MLS 2211 Exam 4
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
Explain how hemoglobin becomes unconjugated bilirubin
When a RBC is old and gets broken down, the porphyrin ring releases unconjugated bili
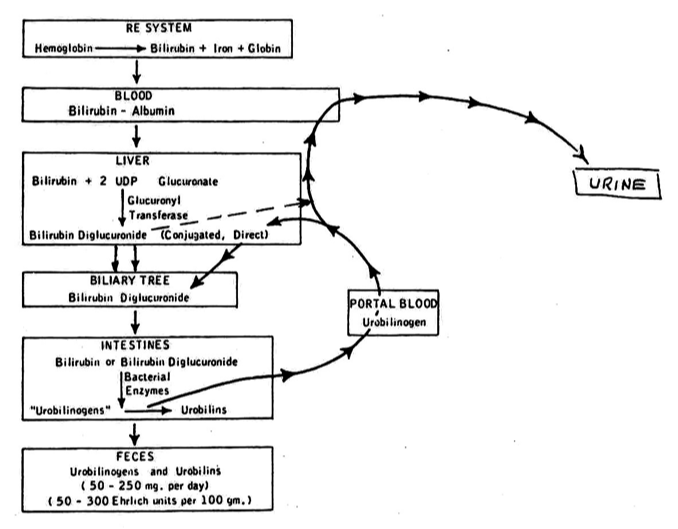
Explain how unconjugated bilirubin to conjugated bilirubin
The unconjugated bili then gets bound to albumin and transported to the liver, where it is converted into conjugated bilirubin through the action of glucuronyl transferase.
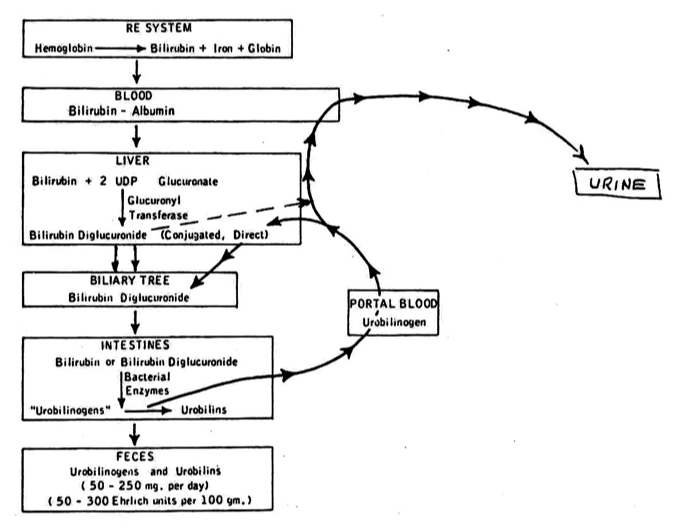
Explain how conjugated bilirubin becomes urobilinogen
Conjugated bilirubin is excreted into the intestines where bacteria convert it into urobilinogen.
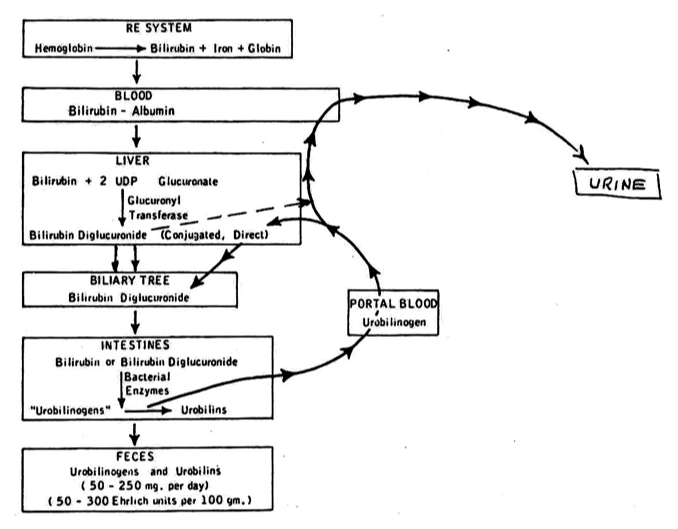
What is a total bilirubin test
Both Conjugated and Unconjugated measured together.
What is in a direct bilirubin test
Only the Conjugated Bili is measured.
What is unconjugated bili
Indirect bili
Most abundant form of Bili normally.
Relatively insoluble in the blood.
Solubility increased by Albumin binding.
Complex is too large to get filtered at the Glomeruli of the Nephrons.
Unbound, behaves more like a Lipid.
What is conjugated bili
Direct bili
Totally harmless.
Does not cause Kernicterus.
Water soluble, almost never Albumin-bound.
Small enough to be filtered at the glomeruli of the nephrons
Eliminated in the urine.
What is an indirect bili test
Total – Direct = Indirect (as in indirectly measured)
Whats the alternate name for direct bili
Conjugated bilirubin
Whats the alternate name for conjugated bili
Direct bili
Whats the alternate name for indirect bili
Unconjugated bilirubin
Whats the alternate name for unconjugated bili
Indirect bilirubin
What is neonatal physiological jaundice
A common condition in newborns caused by elevated bilirubin levels, resulting from the immaturity of the liver in processing bilirubin. It typically resolves without treatment as the infant's liver matures.
Whats a normal total bili for children and adults
0.2-1.0
Whats a normal direct bili for children and adults
0.0-0.4
What type of bilirubin is predominate in children and adults
Unconjugated bilirubin
What is neonatal pathological jaundice
The liver of a newborn is not mature at birth regarding conjugating Bilirubin.
It takes about 3 days for the liver to be able to conjugate.
This causes a normal condition called Neonatal Physiological Jaundice.
Why do neonates only have unconjugated bili
Their liver is not mature enough to conjugate bili
What is kernicterus and what age does it affect
In Neonates, when indirect bilirubin is unbound, it can cross blood-brain barrier and be absorbed into lipid-rich CNS neuron cell membranes.
Forms pathological inclusions in neuron which interfere with myelination process.
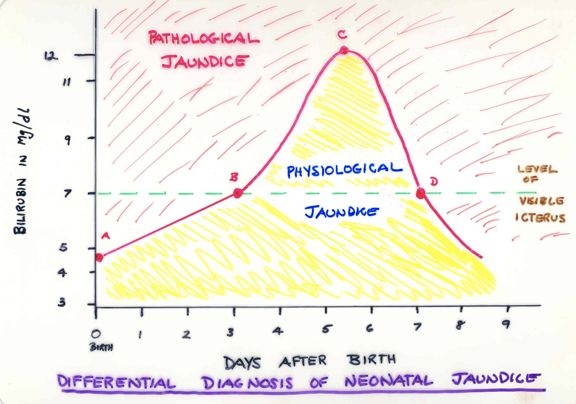
Whats a critical bili level
>20
What is the significance of Delta Bilirubin?
The Delta-Bilirubin represented conjugated (direct) Bilirubin that has been Covalently bound to Albumin.
Remember that this only shows up in Hepatitis and Choleostasis.
It has about 2.5 x the regular half-life of Bilirubin.
As the patient gets better, Bilirubin levels are slow to drop in the blood.
What is happening in the body with pre-hepatic jaundice
Pre-hepatic jaundice occurs when there is increased production of bilirubin. Conditions such as hemolytic anemia lead to elevated unconjugated bilirubin in the bloodstream before it reaches the liver for conjugation.
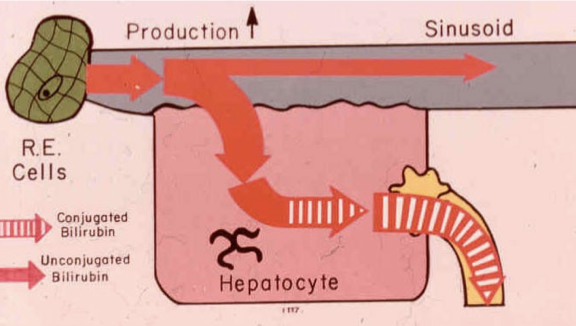
What conditions can cause pre-hepatic jaundice
Normal Neonatal Physiological Jaundice, Gilberts, Criggler-Najjar.
Hemolytic Disease of the Newborn.
Spherocytosis, Elliptocytosis, etc.
Sickle Cell or other Hemoglobinopathies
Transfusion Reactions
What is happening in the body during hepatocellular jaundice
There is a disease process in the liver so hepatocytes are stressed. The liver function is slowed down so there is a slower uptake which will lead to an increased unconjugated bili in the blood steam. The conjugated bili gets spit back into the blood steam
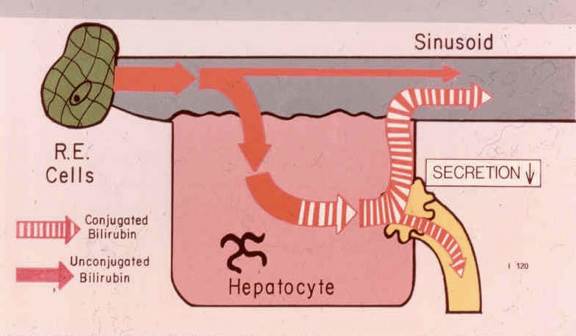
What conditions cause hepatocellular jaundice
Seen in any type of Acute Hepatitis:
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B (or B and D)
Hepatitis C (or E, F, G . . .?)
Chemical Hepatitis (Acetaminophen, ETOH, Chloroform, other Drugs.)
What is happening in the body during post-hepatic jaundice
Theres something wrong with the biliary tract, theres a block in the excreting of bili so conjugated bili gets shot back into the blood stream
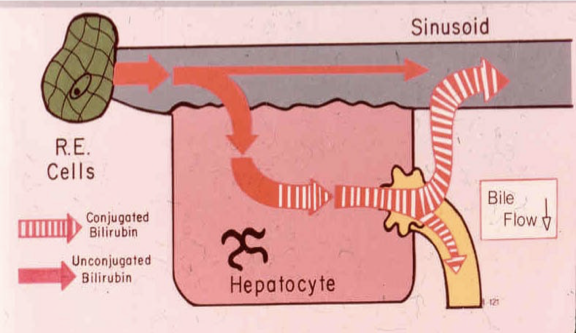
What conditions cause post-hepatic jaundice
Seen in:
Primary Biliary Atresia (rare pediatric disease)
Gallbladder Disease (Choleostasis)
Extra-Hepatic Bile stone in Gallbladder
Intra-Hepatic Bile stone within Liver
in pre-hepatic jaundice what would the total bili and direct bili be
High total bili
Normal direct bili
In pre-hepatic jaundice what would the urine bili and urobili be
>0.2 urobili
negative bili
In hepatocellular jaundice what would the total bili and direct bili be
High total bili, high direct bili
In hepatocellular jaundice what would the urine bili and urbili be
>0.2 urobili
pos urine bili
In post hepatic jaundice what would the total and direct bili be
High total bili, high direct bili
both high due to conj bili
In post hepatic jaundice what would the urine bili and urobili be
Normal urobili
pos urine bili
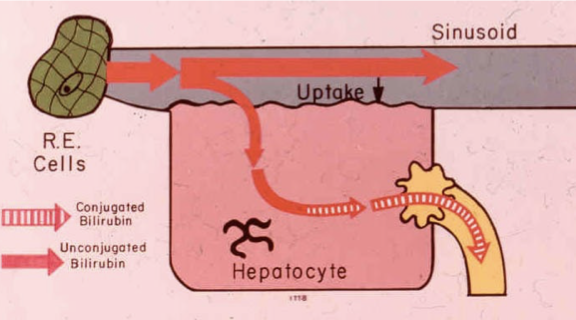
What is gilberts syndrome
A pre-hepatic pattern, a genetic malfunction in the uptake into the hepatocyte causing increased levels of unconjugated bilirubin in the blood.
What is Criggler-Najjar syndrome
A rare genetic disorder affecting bilirubin metabolism, characterized by severely elevated levels of unconjugated bilirubin due to a deficiency in the enzyme UDP-glucuronosyltransferase.
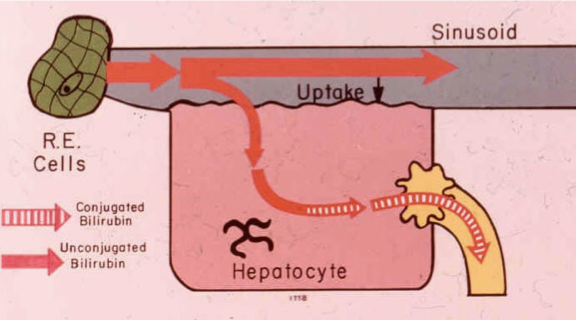
What is Dubin-Johnson syndrome
A genetic disorder where the hepatocytes do not excrete conjugated bili into the biliary tract causing high levels of conjugated bili
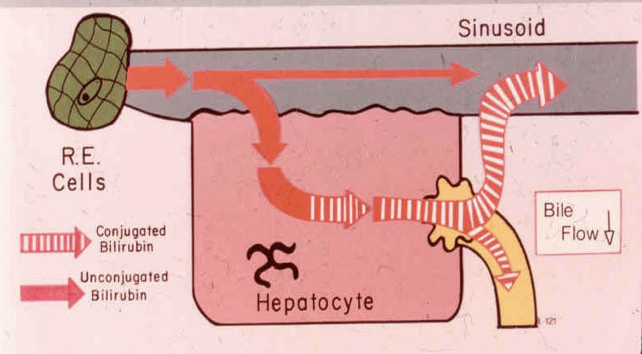
What serum bili would you expect to see in Gilberts syndrome
Elevation in total bili due to high unconjugated levels
normal direct bili
What serum bili would you expect to see in Criggler-Najjar syndrome
Elevated total bili due to unconjugated bili
normal direct bili
What serum bili would you expect to see in Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Elevated total and direct bili to high conjugated bili
What urine bili and urobilinogen would you expect to see in Gilberts syndrome
urine bili negative
urine urobilinogen >0.2
What urine bili and urobilinogen would you expect to see in Criggler-Najjar syndrome
Urobilinogen >0.2
Urine bilirubin negative
What urine bili and urobilinogen would you expect to see in Dubin-Johnson syndrome
Normal urobilingen
urine bilirubin positive
What is the specimen of choice for a bili assay
Fresh, unhemolyzed Serum is specimen of choice.
Fresh, unhemolyzed Heparinized Plasma is acceptable alternate for most platforms.
How does hemolysis effect a bili result
It interferes with the absorbance in the test, it doesn’t actually increase the bili levels
What happens to the bili in a sample if its exposed to light, the wrong temperature, or its old
The bili will be falsely decreased as it degrades
How does the Evelyn-Malloy method work?
Uses Diazo made from Sulfanilic Acid and Sodium Nitrite.
Direct measured in water, total measured in ethanol.
How does the Jendrassic-Grof method work?
Uses Diazo made from Sulfanilic Acid and Sodium Nitrite.
Direct measured in HCl, total measured in Acetate-Caffeine Reagent. Favored method
What is ammonia
End product of protein and amino acid catabolism.
Nasty stuff! Strongest naturally-occurring base. Will rip a Hydrogen right off of a water molecule, leaving the Hydroxide anion.
NH3 + H20 Ouch! + NH4+ + OH-
What is urea
Represents the end product of Protein catabolism.
Synthesized by the Liver from Bicarbonate and Ammonia.
Totally harmless – a true molecule, and is just a renal marker.
Water soluble, never albumin-bound.
Cleared from the blood by the Nephrons of the kidneys.
What disease has high ammonia and why?
Liver disease
Liver is only organ able to detoxify ammonia, by converting it to Urea, which is completely harmless.
What diseases have a high BUN and why
Renal disease, the kidneys cant clear the urea from the blood
What is the conversion factor of urea to BUN
2.14
Urea = BUN x 2.14
BUN = Urea/2.14
How do you get to urea from BUN?
BUN x 2.14 = Urea
How do you get to BUN from urea
Urea/2.14 = BUN
What is creatinine
Waste product from Creatine. Creatine in muscle cells as Creatine-PO4.
A small amount of Creatine passes out of cell through cell membrane. Spontaneously converted to Creatinine.
What diseases would have a high creatinine and why
Assuming muscle mass is constant, then the blood level of Creatinine is influenced by Renal function.
Trauma will not elevate Creatinine directly (Creatine yes, Creatinine no).
Trauma will cause shock, which will cause pre-renal azotemia, and elevate the Creatinine over time.
What is azotemia
Elevated blood levels of NPN waste products
May be caused by many things.
What is uremia
Azotemia plus other signs/symptoms of Renal failure.
What are the symptoms of uremia
High K+ (usually)
Low Bicarbonate
Low Calcium
Na+ high (usually)
Phosphates high
Anemia
Azotemia
Bone resorption
What is meant by pre-renal azotemia
Not perfusing the kidneys with blood, Trauma, shock, congestive heart failure
Diet More protein = more BUN. More nucleoproteins = more Uric Acid
Heavy metal poisoning, Lead and Uric Acid are buddies
What is meant by renal (Intra-renal) azotemia
Intrinsic damage to Nephrons of Kidneys.
May be transient or permanent depending upon the severity of damage.
Can be seen in:
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Interstitial Nephritis (nephrosis)
Acute Pyelonephritis
Acute Tubular Necrosis
Whats acute glomerulonephritis
Usually damage to Basement Membrane of Glomerulus due to partial Complement activation by Immune Complexes
IgG + soluble antigen
Group A Beta Strep is a biggie.
Viral Hepatitis B and C also (hepato-renal syndrome)
What is acute pyelonephritis
Almost always due to complication of urinary tract infection.
Organisms same as those causing lower urinary tract infections.
E. Coli, Proteus vulgaris, mirabilis, Pseudomonas, etc.
WBCs, WBC casts, bacteria, renal epithelial cells are hallmarks.
What is interstitial nephritis
Indirect damage to Tubules of Nephrons by inflammation of parenchymal cells of kidney.
Pressure causes inflammation of tubules.
Aspirin, Anti-freeze (Ethylene Glycol), Yellow Fever toxins, etc.
W
What is acute tubular necrosis
Very similar to Interstitial Nephritis, except toxins are directly damaging to the tubules of the nephrons.
Hypoxia can also cause this if severe enough.
This is mechanism of Shock resulting in bilateral renal damage and disease.
What is meant by post renal azotemia
Urethral obstructions or abnormalities oppose elimination of urine.
Back-up pressure within bladder impedes glomerular filtration.
Kidney Stones are main cause.
Stones form in pelvis of kidney and then try to pass thru the Ureters. Stone blocks urethra, that kidney is shut down.
What conditions are associated with pre-renal azotemia
Trauma, shock, chf, heavy mental poisoning, diet
What conditions are associated with renal azotemia
Acute Glomerulonephritis
Interstitial Nephritis (nephrosis)
Acute Pyelonephritis
Acute Tubular Necrosis
What conditions are associated with post-renal azotemia
Kidney stones
Explain how BUN/Creatinine ratios can distinguish between Pre-renal azotemia and intra-renal disease.
In both Intra-renal diseases and Pre-renal Azotemia, both Creatinine and BUN elevated in the blood.
In Intra-renal disease, Creatinine rises faster than does BUN.
In Pre-renal Azotemia, BUN rises faster than does Creatinine.
Pre-Renal Azotemia = BUN/Creatinine ratio of ______or greater
24
Renal Azotemia/Disease = BUN/Creatinine ratio of ______ or less.
15
What is a normal BUN/Creatinine ratio
10:1 to 20:1
Explain the principle of the Creatinine Clearance test,
Universal Gold Standard for assessing Renal function.
Specifically measures the Glomerular Filtrate Rate, as mL of plasma cleared of Creatinine, per each minute
How is a creatinine clearance test preformed
Measure the 24-hour urine collection.
Dilute the Urine 1:21.
Assay the patient’s serum or plasma for Creatinine, along with the diluted urine.
Multiply the Urine Creatinine value by the dilution factor.
Use the patient’s height and weight to determine the patient’s Body Surface Area (BSA).
Find the BSA using the BSA Nomogram.
How does a creatinine clearance test asses for renal function
Although the Glomerular Filtration Rate is being determined, it is useful for both Glomerular and Tubular Diseases.
If you damage the glomerulus, you decrease nephron tubular function.
If you damage tubular function, you decrease the Glomerular filtration rate.
What is the GFR calculation?
(Urine creatinine/Serum creatinine) x (mL of urine/1440) x (1.73/BSA)
Explain an eGFR and what factors are considered in the calculation.
Serum/Plasma Creatinine as mg/dL.
Age
GFR declines with age
Gender
Females have less muscle mass, lower serum creatinine, GFR often over-estimated.
Race
African American vs. Caucasian African Americans have more muscle mass, higher serum creatinine, which under-estimates the GFR.
For Uric Acid, state where is comes from
End product of Purine catabolism in humans
Small molecule, barely soluble in biological fluids, eliminated from by blood by the Nephrons of the kidney into the urine.
What diseases are associated with uric acid
Renal function loss.
Primary Gout
Cell proliferation for any reason. Leukemias, Polycythemias, malignant tumors.
Cell destruction for any reason. Pernicious anemia, Hemoglobinopathies, tissue necrosis.
Diet – lots of nucleoproteins.
Heavy metal poisoning Makes Purine synthesis less efficient, more Uric Acid.
What is the end product of protein catabolism
Urea/BUN
What is the waste product of creatine
Creatinine
What is the end product of purine catabolism
Uric acid
What is the end product of protein and amino acids?
Ammonia
What can post-renal azotemia be caused by
Urethral obstructions
What is Joe Nebraska's creatinine clearance if he has a urine creatinine of 112 mg/dL, serum creatinine of 1.1 mg/dL, a 24-hour urine volume of 1265 mL, and his Body Surface Area is 2.05?
75.5
What is Hannah Montana's creatinine clearance if she has a urine creatinine of 147 mg/dL, serum creatinine of 2.1 mg/dL, a 24-hour urine volume of 1296 mL, and her Body Surface Area is 1.70?
64.1
What is Hank Brown's creatinine clearance if he has a urine creatinine of 98 mg/dL, serum creatinine of 0.8 mg/dL, a 24-hour urine volume of 1492 mL, and his Body Surface Area is 2.12?
103.6
What is the Grim Reaper's creatinine clearance if he has a urine creatinine of 128 mg/dL, serum creatinine of 4.3 mg/dL, a 24-hour urine volume of 1200 mL, and his Body Surface Area is 2.21?
19.4
If a patient has a BUN of 45 mg/dL, what would this equal as mg/dL Urea?
96
What is a patient has a Urea of 55 mg/dl, what would this equal as mg/dL BUN?
26
Which of the following statements would NOT be true of a patient with Pre-Renal Azotemia?
They may be suffering from pyelonephritis
Their BUN/Creatine ratio would be greater than 24
They may be suffering from trauma and shock
They are experiencing a lab of blood flow to the kidneys
They may be suffering from pyelonephritis
A patient has a serum BUN of 32 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 4.2 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 11.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
In this scenario, is it appropriate to calculate the BUN/Creatinine Ratio?
Correct answer:
Yes, because one or both of the BUN and Creat values are elevated.
A patient has a serum BUN of 32 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 4.2 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 11.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
What is the BUN/Creatinine ratio
8
A patient has a serum BUN of 32 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 4.2 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 11.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
What type of Azotemia would be indicated with the BUN/Creat ratio?
Renal azotemia
A patient has a serum BUN of 65 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 2.1 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 13.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
Would this scenario warrant a BUN/Creatinine ratio?
Yes, both the BUN and Creat are elevated
A patient has a serum BUN of 65 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 2.1 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 13.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
Whats the BUN/Creatinine ratio
31
A patient has a serum BUN of 65 mg/dL (high), a serum Creatinine of 2.1 mg/dL (high), a serum Uric Acid of 13.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
What type of Azotemia does this indicate?
Pre-renal azotemia
A patient has a serum BUN of 14 mg/dL (normal), a serum Creatinine of 1.0 mg/dL (normal), a serum Uric Acid of 13.0 mg/dL (high), and a low-normal serum Ammonia.
Does this scenario warrant a BUN/Creatinine Ratio?
No, both the BUN and Creat are within normal range
What azotemia are assocatied with kidney stones
post-renal