal and can help kill bacteria on your hands.
a. True
b. False
b. false
6. Which of the following is used to create a sterile field in the lab classroom?
a. Sterilizer
b. Incubator
c. Sink
d. Bunsen burner
d. Bunsen burner
1. UTA microbiology lab classrooms are considered ______________?
a. BSL1
b. BSL2
c. BSL3
d. BSL4
b. BSL2
8. The ability to transfer liquid in a uniform and repeatable fashion using a pipettor is called ______________?
a. Precision
b. Accuracy
c. Skill
d. Excellence
a. Precision
9. What is the density of water at room temperature?
a. 1 g/ml
b. 1 mg/ml
c. 1 g/L
d. 1 mg/L
a. 1 g/ml
10. You are allowed to bring a drink into the classroom as long as it has a lid.
a. True
b. False
b. False
11. is a method that involves the use of different chemicals to determine how susceptible a bacterium is to different antiseptics and disinfectants
a. Bacteria diffusion assay
b. Infectivity assay
c. Disk diffusion assay
d. None of the above
c. Disk diffusion assay
12. To determine the effectiveness of a certain chemical agent, _____________ is measured in ____________
a. Area of inhibition, centimeters
b. Zone of inhibition, millimeters
c. Area of inhibition, millimeters
d. Zone of inhibition, centimeters
b. Zone of inhibition, millimeters
13. A test done to determine the susceptibility or resistance of specific microbes to various antimicrobial drugs is known as ________________.
a. Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion
b. Beta-lactam diffusion
c. Kirby-Bauer antibiotics diffusion
d. Antibacterial assay
a. Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion
14. Choose the best option that fits how Question 3 answer is performed in a stepwise manner
i. Divide plate into four quadrants and label each quadrant with letters A, B, C, D representing assigned antibiotics.
ii. Pipette 100µl of bacteria culture to the corresponding agar plate and spread bacteria using a cell spreader
iii. Label each TSA plate with one of the two microorganism
iv. Use forceps to place antibiotics on agar plate and allow agar plate to sit for while
a. i, ii, iii, iv
b. iv, ii, i, iii
c. iii, i, ii, iv
d. ii, iv, i, iii
c. iii, i, ii, iv
15. Antibacterial dilution tests are used to determine a particular’s drug MIC, which stands for
a. Maximal Inhibitory Concentration
b. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
c. Medium Inhibitory Concentration
d. Many Inhibitory Concentration
b. Minimal Inhibitory Concentration
1. MIC is the _________ concentration of drug that ____________ visible bacterial growth.
a. Lowest, inhibits
b. Highest, inhibits
c. Lowest, permits
d. Highest, permits
a. Lowest, inhibits
17. A type of media that allows the growth of only specific microorganisms while inhibiting the growth of others is called ______________ ?
a. General purpose media
b. Enriched media
c. Basal media
d. Selective media
d. Selective media
18. You are viewing a specimen with a microscope that has an ocular lens with 10x magnification and an objective lens with 40x magnification. What is the total magnification?
a. 40x
b. 400x
c. 1000x
d. 10x
b. 400x
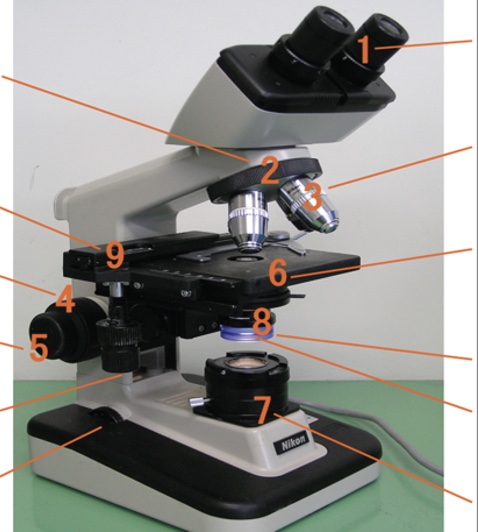
19. Which number is pointing to the condenser lens?
a. 8
b. 3
c. 1
d. 7
a. 8
20. The primary purpose of a heat fixation is to kill the microbes being stained. The secondary purpose is to attach bacteria to a slide.
a. True b. False
b. False
21. What is the purpose of immersion oil in microscopy?
a. To increase magnification
b. To increase numerical aperture
c. To increase contrast of the stain
d. To inactivate the microorganism
b. To increase numerical aperture
22. Which may lead to a false negative in a Gram stain?
a. Cells are too old and have damaged cell walls.
b. Using safranin as the counterstain
c. Using ethanol to decolorize the crystal violet
d. Cells have grown too fast.
a. Cells are too old and have damaged cell walls.
23. _______________. is the pattern that forms during cell division while ________________ is the shape of individual microbial cell.
a. Cellular morphology and arrangement
b. Cellular effect and function
c. Cellular arrangement and morphology
d. Cellular function and effect
c. Celluar arrangement and morphology
24. In differential staining, the first stain is known as __________ while the second stain is _______________
a. Live stain and tertiary stain
b. Primary stain and counterstain
c. Live stain and dual stain
d. Mordant stain and counterstain
b. Primary stain and counterstain
25. Gram negative bacteria appear under the microscope as ____
a. pink
b. purple
c. blue
d. green
a. pink
26. Which is used to examine and observe biofilm development?
A. Crystal violet
B. Safranin
C. Carbolfuchsin
D. Malachite green
A. Crystal violet
27. Which of the following is a common characteristic of biofilms?
A. Increased antibiotic susceptibility
B. Formation of a protective extracellular matrix
C. Complete absence of microbial diversity
D. Only one species of microorganisms is present
B. Formation of a protective extracellular matrix
25. Glycolysis is considered an anabolic reaction. (True/False)
False
29. In the API test, the URE test detects a microbe’s ability to break down urea. This is considered a _________ reaction.
A. Catabolic
B. Anabolic
C. Fermentative
D. Anoxygenic
A. Catabolic
30. What is the total magnification when viewing a microscope with a 100x objective lens and a 10x ocular lens?
A. 100x
B. 10x
C. 1000x
D. This cannot be calculated from the given information
C. 1000x
31. Streptococcus refers to:
A. Chains of cocci cells
B. Chains of bacilli cells
C. Clusters of cocci cells
D. Pairs of cocci cells
A. Chains of cocci cells
32. What color is Gram-Negative organism?
A. Purple
B. Black
C. Blue
D. Pink/Red
A. Pink/Red
33. Cellular morphology refers to the pattern that forms during cellular division. (True/False)
False
34. In a Gram stain, iodine is considered a _______________ and makes dye less soluble so it adheres to the cell wall.
A. Mordant
B. Decolorizer
C. Primary stain
D. Counterstain
A. Mordant
35. Which best describes anabolism?
A. When small molecules are assembled into larger ones.
B. When large molecules are broken down into smaller ones.
C. Exergonic reactions int the cell.
D. More than one of these answers is correct.
A. When small molecules are assembled into larger ones.
36. An indirect ELISA (like that performed in Lab 5) can detect for current COVID infections only.
A. True B. False
False
37. The spike protein of the SARS-COV-2 virus is considered a/an:
A. Antigen
B. Antibody
C. Enzyme chromogen
D. Metabolite
A. Antigen
38. If you have a patient that tests positive in the ELISA performed during Lab #5, then the patient:
A. has an active infection of the SARS-COV-2
B. had a past infection of the SARS-COV-2
C. has been successfully vaccinated against the SARS-COV-2 virus.
D. more than one of these statements is correct.
D. more than one of these statements is correct.
39. If you are vaccinated for a disease like the flu virus, this means your body can produce ___________ that work against viral ___________.
A. antibodies; antigens
B. antigens; antibodies
C. chromagens; antibodies
D. chromagens; antigens
A. antibodies; antigens
40. One explanation for higher rates of antibiotic resistance in biofilms is that there is frequent exchange of extrachromosomal DNA among bacteria that reside within the biofilm.
A. True B. False
A. True
41. One explanation for higher rates of antibiotic resistance within biofilms is that bacterial cells found deep within the biofilm have higher metabolic activity.
A. True B. False
B. False
42. Staphylococcus aureus and Clostridium difficile are both common biofilm formers and are associated with hospital acquired infections (HAI).
A. True B. False
A. True
43. ELISA uses two types of antibodies which are ________ & _______
primary and secondary antibodies
44. Full meaning of ELISA is ___________
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay