BCM. 38 Bacterial Metabolic Diversity
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
chemoorganoheterotrophs
Chemo-:
The energy is derived from chemical reactions, specifically the oxidation of organic molecules.
Organo-:
The "electron donors" that provide the energy are organic compounds like sugars, fats, and proteins.
Hetero-:
The organism gets its carbon from external organic sources, rather than making it from carbon dioxide.
examples -
Metabolism in a chemoorganoheterotroph
the food and nutrients enter catabolism to form three products - Energy (ATP/change in P), reducing power (NAD(P)H), and precursor metabolites
these three products are then used in biosynthesis resulting in cell growth
Two ways that any living cell can generate utilisable energy
substrate level phosphorylation
e.g. some phosphorylated metabolic intermediate reacts with ADP which forms substrate + ATP
e.g. PEP + ADP → Pyruvate + ATP (via pyruvate kinase
Oxidative/electron transport phosphorylation
vectoral process which occurs in membranes (cytoplasmic membrane)
hydrogen donor is oxidised, electrons are passed through the chain and then the hydrogen acceptor is reduced (free energy is released in this process)
e.g. NADH is oxidised to NAD+ producing H+, H202 is reduced to H20 as the e- acceptor
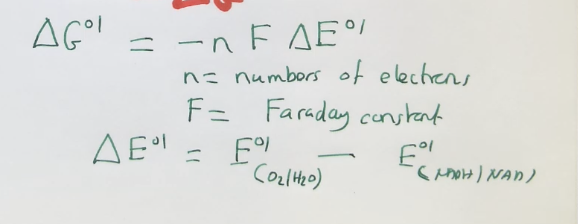
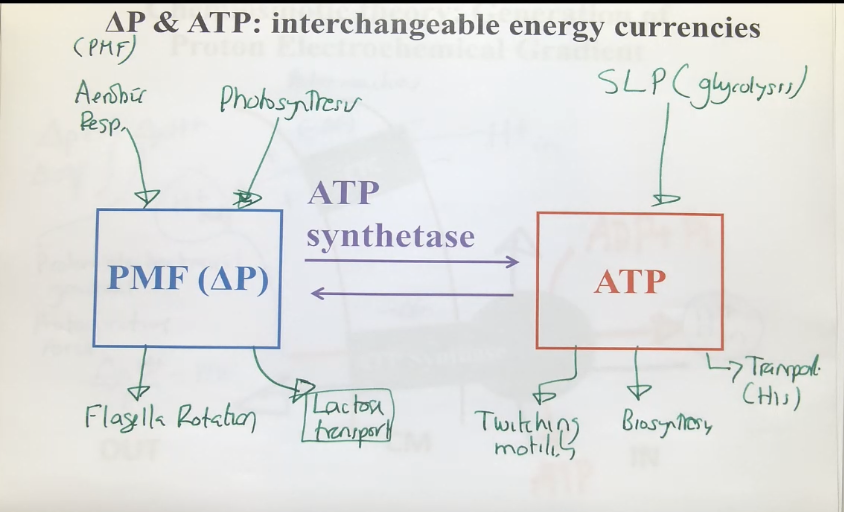
PMF (Change in P) and ATP - interchangeable energy currencies
Comparison between mitochondrion and E.coli electron transport chain
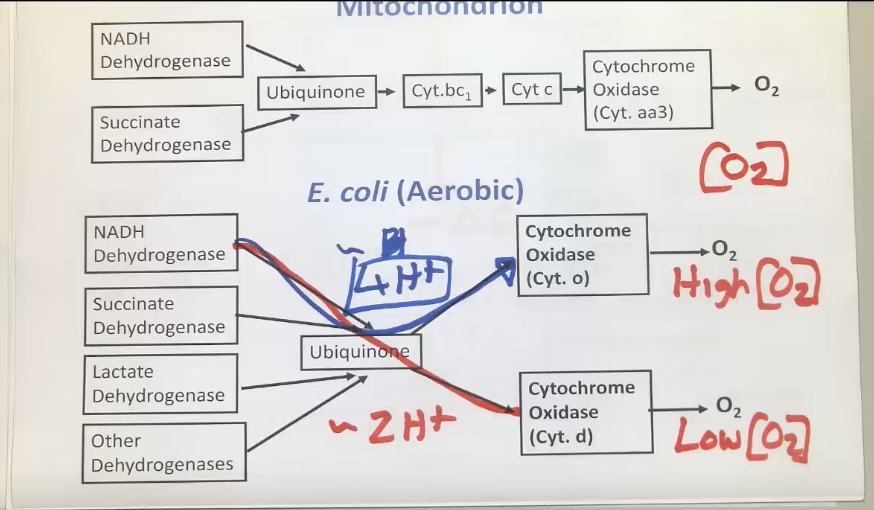
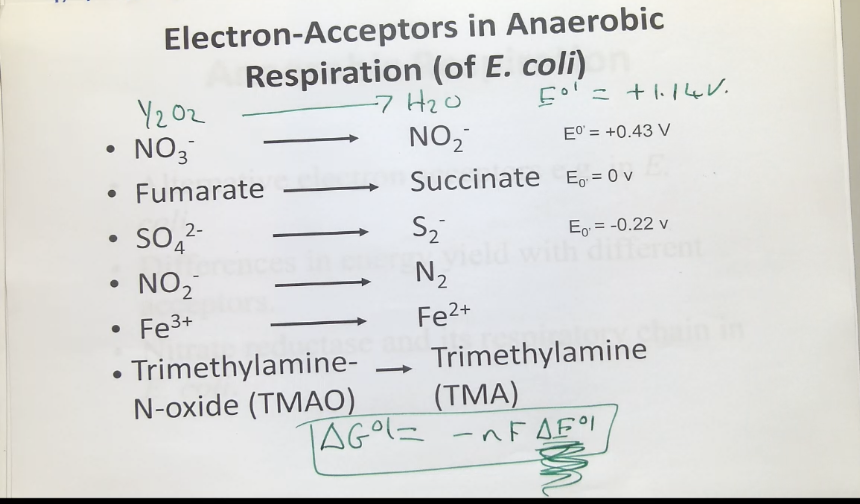
Anaerobic respiration in E.coli
alternative electron acceptors
differences in energy yield with different acceptors
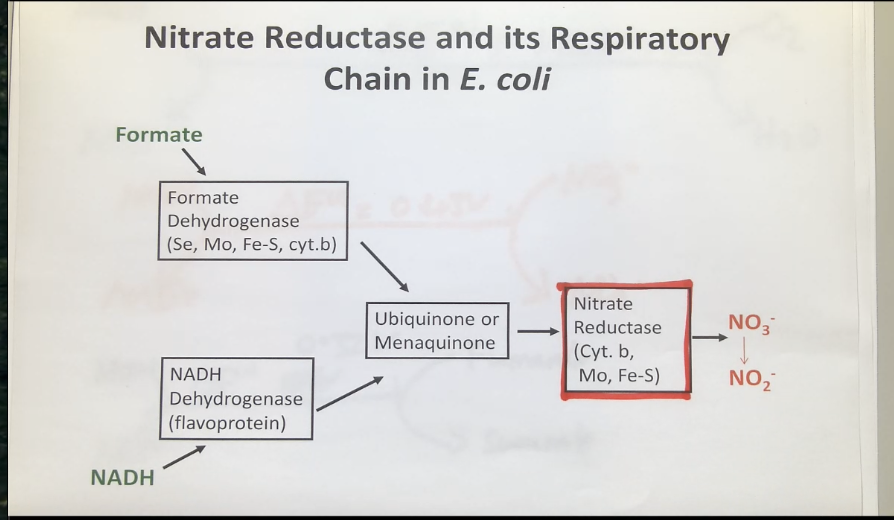
nitrate reductase and its respiratory chain in E.coli
using nitrate as the electron acceptor results in the delta E01 to become shorter (producing less energy) - this becomes even shorter when using fumarate as the electron acceptor
Nitrate reductase and its respiratory chain in E.coli