Semester 2 Final Exam Vocab Review Set 2: Cell Cycle, Meiosis, and Genetics Mrs. K
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
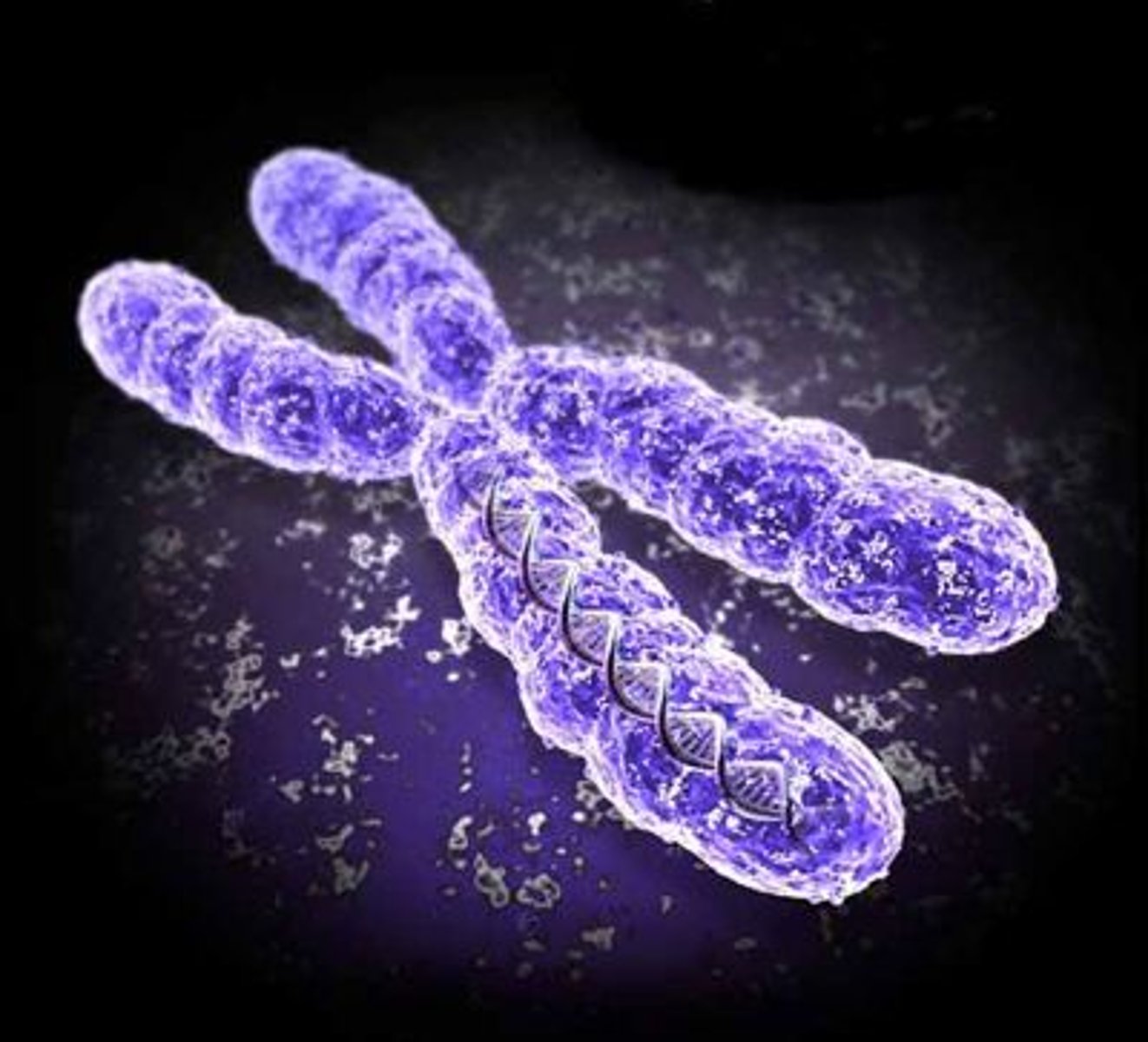
chromosome
condensed threads of genetic material formed from chromatin as a cell prepares to divide
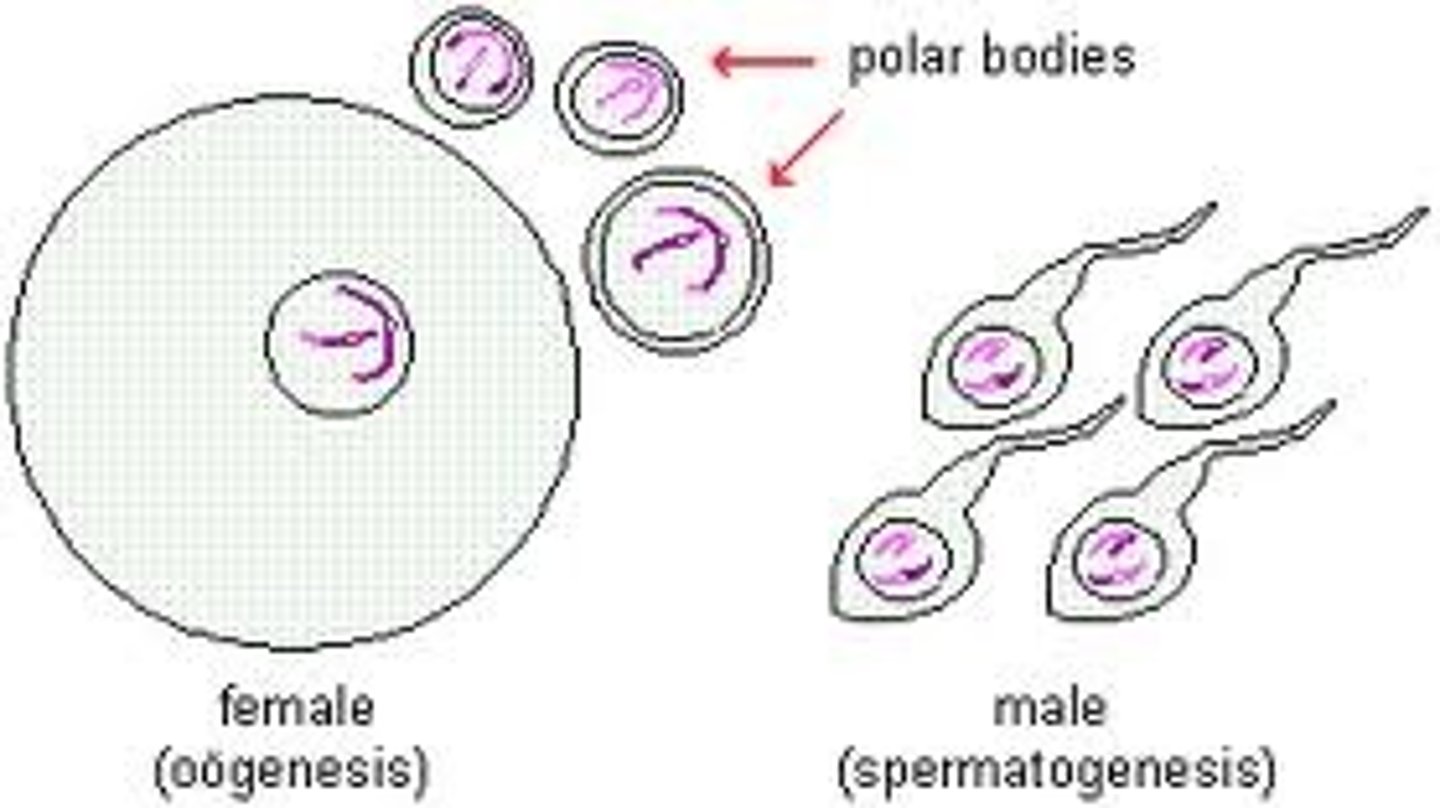
gamete
egg or sperm sex cell that contains a single set of chromosomes, one from each homologous pair (haploid)
sex chromosome
one of the pair of chromosomes that determine the sex of an individual (XX- female, XY- male)
mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into TWO nuclei containing the SAME number of chromosomes
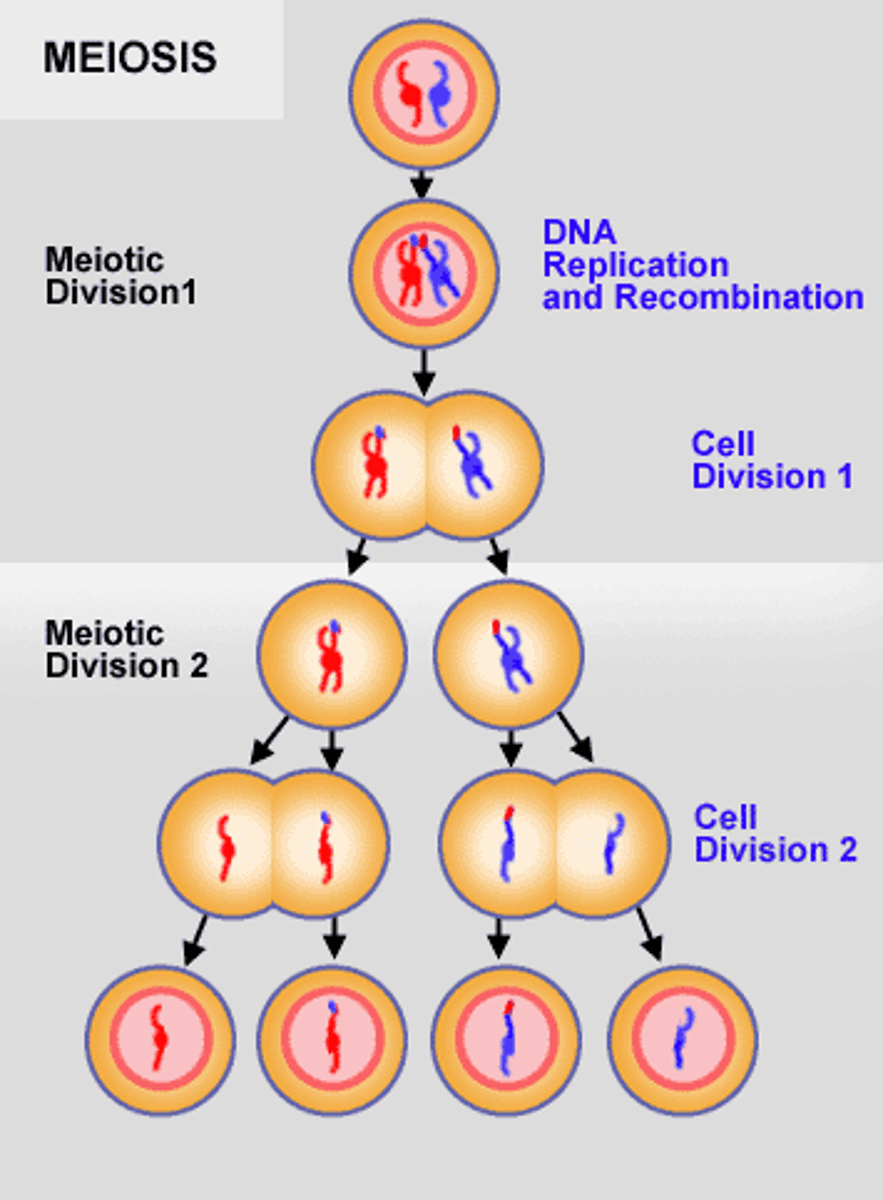
meiosis
the process by which the number of chromosomes is reduced by half to form 4 haploid sex cells/gametes
trait
A characteristic that an organism can pass on to its offspring through its genes.
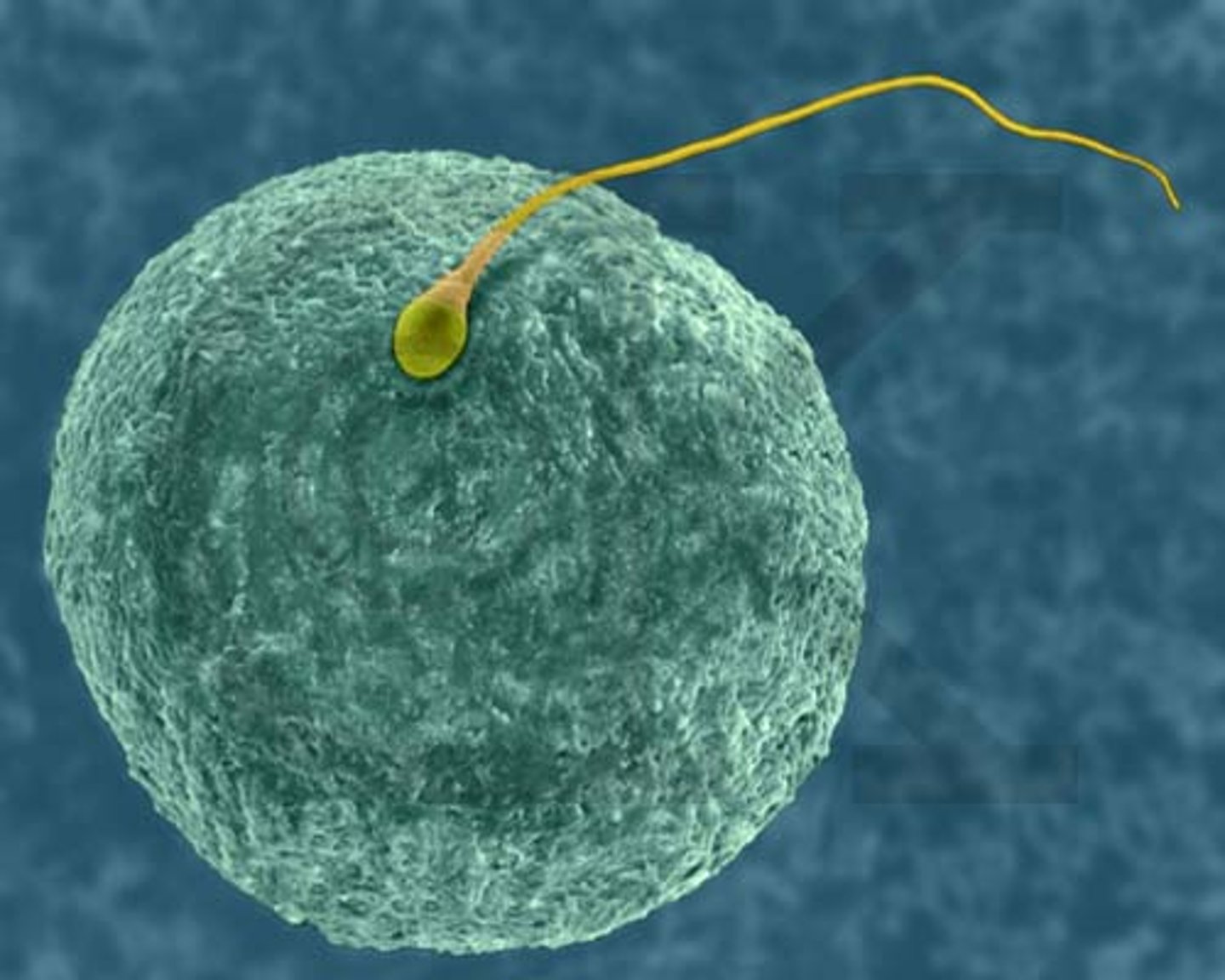
fertilization
Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female sex cells join to form a new cell/baby
allele
A version of a particular gene
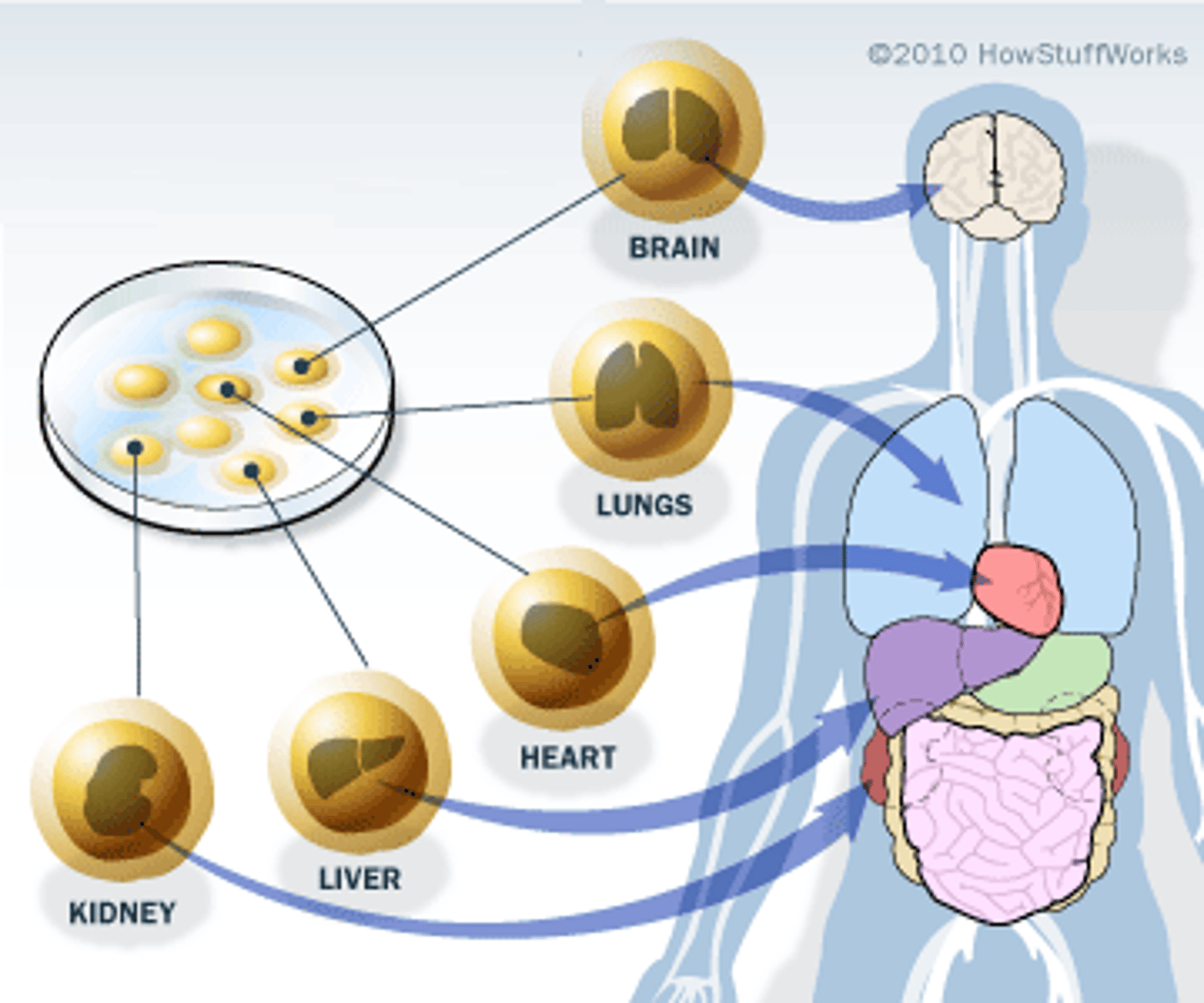
Cancer
disorder in which some of the body's cells lose the ability to control growth and divide uncontrollably. The resulting cells that interfere with the normal function of other cells.
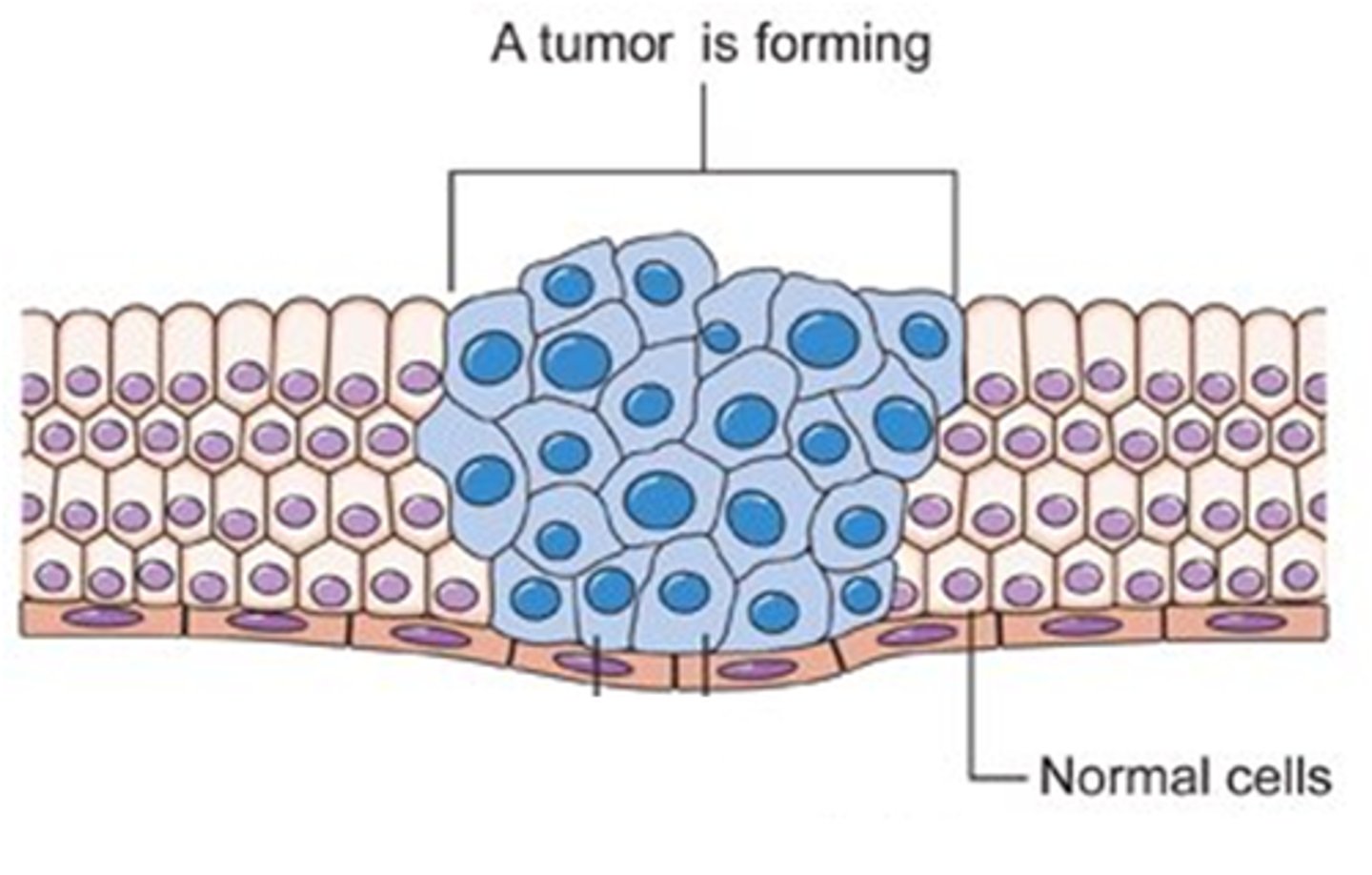
Carcinogen
A cancer-causing substance

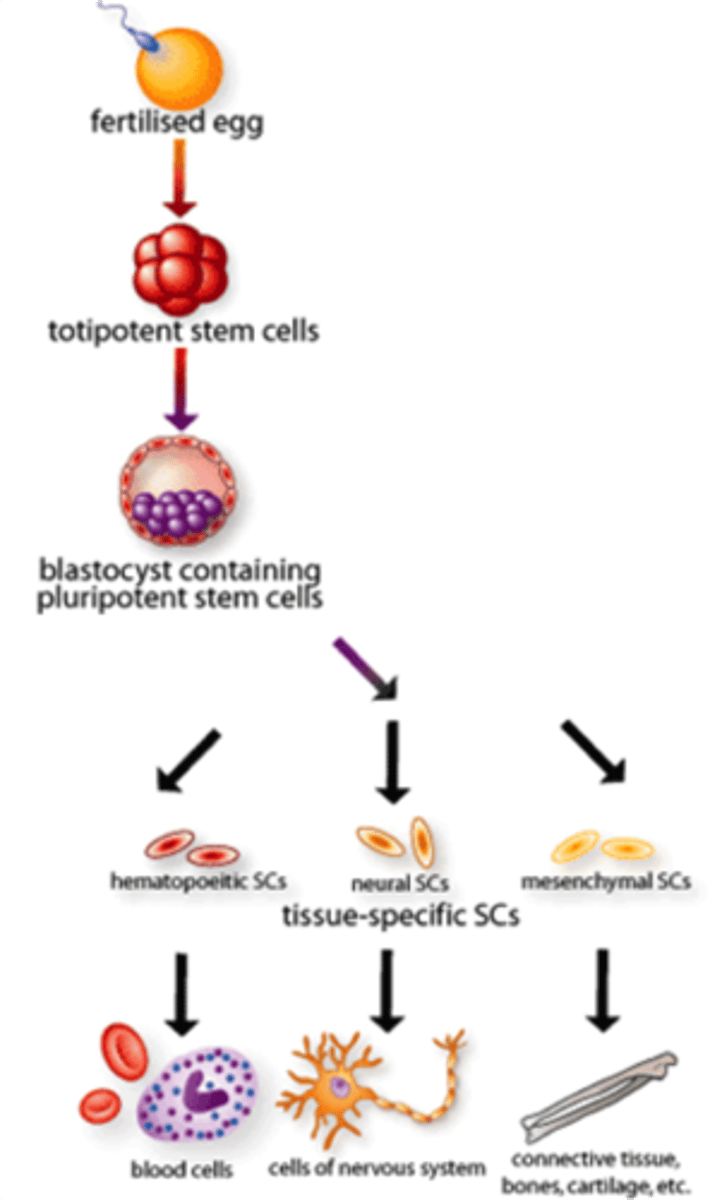
stem cells
An undifferentiated cell that is capable of dividing and giving rise to one or more distinct types of differentiated cell(s).
Cell Differentiation / Specialization
The process by which stem cells acquire specific functions and structures.
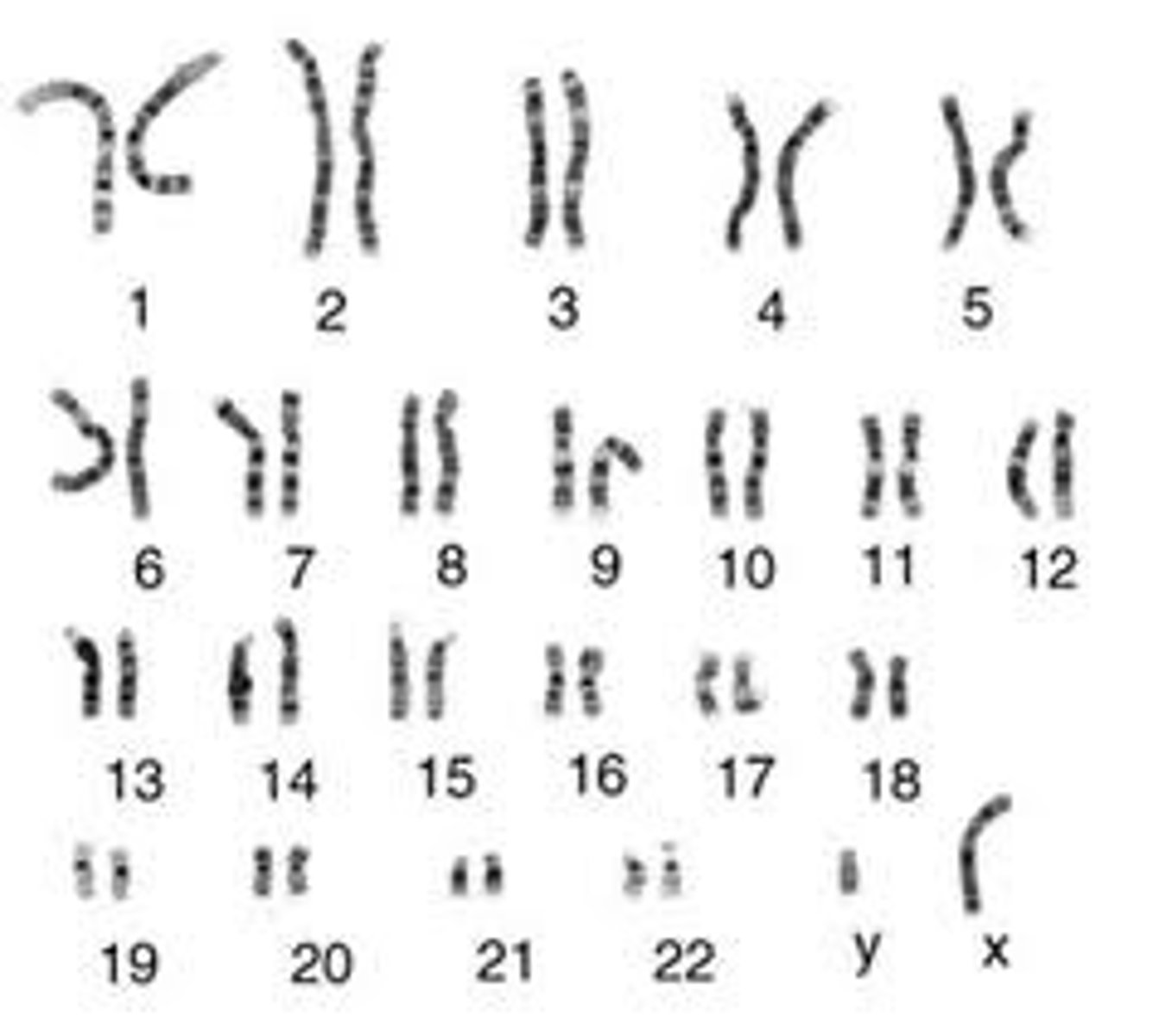
Karyotype
A display of the chromosome pairs of a cell arranged by size and shape.
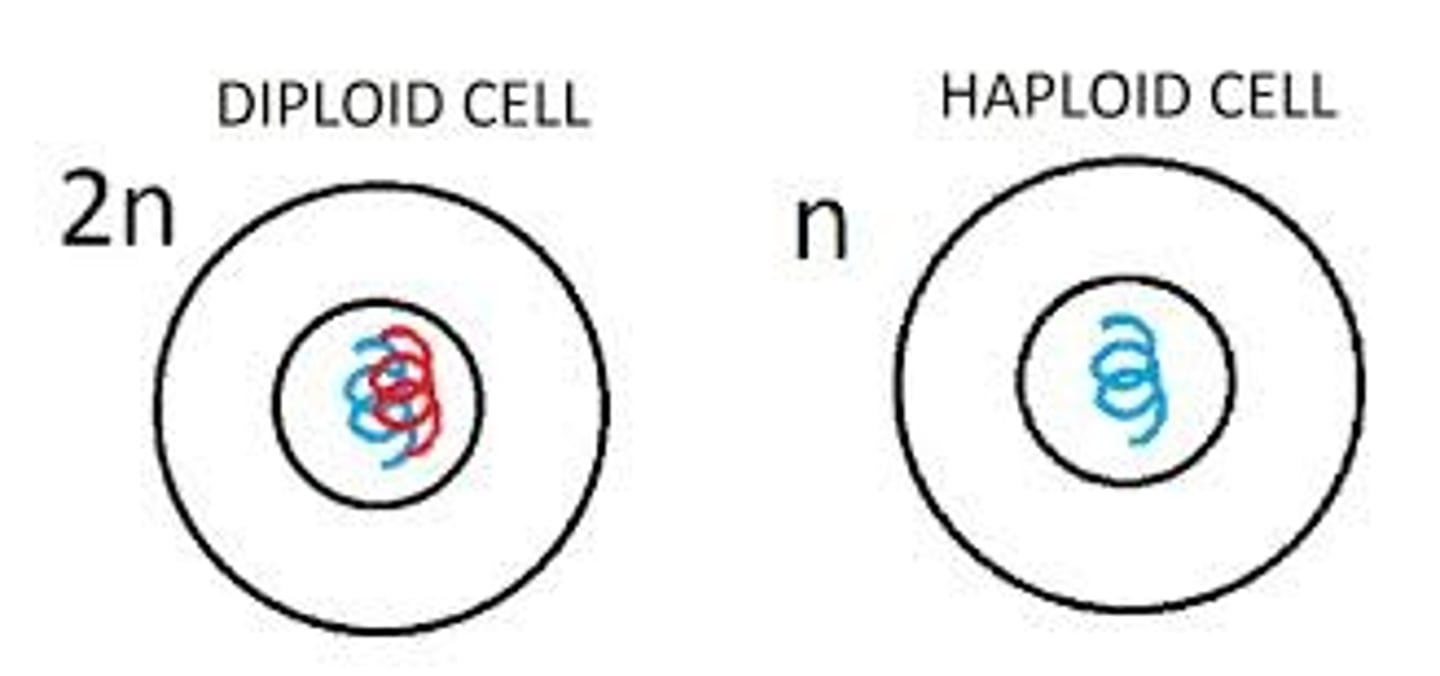
Haploid
sex cells/gametes having only one complete set of chromosomes. (23 chromosomes in humans)
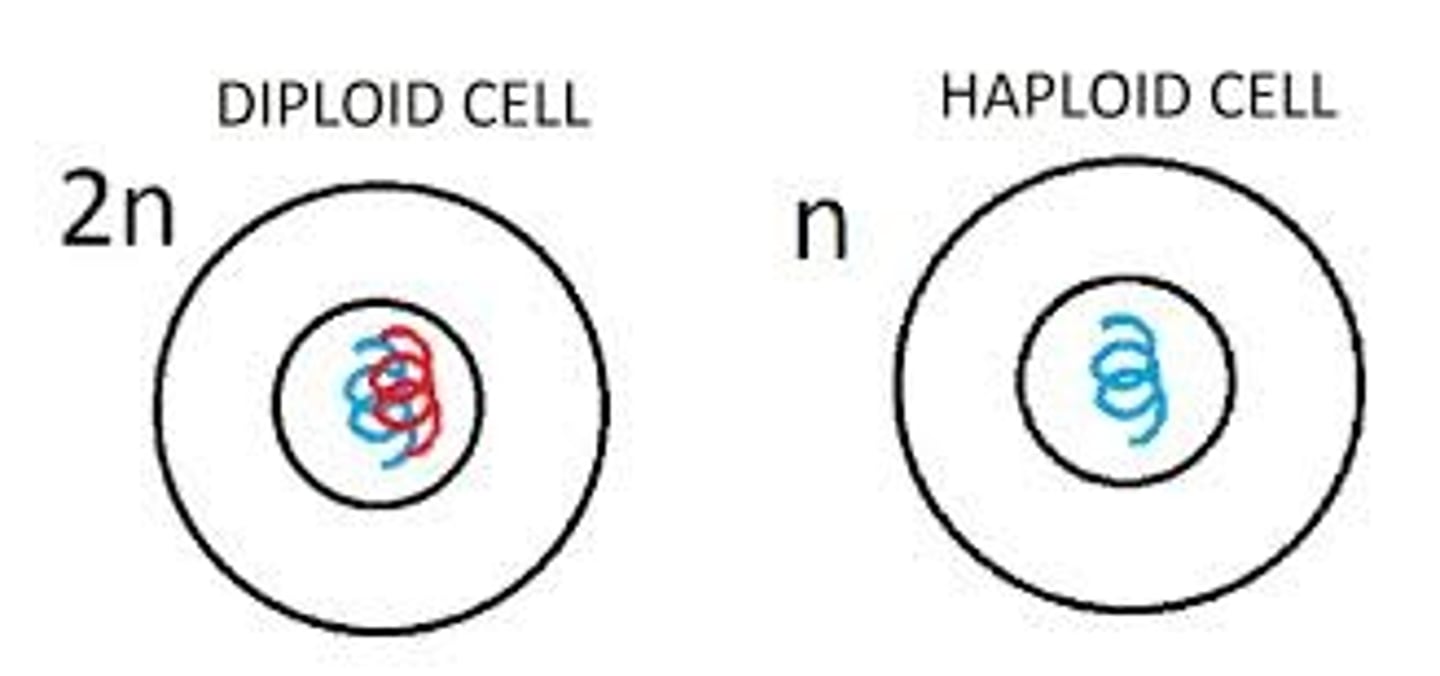
Diploid
a body/somatic cell having two sets of chromosomes or twice the haploid number (46 chromosomes in humans)
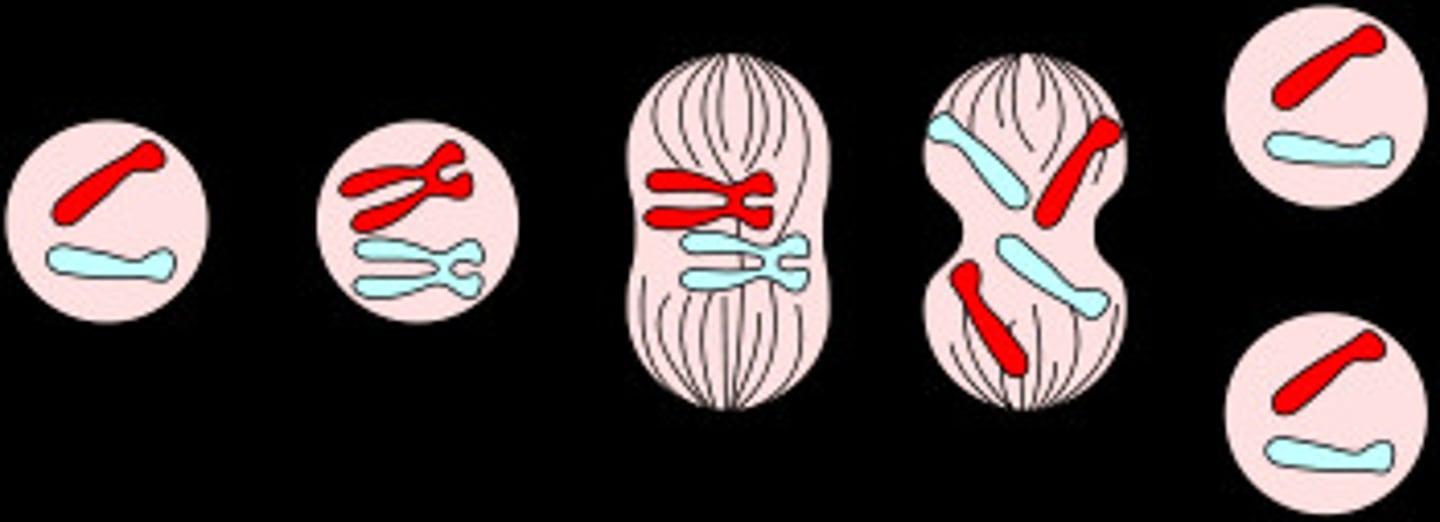
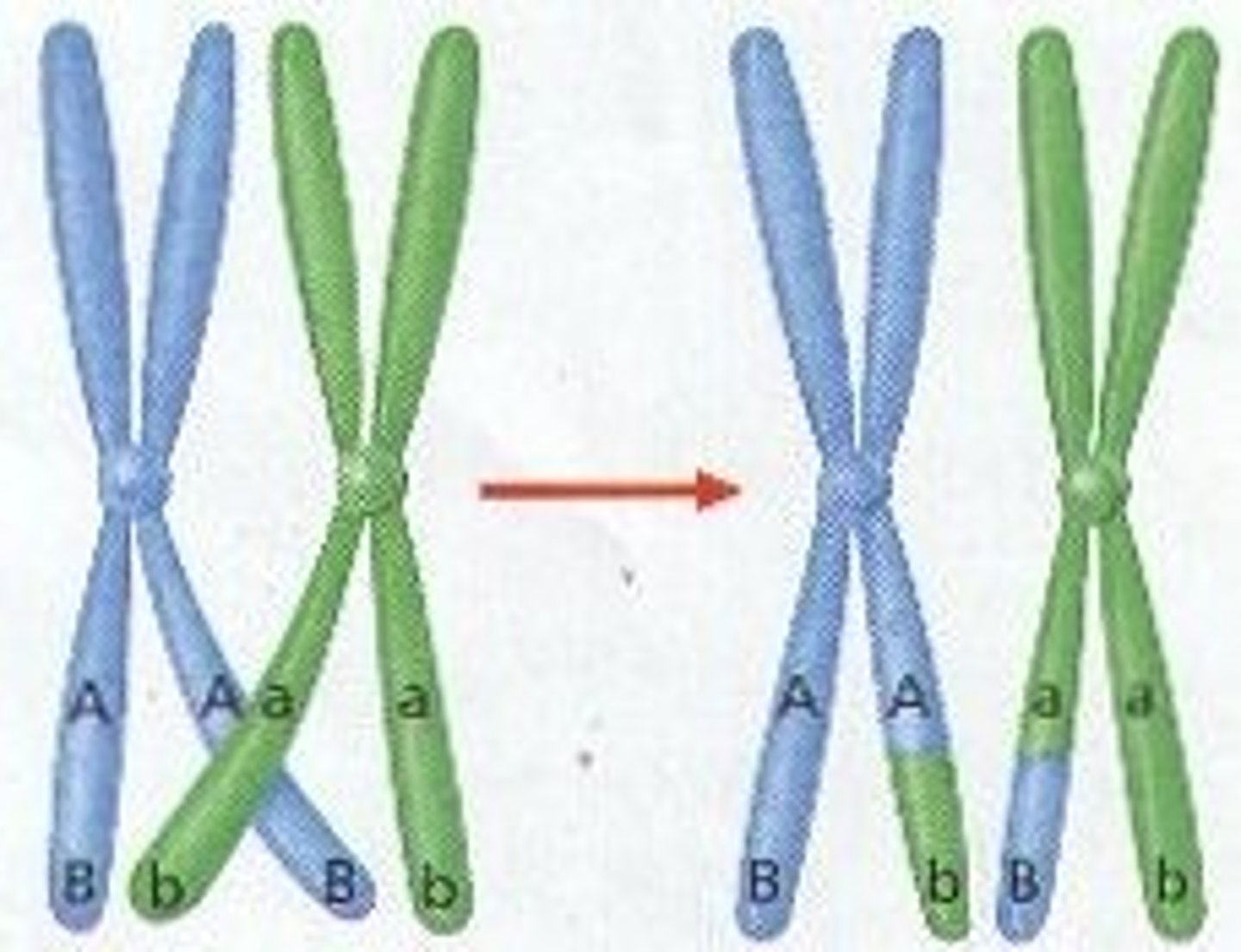
crossing over
Process that contributes to genetic variation in which homologous chromosomes exchange portions of their chromatids during meiosis.
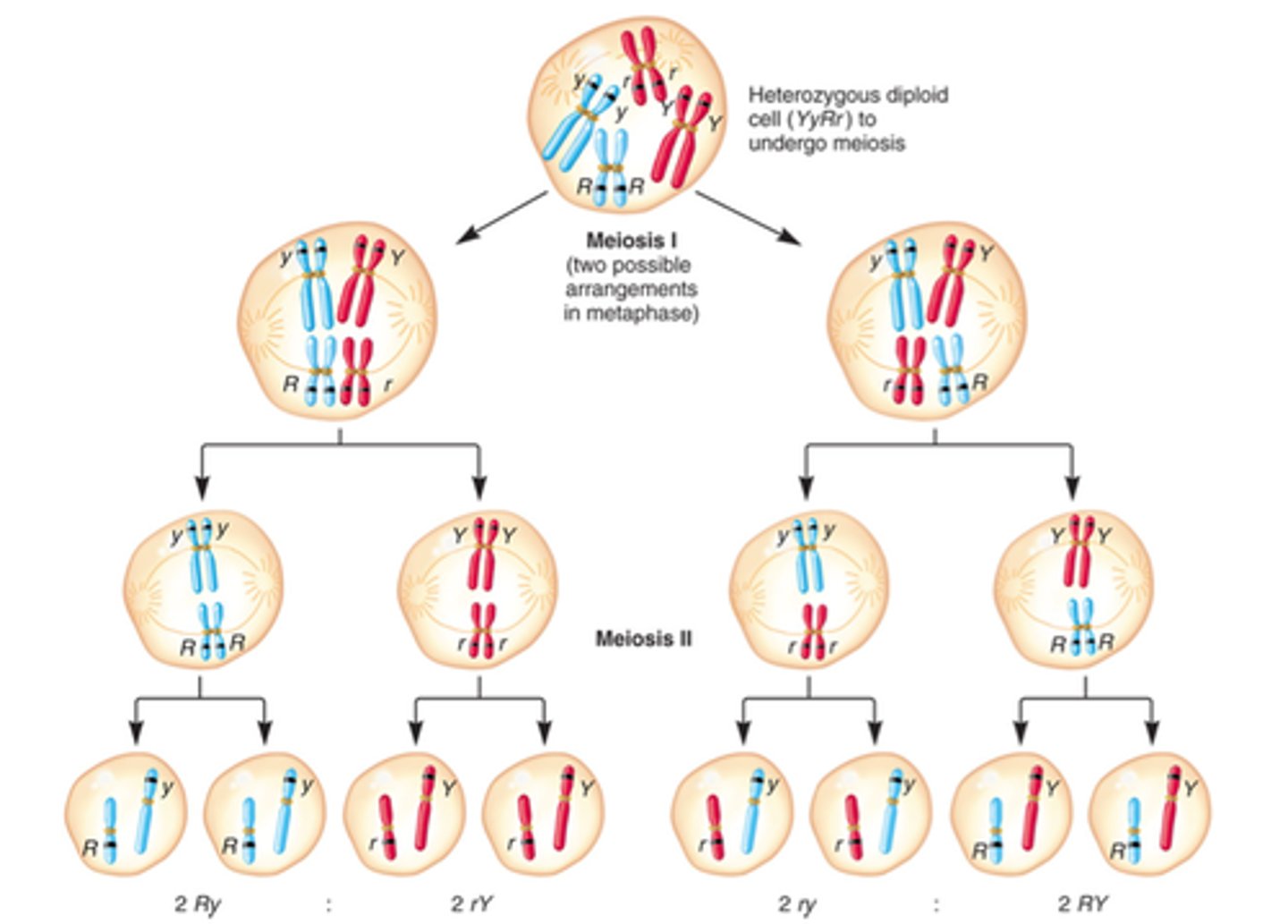
independent assortment
Process that contributes to genetic variation states that genes for different traits can segregate independently during the formation of gametes
S Phase (interphase of mitosis)
The synthesis phase of the cell cycle; the portion of interphase during which DNA is replicated.
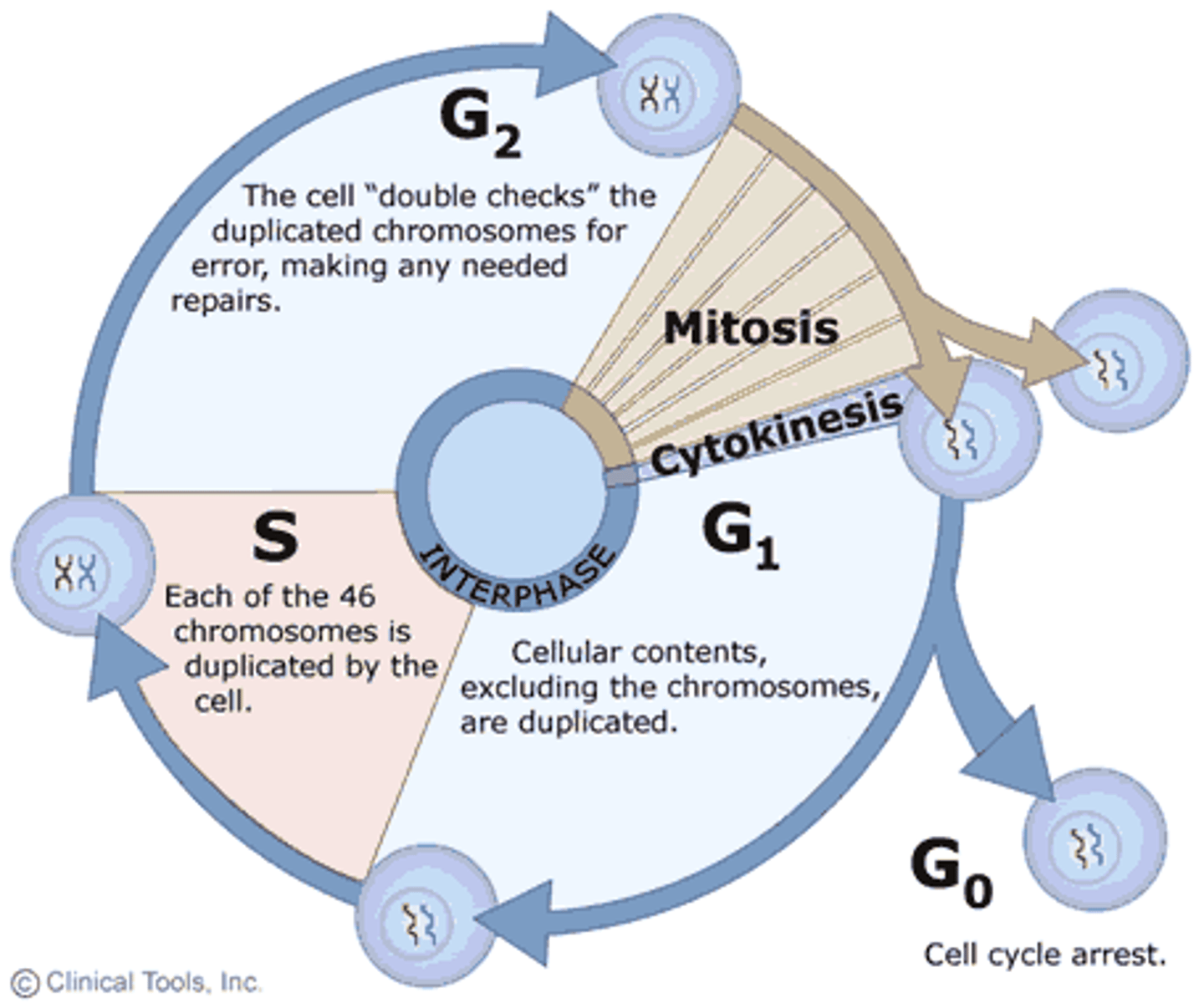
The normal chromosome number in a human cell is
46
somatic cells
Any diploid cells in the body that are NOT reproductive cells
Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene (i.e. AA or aa)
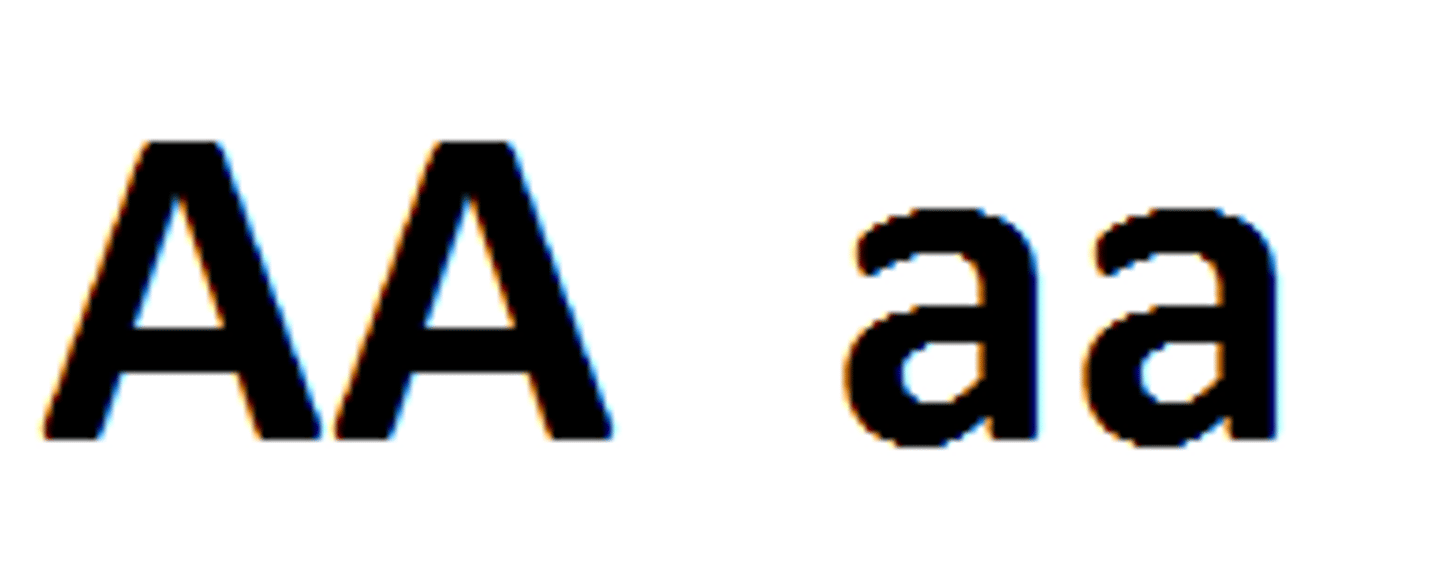
Heterozygous
having two different alleles for a trait (i.e. Aa)

Phenotype
physical characteristics/appearance of an organism (i.e. Tall)
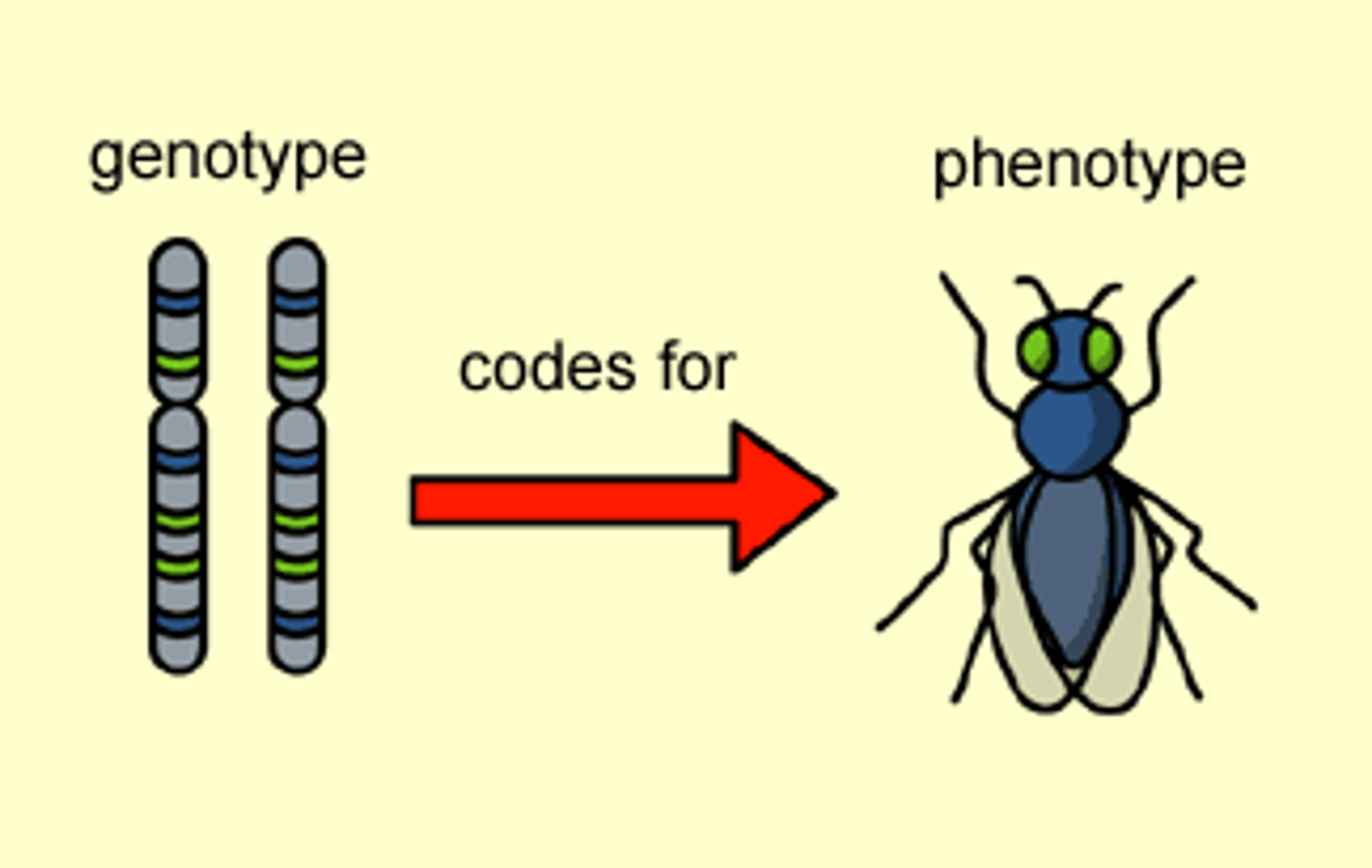
Genotype
An organism's genetic makeup, or allele combinations.
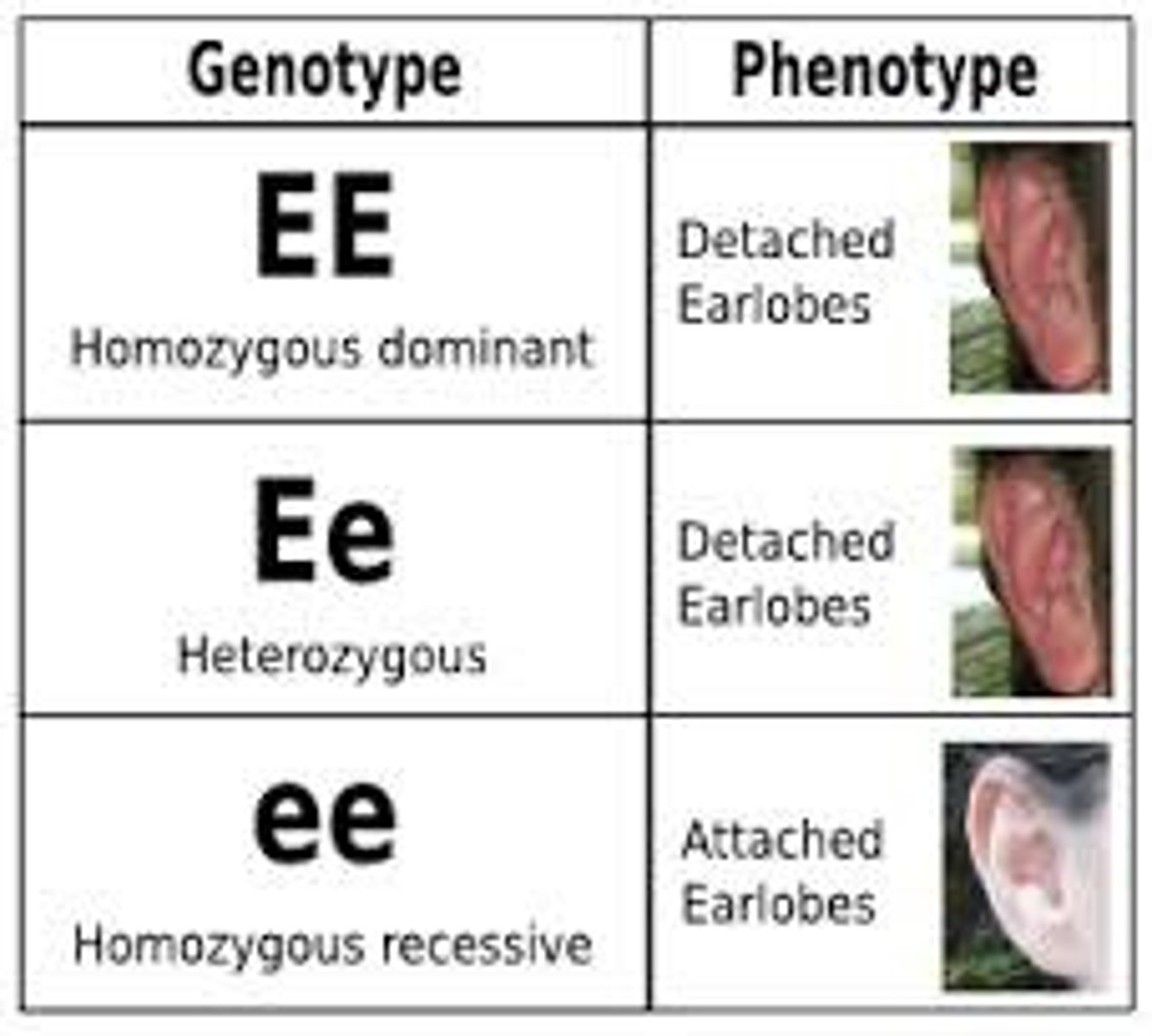
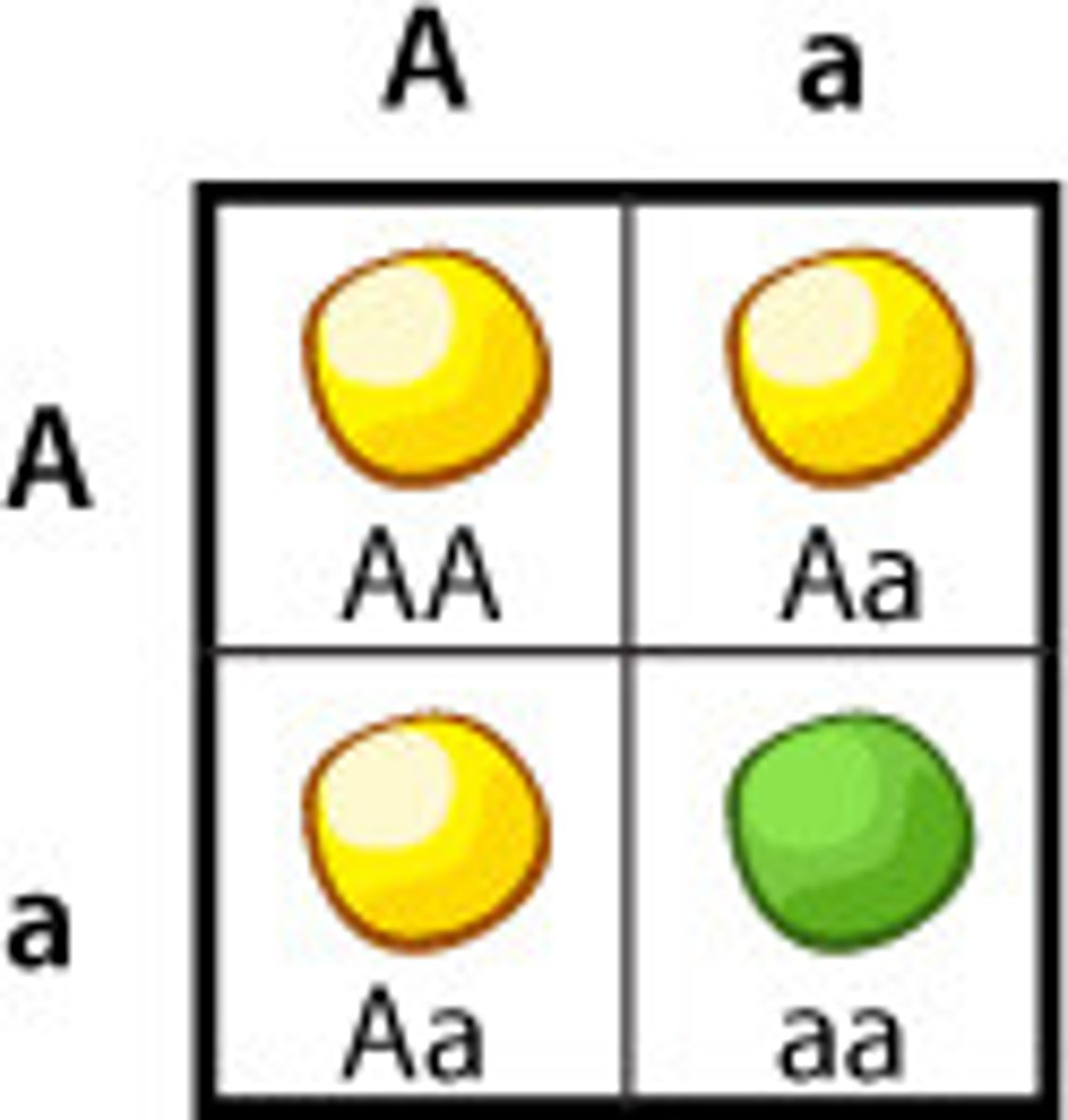
Punnett Square
A chart that shows all the possible combinations of alleles that can result from a genetic cross
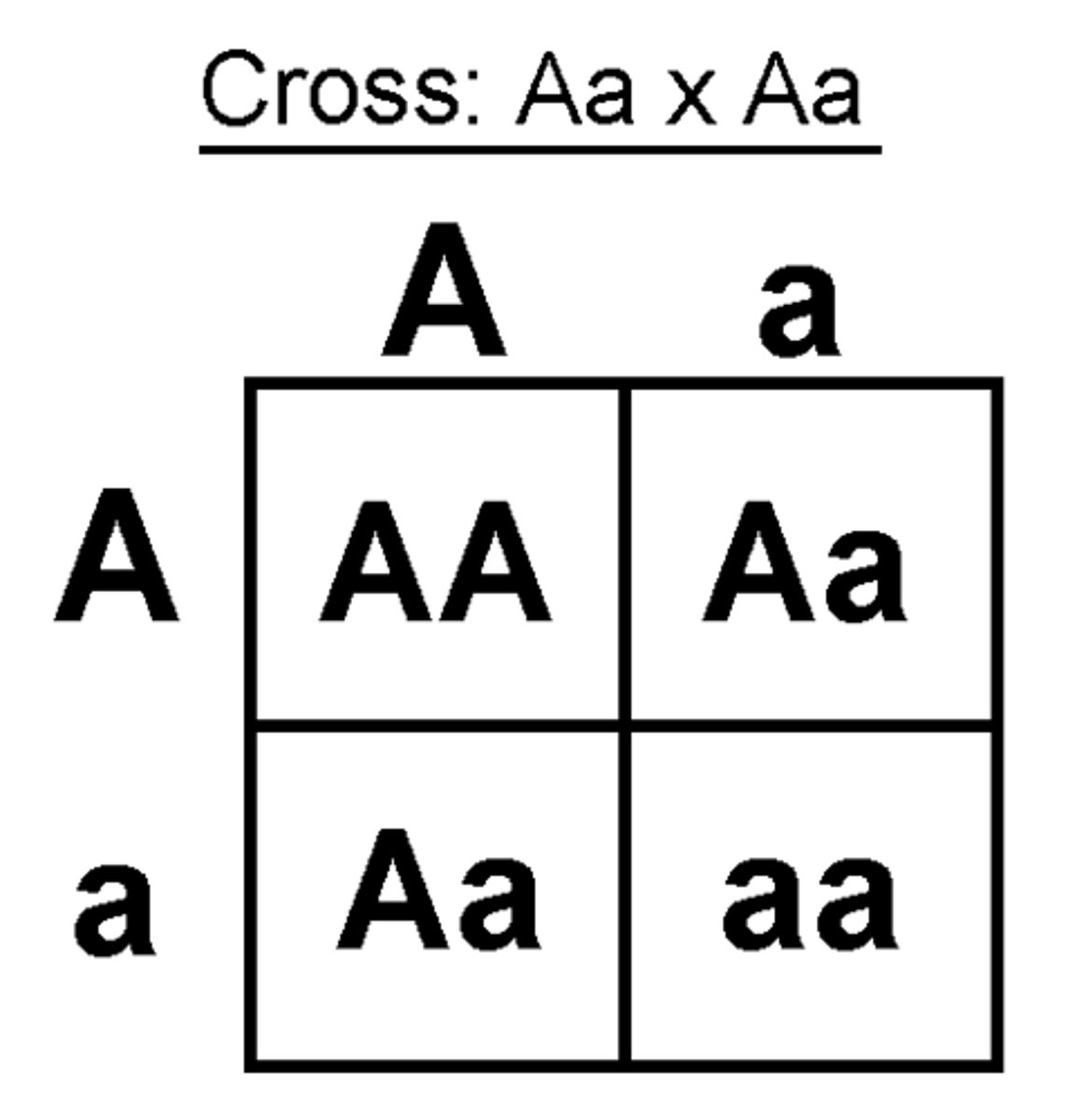
homozygous dominant
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and dominant (AA)
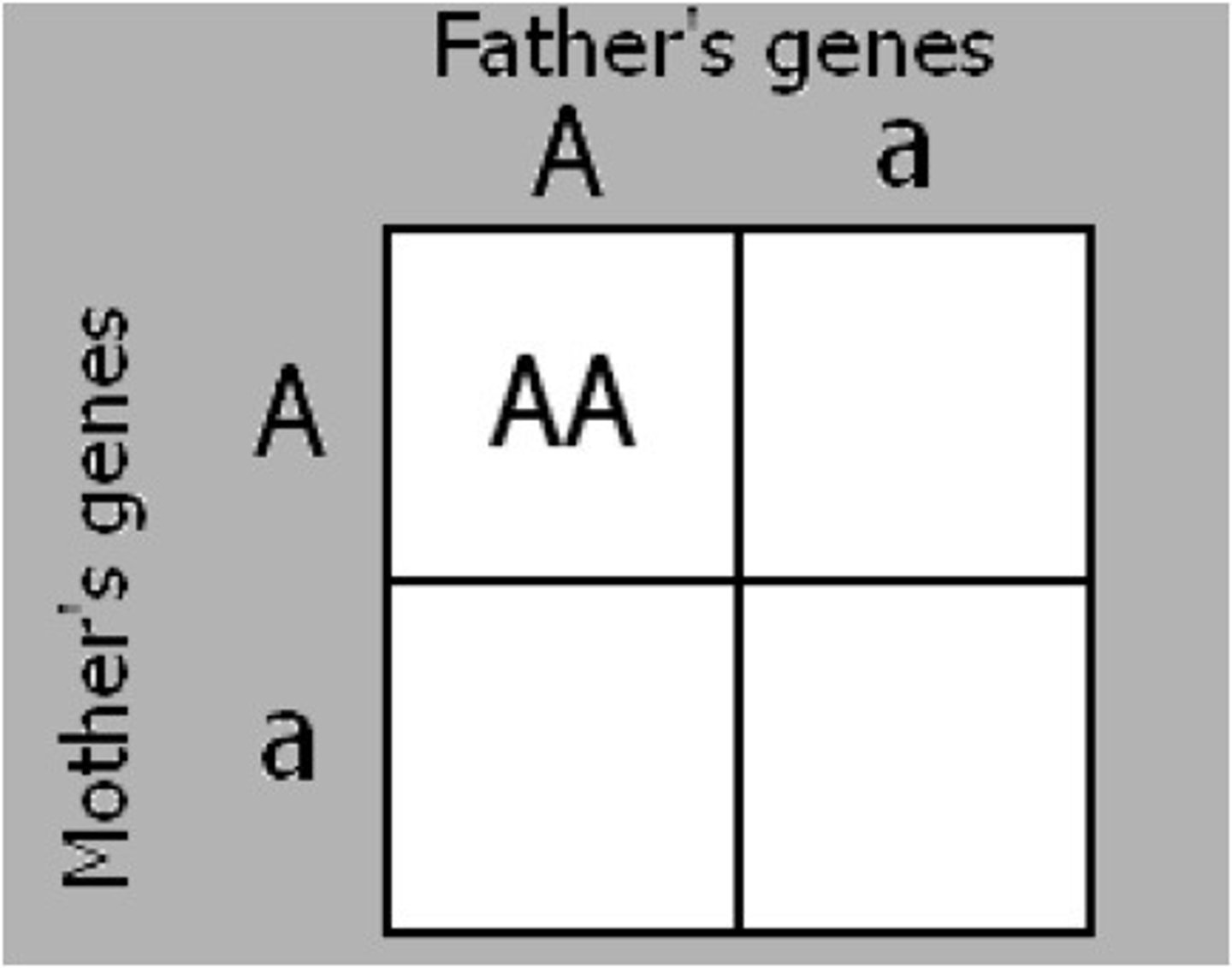
homozygous recessive
Both alleles (factors) for a trait are the same and recessive (aa)

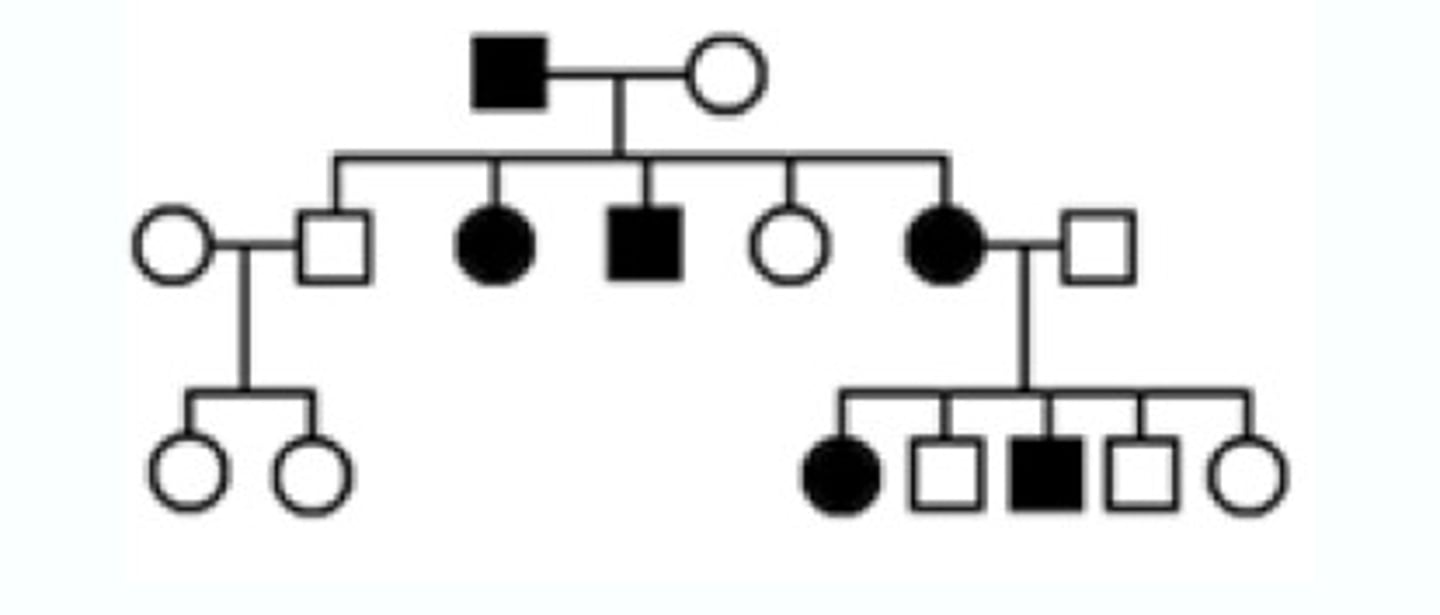
Pedigree
A chart or "family tree" that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait
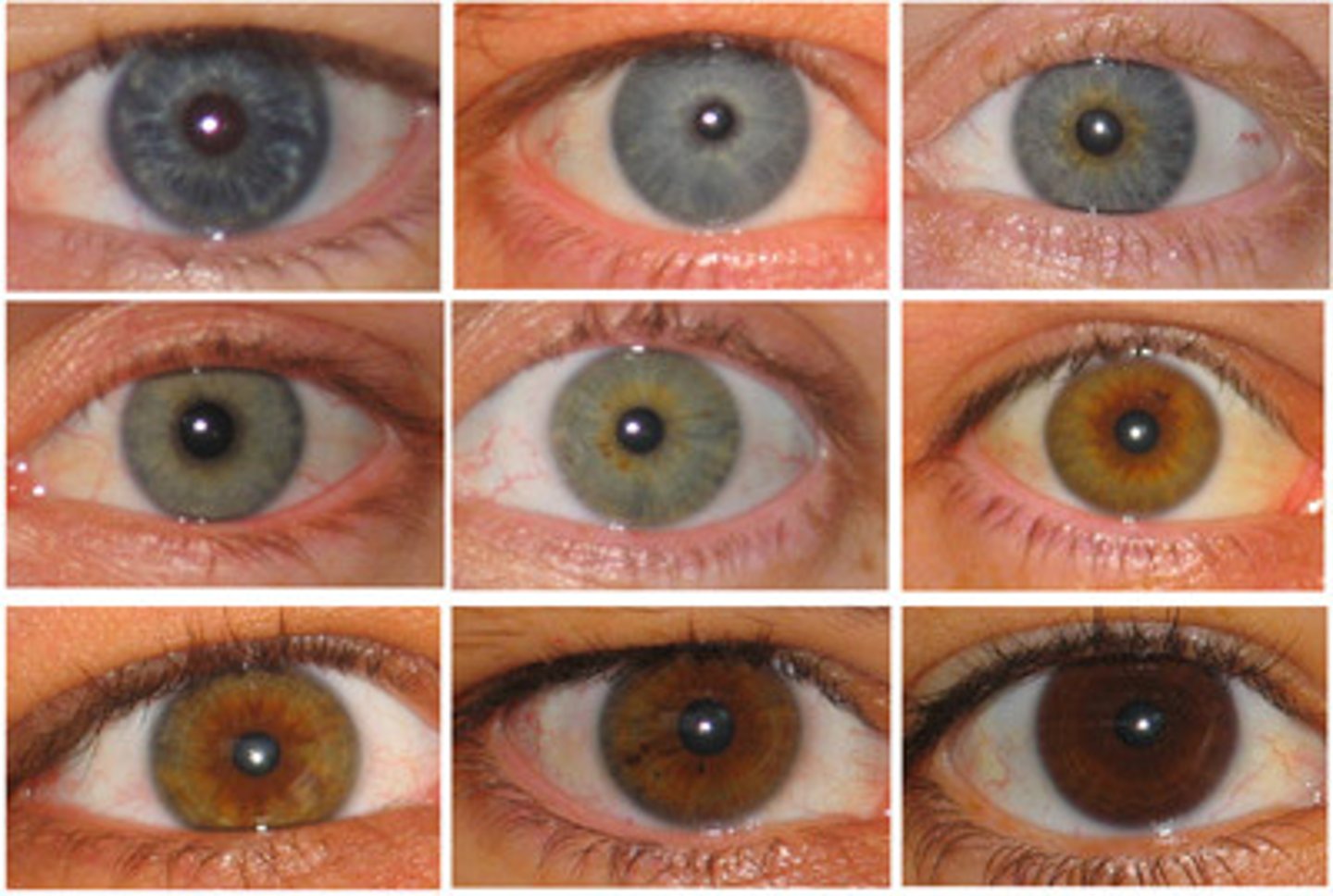
multiple alleles
three or more forms of a gene that code for a single trait

Codominance
A condition in which both alleles for a gene are fully expressed
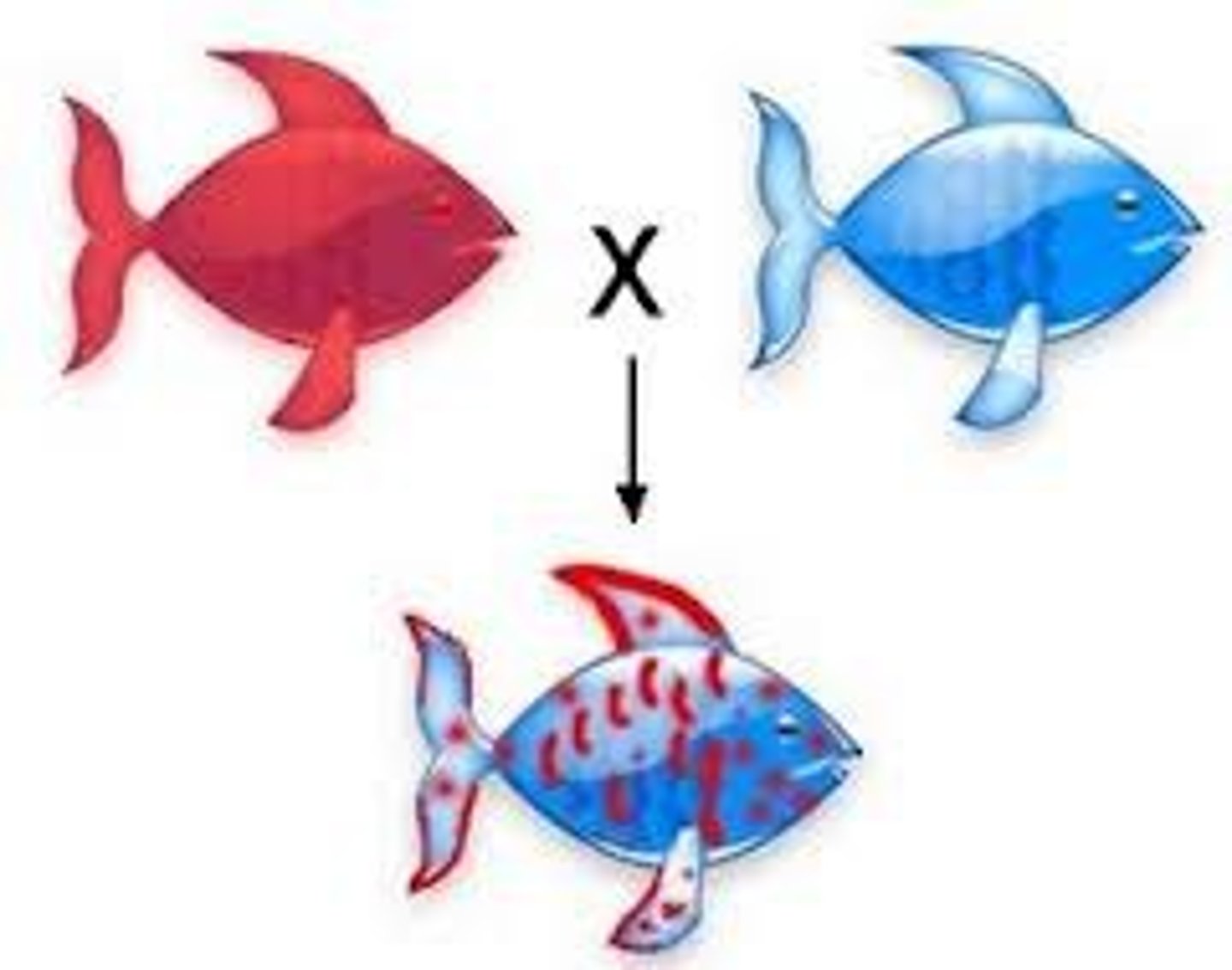
incomplete dominance
A pattern of inheritance in which two alleles, inherited from the parents, are neither dominant nor recessive. The resulting offspring have a phenotype that is a blending of the parental traits.
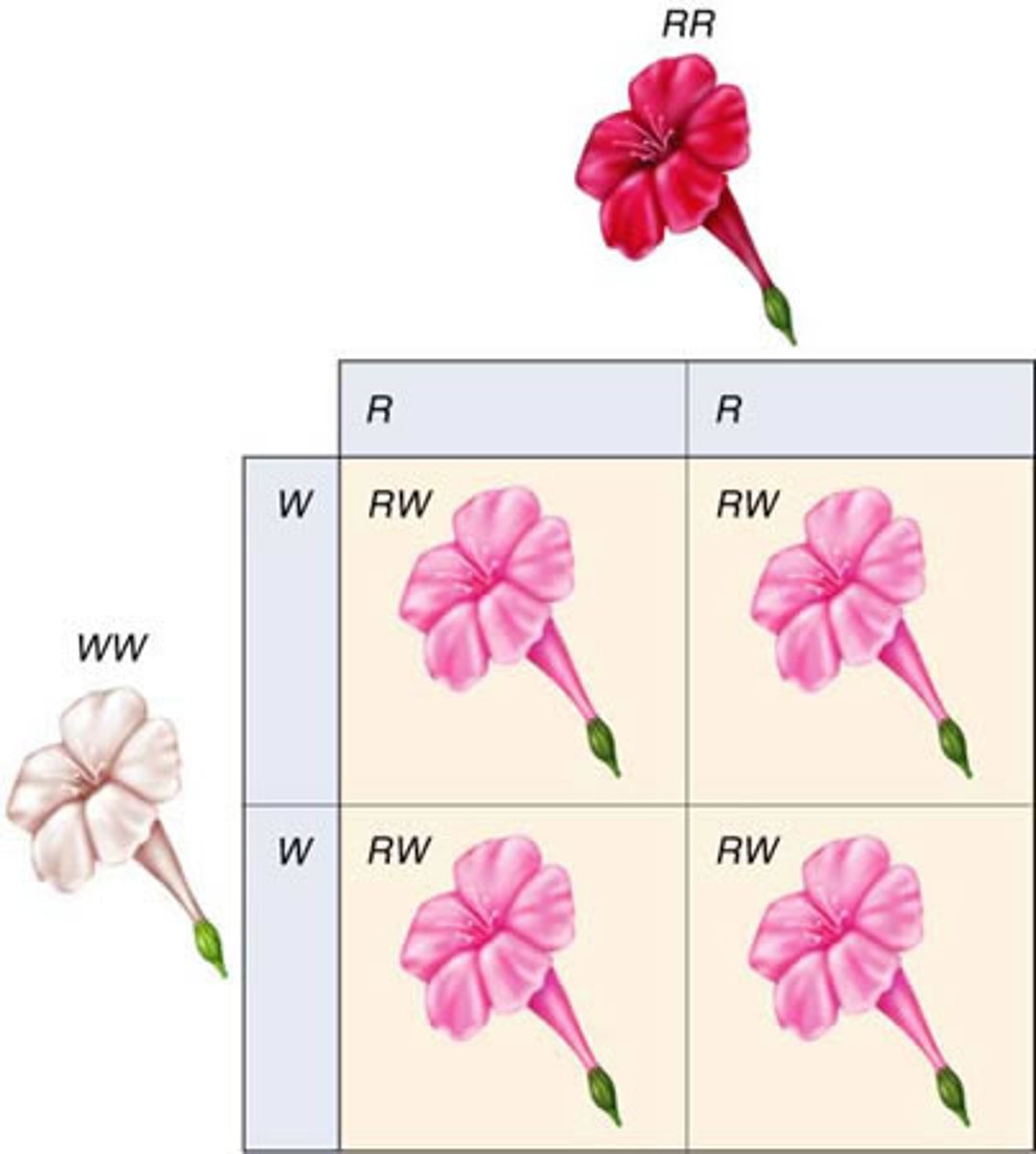
polygenic inheritance
occurs when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait