PT15 - Midterms
1/194
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
195 Terms
ATPase
The enzyme found on the head of the thick myofilament that splits ATP into ADP and phosphate.
Power Stroke
When thin myofilaments are dragged and pulled toward the middle of the sarcomere, this dragging movement is known as the ___.
H zone
central, bare region occupied by the thick myofilaments
I band
light-colored bands, occupied by thin myofilaments
Z disc
zigzag, coin-shaped sheet of proteins (connectins) in a sarcomere which serves as attachment site of thin actin filaments
M line
represents as an attachment site for the thick myofilaments
A band
darkest band in a sarcomere, occupied by the entire length of the thick myofilament
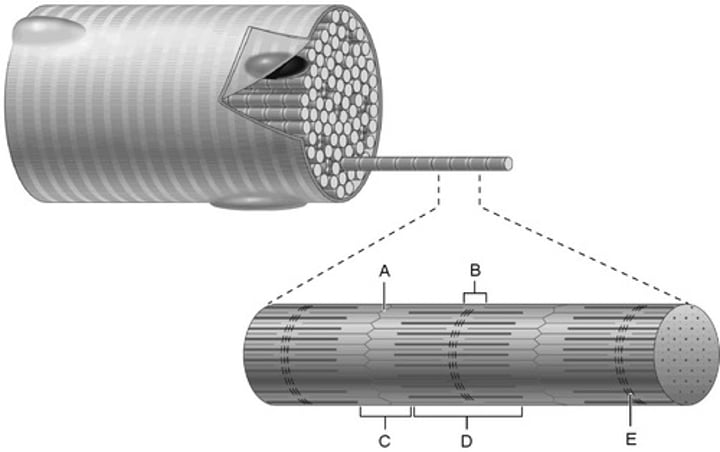
A band
D
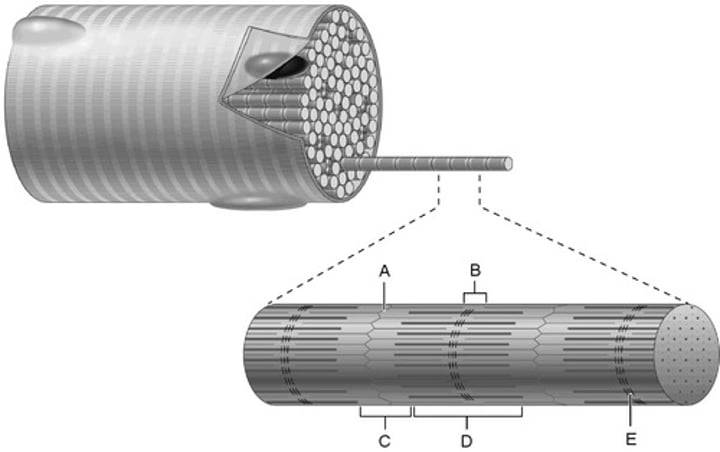
M line
E
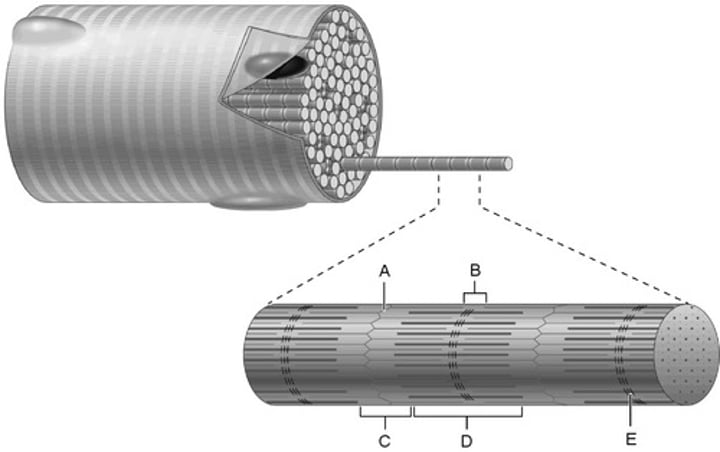
Z disc
A
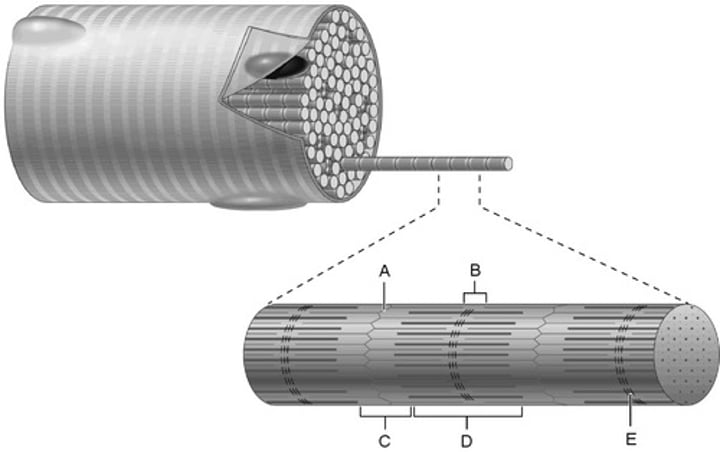
I band
C
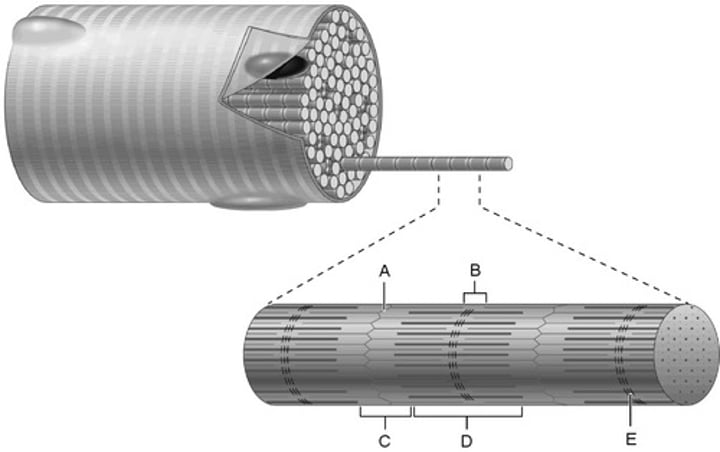
H zone
B
Calcium
The ion responsible for removing the inhibitory effect of the regulatory proteins away from the active binding site on the thin filaments making it available and bind with the thick filaments.
D. In response to a stimulus, no tension will develop at all if sarcomeres are less than 60 percent or more than 175 percent of their optimal length.
True of the length tension relationship of skeletal muscles:
A. Skeletal muscle contracts twice its normal length to half its normal resting length
B. Skeletal muscle contracts strongest when muscle fibers are 80 to 120 percent of their resting length
C. Skeletal muscle contract forcefully when they are overly stretched
D. In response to a stimulus, no tension will develop at all if sarcomeres are less than 60 percent or more than 175 percent of their optimal length.
E. Irregular, overlapping arrangement of skeletal muscle myofilaments generate stronger force of contraction despite being stretched
B. A single twitch is strong enough to do useful work
Which of the following statement is not correct:
A. Twitch varies with temperature of the muscles
B. A single twitch is strong enough to do useful work
C. Twitch strength depends on how stretched the muscle was before it was stimulated
D. Twitch becomes weaker as muscle fatigues
E. Twitch strength varies with the state of hydration of muscles
D. Accumulation of intracellular calcium ion concentration in the sarcoplasm due to the deteriorating sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum
The following are causes of muscle fatigue, except:
A. Inadequate blood flow
B. Depleted muscle glycogen
C. Lactic acid accumulation in the muscles
D. Accumulation of intracellular calcium ion concentration in the sarcoplasm due to the deteriorating sarcolemma and sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Diminished neuromuscular transmission of nerve impulses
T tubules
Intracellular structures in the sarcoplasm of skeletal muscle cells not found in smooth muscle cells
D. The number of mitochondria
Which of the following does not affect the force of skeletal muscle contraction?
A. The degree of muscle stretch
B. The number of muscle fibers contracting
C. The relative size of the muscle
D. The number of mitochondria
E. The presence of the series elastic elements
A. Provides most number of ATP used for muscle contraction
Roles of ionic calcium in muscle contraction, except:
A. Provides most number of ATP used for muscle contraction
B. Trigger ATPase activity and sliding of myofilaments
C. Promotes neurotransmitter release
D. Promotes breakdwon of gylcogen and ATP synthesis
E. Triggers release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum
A. States that the thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that the actin and myosin filaments overlap to a greater degree in an energy requiring process resulting to muscle contraction wherein the thin and thick filaments do not change in length or shorten but slide past each other.
Sliding filament theory of muscle contraction:
A. States that the thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that the actin and myosin filaments overlap to a greater degree in an energy requiring process resulting to muscle contraction wherein the thin and thick filaments do not change in length or shorten but slide past each other.
B. States that the greater amount of work performed by the muscle, the greater is the amount of ATP that is cleaved to form ADP during the contraction process
C. Postulates that when a head of myosin attaches to an actin active site, it causes changes in intramolecular forces between the head and arm of the cross bridge creating a new alignment of forces causing the head to tilt a power stroke toward the arm, dragging the actin filament along with it
D. The state wherein the strength of muscle contraction reaches a plateau when a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest
E. The mechanism where there is prolonged attachment of myosin cross bridges with the actin filaments and once the muscle has developed full contraction, the full force of contraction is maintained with less amount of energy consumed, sustaining muscle tension and muscle contraction without developing muscle fatigue
Slow muscle fibers
Functional types of skeletal muscle fiber based on the speed of contraction as determined by the speed in which ATPases split ATP
Titin
Huge, giant, elastic, springy protein filament molecules extending from Z disc to the next M line in a sarcomere
Acetylcholine
The neurotransmitter contained within synaptic vesicles at each axonal nerve endings along the neuromuscular junction of skeletal muscles
B. Globular heads has high affinity with calcium ions
The following correctly describes the myosin filaments in skeletal muscle, except:
A. Globular heads contain ATPases
B. Globular heads has high affinity with calcium ions
C. Extends the entire length of the A band
D. Globular heads can create a power stroke
E. Globular head can form cross-bridges
D. Represents as an attachment site for the thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
The M line in a sarcomere is described by which of the following statements
A. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
B. Light colored bands consisting of the thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
C. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filaments only
D. Represents as an attachment site for the thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
E. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
Troponin C
high affinity with calcium ions
Synaptic Cleft
space between the axon terminals and the muscle fiber membrane filled with glycoprotein rich gel like extracellular substance of interstitial fluid
Synaptic Gutter
invaginated membrane of the muscle fiber
Nebulin
inelastic giant protein
Myofibril
bundle of ribbon like contractile protein elements filling most of the sarcoplasm, each is surrounded by a sarcoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
Muscle Fiber
a single muscle cell enclosed in a sarcolemma
Motor End Plate
complex formed by branching ends of large myelinated nerve axon terminals of the somatic motor neurons surrounded by Schwann cells
Fascicle
a bundle of muscle fibers enclosed in a perimysium within a muscle
Myofilaments
fibrous contractile proteins responsible for the banding pattern and carry out the contractile process
Junctional Folds
numerous in folding of the sarcolemma at the bottom of the gutter that increases the surface area at which the neurotransmitter can act
Synaptic Vesicles
numerous, small membranous sacs within the axon terminals that stores neurotransmitter
E. Helps align the thin myofilaments of the sarcomere
Which of the following is not considered a function of the titin molecules in a sarcomere?
A. Act as a framework that holds and lines up the thick and thin myofilaments to make contractile machinery of the sarcomere work
B. Act as template for initial formation of portions of the contractile filaments of the sarcomere, especially the thick myofilaments
C. Prevents overstretching, recoiling when a muscle is stretched and returning back the stretched muscle into its original resting length
D. Stabilizes the thick myofilaments, positioning them in the center between the thin myofilaments
E. Helps align the thin myofilaments of the sarcomere
A. Light colored bands consisting of thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
The I band in a sarcomere is best described by which of the following statements:
A. Light colored bands consisting of thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
B. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
C. Represents as an attachment site for the thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
D. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
E. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filaments only
Actin

Myosin
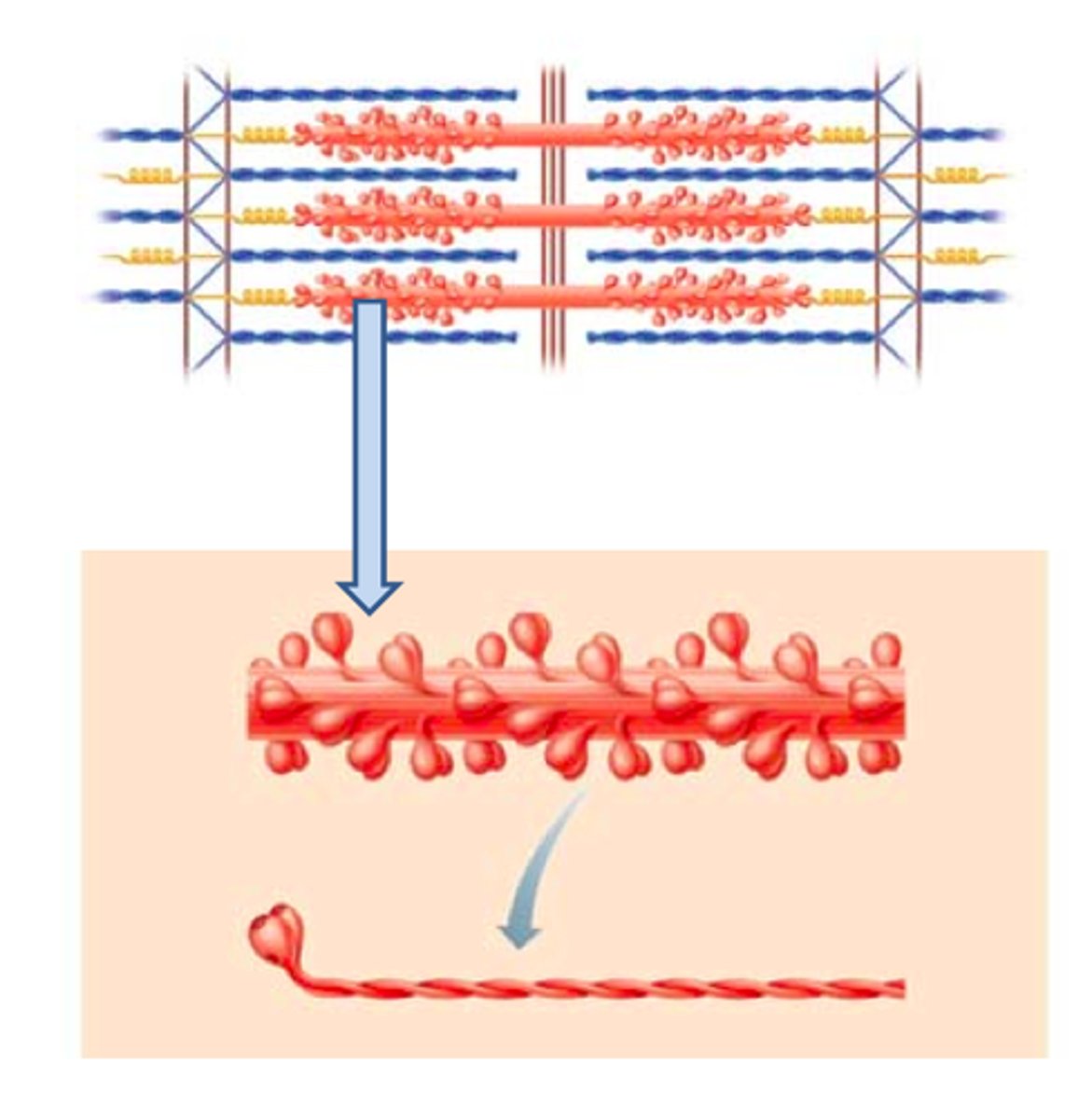
Sarcomere
the smallest contractile unit in a skeletal muscle
Isotonic Contraction
When a muscle contracts, the length changes leading to a decrease in the angle of the joint, and moving the load is called ___.
C. Doing 3 sets of 20 reps of biceps curl in each arm with a 25 kilogram dumbbells, with gradual increase in weights every 3 weeks interval for the duration of 12 months.
Performing which of the following activities or exercises will increase muscle strength and thereby increase the muscle mass:
A. Finishing a 50 kilometer race in 10 hours last weekend.
B. Swimming for two hours every other day at Bacong beach since childhood until at present.
C. Doing 3 sets of 20 reps of biceps curl in each arm with a 25 kilogram dumbbells, with gradual increase in weights every 3 weeks interval for the duration of 12 months.
D. Endless chatting with friends through messenger or other social media platform for hours since the start of the Covid19 pandemic.
E. Spending an hour of daily brisk walking at the Rizal boulevard to catch the sunrise since last month.
D. Hydrolysis
Functional characteristics of all muscles include which of the following, except:
A. Contractility
B. Elasticity
C. Extensibility
D. Hydrolysis
E. Irritability
Fused (Complete) Tetanus
the response of muscles to frequency of stimulation wherein the stimuli are given quickly enough, rapidly stimulating the muscles with no evidence of relaxation seen, resulting to a completely smooth and sustained muscle contractions
A. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
The H zone in a sarcomere is described by which of the following statements:
A. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
B. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filaments only
C. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
D. Represents as an attachment site for the thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
E. Light colored bands consisting of the thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
Calcium
An increase of this intracellular ion concentration within the sarcoplasm triggers the sliding of the myofilaments against each other
Myofibrils
Densely packed, long, rod like, ribbon like contractile elements in skeletal muscles running parallel the entire length of the muscle cell
Motor Unit
Refers to a motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it supplies
C. Contraction is prolonged due to the slow cycling of the myosin cross bridges
In the velocity and duration of skeletal muscle contraction, which of the following statement is incorrect?
A. Predominace of slow oxidative muscle fibers increases the duration of skeletal muscle contraction
B. The greater the load, the slower is the duration of contraction
C. Contraction is prolonged due to the slow cycling of the myosin cross bridges
D. Fast glycolytic fibers increases contractile activity of skeletal muscles
E. Smaller load increases both contractile velocity and duration of contraction
B. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filament only
The A band in a sarcomere is best described by which of the following statements:
A. Represents as an attachment site for the thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
B. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filament only
C. Light colored bands consisting of thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
D. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
E. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
Muscle Fatigue
This is the state of physiological inability of a muscle to contract
B. Results in muscle hypertrophy from sustained muscle activity
True if endurance exercises, except:
A. Improves fatigue resistance of the muscles by enhancing the delivery and use of oxygen
B. Results in muscle hypertrophy from sustained muscle activity
C. Increase capillaries around the muscle fiber, increasing the blood supply to the skeletal muscles
D. Efficient muscle metabolism because of increase in the number of red blood cell count
E. Increase myoglobin synthesis, increasing the capacity to store oxygen
C. Postulates that when a head of the myosin attaches to an actin active site, it causes changes in intramolecular forces between the head and arm of the cross bridge creating a new alignment of forces causing the head to tilt a power stroke toward the arm, dragging the actin filament along with it
Ratchet Theory:
A. States that there is an increase muscle contraction in response to multiple stimuli of the same strength
B. The mechanism where there is prolonged attachment of myosin cross bridges with the actin filaments and once the muscle has developed full contraction, the full force of contraction is maintained with less amount of energy consumed, sustaining muscle tension and muscle contraction without developing muscle fatigue
C. Postulates that when a head of the myosin attaches to an actin active site, it causes changes in intramolecular forces between the head and arm of the cross bridge creating a new alignment of forces causing the head to tilt a power stroke toward the arm, dragging the actin filament along with it
D. States that thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that the actin and myosin filaments overlap to a greater degree in an energy requiring process resulting to muscle contraction wherein the thin and thick filaments do not change in length or shorten but slide past each other
E. States that the greater amount of work performed by the muscle, the greater is the amount of ATP that is cleaved to form ADP during the contraction process
Isometric Contraction
This occurs if the load is greater than the tension the muscle is able to develop. Tension increases to the muscle capacity but the muscle neither shortens nor lengthens.
E. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
The Z disc is best described by which of the following statements:
A. Light colored bands consisting of thin myofilaments, with the Z disc running through the middle, so each half belongs to two different sarcomere
B. Central region of A band, known as the bare region occupied by thick filaments only
C. Represents as an attachment site for thick filaments, dividing darkest bands in half
D. Darkest bands, made up of the entire length of the thick filaments, and the thick and thin filaments overlap in the outer edges, while the center is occupied by thick filaments only
E. Coin shaped, zigzag sheet of protein connectins, that serve as an attachment site of the thin filaments, anchoring the thin filament, and connecting myofibrils to one another
Neuromuscular Junctions
A junction with a wide synaptic cleft formed between axonal innervations of nerve fiber endings of the somatic nervous system and a skeletal muscle fiber
A. Period of contraction
The following are the phases of a muscle action potential, except:
A. Period of contraction
B. Resting membrane potential
C. Repolarization
D. Depolarization
D. Latent period
Which of the following is a phase of a muscle twitch?
A. Resting membrane potential
B. Plateau
C. Repolarization
D. Latent period
E. Depolarization
D. States that the greater amount of work performed by the muscle, the greater is the amount of ATP that is cleaved to form ADP during the contraction process
FENN Effect:
A. States that there is an increase muscle contraction in response to multiple stimuli of the same strength
B. Results from prolonged period of attachment of myosin cross-bridges with actin myofilaments maintaining a prolonged tonic contraction and muscle tension with less ATP expenditure.
C. Response of a muscle to a single, brief stimulus
D. States that the greater amount of work performed by the muscle, the greater is the amount of ATP that is cleaved to form ADP during the contraction process
E. Results from different motor units scattered throughout the muscle, receiving low rate of nerve impulses from the spinal cord.
Cross Bridges
Considered as the business end in the myosin filament of skeletal muscle cells
E. The state wherein the strength of muscle contraction reaches a plateau when a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest
TREPPE Effect:
A. States that thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that the actin and myosin filaments overlap to a greater degree in an energy requiring process resulting to muscle contraction wherein the thin and thick filaments do not change in length or shorten but slide past each other.
B. States that the greater amount of work performed by the muscle, the greater is the amount of ATP that is cleaved to form ADP during the contraction process
C. The mechanism where there is prolonged attachment of myosin cross bridges with the actin filaments and once the muscle has developed full contraction, the full force of contraction is maintained with less amount of energy consumed, sustaining muscle tension and muscle contraction without developing muscle fatigue
D. Postulates that when a head of the myosin attaches to an actin active site, it causes changes in intramolecular forces between the head and arm of the cross bridge creating a new alignment of forces causing the head to tilt a power stroke toward the arm, dragging the actin filament along with it
E. The state wherein the strength of muscle contraction reaches a plateau when a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest
Myoglobin
Specifically, the iron containing red pigment protein that stores oxygen within the muscle cells
D. Glycogen breakdown or directly delivered from blood glucose via aerobic cellular respiration in the mitochondria
In muscle metabolism, the source of energy for muscle contraction is from ATP regenerated from the phosphorylation of ADP and Pi. This of the following three pathways generates most of the ATP to power muscle contraction:
A. ATP regenerated through the phosphagen system
B. Aerobic respiration using oxygen from myoglobin
C. Interaction of ADP with creatine phosphate through direct phosphorylation
D. Glycogen breakdown or directly delivered from blood glucose via aerobic cellular respiration in the mitochondria
E. Glycolysis from stored glycogen or directly delivered from blood glucose via anaerobic pathway producing pyruvic acid and lactic acid
True
Myosin filaments in smooth muscle cells are bundled between the actin filaments and the entire surface of the myosin is covered by myosin heads with no bare areas. (True/False)
B. Failure of calmodulin to immediately activate the myosin light chain kinase in the sarcoplasm
The slow onset of smooth muscle contraction and relaxation can be explained by all of the following statements, except:
A. Sluggish ATPases activity
B. Failure of calmodulin to immediately activate the myosin light chain kinase in the sarcoplasm
C. Slow cycling of the myosin cross bridges
D. Slow calcium pumps in removing the calcium ions out from the sarcoplasm into the ECF
E. Slow response to initiation of contraction of calcium ions
Varicosities
Bulbous swellings at axonal nerve endings that branch profusely on top of the sheet of smooth muscle fibers
D. Extensive cytoskeletal network of longitudinal bundles of non contractile filaments that resist tension
True of dense bodies, except:
A. Often arranged directly across from those of one smooth musce cell to another with linkages between the cells, transmitting contractile force from cell to cell.
B. Intracellular cytoskeleton that harness the pull of myosin on the actin, shortening the muscle
C. Protein plaques attached to the sarcolemma
D. Extensive cytoskeletal network of longitudinal bundles of non contractile filaments that resist tension
E. Act as anchoring points for the thin filaments
B. Ratio of thick and thin filaments in smooth muscles is much greater and higher than skeletal muscles
Which of the following statements on the physical basis for smooth muscle contraction is not correct?
A. Actin and myosin filaments are not arranged in striations
B. Ratio of thick and thin filaments in smooth muscles is much greater and higher than skeletal muscles
C. Longer actin and myosin filaments
D. Contractile fibers are not arranged in sarcomeres
E. Myofilaments are arranged in long bundles extending diagonally around the periphery of the cell, forming a lattice around the central nucleus
Plasticity
A hollow organ can be greatly stretched, yet not become flabby after prolonged stretching can be explained by ___.
True
Fraction of time that the cross bridge remain attached to the actin filaments is the major factor that determine the force in smooth muscle contraction. (True/False)
False
Onset of smooth muscle contraction is 30X shorter than skeletal muscles. (True/False)
Myosin Light Chain
Regulatory protein on the myosin head of smooth muscle cells which controls the contraction and relaxation of smooth muscle fibers
E. Arrector pili
Single unit smooth muscles is not found in which of the following?
A. Arterioles
B. Urinary bladder
C. Uterus
D. Esophagus
E. Arrector pili
E. Increase pH can cause vasodilation
The following statements correctly explain the effects of changes in local tissue factors on the blood vessels, except:
A. Excess carbon dioxide can cause vasodilation
B. Increase potassium and low calcium ions can cause vasoconstriction
C. Lack of oxygen cause smooth muscle relaxation
D. Increase in hydrogen ions can cause vasodilation
E. Increase pH can cause vasodilation
True
Thin and thick filaments are arranged diagonally, causing the smooth muscle to contract in a corkscrew manner as it shortens. (True/False)
Extracellular Fluid Compartment
Calcium that activates the contraction process in smooth muscle cells mostly comes from the ___.
False
The diffuse junctions in multi unit smooth muscles is the same as the synaptic cleft of the neuromuscular junctions of skeletal muscle cells. (True/False)
True
Smooth muscle cells contract 80 percent X their lengths because of the side polar cross bridges on the myosin allows the pulling of the actin filaments simultaneously on both sides in opposite direction. (True/False)
B. The pacemaker cells in smooth muscle cells of some hollow, visceral organs act as drummers setting the contractile pace for the whole muscle sheet, that is, smooth muscle cells are self excitatory and can depolarize without a stimulus
Which of the following correctly describes the electrical basis for smooth muscle contraction, differentiating smooth muscle contraction from skeletal muscle contraction:
A. Electrical impulses can jump from one smooth muscle cells to adjacent muscle cells through the surrounding myelin sheaths in the neuromuscular junction.
B. The pacemaker cells in smooth muscle cells of some hollow, visceral organs act as drummers setting the contractile pace for the whole muscle sheet, that is, smooth muscle cells are self excitatory and can depolarize without a stimulus
C. T tubules allow for rapid transmisison of impulses from the sarcolemma down into the deeper substance of the smooth muscle cells
D. Contact junctions in smooth muscle cells allow transmission of action potentials from cell to cell
E. Adjacent smooth muscle cells are independent, does not exhibit slow, synchronized contractions and the whole muscle sheet contracts as one.
D. Contraction of the inner circular layer dilates and shortens the organ propelling substances through the lumen
Which of the following statements is not correct?
A. Contraction of the outer longitudinal layer dilates and shortens the organ propelling substances through the lumen.
B. The smooth muscle fibers of the inner circular layer runs around the circumference of the organ
C. Alternating contraction and relaxation of the two opposing layer mixes and squeezes substances through the lumen of the hollow organs.
D. Contraction of the inner circular layer dilates and shortens the organ propelling substances through the lumen
E. Contraction of the two layers of closely apposed fibers alternately constricts or dilates the organ
Calmodulin
Calcium binding protein in the sarcoplasm of smooth muscle cells
D. Contract rhythmically as a single unit, electrically coupled to one another via gap junctions
Characteristics of multi unit smooth muscle, except:
A. In the absence of electrical stimulation, responds to hormones.
B. Found in the internal eye muscles adjusting pupil size and allowing to visually focus on objects
C. Structurally independent muscle fibers richly supplied with nerve endings, each of which forms a motor unit with a number of muscle fibers
D. Contract rhythmically as a single unit, electrically coupled to one another via gap junctions
E. Responds to neural stimulation with graded contractions via the autonomiic nervous system
False
The troponin complex in the actin filament in smooth muscles inhibit the active binding sites for attachment of myosin filaments. (True/False)
True
The pacemaker cells are autorhythmic cells allowing smooth muscle cells to produce spontaneous depolarization that can initiate an electrical stimulus and activate the contractile mechanism in smooth muscles. (True/False)
Troponin
Which of the following is not found in the myofilaments of smooth muscle fibers:
A. Myosin light chain
B. Calmodulin
C. ATPase
D. Tropomyosin
E. Troponin
False
Force of smooth muscle contraction is lesser than the force of contraction of skeletal muscle due to fewer myosin filaments in smooth muscles. (True/False)
C. A state wherein the strength of muscle contraction reaches a plateau when a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest
Which of the following is not true of the stress relaxation response of smooth muscles:
A. The response of smooth muscles to stretch and stimulating them to contract
B. Also known as receptive relaxation response
C. A state wherein the strength of musce contraction reaches a plateau when a muscle begins to contract after a long period of rest
D. The phenomenon in which smooth muscles respond to stretch only briefly, then adapt to its new length and retain its ability to contract
E. The ability to return nearly its original force of contraction after it has been elongated or stretched
Calmodulin
Intracellular structures in the sarcoplasm of smooth muscle cells not found in skeletal muscle cells
True
Smooth muscles often exhibits tetanus. (True/False)
True
Peristalsis is a wave like, around contraction which is an alternating contraction and relaxation of the two opposing layers of the smooth muscles on the walls of hollow visceral organs. (True/False)
D. Intercostal muscles
Which of the following is not lined by smooth muscles?
A. Stomach
B. Esophagus
C. Aorta
D. Intercostal muscles
E. Gall bladder
C. Mechanism wherein there is prolonged attachment of myosin cross bridges with the actin filaments and once the muscle has developed full contraction, it maintains its full force of contraction with less amount of energy consumed to maintain contraction thus maintaining muscle tension in the muscle fiber without using much ATP and sustains contraction without developing muscle fatigue
LATCH mechanism of smooth muscle contraction:
A. The mechanism wherein the thin filaments slide past the thick ones so that the actin and myosin filaments overlap to a greater degree in an energy requiring process that leads to muscle contraction. The thick and thin filaments do not change in length or shortens but slide past each other
B. Are variations in the degree of muscle contraction and is required for proper control of muscle movement
C. Mechanism wherein there is prolonged attachment of myosin cross bridges with the actin filaments and once the muscle has developed full contraction, it maintains its full force of contraction with less amount of energy consumed to maintain contraction thus maintaining muscle tension in the muscle fiber without using much ATP and sustains contraction without developing muscle fatigue
D. States that there is an increase muscle contraction in response to multiple stimuli of the same strength
E. Postulates that when a head of myosin attaches to an actin active site, it causes changes in intramolecular forces between the head and arm of the cross bridge creating a new alignment of forces causing the head to tilt a power stroke toward the arm, dragging the actin filament along with it
A. Allow how organs to maintain the same amount of intraluminal pressure despite long term changes in the length of the muscle fibers
Importance of stress relaxation response:
A. Allow how organs to maintain the same amount of intraluminal pressure despite long term changes in the length of the muscle fibers
B. Allow hollow organs to tolerate tremendous changes in volume without losing its tone when completely empty
C. Keep the intestines partially constricted
D. Generates stronger force of smooth muscle contraction despite being stretched
E. Maintains prolonged tonic contraction and tension in smooth muscles with less use of ATP
False
Smooth muscles cannot contract very forcefully when they are overstretched. (True/False)
Diffuse Junctions
Junction with a wide synaptic cleft formed between axonal innervations of nerve fiber endings from the autonomic nervous system and the single unit smooth muscle fibers
Caveoli
Multiple, pouch like infoldings in the sarcolemma of smooth muscle cells
True
Loss or absence of contact inhibition between normal cells can lead to uncontrolled cell division in which malignant cells behave by proliferating rapidly. (True/False)
False
In the synthesis of DNA, a high incidence of DNA mutations occur due to replication errors since only 2% of the DNA in the nucleus are functional and 98% are non-coding DNA. (True/False)
False
Mitochondria is not capable of reproducing itself. (True/False)