Chemistry Test 2: Bonding
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
What are ions?
An atom or molecule with an overall positive or negative charge due to the loss or gain of an electron
What are cations?
Positively charged ions (lose electrons)

What are anions?
Negatively charged ions (gain electrons)

What is electrostatic attraction?
Attraction between opposite charges
What is an ionic lattice?
A giant structure of ions that held together by ionic bonds that have a regular, repeating arrangement
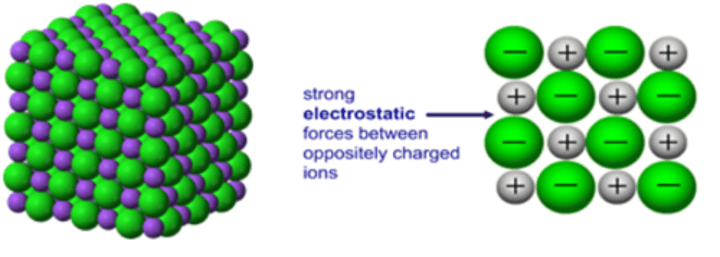
Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points?
They have strong ionic bonds so it takes large amounts if energy to overcome forces
Why don't ionic compounds conduct electricity when solid?
The ions in solids are not free to move as they are held together by strong forces
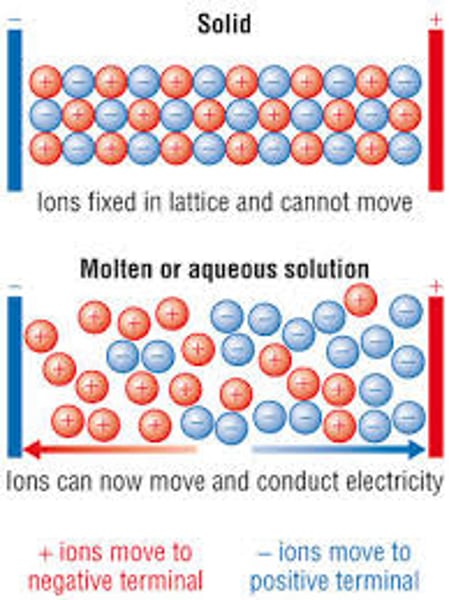
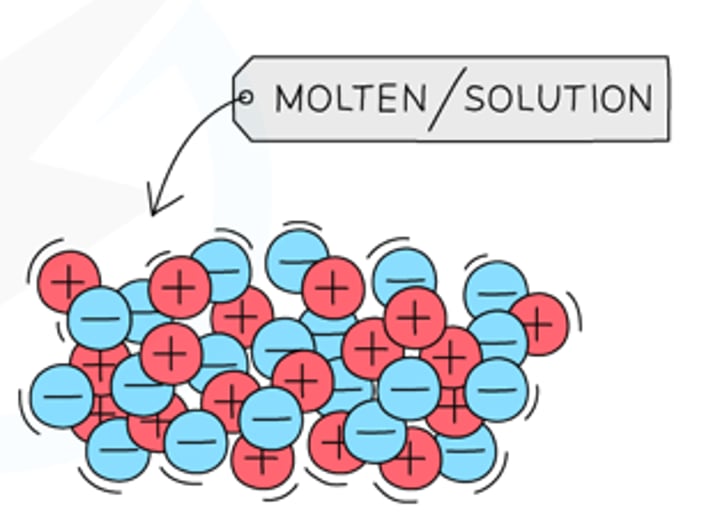
In what state do ionic compounds conduct electricity?
Molten or aqueous state
What is covalent bonding?
The strong electrostatic attraction between a shared pair of electrons and the nuclei of the bonded atoms
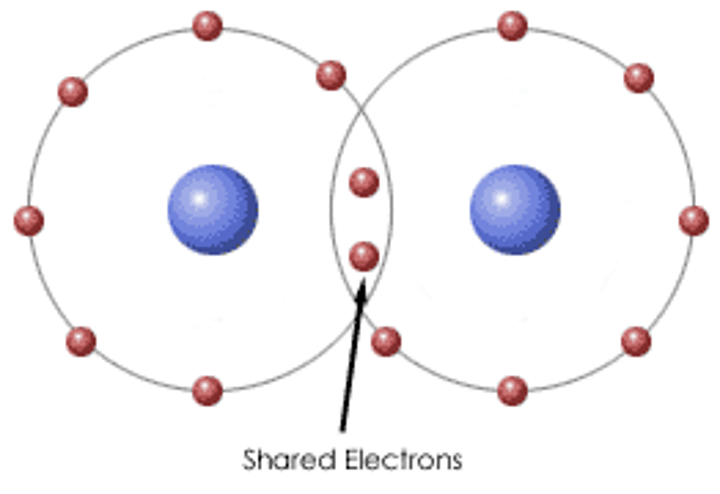
What are simple molecular structures?
When a substance consists of molecules with inter molecular forces of attraction
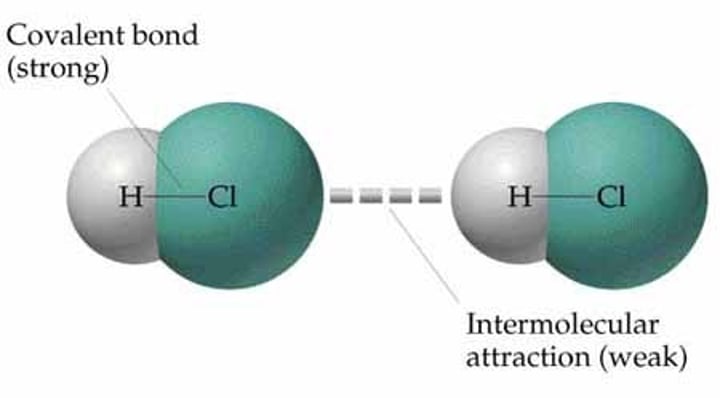
Why do simple molecular substances have low melting and boiling points?
There are weak intermolecular forces although the covalent bonds or intramolecular forces are not broken
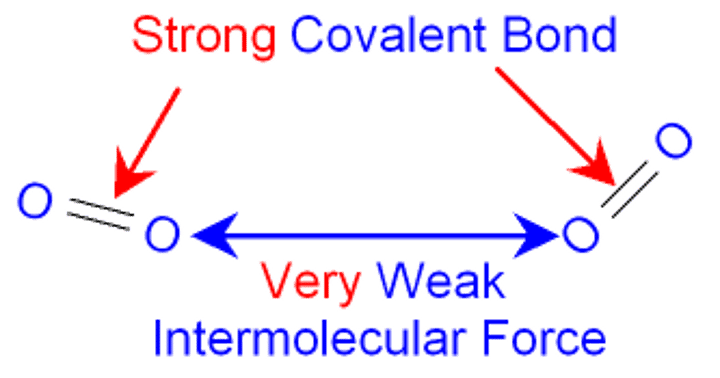
Why does relative molecular mass increase the melting point and boiling point?
There are more inter molecular forces that need to be broken

What is a giant covalent structure?
A huge 3D network of covalently bonded atoms
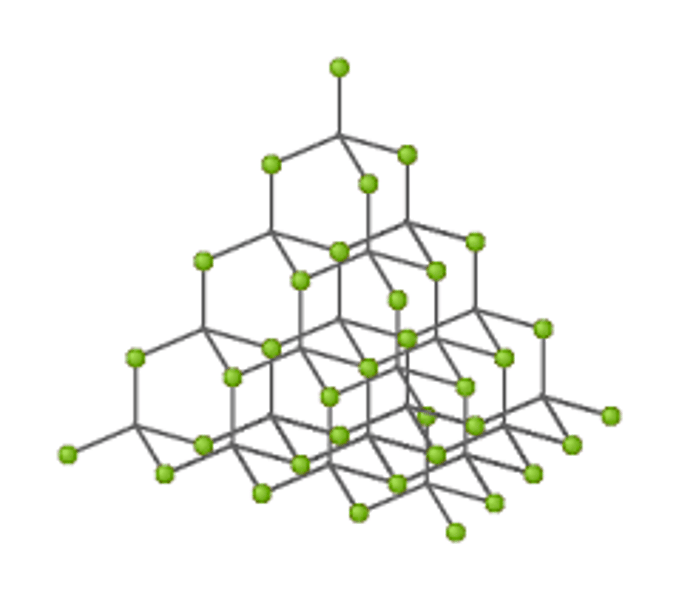
Why do giant covalent structures have high melting and boiling points?
Large amounts of energy are needed to overcome strong covalent bonds
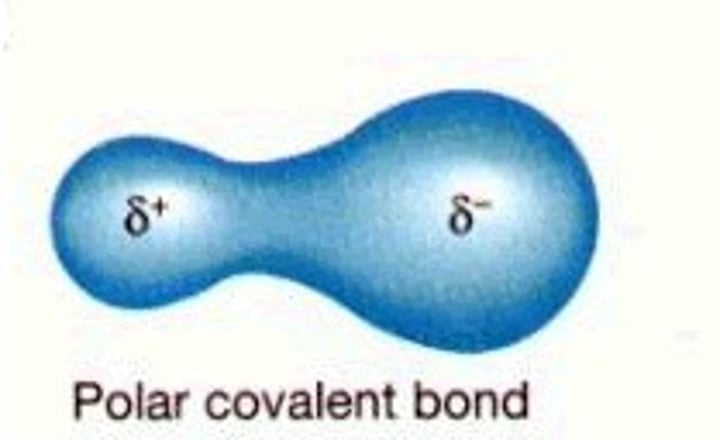
What is a polar covalent bond?
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally
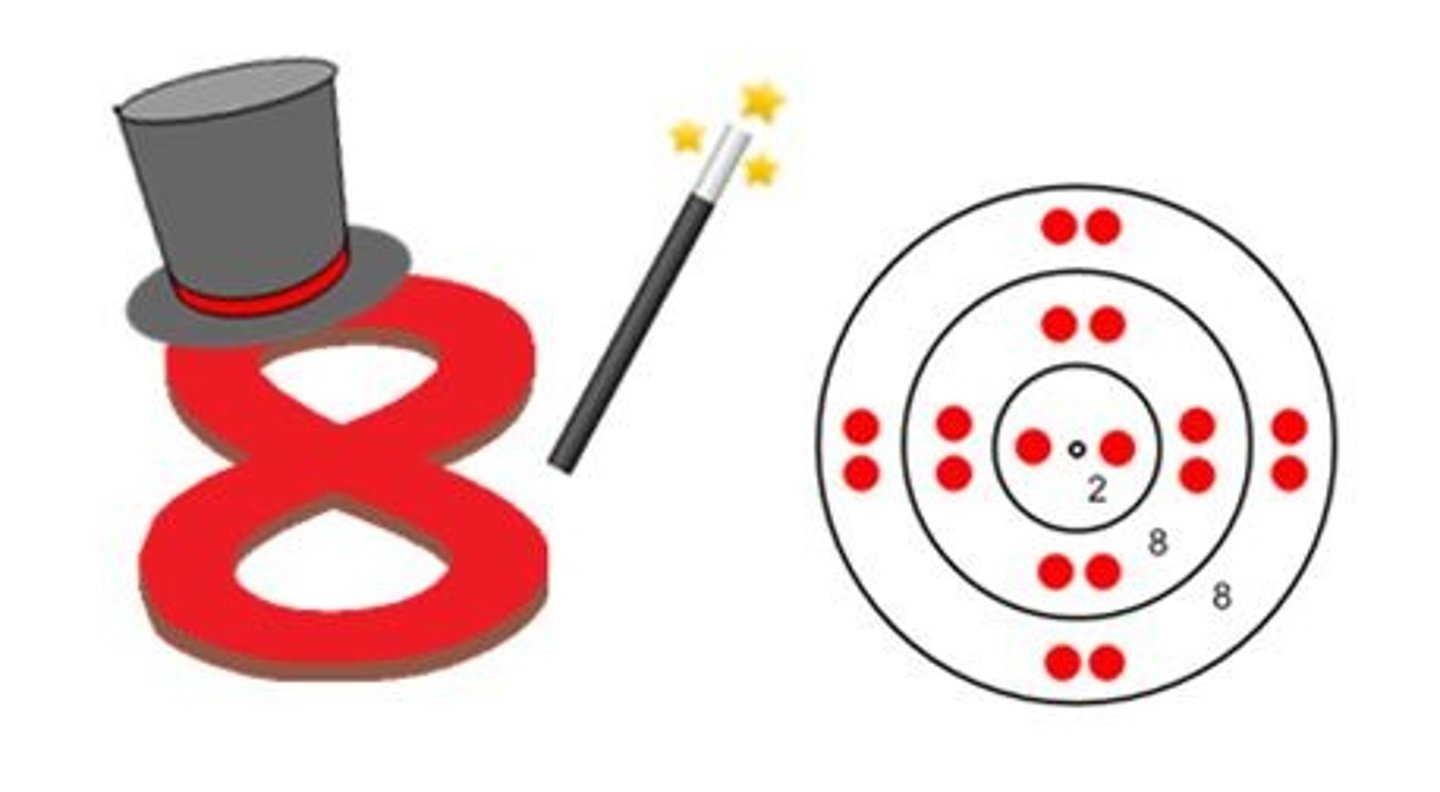
Why do atoms bond?
Because they want to be stable by gaining a full valence shell
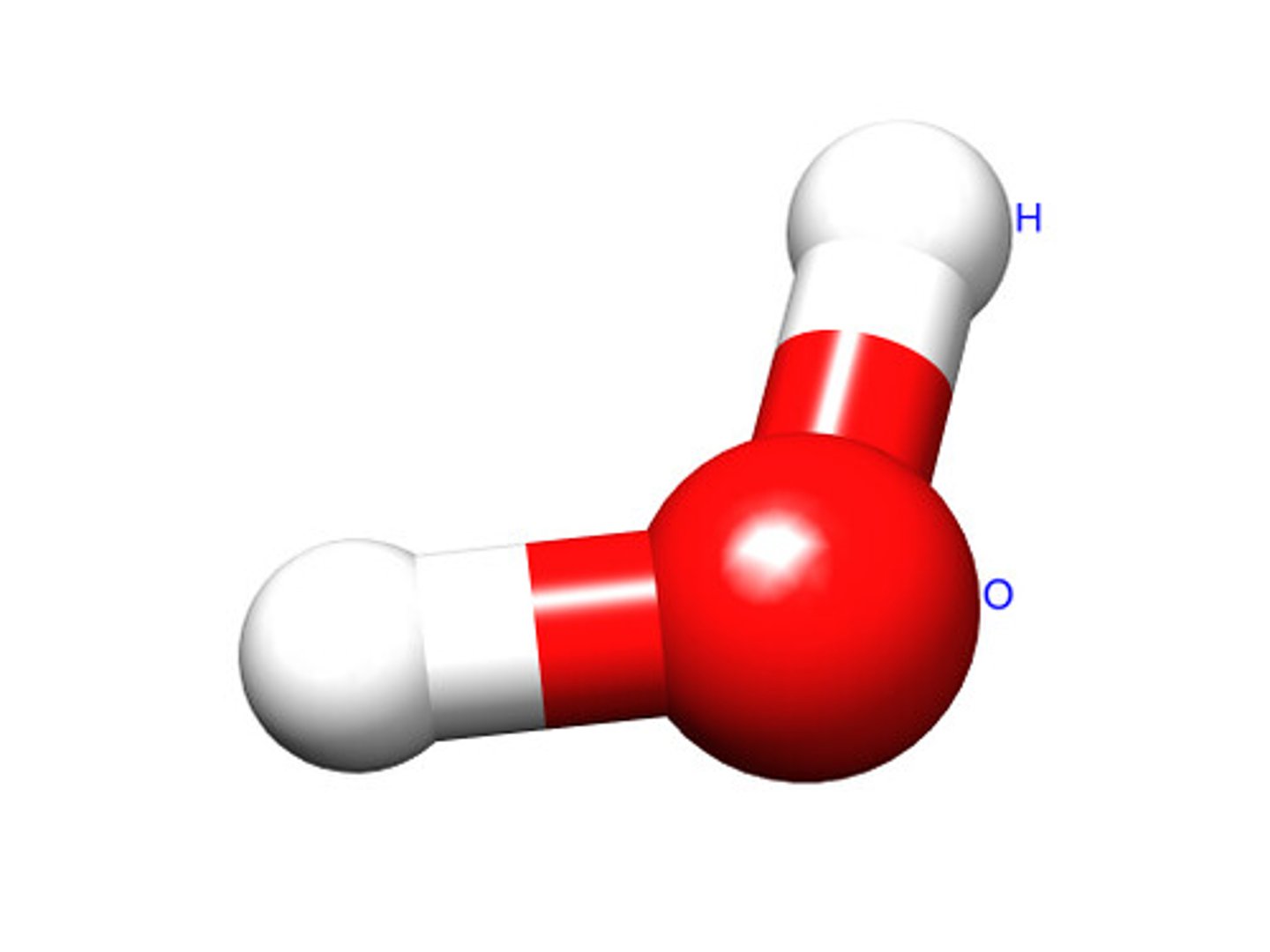
What is a molecule?
A group of atoms bonded together
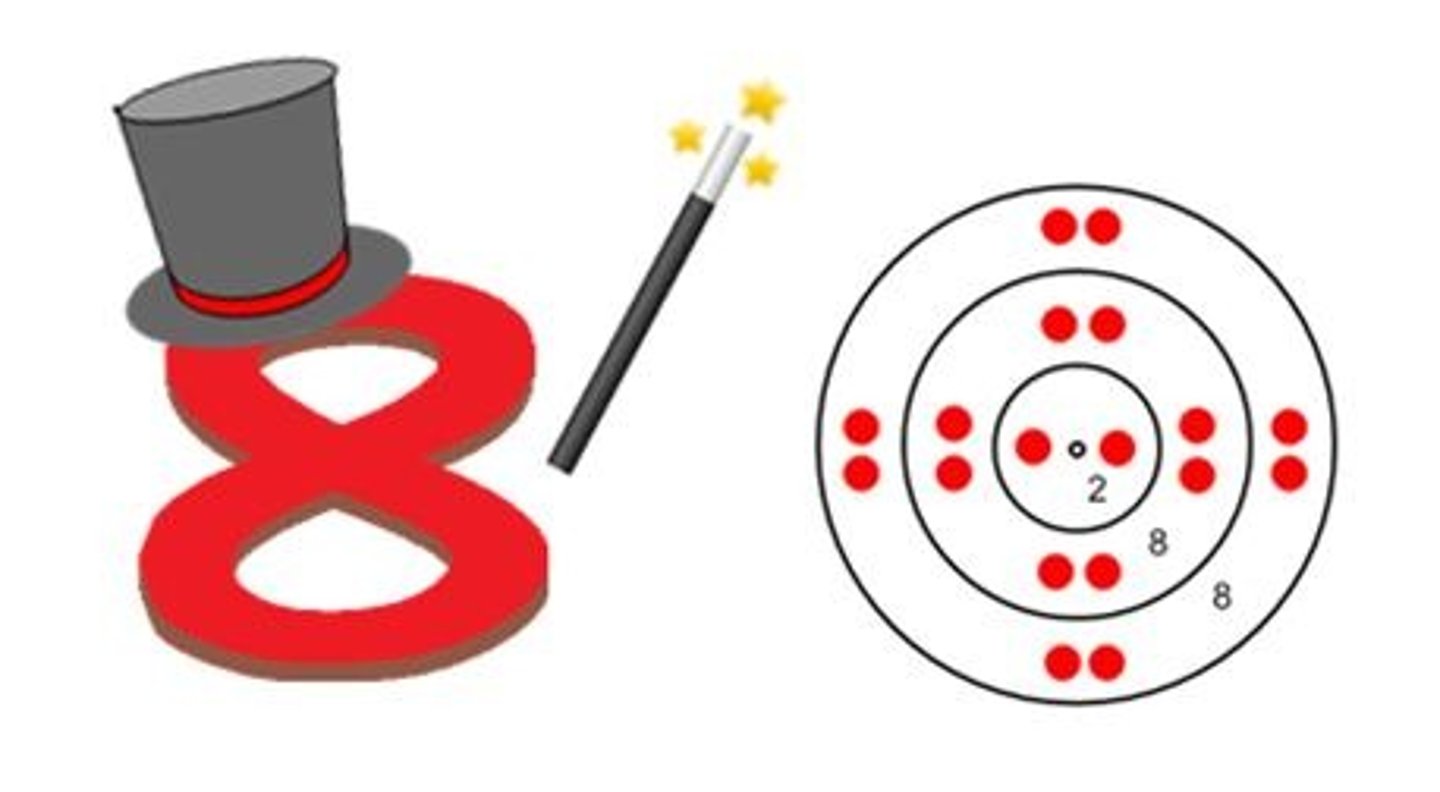
What is an octet?
8 valence electrons
What is valence?
The outershell
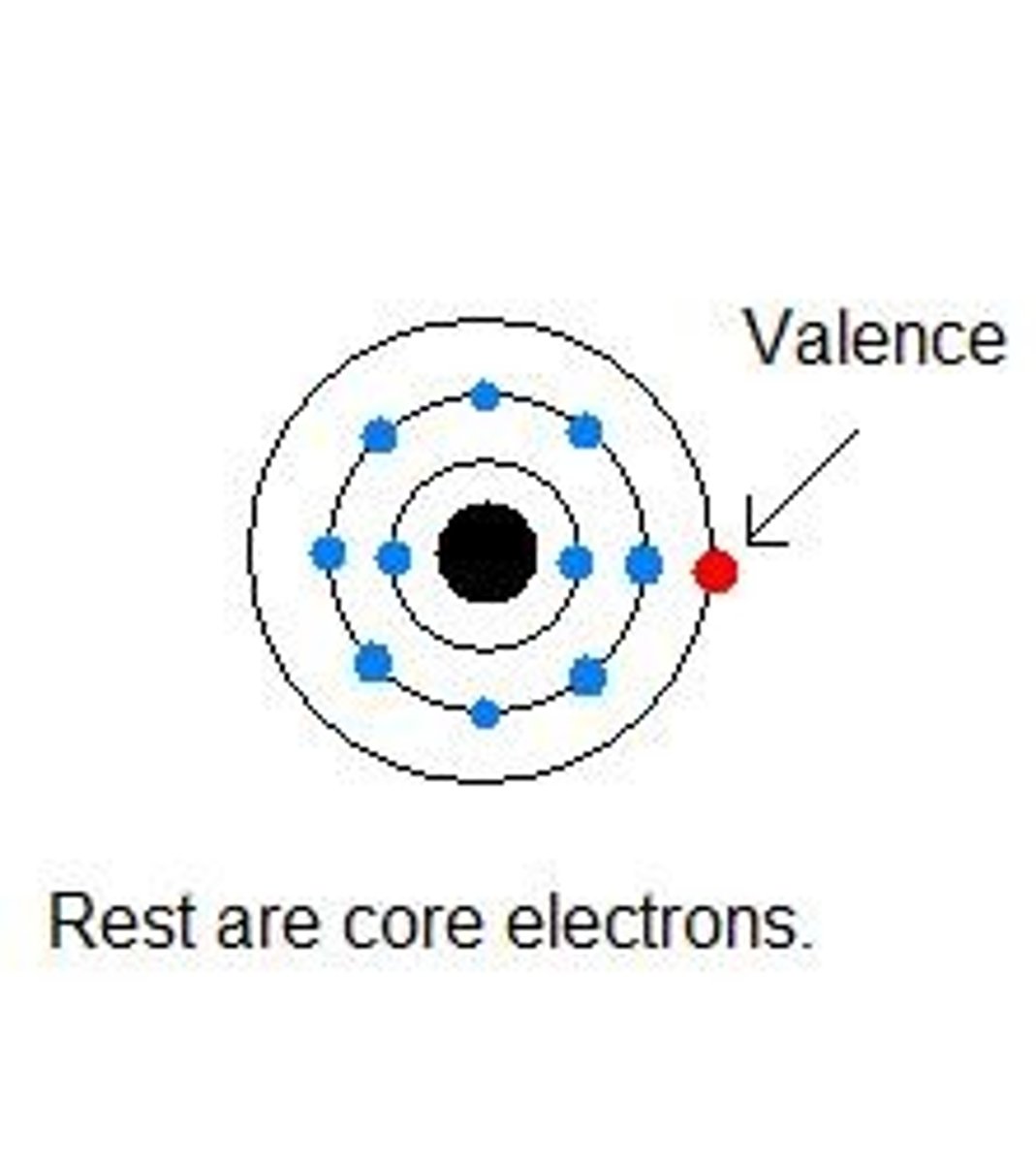
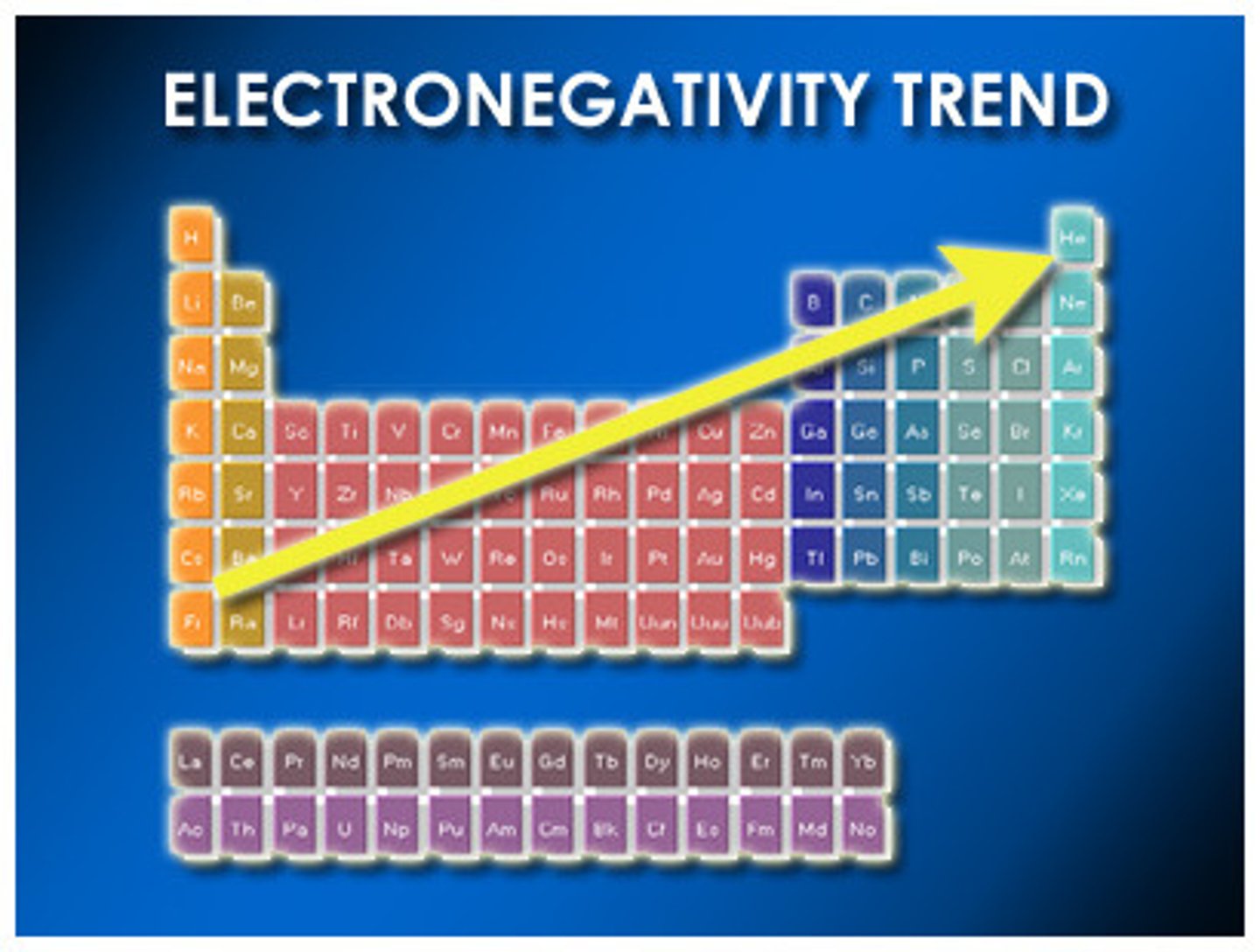
What is electronegativity?
Ability to attract electrons
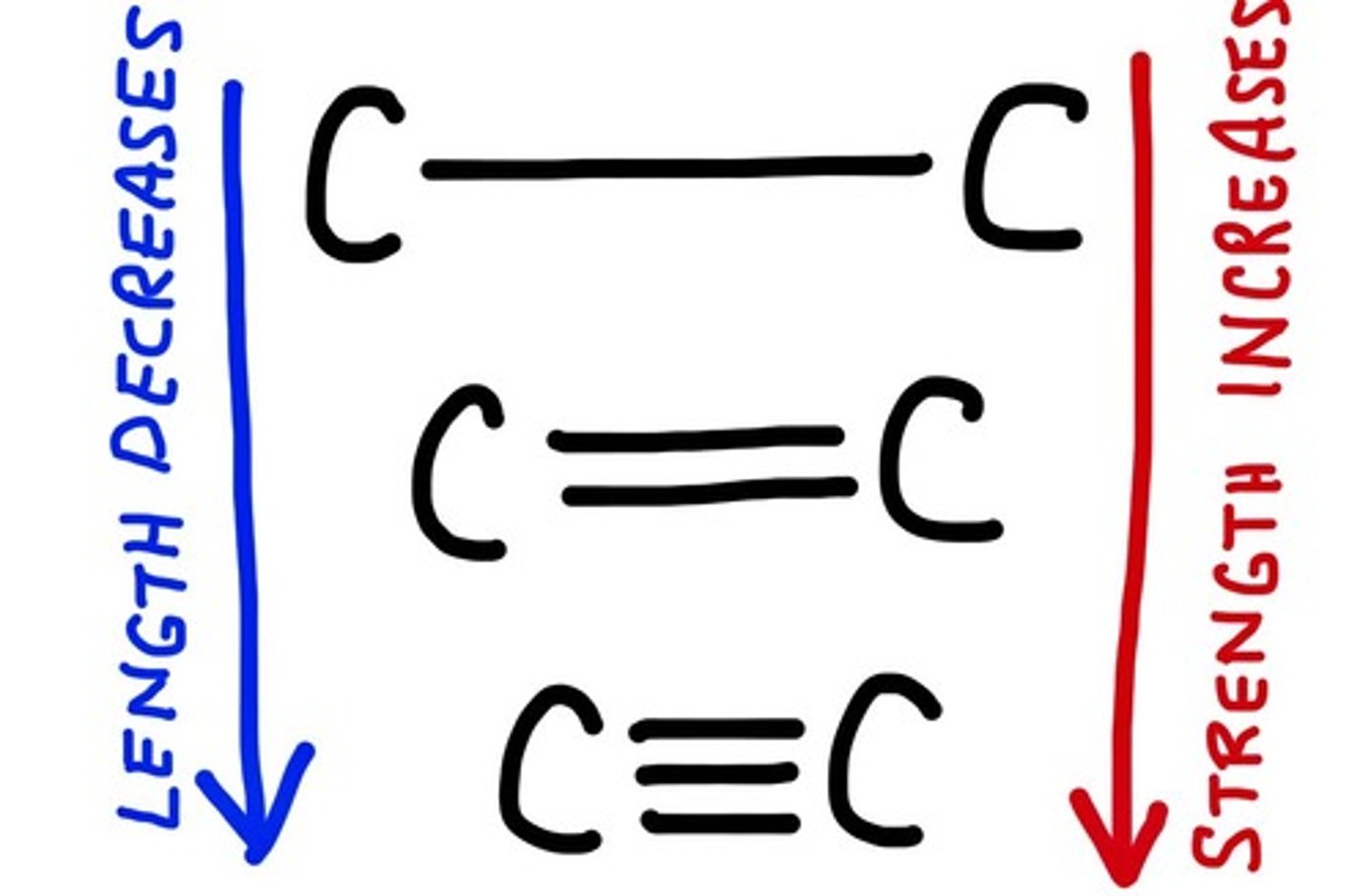
What is bond length?
The distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms
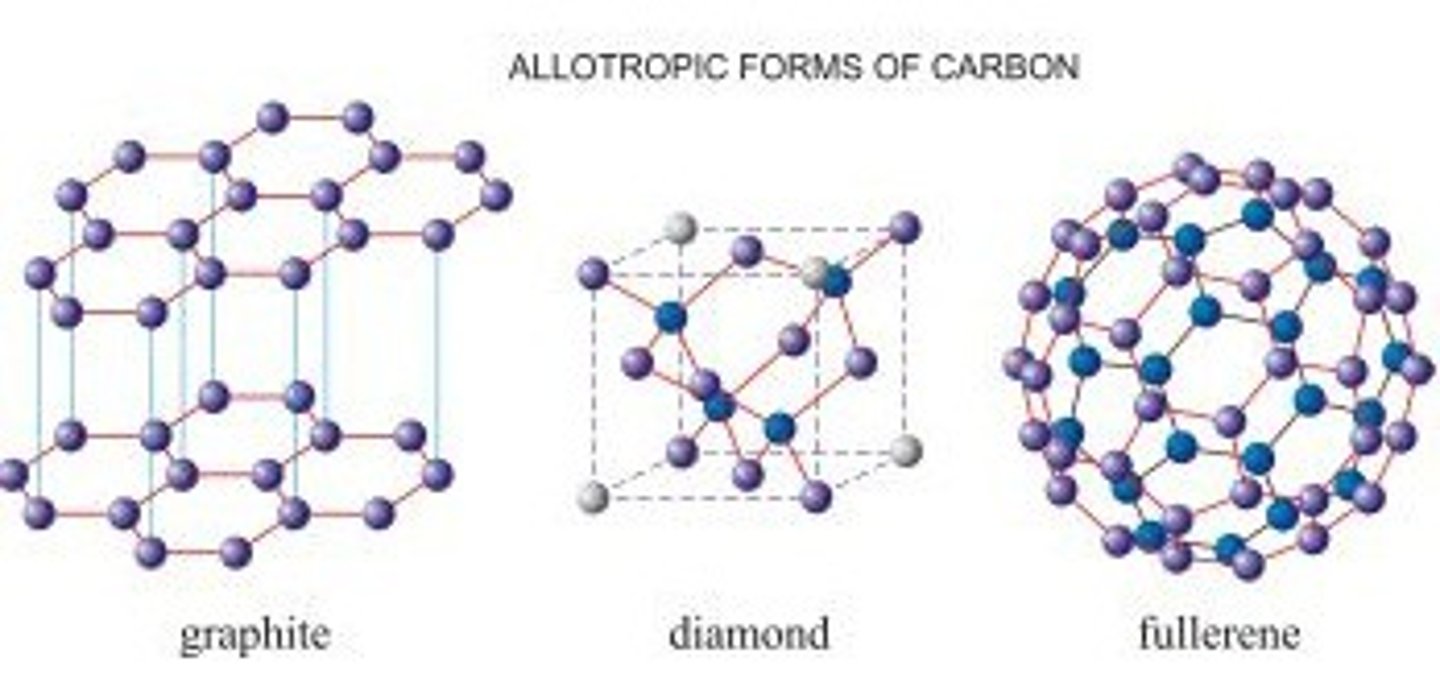
What are allotropes?
Different forms of the same element
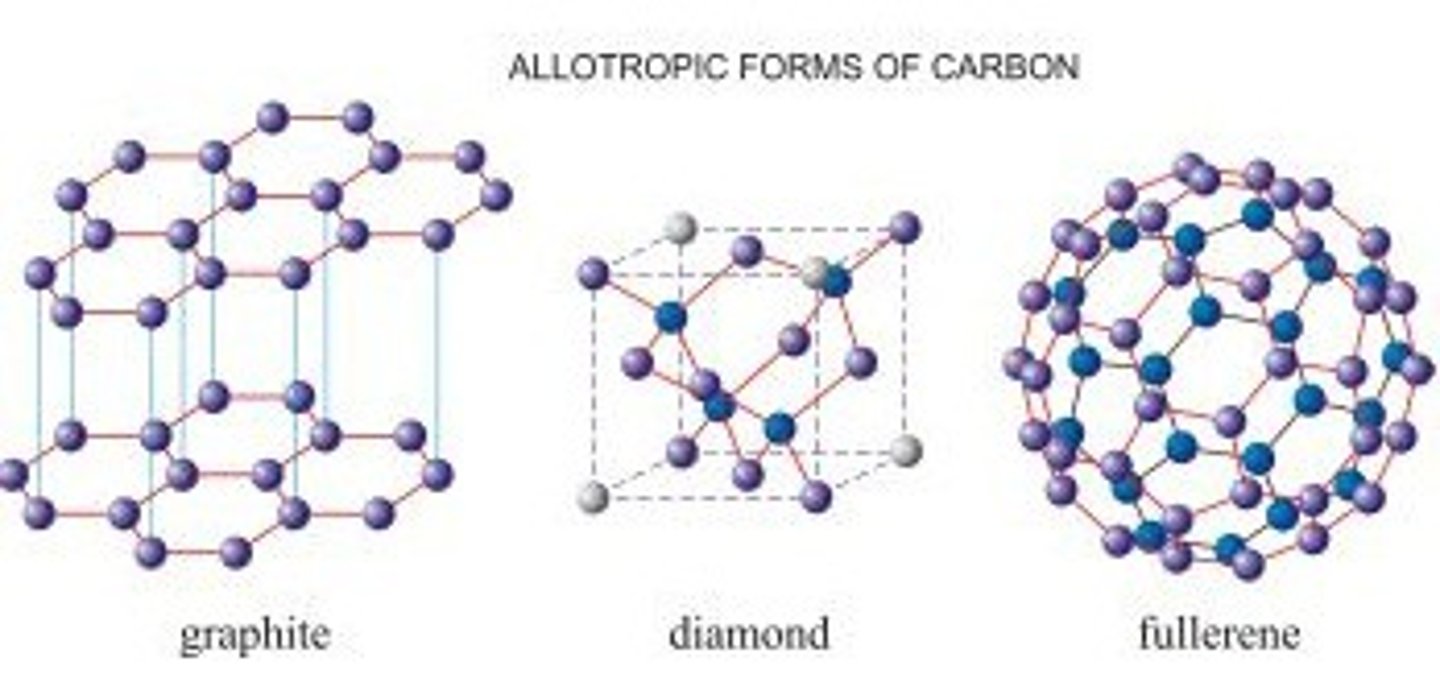
What are the allotropes of carbon?
Diamond, graphite, graphene, fullerenes
Hydrogen
H⁺

Hydroxide
OH⁻
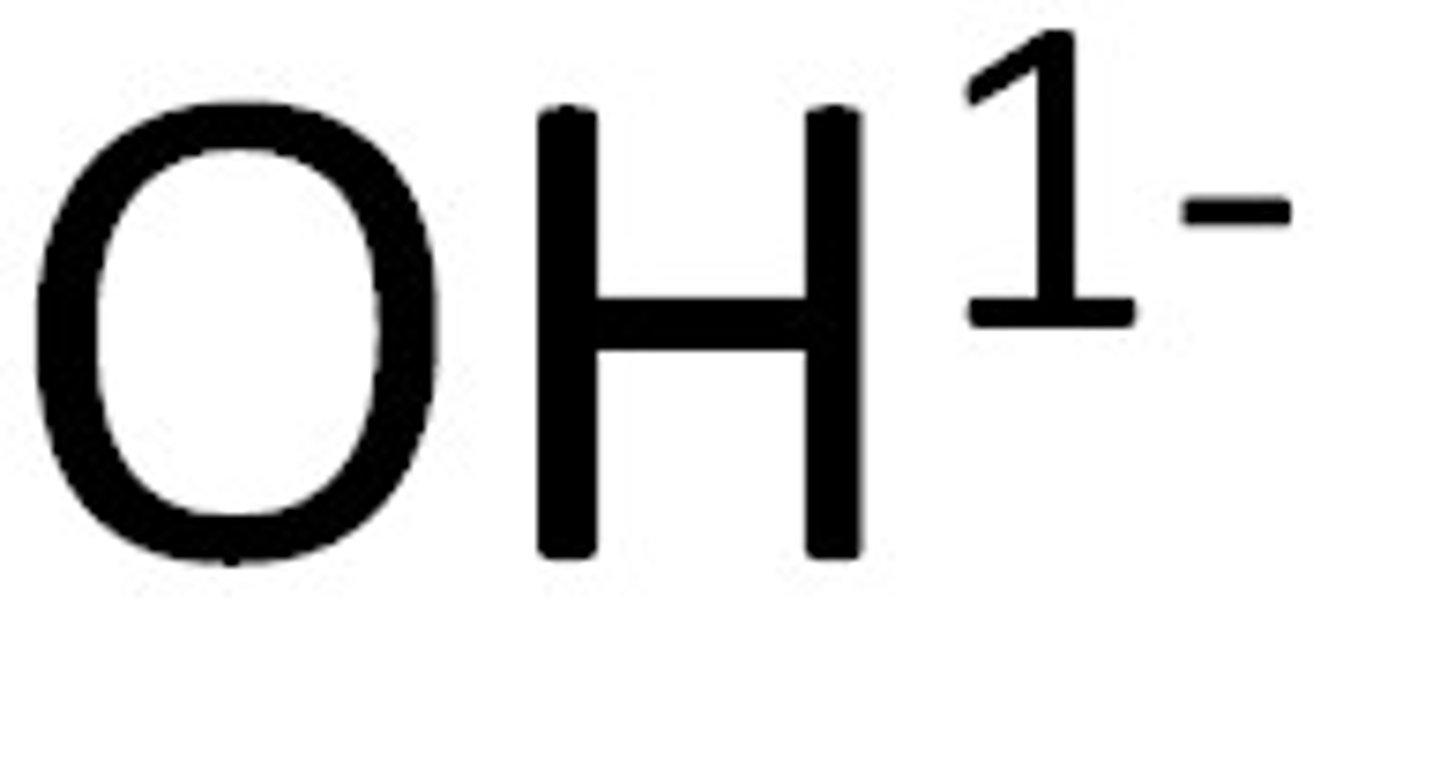
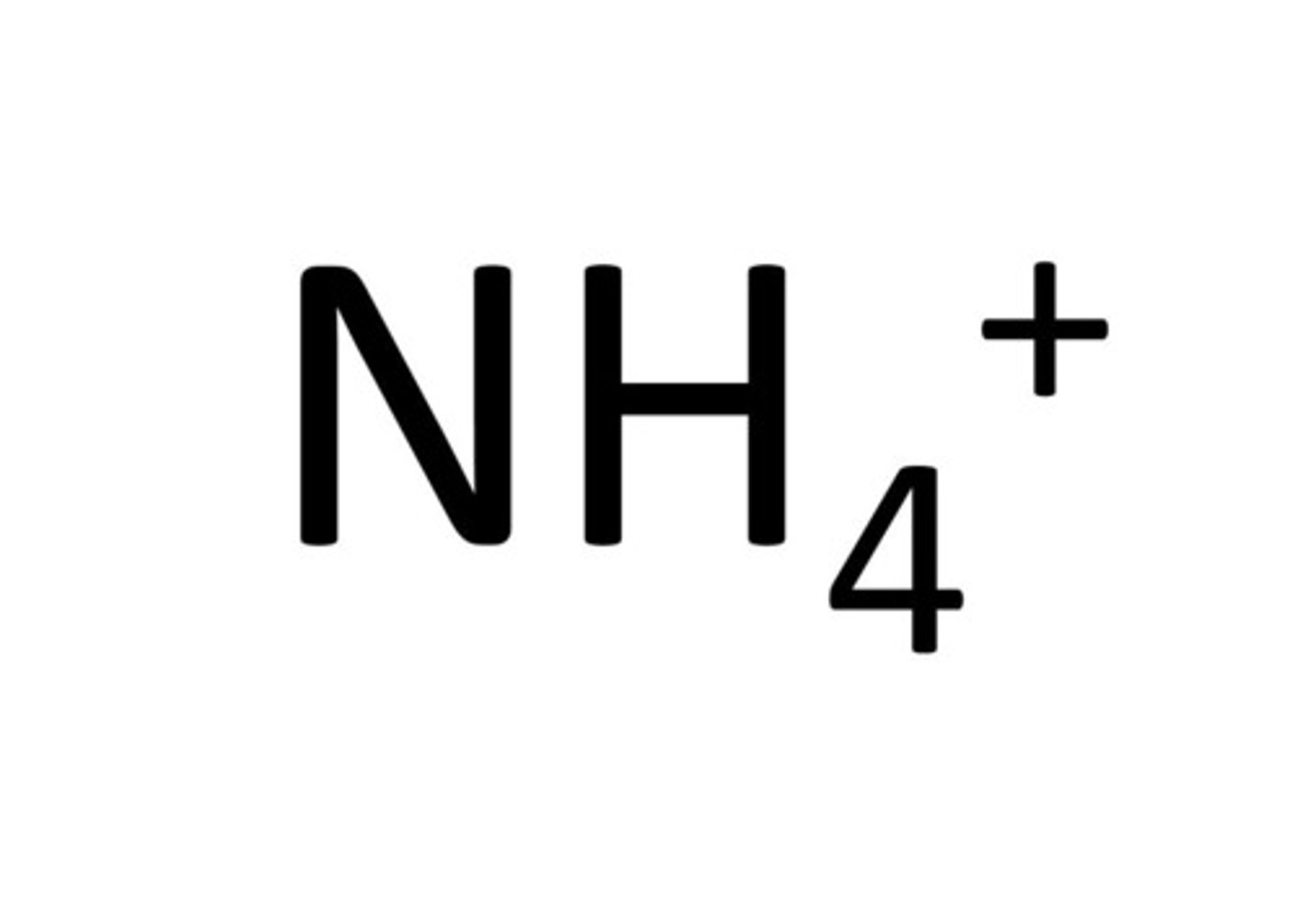
Ammonium
NH₄⁺
Carbonate
CO₃²⁻
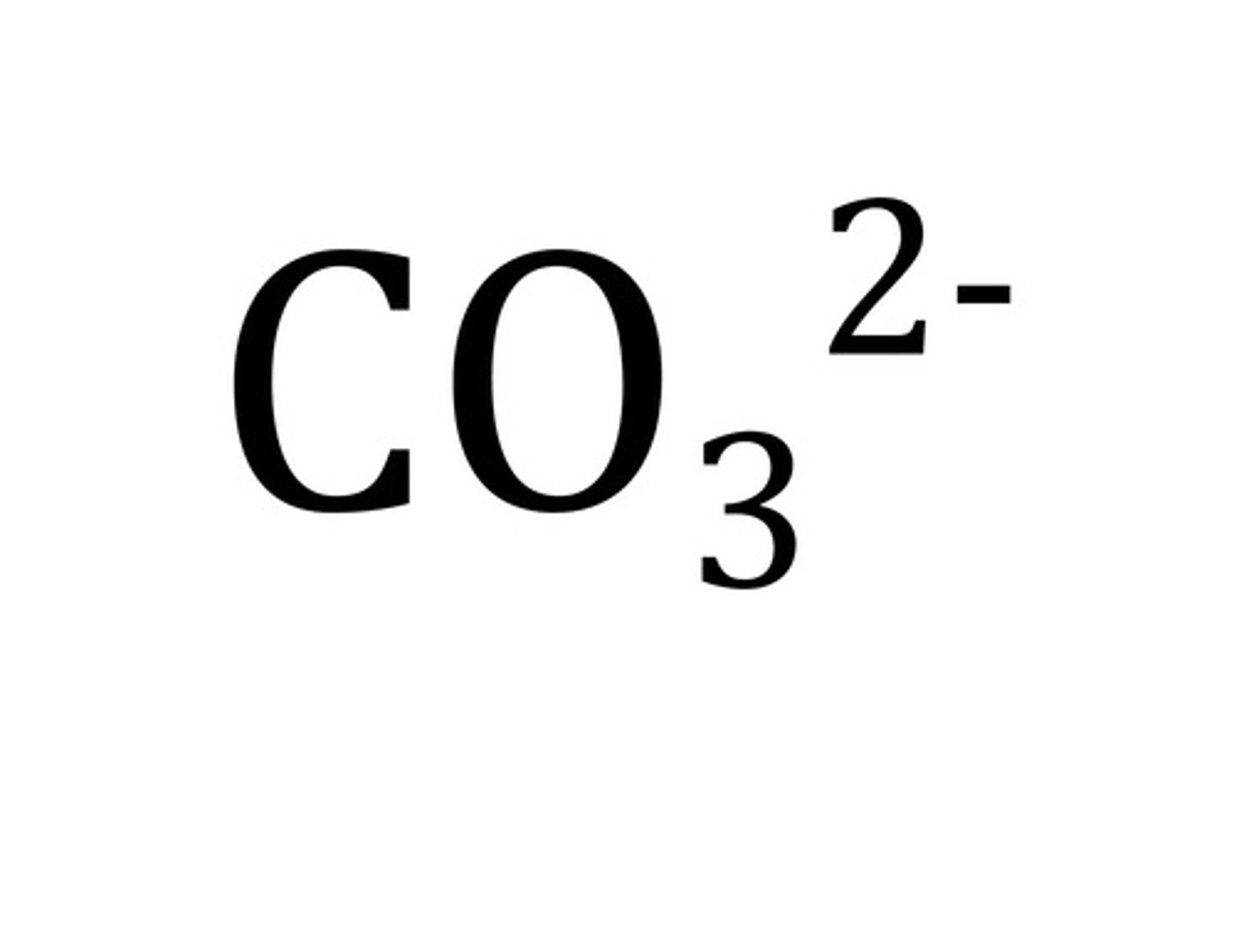
Nitrate
NO₃⁻
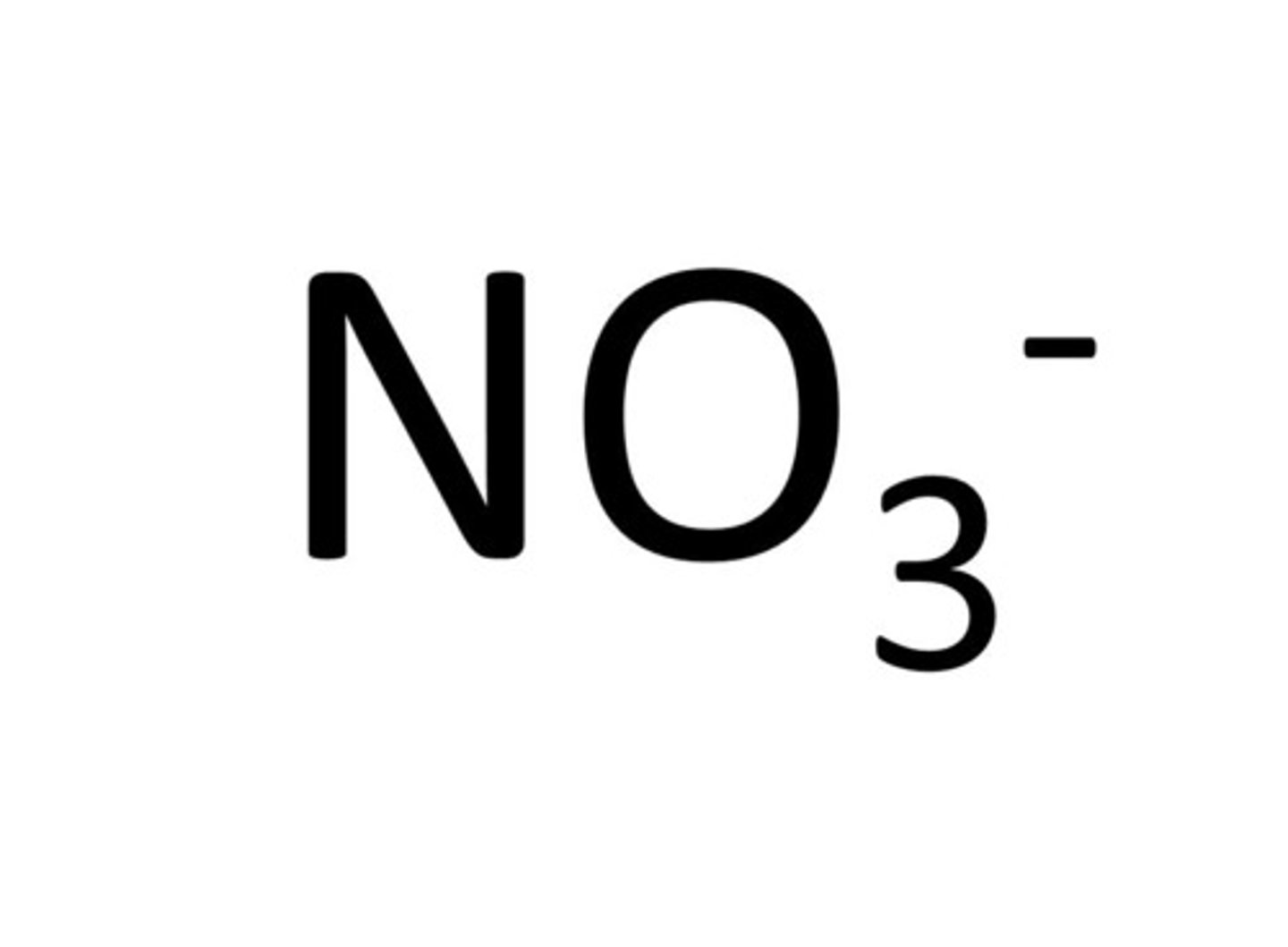
Sulfate
SO₄²⁻
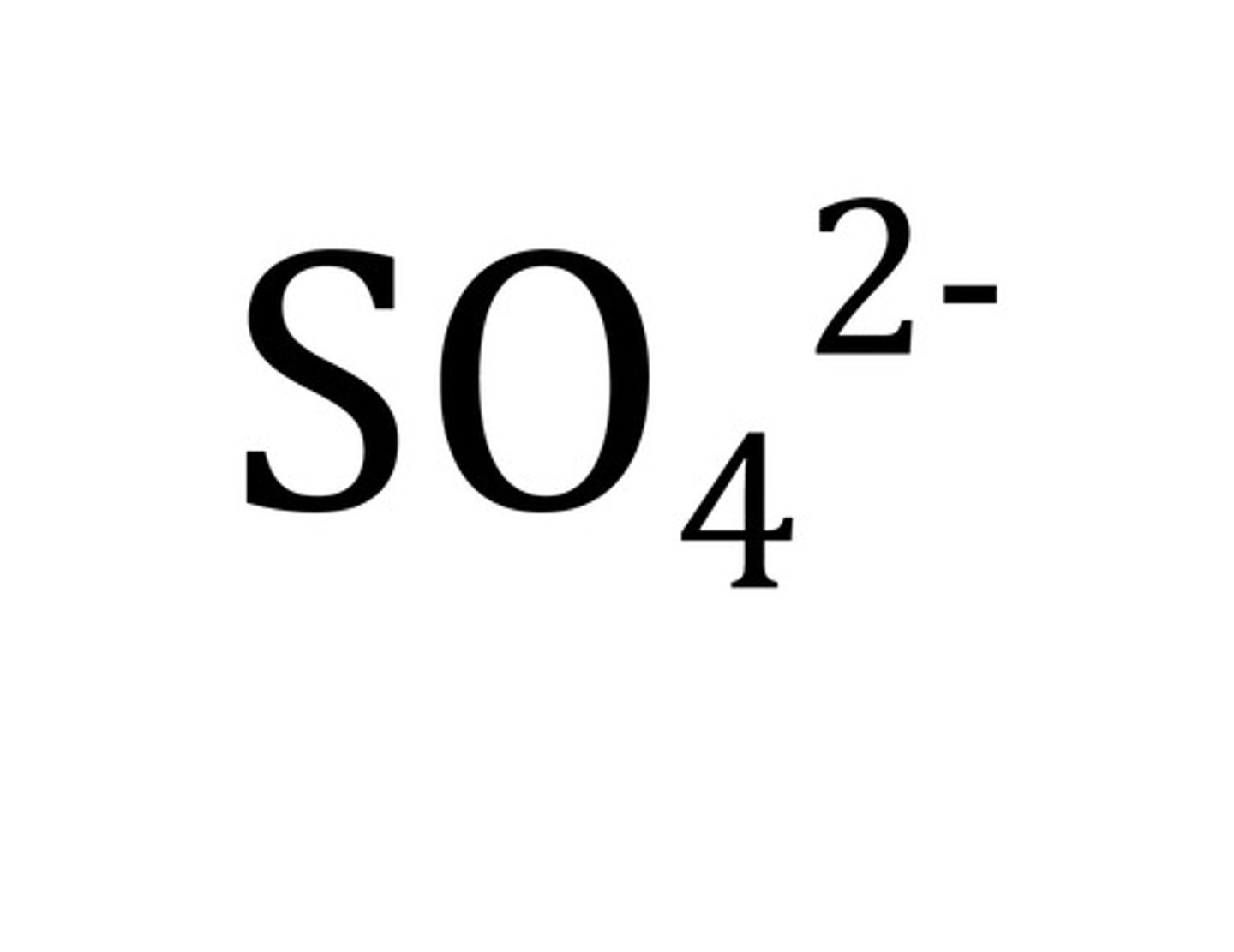
Copper
Cu²⁺
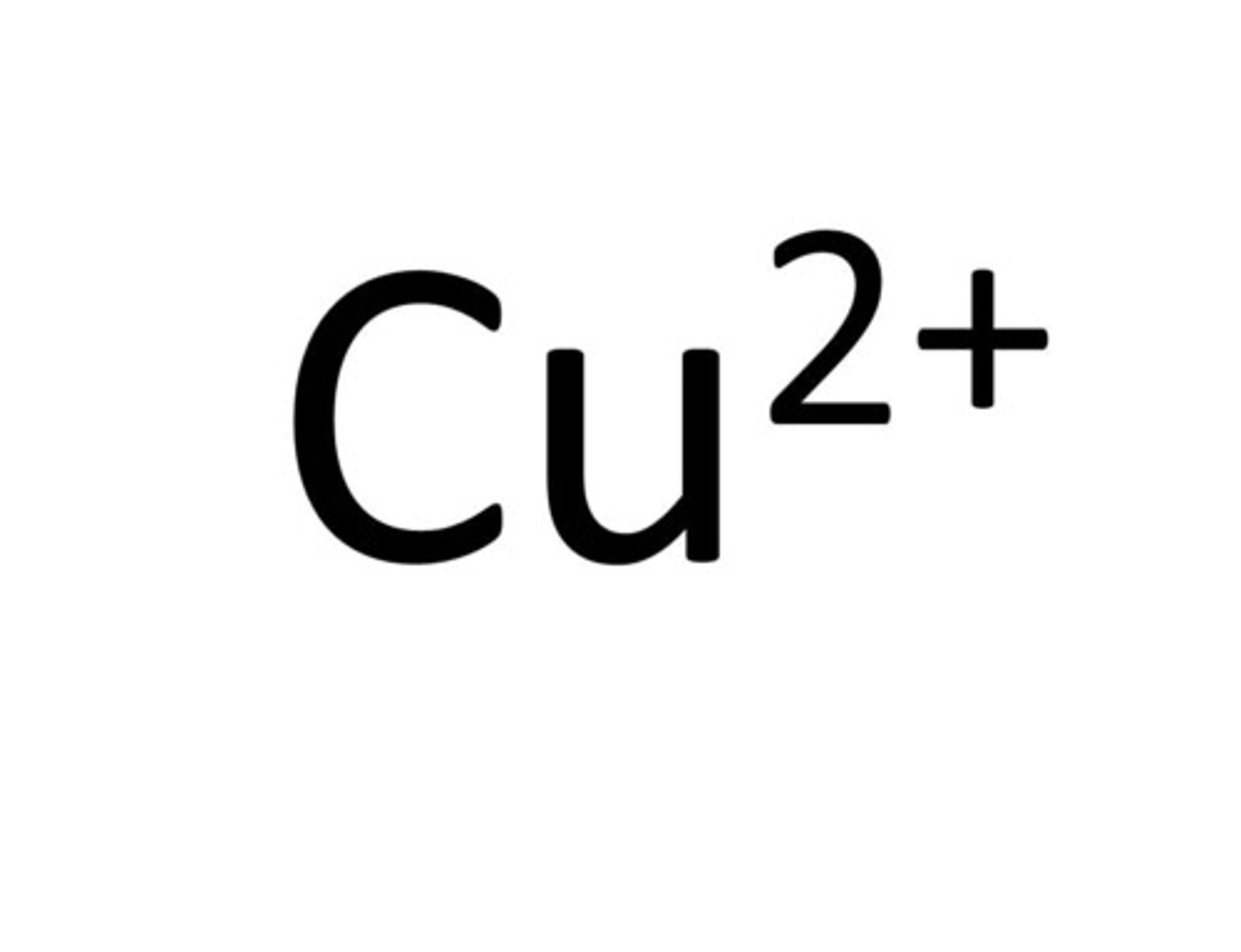
Silver
Ag⁺
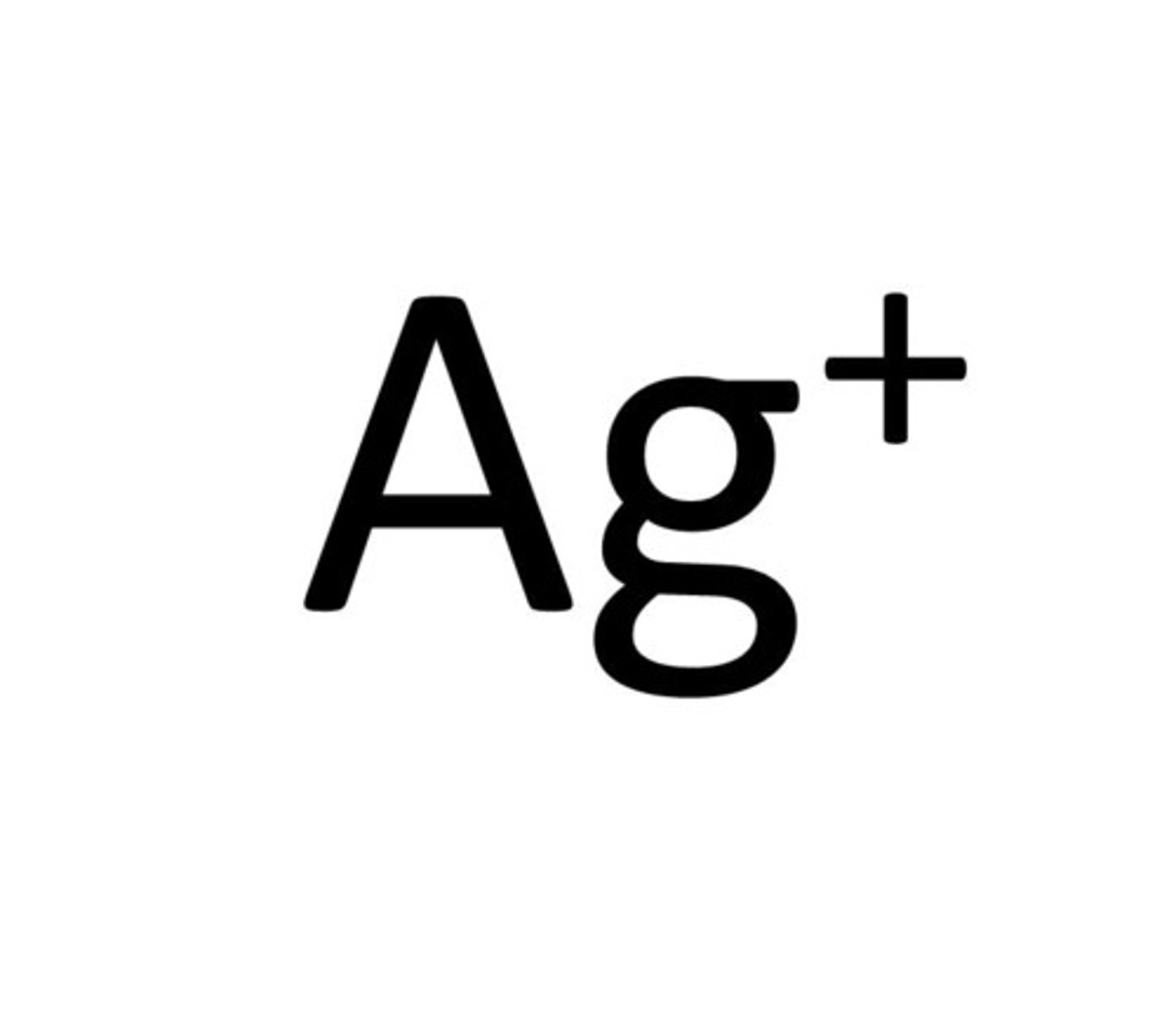
Lead
Pb²⁺
Zinc
Zn²⁺
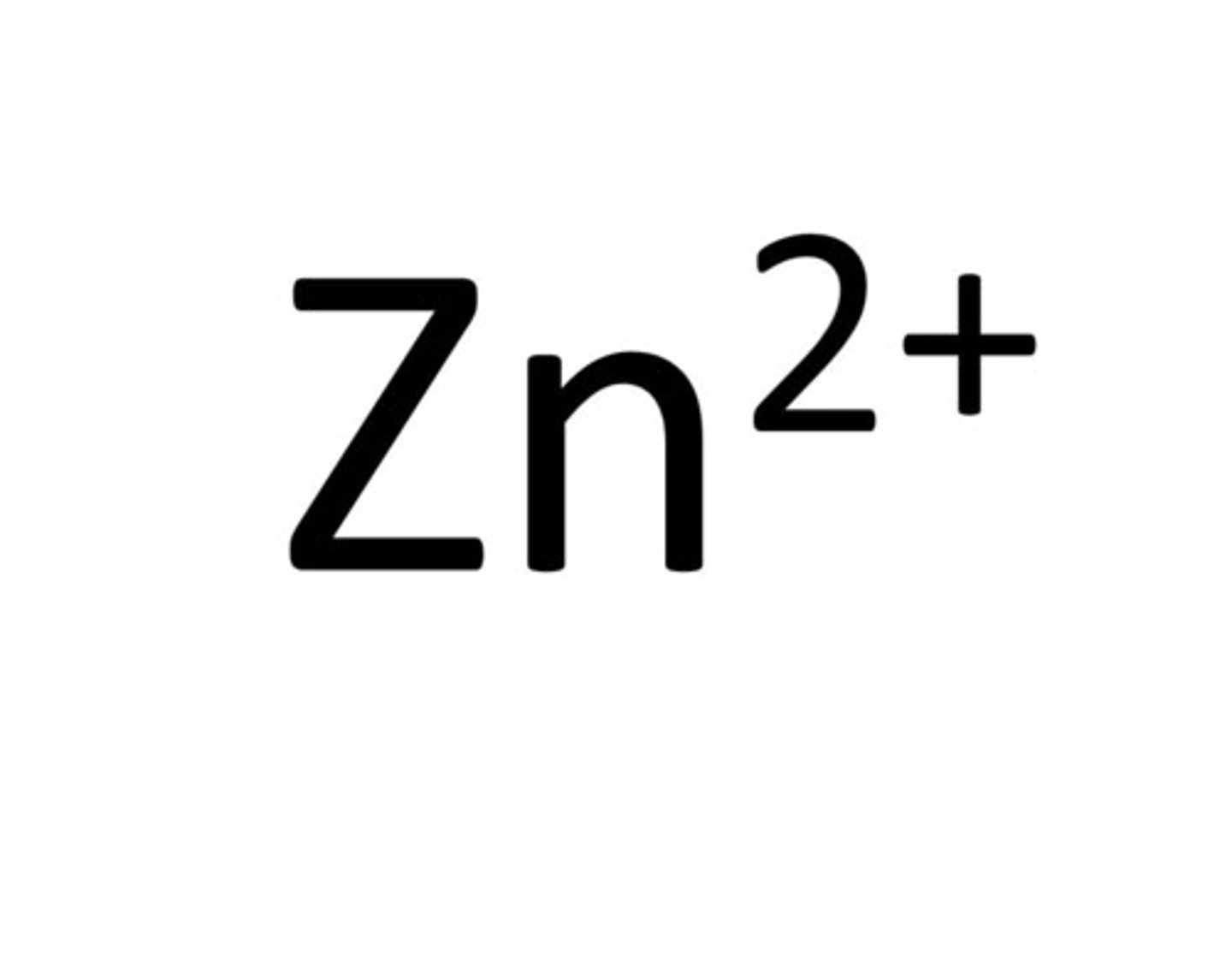
Iron (II)
Fe²⁺
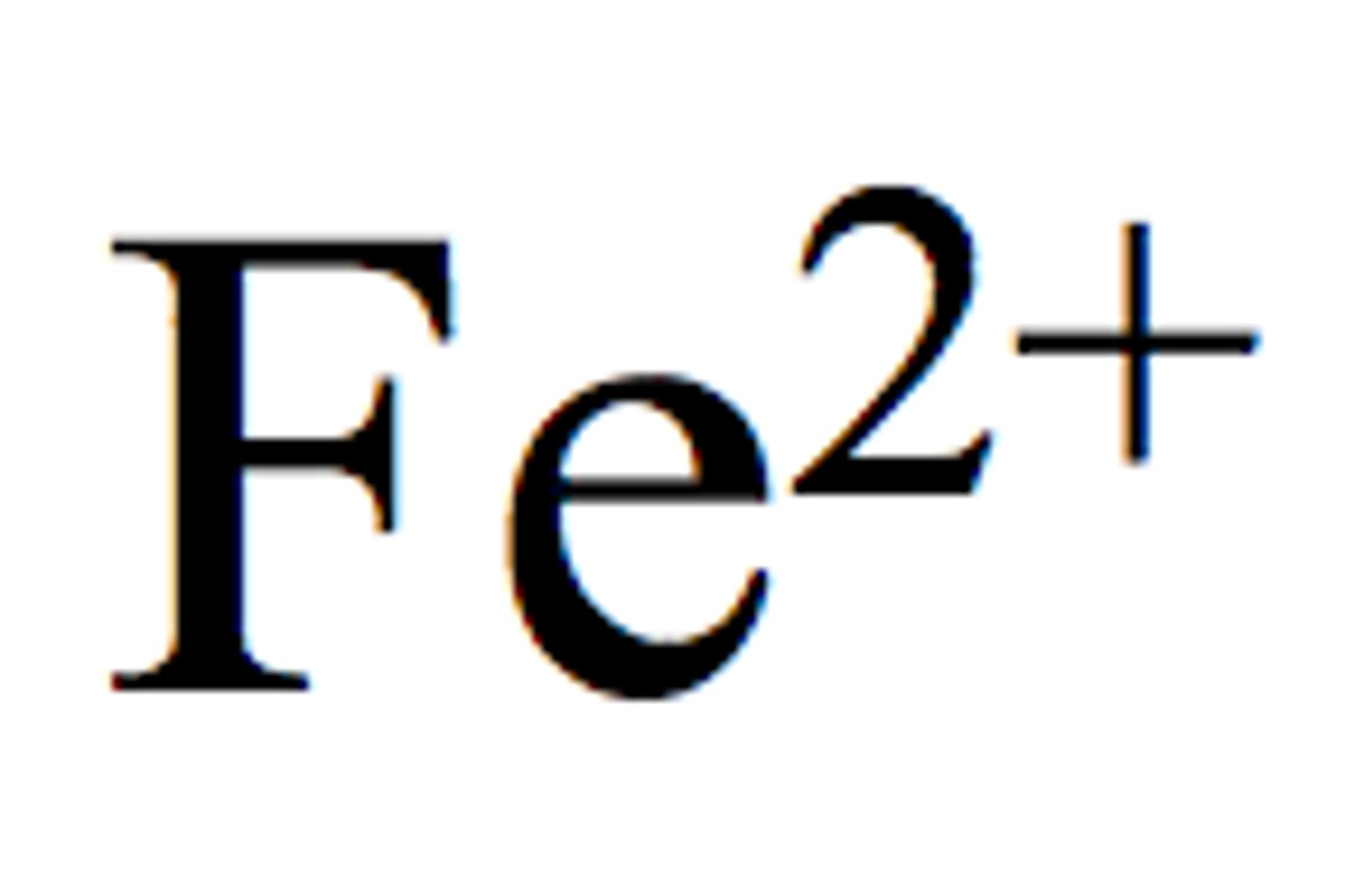
Iron (III)
Fe³⁺

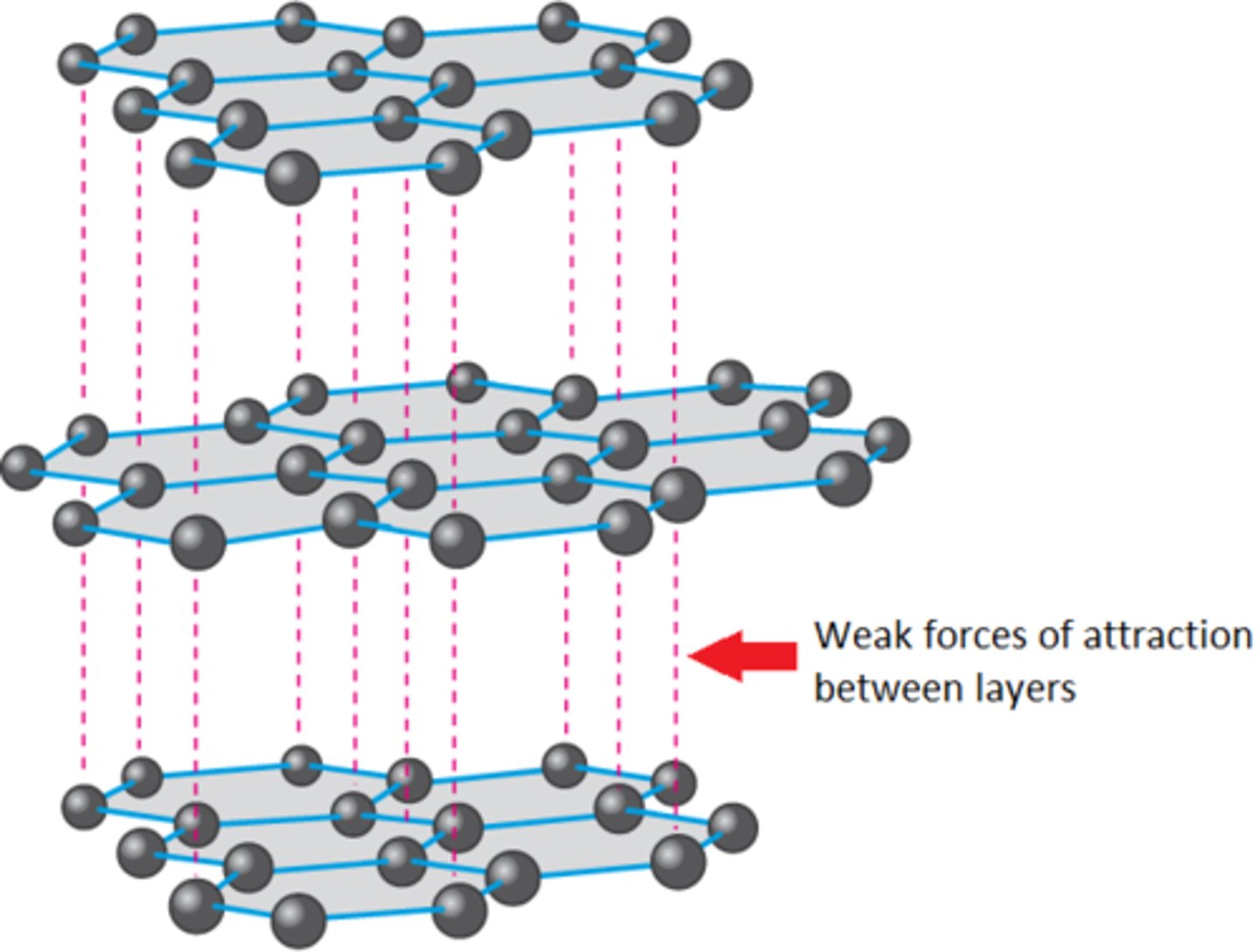
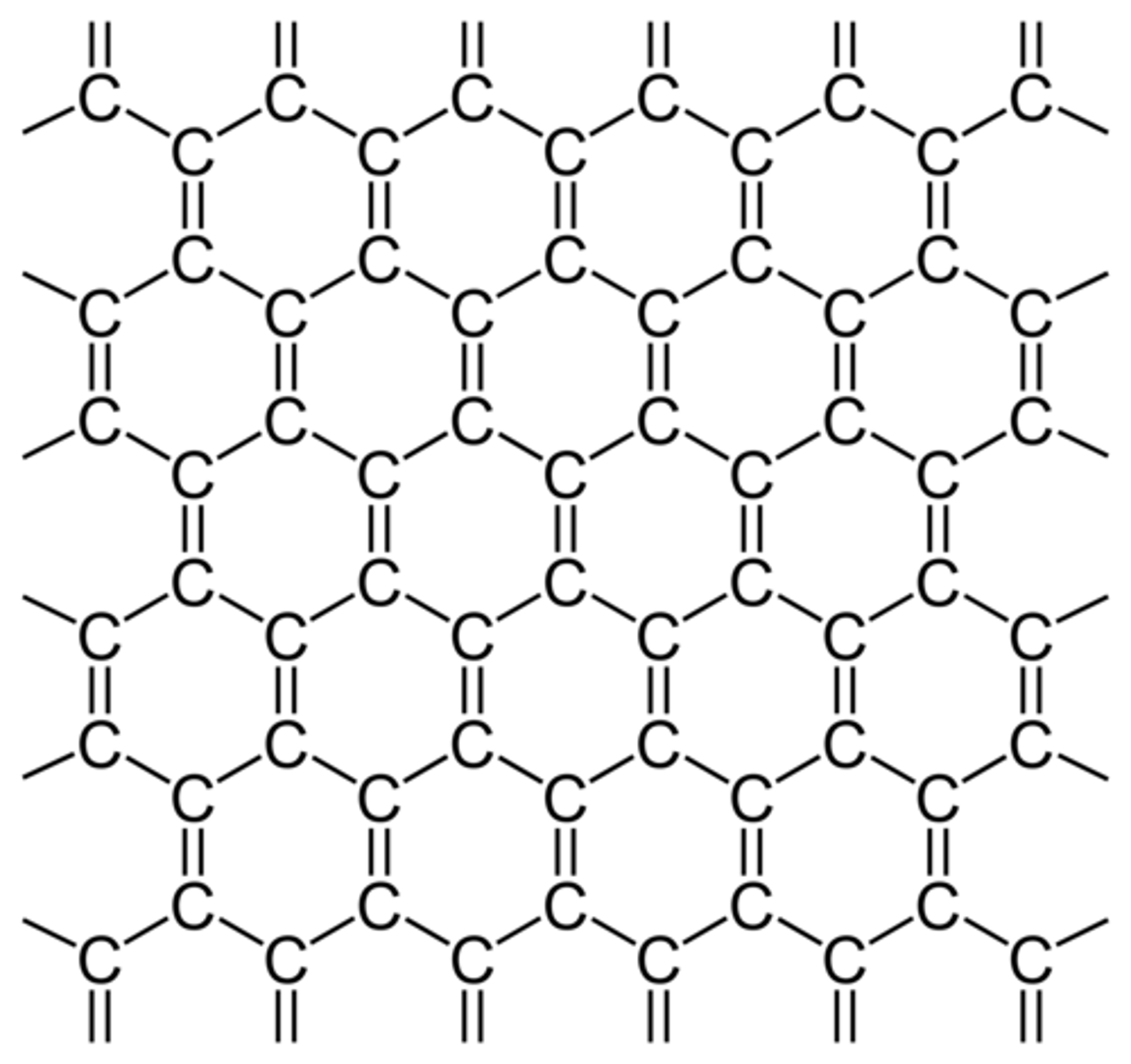
Why is graphite soft?
The weak inter molecular forces between layers allow the layers to slide over each other
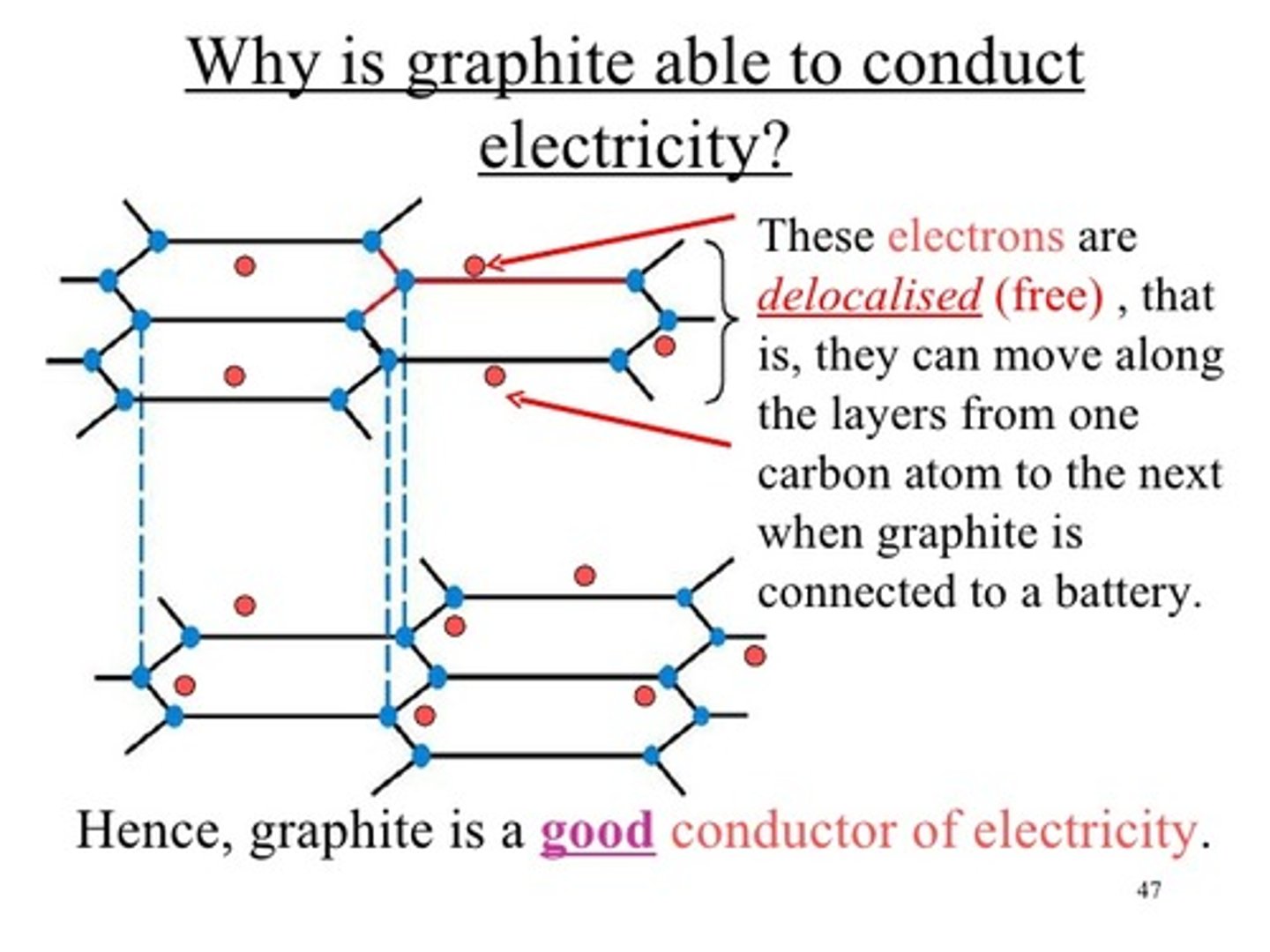
Why does graphite conduct electricity?
The delocalised electrons are free to move and can carry a charge through the structure
How thick is graphene?
One atom thick
Why does buckminsterfullerene have a low melting point?
They have low inter molecular forces thus it takes less energy to overcome forces
What are the uses of diamond?
Cutting tools and jewellery
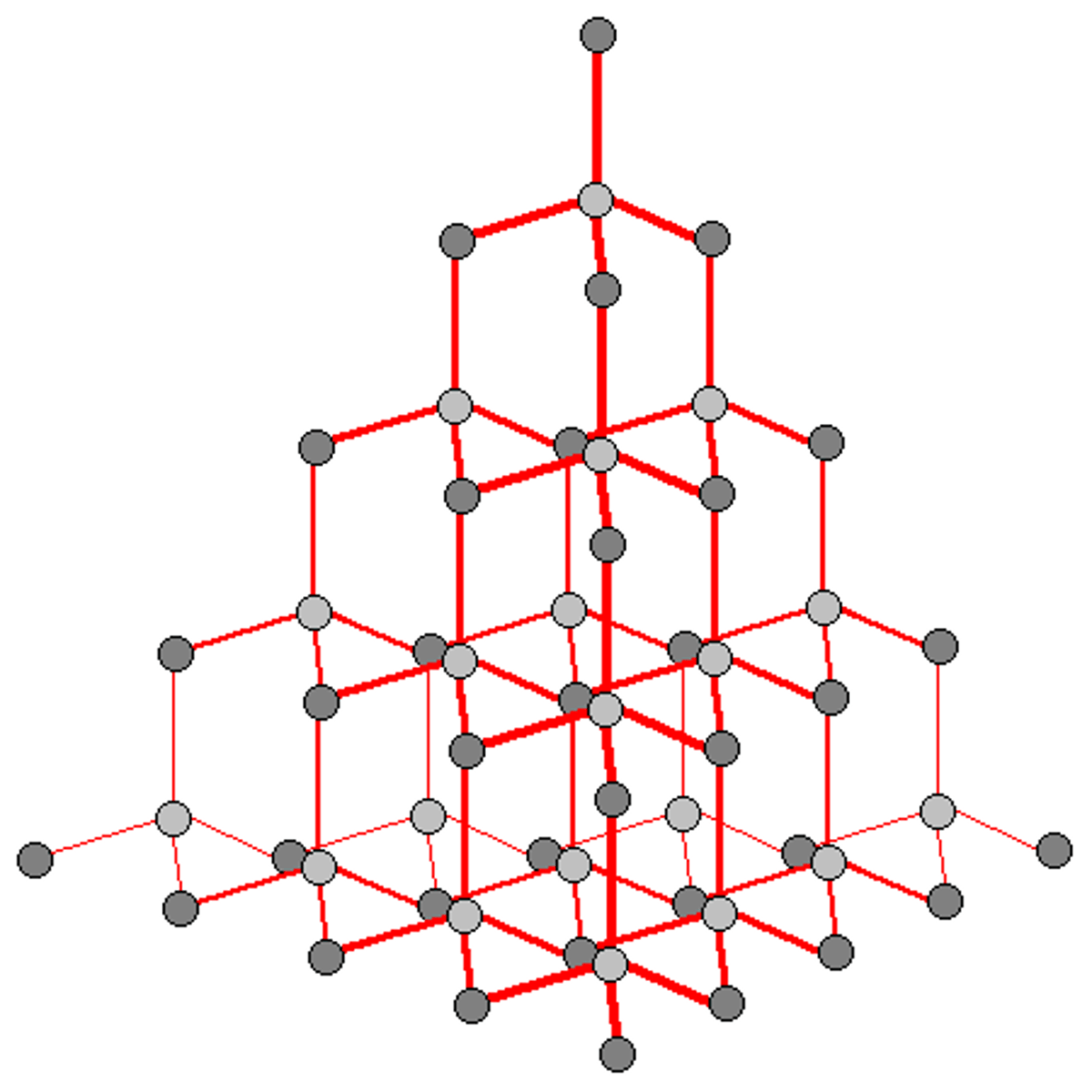
What are the uses of graphite?
Pencils and lubricants
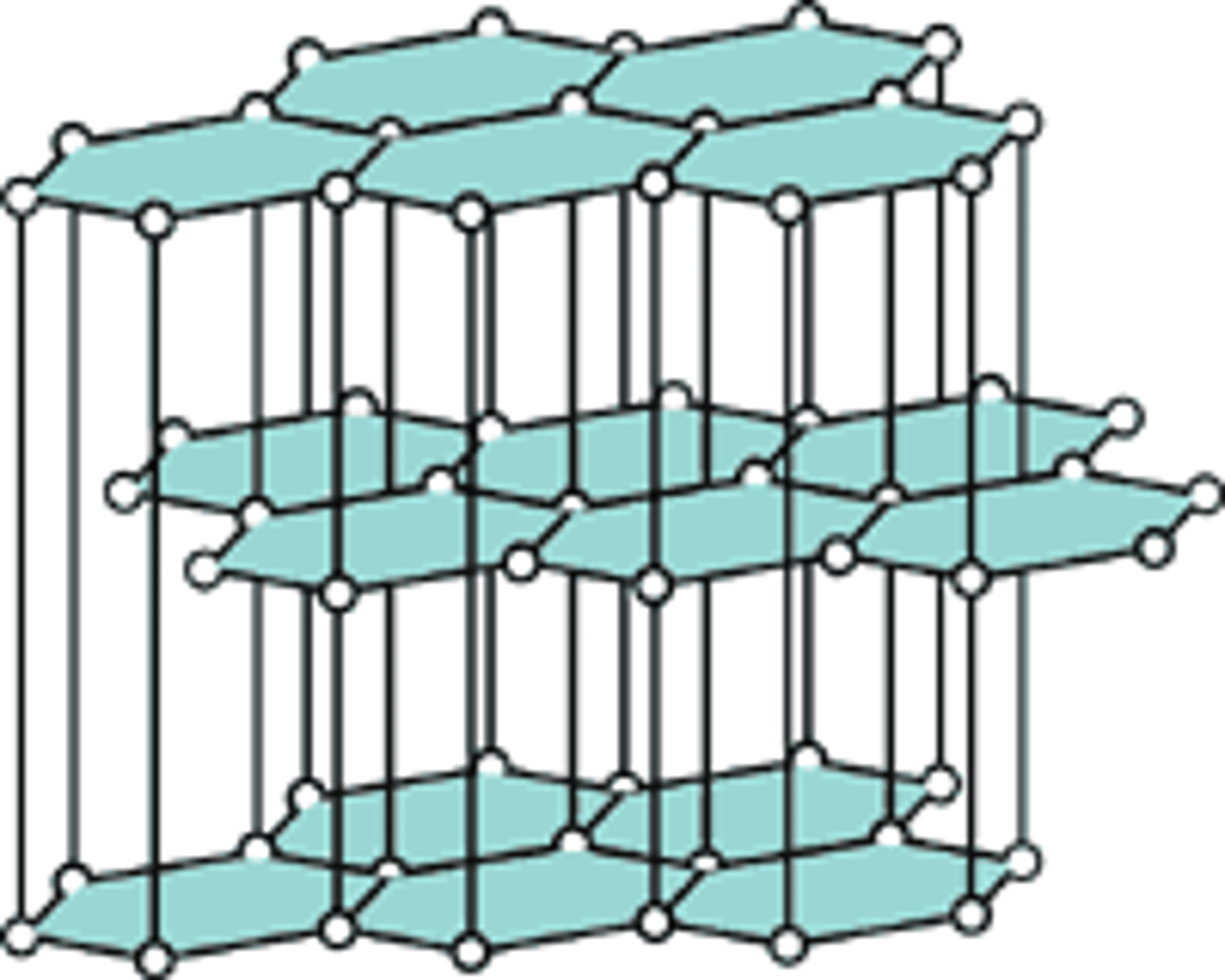
What are the uses of graphene?
Computer screens
What are the uses of buck minister fullerene?
Drug delivery systems
How many carbon atoms are there in buck minister fullerene?
60
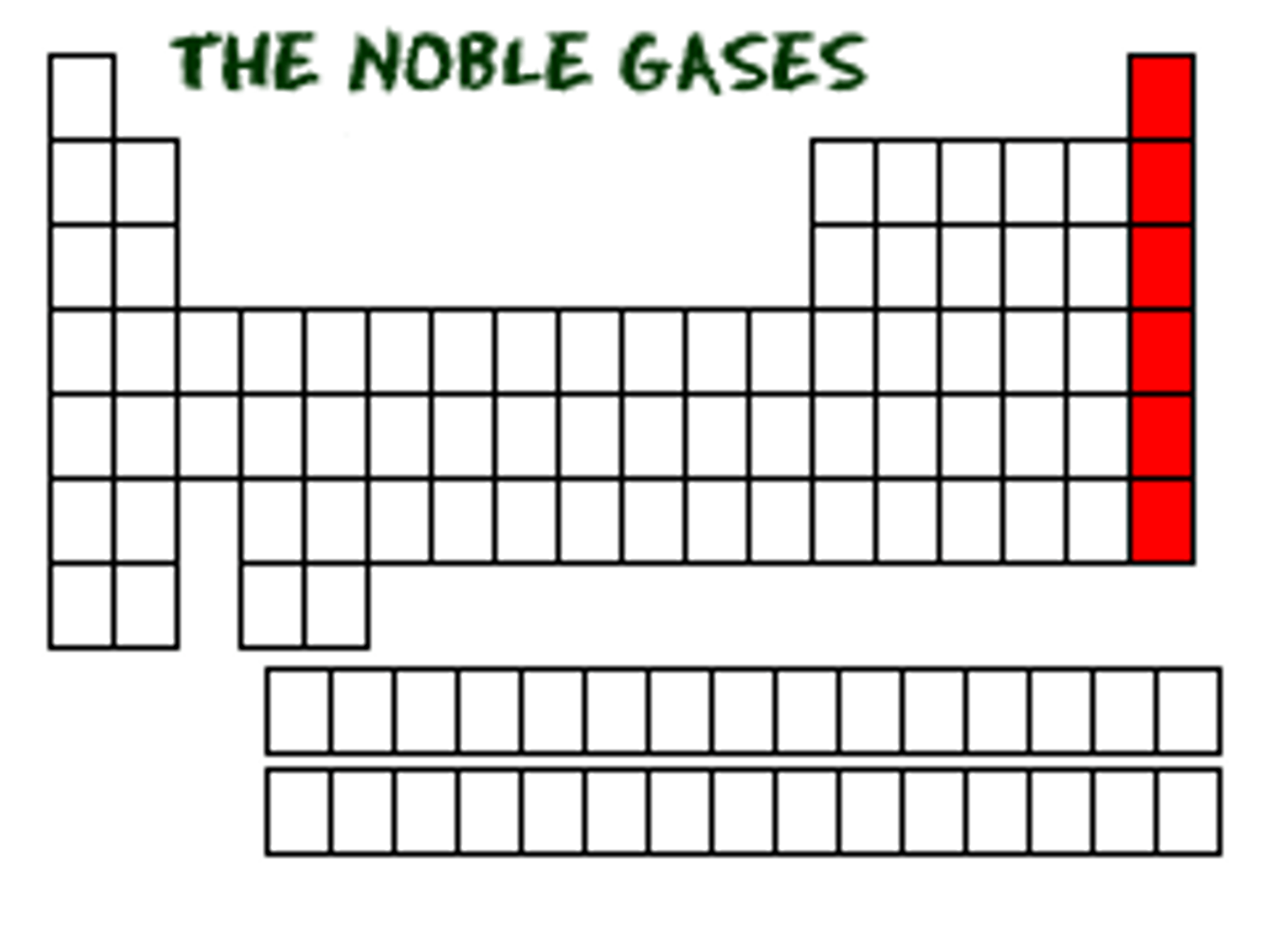
What group are the noble gases in?
Group 0 or 8
What group are the halogens in?
Group 7
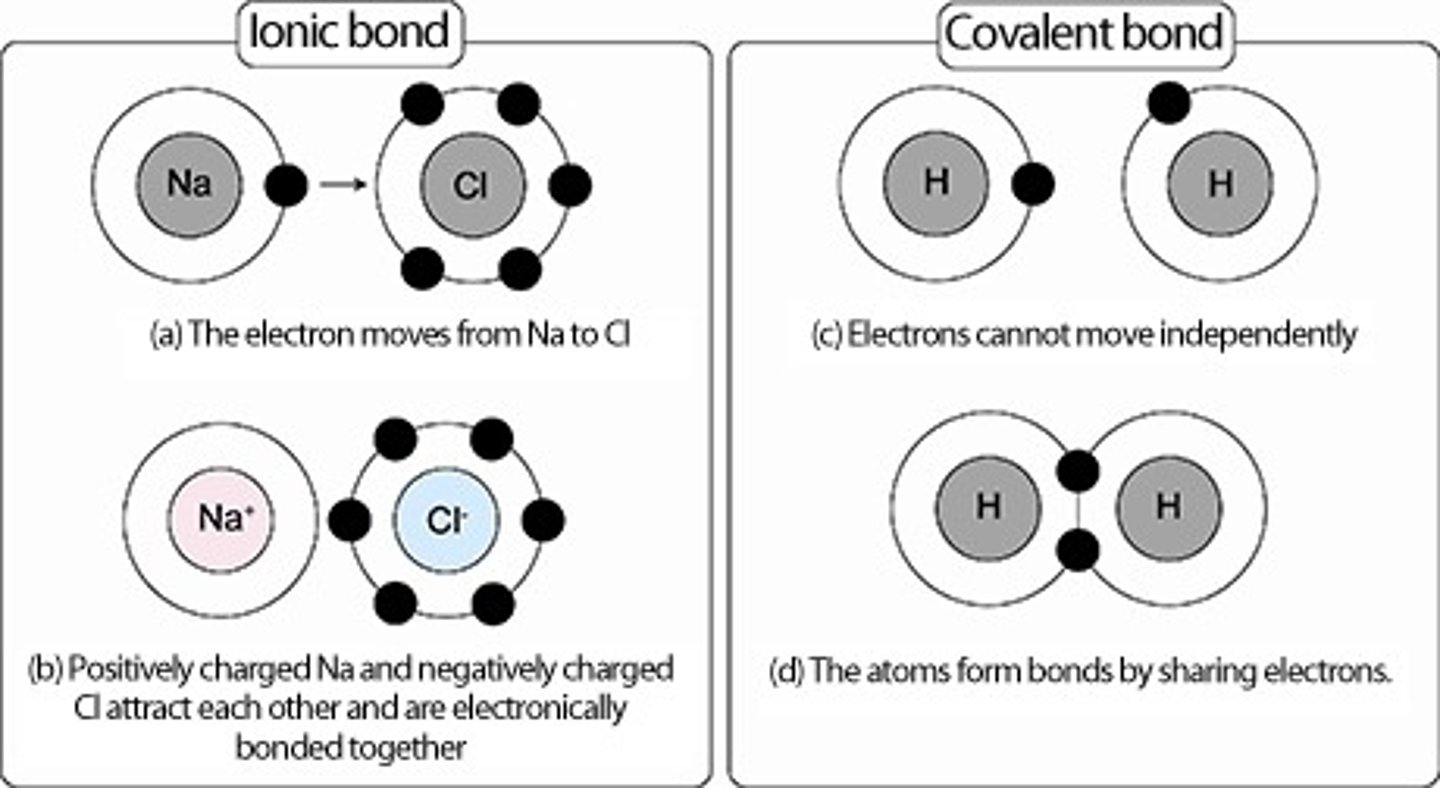
What is the difference between ionic and covalent bonding?
Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons whereas ionic bonding is the complete transfer of electrons
What group of the periodic table do atoms 'try to be like'?
Group 0 or 8
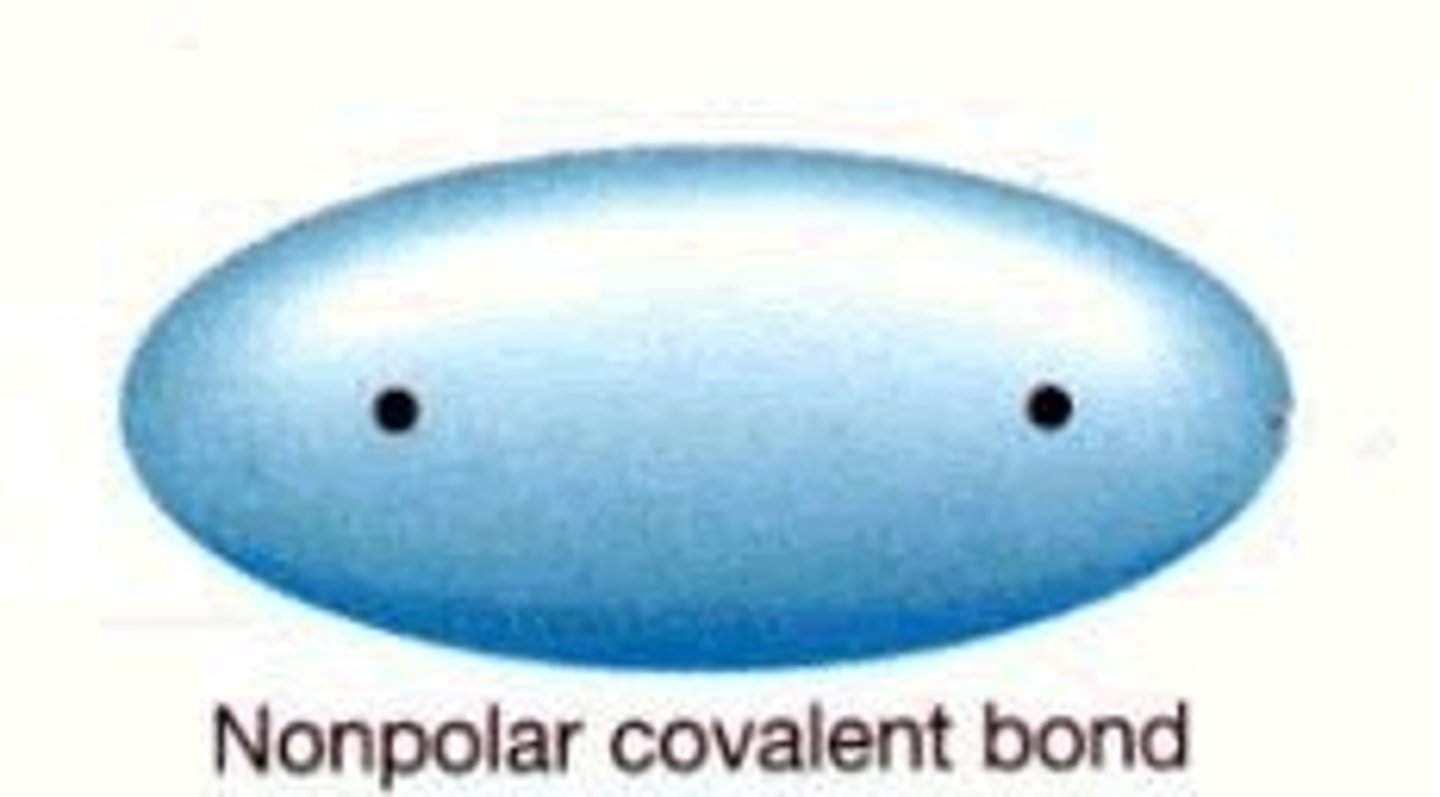
What is a non-polar bond?
A covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally
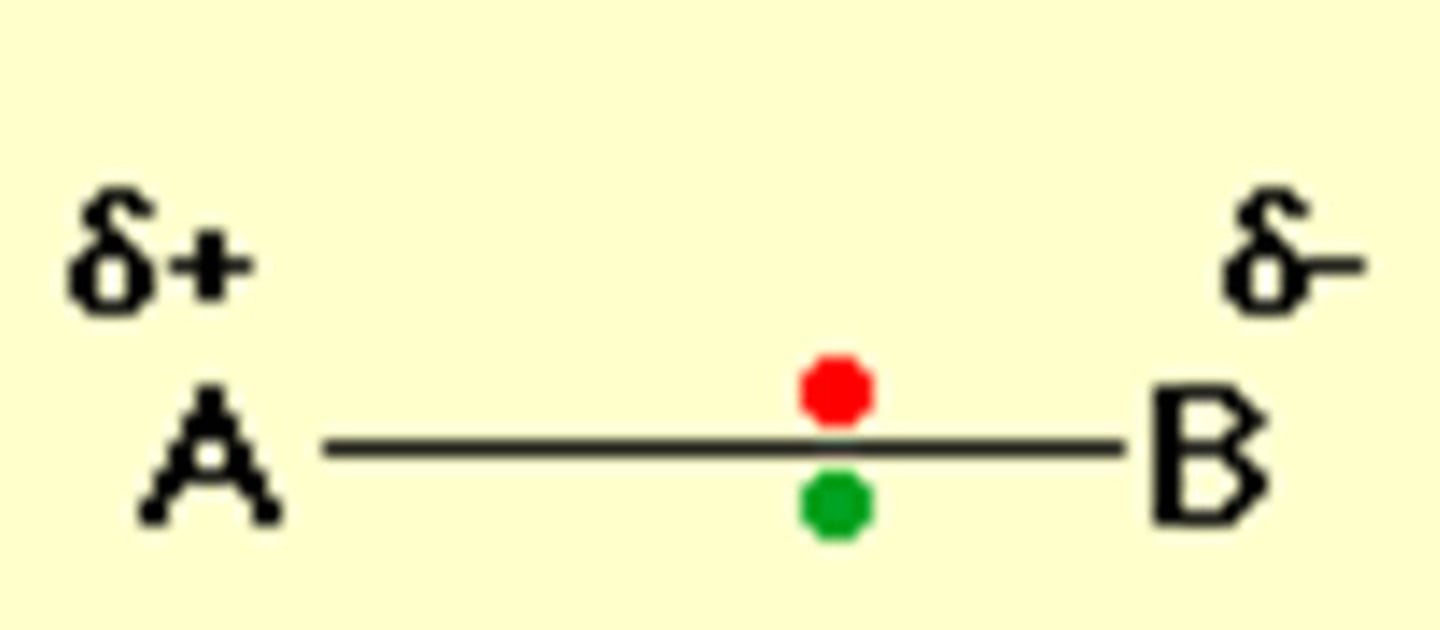
How does electronegativity affect polarity?
The larger the difference in electronegativity between the two atoms, the more polar the bond
What are group 1 elements called?
Alkaline metals
Why are group 1 metals so reactive?
They only have one electron in their outer shell, so it is easily lost, making it very reactive
What is the octet rule?
Atoms gain, lose or share electrons to acquire the structure of a noble gas
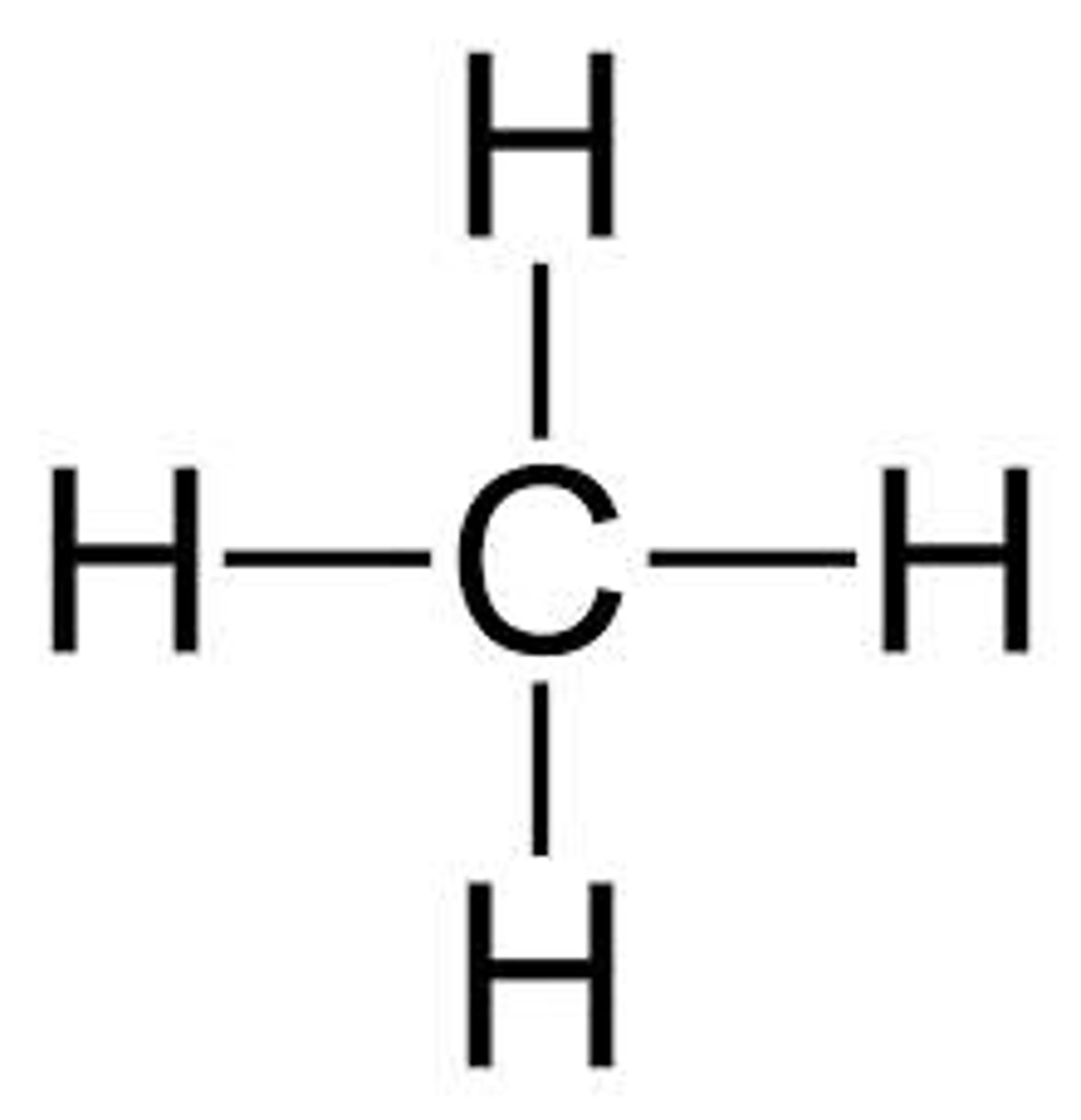
Methane
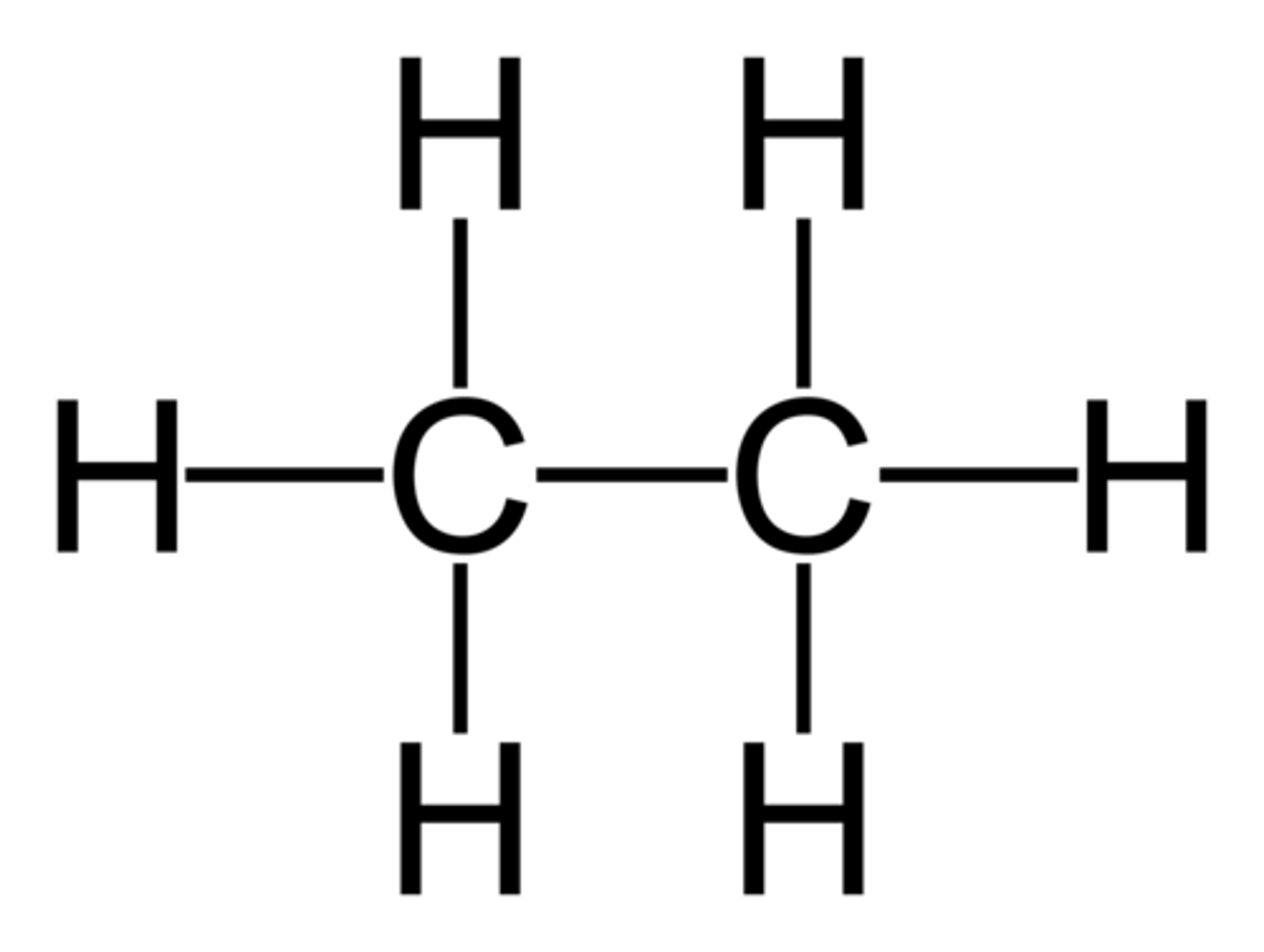
Ethane
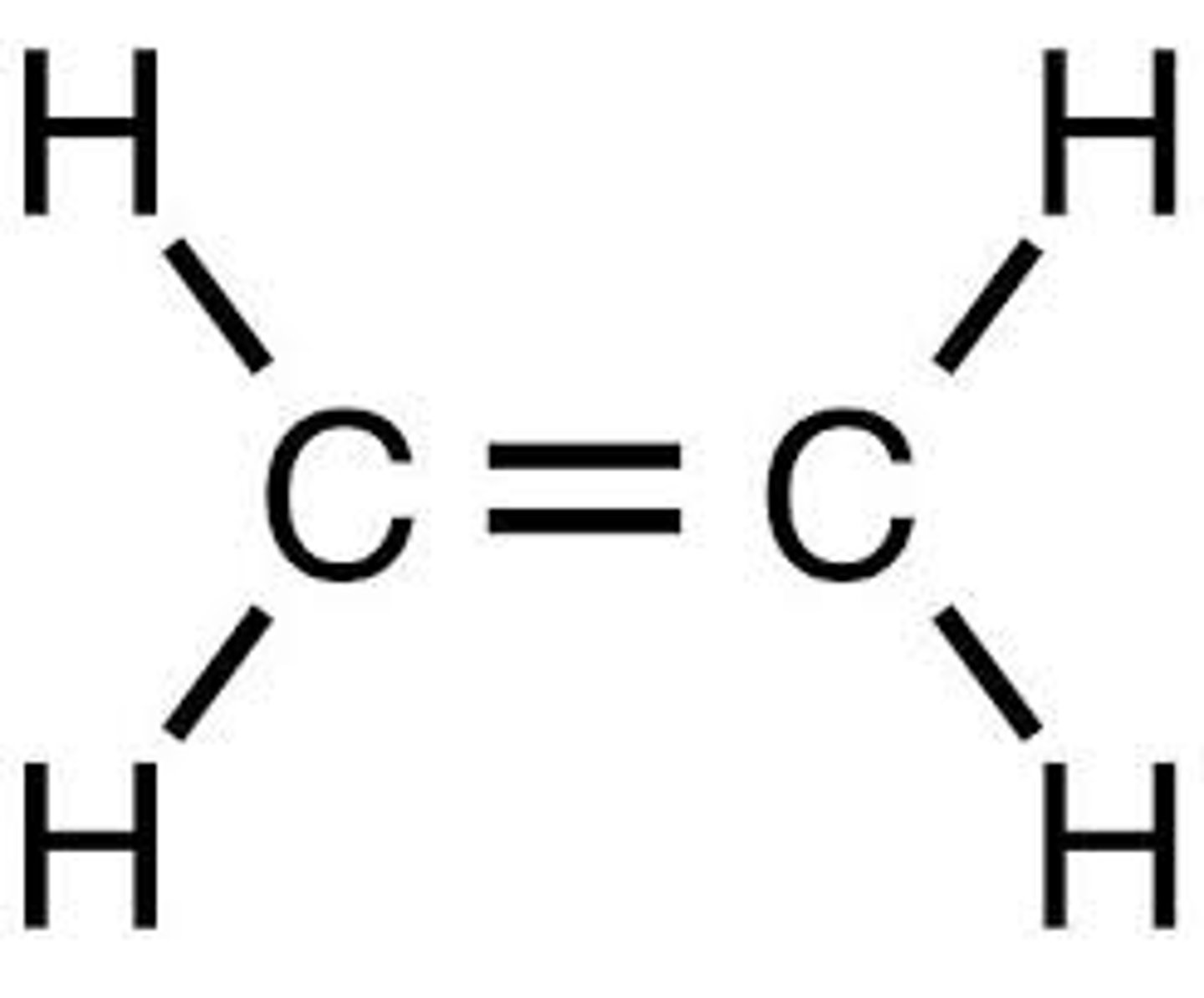
Ethene
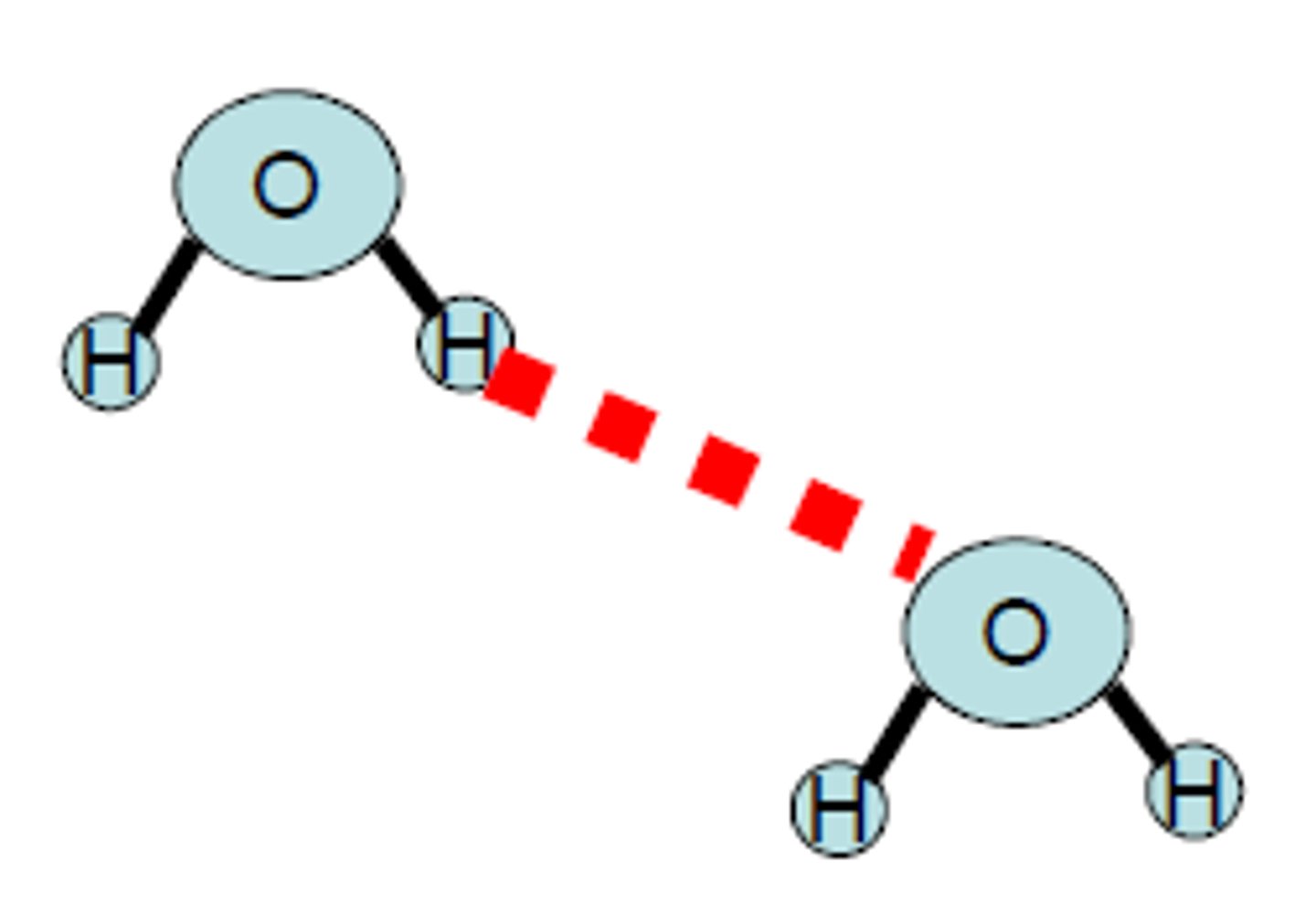
What are intermolecular forces?
Forces of attraction between molecules
What are intramolecular forces?
Forces that hold atoms together in a molecule
Why is fullerene not a giant covalent structure?
A molecule has a known number of atoms and because we know C60 has 60 atoms it is a molecule