Lecture 15 - neuroanatomy
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What pathway does sensory information enter the CNS?
via the dorsal portion of the spinal cord
What pathway does sensory information leave the CNS?
via the ventral portion of the spinal cord
What does superior, inferior, anterior, posterior correlate to with the cerebrum in terms of orientation?
superior: dorsal
inferior: ventral
anterior: rostral
posterior: caudal
What does superior, inferior, anterior, posterior correlate to with the cerebellum in terms of orientation?
superior: rostral
inferior: caudal
anterior: ventral
posterior: dorsal
what does ipsilateral mean?
on the same side
what does contralateral mean?
on the opposite side
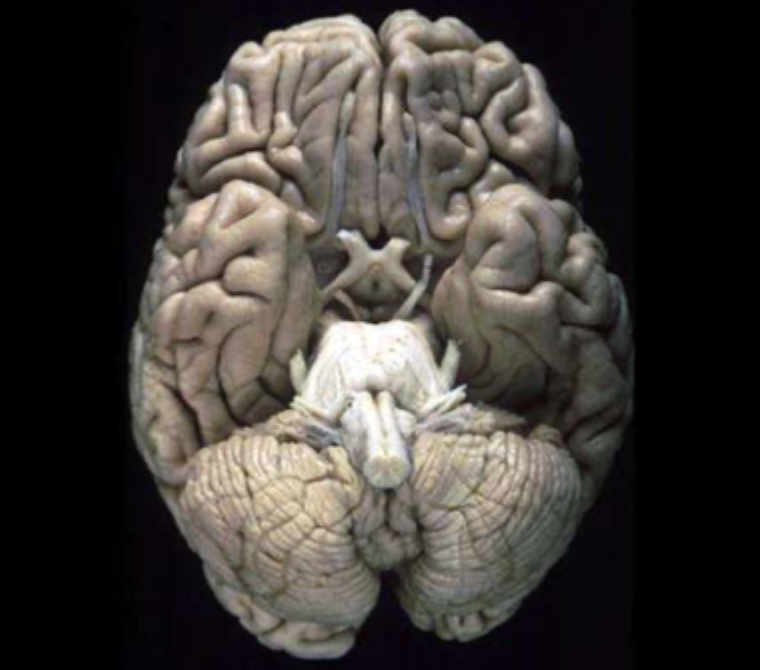
What view of the brain is this?
the ventral/inferior view
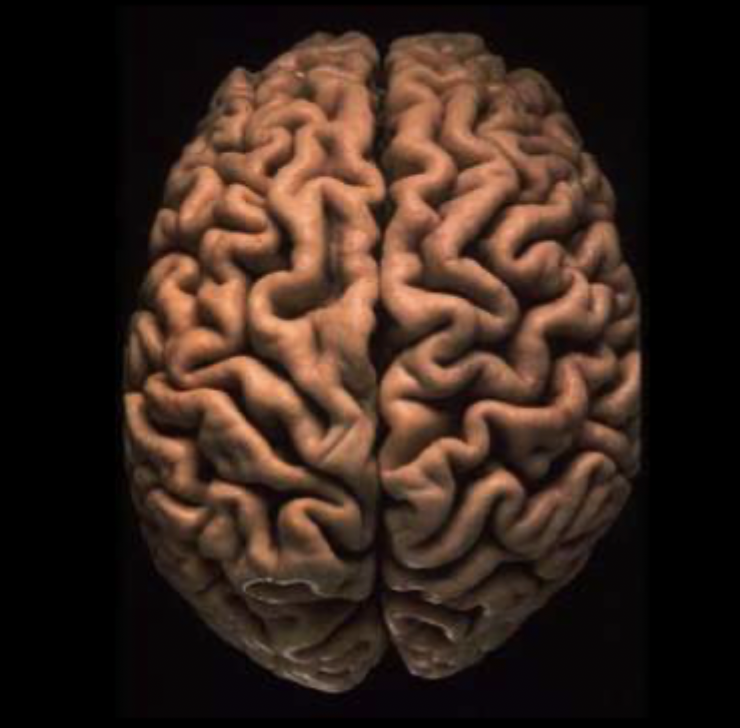
what view of the brain is this?
the dorsal/superior view
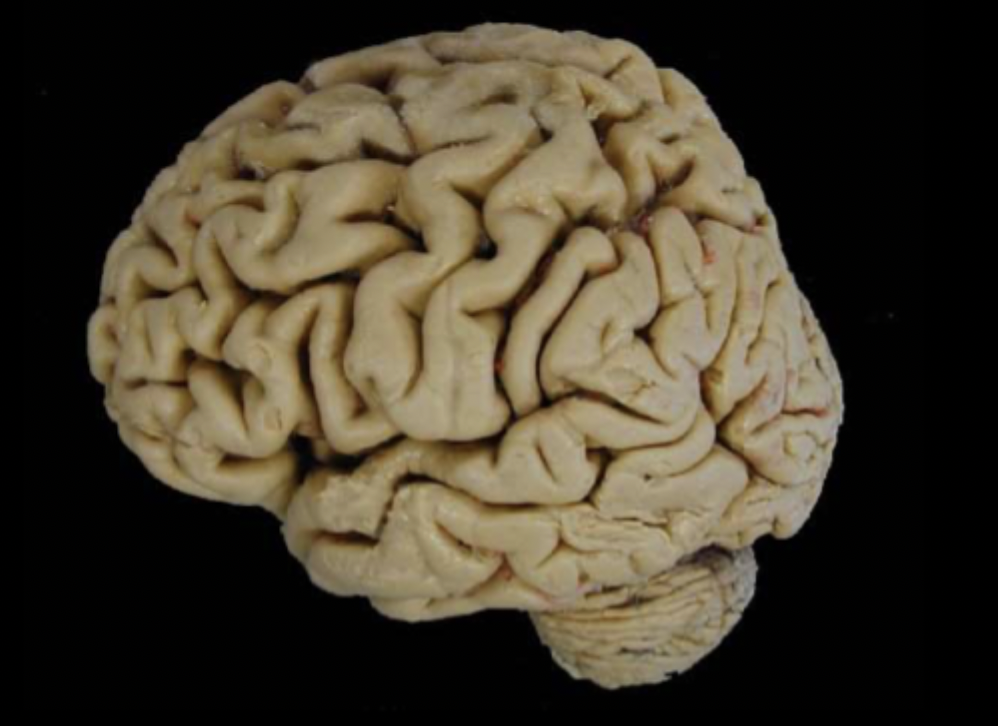
What view of the brain is this?
lateral view
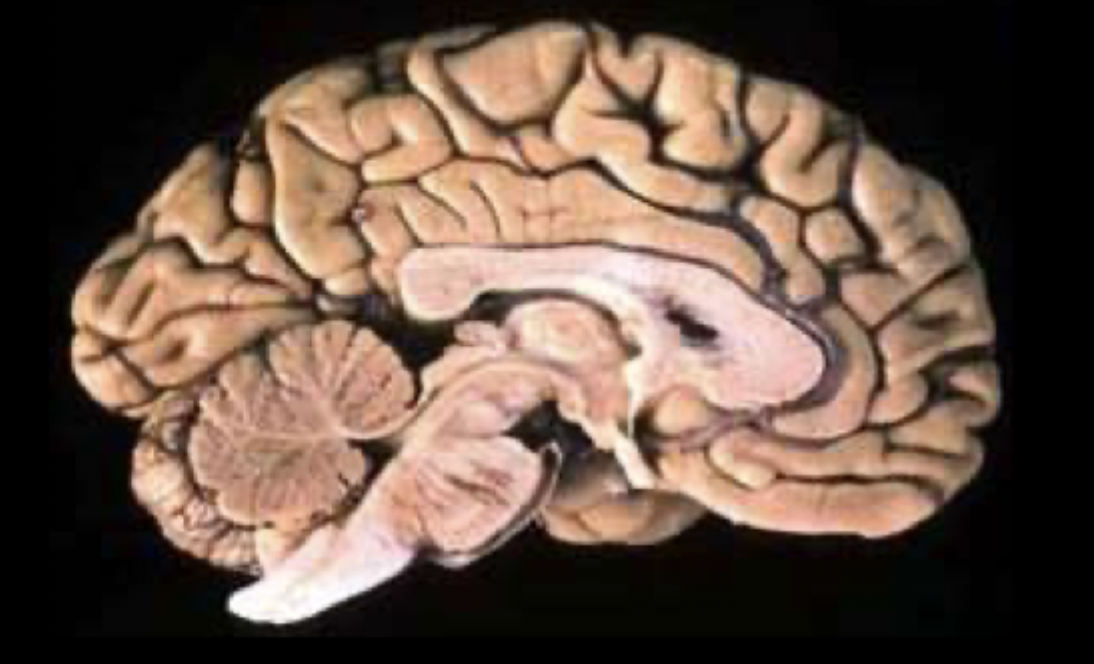
What view of the brain is this?
the medial/midsagittal view
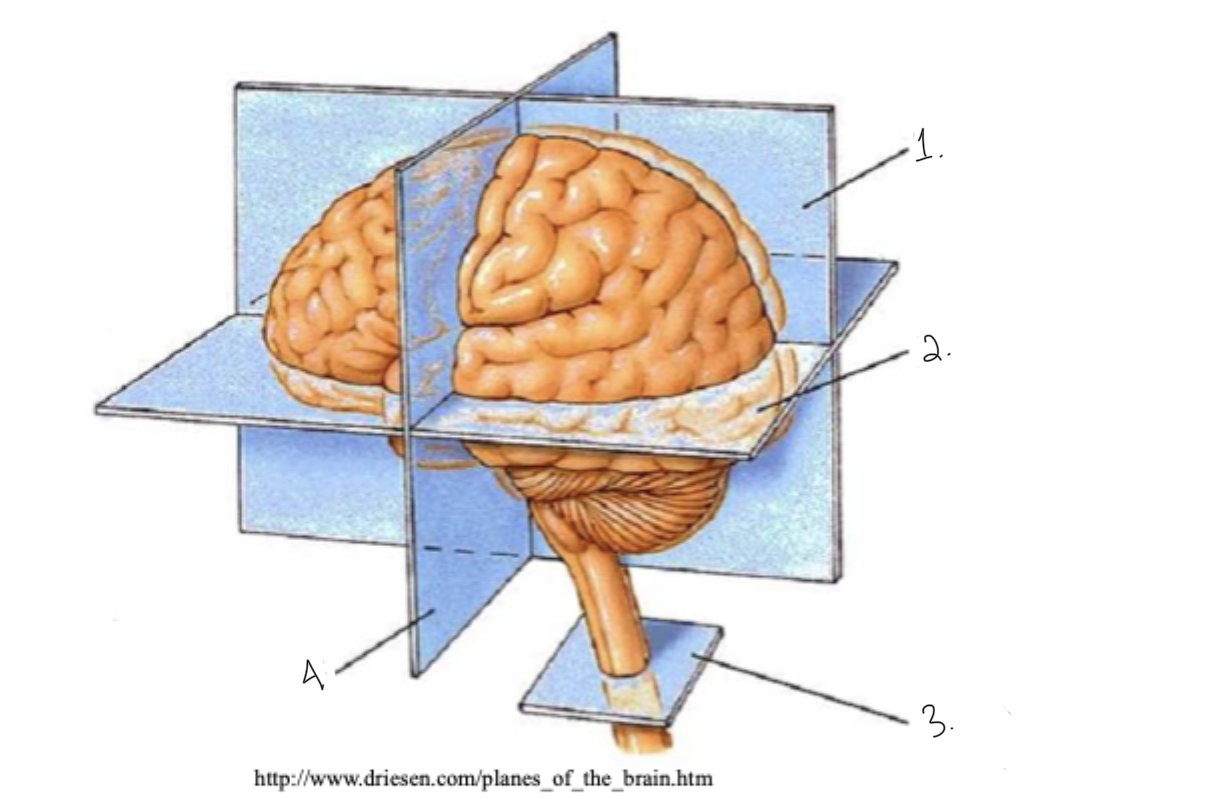
label this diagram: terms for brain slices
sagittal
horizontal
cross section
coronal
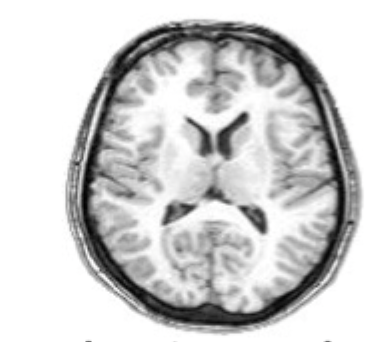
what slice of brain is this?
horizontal slice
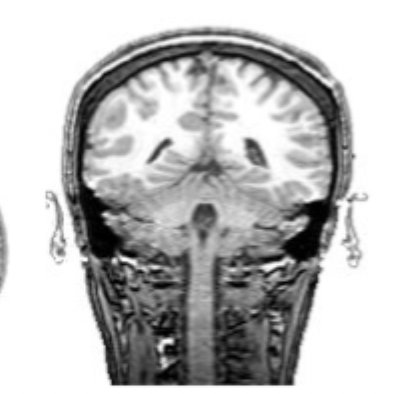
what slice of brain is this?
coronal slice
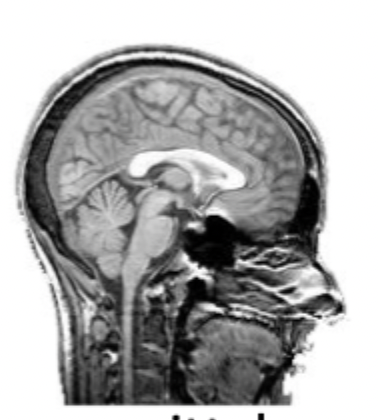
what slice of the brain is this?
What are the 5 lobes of the brain
frontal lobe, parietal lobe, occipital lobe, temporal lobe, insular cortex
where is the insular cortex located?
inside the lateral sulcus
what does the longitudinal fissure separate?
separates the two hemispheres
what does the lateral sulcus separate?
separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
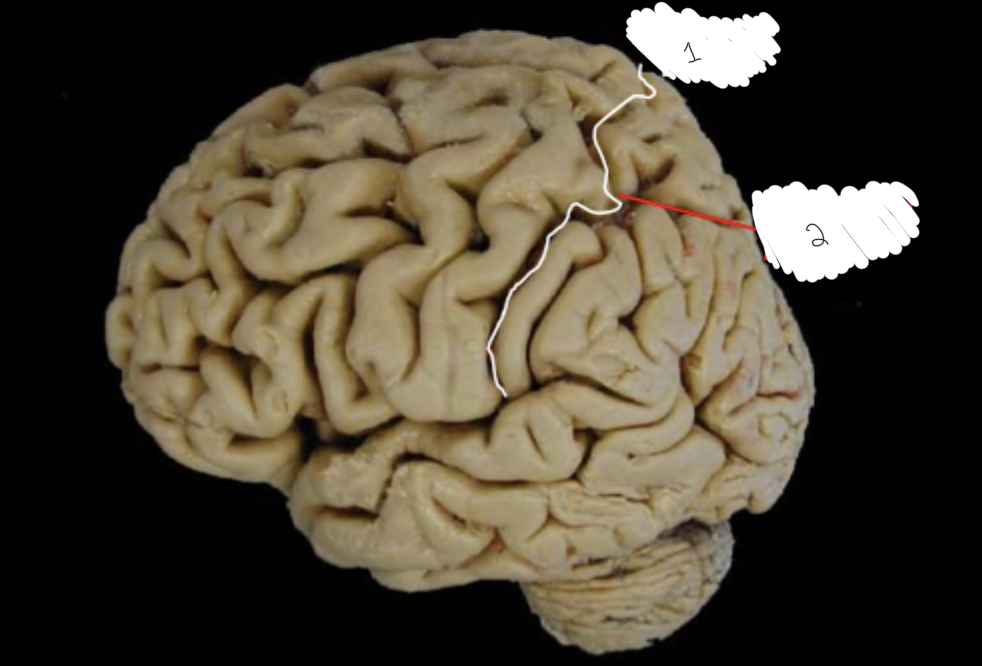
what does the central sulcus separate?
separates the frontal and parietal lobes
What are the gyri of the frontal lobe?
3 gyri, the superior, middle and inferior
they run anterior to posterior , meeting the precentral gyrus at the precentral sulcus
what is the gyri of the temporal lobe?
superior, middle and inferior gyri
what are the sulcus of the parietal lobe?
postcentral gyrus, intraparietal sulcus (IPS) separates the superior and inferior portions of the partietal lobe
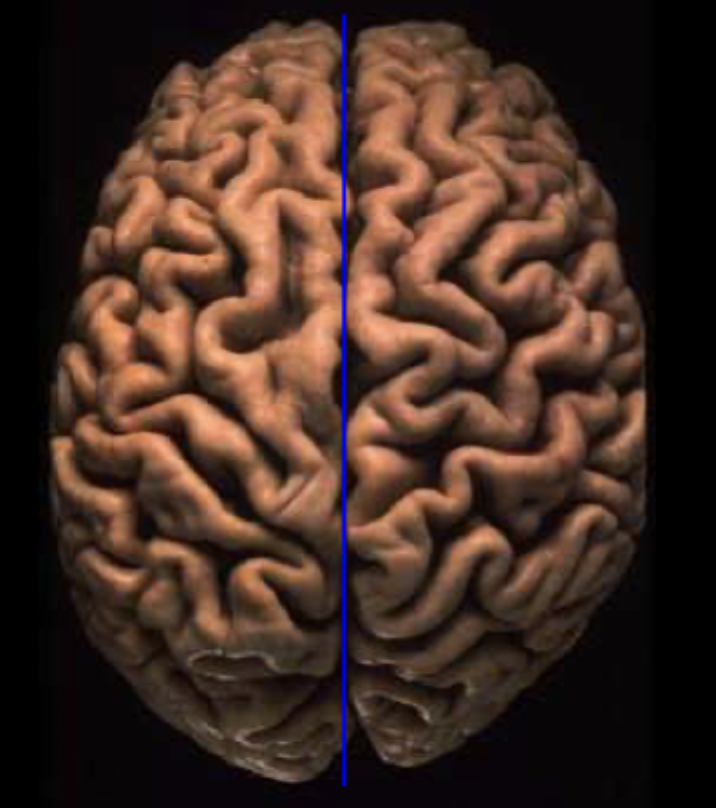
What sulcus fissure/sulcus is this?
longitudinal fissure
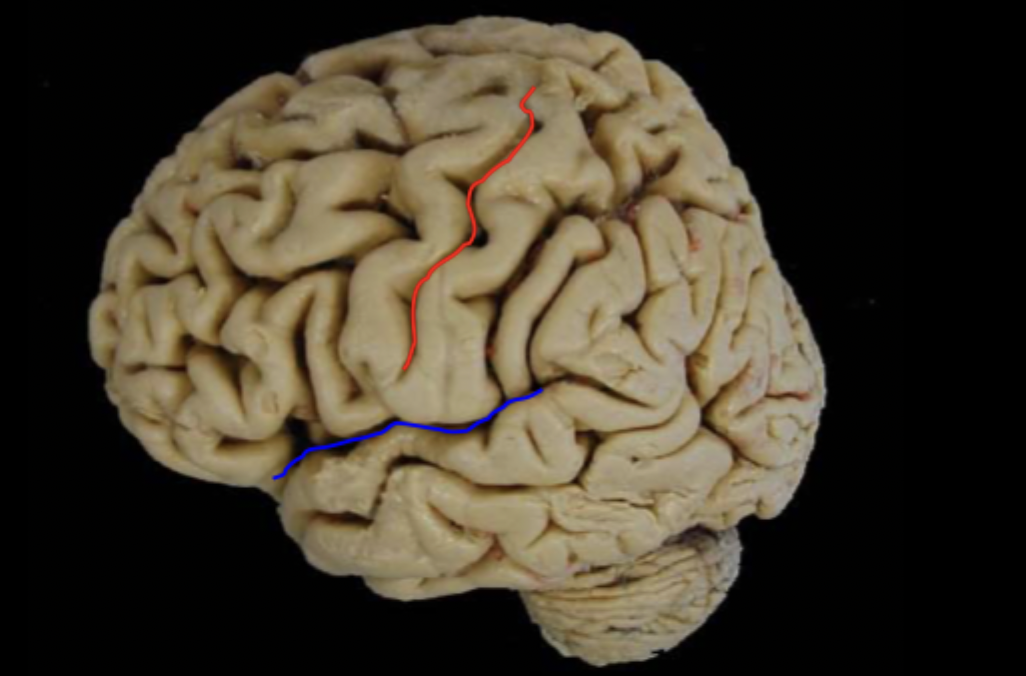
What sulcus fissure/sulcus is labeled in red and blue?
blue: lateral sulcus
red: central sulcus
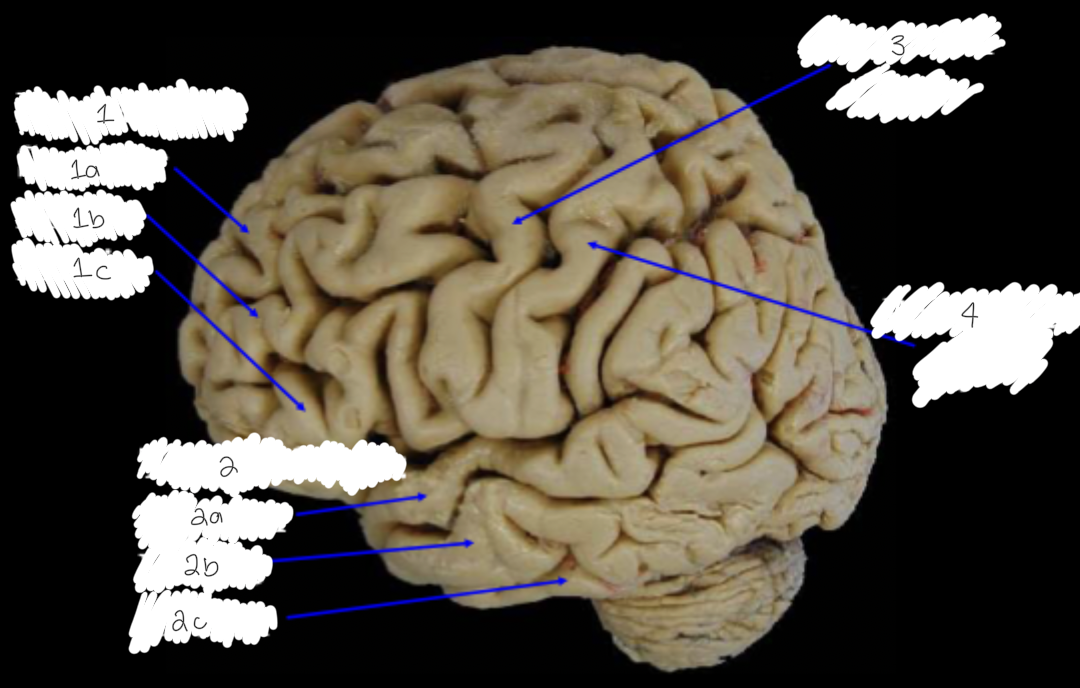
Label this diagram
1: frontal gyri: a) superior, b) middle, c) inferior
2: temporal gyri: a) superior, b) middle, 3) inferior
3: precentral gyrus
4: postcentral gyrus
Label this diagram:
post central sulcus
Intraparietal sulcus
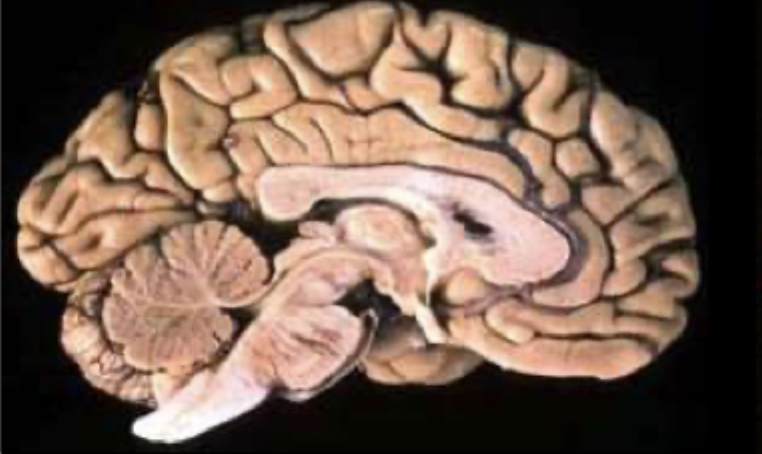
What is the C shaped structure in the centre of the cerebrum?
the corpus callosum- Fibers that link both hemispheres - good for intercommunication between the two hemispheres
What is the difference between cortical and subcortical brain structures?
Cortical structures are located in the outer layer of the brain (cerebral cortex) and handle higher-order functions like perception and cognition, while subcortical structures lie beneath the cortex and regulate essential processes such as movement, emotion, and memory
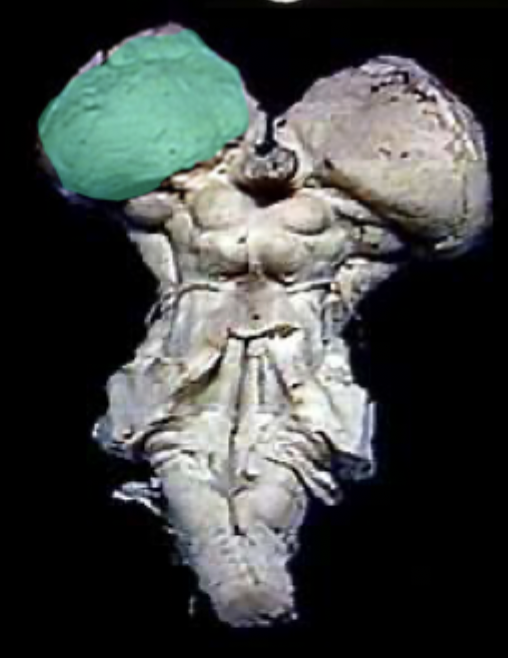
What structure is highlighted in green?
the thalamus
What type of brain structure is the thalamus?
The thalamus is a subcortical structure that relays sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex
How many thalami does the brain have?
Each hemisphere contains a thalamus, so there are two in total
What are the major structures of the basal ganglia?
The basal ganglia include the caudate nucleus, putamen, globus pallidus, subthalamic nucleus, and substantia nigra
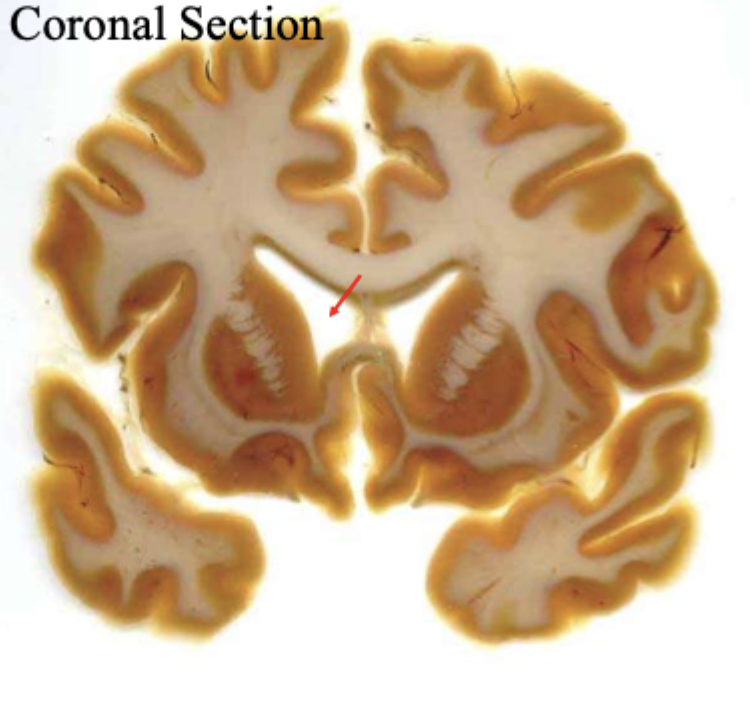
What is the red arrow pointing to?
the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle
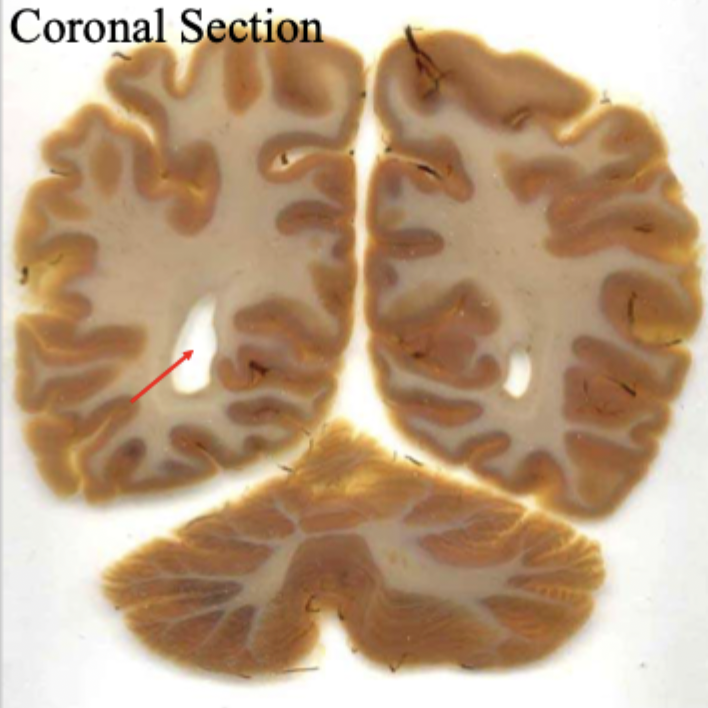
what is the red arrow pointing to?
posterior horn of lateral ventricle
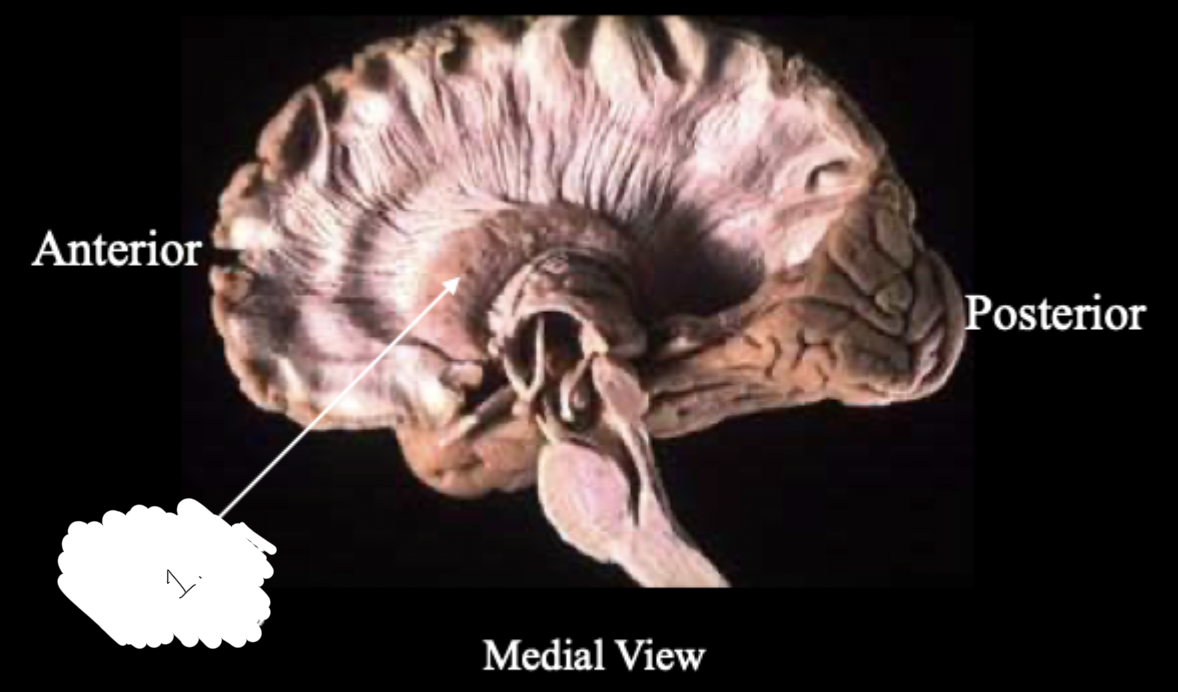
label this diagram
1: caudate nucleus
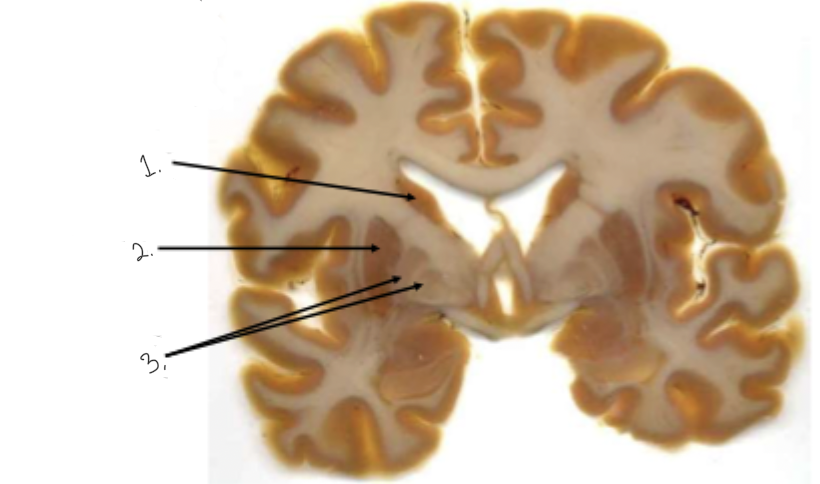
label this diagram
1: caudate nucleus
2: putamen
3: globus pallidus
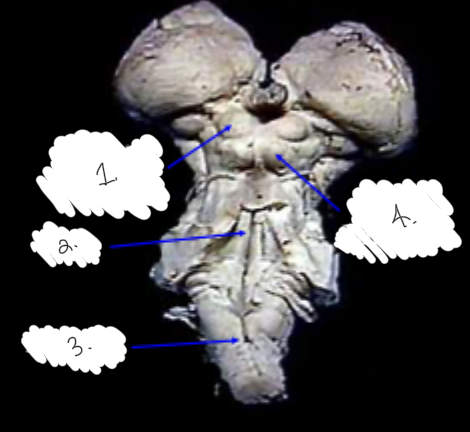
label this diagram
1: superior colliculus
2: inferior colliculus
3: pons
4: medulla
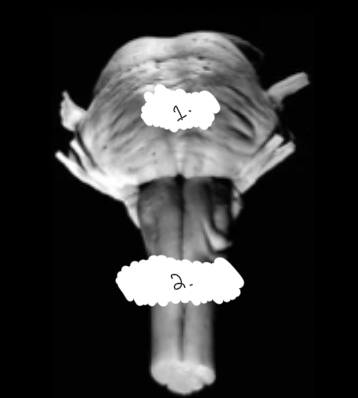
label this diagram
1: pons
2: medulla
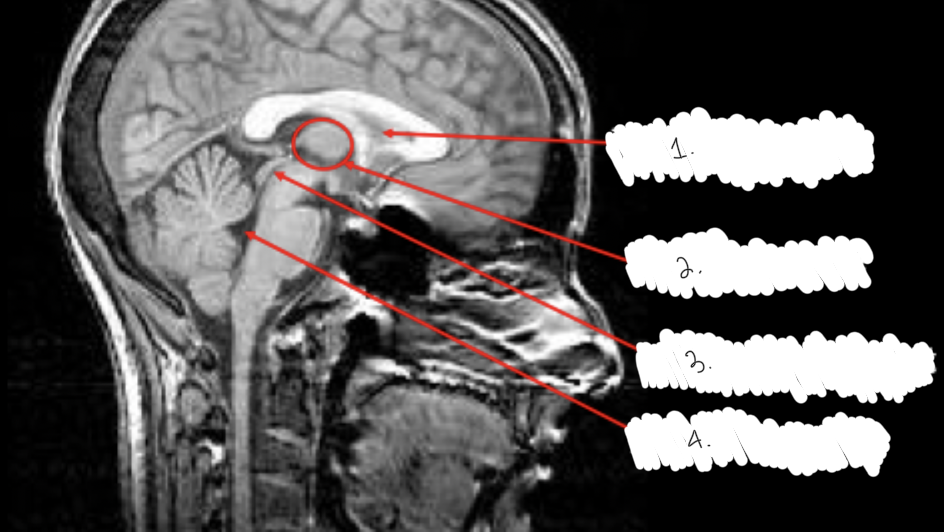
label this diagram
1: lateral ventricle
2: third ventricle
3: cerebral aqueduct
4: fourth ventricle
What is Brodmann’s map of the cerebral cortex based on?
Differences in the microscopic structure (cytoarchitecture) of neurons, including size, density, and layering
Why is Brodmann’s map important in neuroscience?
Because structural differences in cortical areas often correlate with functional specializations, such as sensory, motor, or association areas
How does gross anatomy differ from brain scans?
Gross anatomy refers to large-scale structures visible to the naked eye (e.g., gyri, sulci, lobes), while brain scans visualize these structures and functional activity using imaging techniques like MRI or CT
What is an important consideration when interpreting brain scans?
Left and right sides are reversed in images; structures on the left of the image correspond to the right hemisphere
What functional information can Brodmann’s areas provide?
They suggest the location of functions like sensory processing, motor control, or higher-order association tasks