Chapter 26 - Carbonyl Compounds
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
carbonyl group + aldehydes and ketones
C=O
aldehyde = RCHO, -al, C=O at end
ketone = RCOR’, -one, C=O in middle
oxidation of aldehydes
aldehyde + [O] → carboxylic acid
-refluxed with acidified potassium dichromate (VI)
why do aldehydes/ketones react differently to alkenes?
-in alkenes, the C=C bond has no difference in electronegativity so non-polar but in aldehydes/ketones C=O bond is polar as oxygen is more electronegative
-so nucleophiles are attracted towards the slightly positive carbon so undergo nucleophilic addition
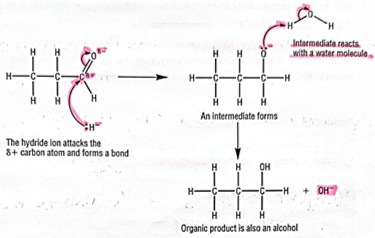
nucleophilic addition -with H- and WATER (DRAW) -propanal
-reacts with hydride ion first then intermediate reacts with water
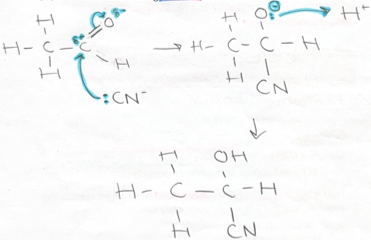
nucleophilic addition -with CN- and H+ (DRAW) -ethanal
reacts with cyanide ion first then intermediate reacts with H+
reduction of carbonyls
-reducing agent = [H] = sodium tetrahydridoborate(III) NaBH4
-forms a H- ion
aldehyde + 2[H] → primary alcohol
ketone + 2[H] → secondary alcohol
reactions with HCN
-reacts to form a hydroxyl nitrile compound
-aldehyde - e.g. ethanal reacts and forms 2-hydroxypropanenitrile
-ketone - e.g. propanone reacts and forms 2-hydroxy-2-methylpropanenitrile
-HCN is highly poisonous so made in situ
Brady’s reagent
2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNP) dissolved in methanol and sulfuric acid as a pale orange solution
Brady’s reagent TEST
1) add 5cm depth of a solution of 2,4-DNP to clean test tube in excess
2) using a dropping pipette, add 3 drops of unknown compound + leave to stand
3) if no crystals form, add a few drops of H2SO4
4) yellow/orange precipitate formed if carbonyl group present
Tollen’s reagent
a solution of silver nitrate dissolved in aqueous ammonia and with added NaOH
Tollen’s reagent TEST
1) pour 2cm depth of unknown solution into clean test tube
2) add an equal volume of the fresh Tollen’s reagent
3) leave test tube to stand in beaker of warm water
4) will form a silver mirror if aldehyde
Tollen’s reagent REDOX reactions
Ag+ + e- → Ag(s) - reducing
RCHO + [O] → RCOOH - oxidising
obtaining a pure sample + checking its purity
1) dissolve impure solid in minimum volume of hot water
2) cool solution and filter solid - wash with cold water and dry
3) solid is recrystallised to produce pure sample of crystals
4) obtain melting point of crystals then compare to known data values
carboxylic acids PROPERTIES
-soluble - the C=O and O-H bonds are polar so are able to form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
→ as the number of carbon atoms increases, the solubility decreases as the non-polar carbon chain has a greater effect on polarity
-weak acids - can partially dissociate in water - form carboxylate ion
HCOOH ⇌ H+ + HCOO-
reactions of carboxylic acids
REDOX: metal + carboxylic acid → salt + water
NEUTRALISATION: metal oxide + carboxylic acid → salt + water
metal hydroxide + carboxylic acid → salt + water
metal carbonate + carboxylic acid → salt + water + carbon dioxide
- used to identify carboxylic acids as they are strong enough to only react with carbonates
carboxylic acid derivatives
compound that can be hydrolysed to form a carboxylic acid
-acid anhydrides
-esters
-acyl chlorides
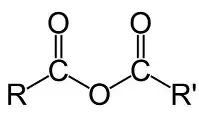
1) acid anhydrides
-formed by removal of water from 2 carboxylic acids
conditions: dehydration + heat
naming: keep prefix of carboxylic acid then add anhydride
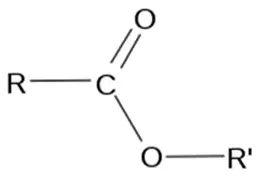
2) esters
-formed by reacting alcohol with carboxylic acid
conditions: alcohol, concentrated H2SO4 acid
naming: prefix = alcohol with -yl, suffix = carboxylic acid with -oate e.g. ethyl butanoate = ethanol + butanoic acid
WHEN DRAWING - draw carboxylic acid first
hydrolysis of esters
C-O bond breaks in ester
-acid hydrolysis = ester heated under reflux with water to form carboxylic acid + alcohol - atoms from water added on - acid is a catalyst
-alkali hydrolysis = ester heated under reflux with aqueous hydroxide ions to form carboxylate salt + alcohol e.g. ONa - atoms from alkali added on
3) acyl chlorides
-formed by reacting SOCl2 with carboxylic acid
-also forms HCl + SO2 which are acidic gases so carried out in fume cupboard
naming: replace -oic acid with -oyl chloride
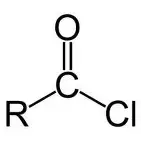
reactions of ACYL CHLORIDES
acyl chloride + alcohol → ester + HCl
acyl chloride + phenol → aromatic ester + HCl
acyl chloride + water → carboxylic acid + HCl
reactions of ACID ANHYDRIDES
anhydride + alcohol → ester + carboxylic acid
anhydride + phenol → aromatic ester + carboxylic acid
anhydride + water → carboxylic acid + carboxylic acid