B7 Cell Bio FINAL
1/486
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
487 Terms
blood plasma
top layer of blood sample
buffy coat
middle layer of blood sample
RBCs
bottom fraction of blood sample
WBCs & platelets
components of the buffy coat
increases
how does hematocrit change with dehydration?
cytoskeleton that is anchored to the plasma membrane by glycophorin and the band 3 Cl-HCO3 exchanger
what helps maintain the shape of erythrocytes
-mainly hemoglobin
-also carbonic anhydrase, 2,3BPG, glutathione
what are the cytoplasmic components of erthrocytes
anaerobic glycolysis (90%)
pentose shunt (10%)
energy source of RBCs
12 weeks
at what week of gestation are RBCs start to be produced by spleen, lymphoid tissue, bone marrow
12 weeks
at _____ weeks gestation iron accumulates rapidly and is used for hemoglobin production and stored in liver
-this is important bc there is little iron in breast milk!
bone marrow of all bones
from the last month of gestation to 5 years old, where doe RBCs come from
bone marrow of vertabrae, sternum, ribs
beyond 5 years of age, where do RBCs come from?
Hematopoiesis
the process of generating all of the cell types present in blood
IL-3, low blood oxygen
growth inducers of hematopoietic stem cell growth
low blood oxygen, EPO
inducers of hematopoietic stem cell differentiation
Erythropoieten (EPO)
hormone essential for the differentation of burst forming erythroid cells to proerythroblasts
proerythroblasts
EPO helps differentiate cells to this RBC precursor which lacks hemoglobin
polychromatic erythroblasts
at what stage of erythropoiesis doe hemoglobin first appear?
reticulocyte
exocytosis of the nucleus results in what RBC precursor?
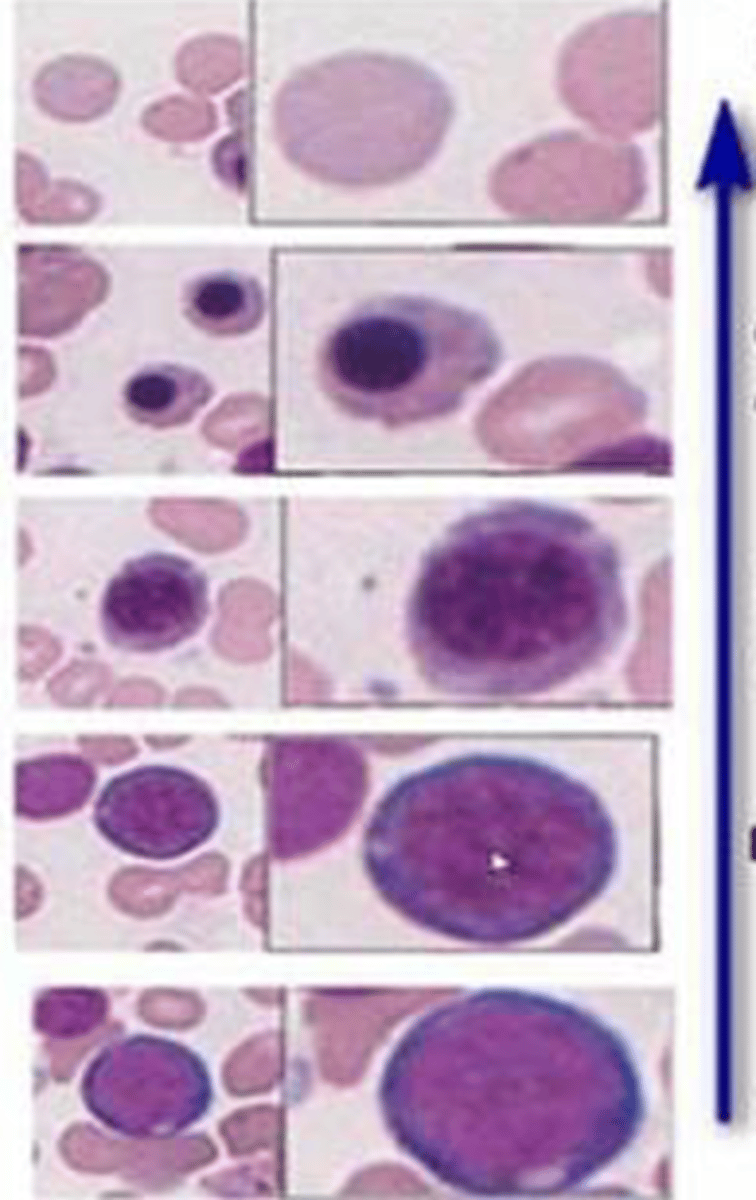
-proerythroblasts: light, spherical nucleus with thin rim of cytoplasm
-basophilic erythroblasats: fractured
-polychromatophilic: darkening, pools of grey
-orthochromaatophilic: dark, small nucleus
-reitculocytes: no nucleus and blue cytoplasm
-erythrocytes: no nucleus and red cytoplasm
name the stages of erythropoiesis and their histology (bottom to top)
-make sure adequate RBCs are available for O2 transport
-make sure excessive number of RBCs do not impede blood flow
regulation considerations of EPO
tissue oxygenation
most important regulator of RBC production
high HIF1a transcription factor is a hypoxia sensor that tells EPO in the kidney to turn up
how does hypoxia activate EPO
PGE2, adenosine, NE, thyroid hormone, androgens (estrogen inhibits)
stimuli of EPO production
-vitamin B12 and folic acid are essential for synthesis of DNA
vitamins essential for RBC maturation
-abnormal or diminished DNA resulting in failure of nuclear maturation
-macrocytes
-fragile RBCs
lack of vitamin B12 or folic acid causes maturation failure of RBCs due to:
globin
a polypeptide, either alpha chain or Beta chain
-synthesis begins in the proerythroblast
Orthochromatic erythroblast
by what stage of erythropoiesis has the cell synthesized all the hemoglobin it will ever carry?
glycine and succinyl coA
from what amino acids is heme formed?
condense via δ-ALA synthase
form δ-aminolevulinic acid
in the formation of heme, glycine and succinyl CoA condense via _______ to form _____
Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
what vitamin is required in the formation of heme?
-required for Succinyl-CoA and Gly condense via δ-ALA synthase to form δ-aminolevulinic acid
mitochrondria
first step of heme synthesis occurs in
cytosol
where in the cell are prophyrinogens formed during heme synthesis
-in the mitochondria
-iron (Fe2+) is incorporated into protoporphyrin IX in a reaction catalyzed by ferrochelatase (heme synthase)
-generating heme
describe the final step of heme synthesis
ALA-dehydrase (beginning)
ferrochelatase (final step)
what enzyme does lead poisoning inhibit in heme synthesis
-increased H+ (low pH)
-increased CO2
-increased temp
-increased DPG
causes of right shift in oxygen binding curve (decreased affinity)
2,3-diphosphoglycerate (2,3-DPG)
component of RBCs
-when bound to hemoglobin, it stabiilizes the T state conformation and decreases hemoglobin affinity for O2
HbF α2γ2
-quiclly replaced after birth with beta
Hb subunits in fetal development
α2δ2
hemoglobin type highly associated with thalassemias
sub valine for glutamate in the 6th amino acid of the β-globulin gene
genetic substitution associated with sickle cells anemia (HbS)
-makes the Hb less soluble resulting in its polymerization and precipitation
sub lysine for glutamic acid in the 6th position of the β-globulin chain
genetic substitution associated with HbC (mild form of sickle cell, cliniclaly silent)
thalassemia major (cooley's anemia)
homozygous B-thalassemia that results in severe hemolysis, ineffective erythropoiesis, transfusion dependency, iron overload
Hemoglobin H (alpha thalassemia)
thalassemia associated with mild hemolysis; not transfusion dependent
Hemoglobin is broken down into heme, which is converted to biliverdin, and finally into unconjugated bilirubin (which is not water-soluble).
-unconjugated bilirubin binds to albumin and takin to the liver to become conjugated and ultimately excreted
breakdown of hemoglobin into bilirubin
megaloblastic anemia
anemia associated with incomplete maturation of RBC precursor cells
microcytic, hypochromic anemia
anemia associated with aberrant O2 carrying capacity of RBCs
-more RBCs being made by bone marrow
-high altitude
high values of reticulocyte count indicate
aplastic anemia
iron deficiency anemia
radiation
chronic infection
causes of low reticulocyte count
reticulocyte count
marker of effective erythropoiesis
hematocrit
percentage of whole blood volume composed of erythrocytes
hemoconcentration (burns, dehydration, vomiting)
polycythemia
extreme physical exercise
increased hematocrit indicates
Macrocytic, microcytic, and normocytic anemia
decreased hematocrit indicates:
Mean Corpuscular Volume (MCV)
average volume of red cells
Liver disease, alcohol abuse, hemochromatosis, vitamin B12 deficiency, reticulocytosis, chemotherapy
increasaed MCV indicates
Iron deficiency, polycythemia vera, thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, lead poisoning
decreased MCV indicates
mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration
the average hemoglobin concentration in the RBCs
Hypochromic anemia (iron deficiency, thalassemia, lead poisoning)
sideroblastic anemia
anemia of chronic disease – various forms of microcytic anemia
decreased MCHC indicates
increase in the mass of red blood cells (absolute polycythemia)
problem with plasma (relative polycythemia)
main two causes of polycythemia
Blood becomes more viscous, slows its flow through the body
-inc risk of a thrombotic event and related symptoms (clots that lead to stroke or MI or DVTs, blurred vision etc.)
what is the main problem of polycythemia
Reduced plasma volume (hemoconcentration) due to dehydration (diarrhea and severe vomiting) or diuretics
cause of relative polycythemia
absolute polycythemia
primary polycythemia in presence of low erythropoietin
activating mutation in JAK2
mutation associated with polycythemia vera
-increase in mast cells---> itching after hot shower
-erythromelagia--> redness in hands and feet
weird symptoms of polycythemia vera
natural or artificial increases in EPO
-ex: steroids, testesterone, tumors, renal disorders, elevated carboxyhemoglobin
secondary polycythemia is induced by
<65mmHg
PO2 criteria threshold for development of secondary polycythemia
relative polycythemia
plasma volume has decreased by BVC mass has not changed
-normal EPO and no hypoxia
secondary polycythemia
high red blood cell mass due to high EPO
primary polycythemia
erythrocytosis due to neoplastic growth of RBCs even when unstimulated (EPO is low)
mutation of JAK2 associated with EPO receptor---> erythroid lineage cells in bone marrow become hypersensitive to EPO
what causes polycythemia vera?
erythroblastosis fetalis
Hemolytic disease of the new born due to Rh-incompatibility between the mother and the fetus
-antibodies cause baby RBC to be destroyed--> anemia
-compensatae anemia by releasing erythroblsts from bone marrow and liver
-overproduction of erythrroblasts--> liver and spleen enlargement--> rupture
-bilirubiin accumulates---> kernicterus
manifestations of erythroblastosis fetalais
iron deficiency
anemia of chronic disease
thalassemia
sideroblastic anemia
name the microcytic anemias
folate deficiency
vitamin B12 deficiency
name the macrocytic anemias
microcytosis and hypochromia
hallmarks of microcytic anemia
-iron deficiency
-sideroblastic anemia
-lead poisoning
-anemia of chronic disease or inflammation
microcytic anemias secondary to defects in heme synthesis
Sideroblastic anemia
microcytic anemia marked by genetic defects in heme synthesis pathway causing failure to synthesize porphyrin ring
lead poisoning
blocks incorporation of iron into heme----> microcytic anemia
microcytic anemia
in chronic disease, secretion of inflammatory markers impair RBC synthesis by interfering with iron absorption and erythropoietin function--->
thalassemias
example of microcytic anemia caused by failure of globin synthesis
-peptic ulcer
-celiac disease
-gasterctomy
-infections (hookworm)
causes of impaired iron absorption
cytochrome B and vitamin C
non heme ferric (Fe3+) reduced by ferrous (Fe2+) by
vitamin C
vitamin to help absorb Fe2+
DMT1
non-heme iron is taken up into enterocyte via
HCP1
heme iron is taken up into enterocyte by
Plants
non-heme iron comes from
meat
heme iron in diet comes from
hephaestion
-converts ferrous iron into ferric iron after absorption by enterocytes
-ferric (Fe3+)iron is then transported into blood by ferroportiin
ferroportin
ferric iron is transported in blood via
Transferrin
ferritin is transported to tissues via
high ferritin--> iron overload
defect in ferroportin leads to
hepcidin
central regulator of iron homeostasis, found in liver parenchymal cells and induced by inflammation
ferroportin
hepcidin interracts with _______ to iinhibit iron absorption
-Internalized and degraded thus decreasing intestinal iron absorption and inhibiting release of iron from enterocytes and macrophages
HFE gene
protein that inhibits release of Fe from the cytoplasm to mitochhondria
-defect causes hemochromatosis
serum iron
ferric (Fe3+) iron bound to serum transferrin
increases
transferrin _____ in iron deficiency to maximize the utilization of availaable iron
chronic infections
hemochromatosis
protein deficiency
transferrin is decreased in:
iron deficiency anemia, pregnancy
transferrin is increased in
direct
relationship of TIBC and transferrin
iron deficiency anemia
low serum iron
low ferritin
low transferrin saturation
high TIBC
high transferrin
hemochromatosis
high serum iron
high ferritin
high transferrin saturation
low TIBC
low transfferrin