bi 114 - disease presentations for final
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
(polio, norovirus, botulism, HIV, influenza, bubonic plague, rubella, strep throat, TB)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
What causes polio (poliomyelitis)?
Poliovirus
Describe the poliovirus
non-enveloped
RNA virus
Enterovirus genus
How many kinds of poliovirus exist?
There are 3 types.
Type 1 is the most common and causes outbreaks in Afghanistan.
Type 2 was eradicated in 2015.
Type 3 was eradicated in 2019.
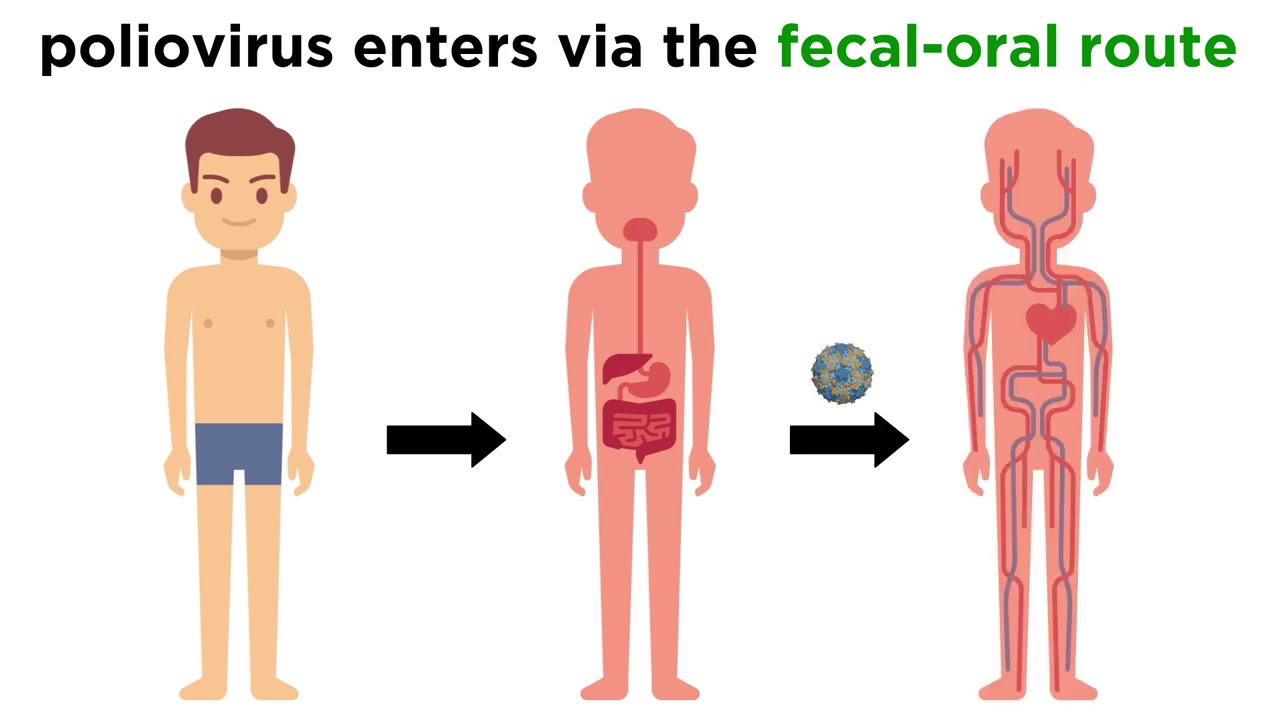
How is polio transmitted?
Polio is transmitted through the fecal oral route
p.f.o.r.u = polio fecal oral route = party 4 u
T/F: most poliovirus infections are asymptomatic
True, most poliovirus infections are asymptomatic
Symptoms of poliovirus
Poliovirus symptoms include
flu-like symptoms
]GI distress
muscle ache
stiffness
What is the target body system of polio?
nervous system.
infects and damages motor neurons in the spinal cord and brainstem.
causes paralysis.
Who identified poliovirus
Karl Landsteiner & Erwin Popper: Identified poliovirus by transmitting it to monkeys using spinal cord samples from an infected child (1908).
How is Poliovirus diagnosed?
laboratory testing of stool samples
throat swabs
cerebrospinal fluid
via PCR or cell culturing
How is poliovirus treated?
effective antiviral therapy exists for poliomyelitis so prevention via the inactivated polio vaccine (IPV) is critical.
What causes norovirus?
Calciviridae NOROVIRUS
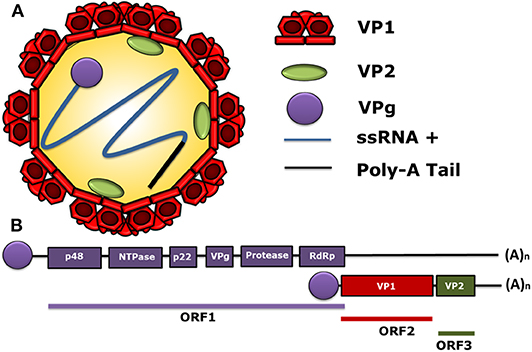
What kind of virus is norovirus?
Non-enveloped
(+) Positive-sense
Single-stranded RNA virus
genus Norovirus
belonging to the caliciviridae viral family.
What kind of cells does norovirus primarily affect?
Intestinal epithelial cells
What is norovirus?
virus that causes contagious gastrointestinal illness (STOMACH FLU).
triggers sudden outbreaks of vomiting and diarrhea.
How does norovirus spread?
Norovirus spreads through the fecal-oral route
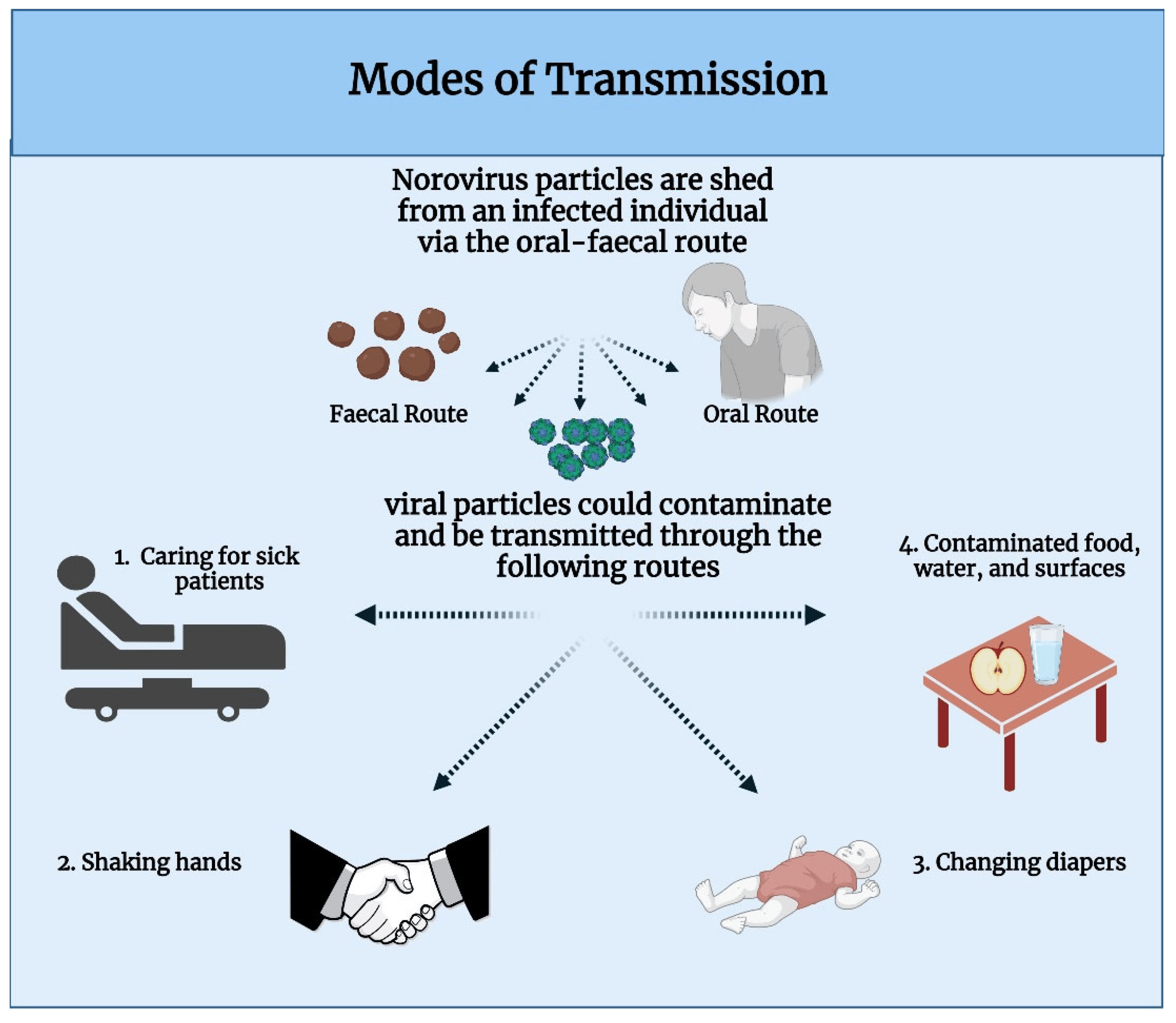
Is the norovirus vaccine licsenced/available?
Not yet, the oral tablet vaccine is still being researched!
What causes botulism?
The neurotoxins produced by Clostridium botulinum.
T/F: botulism is fatal if left untreated
True, botulism is fatal if left untreated
In what conditions does C. Botulinum produce toxins?
In anaerobic environments (sealed cans, wounds, intestine)
What kind of bacteria is c. botulinum?
gram-positive (+)
anaerobic
spore-forming rods
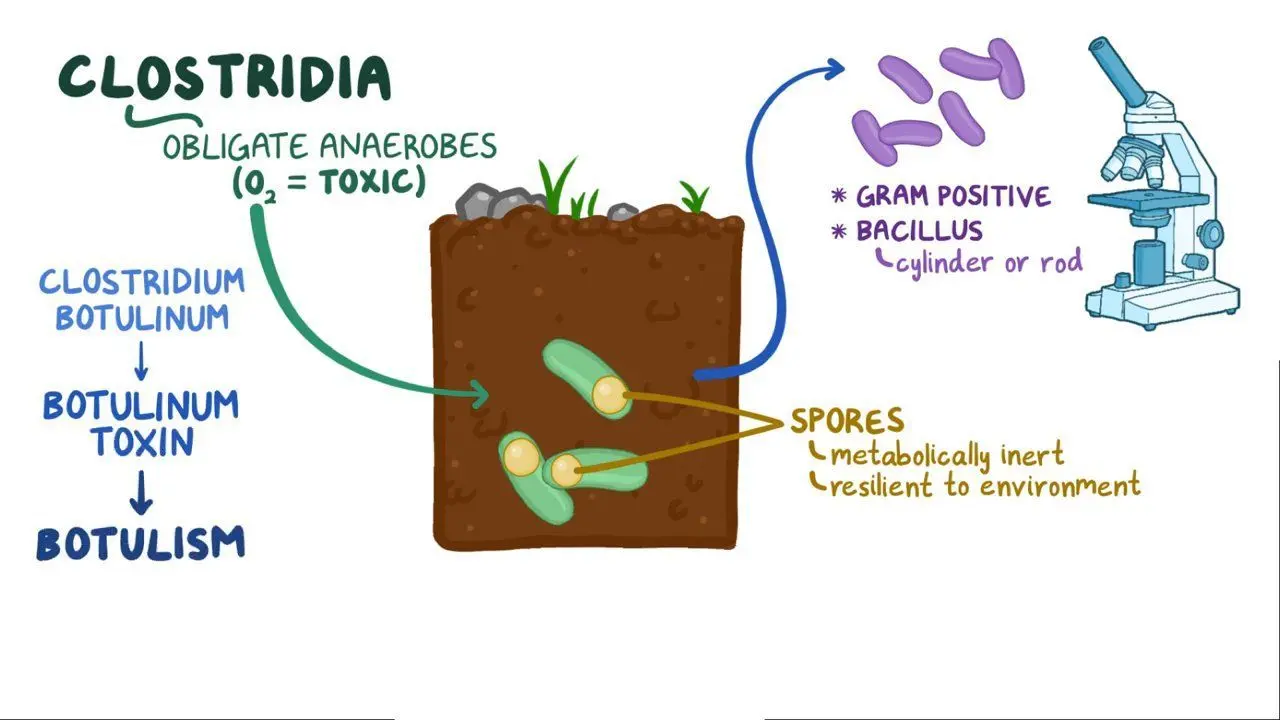
Main cases of botulism are from what?
Infants, food-borne, wound botulism
Symptoms of botulism include
blurred vision
Respiratory/muscle paralysis
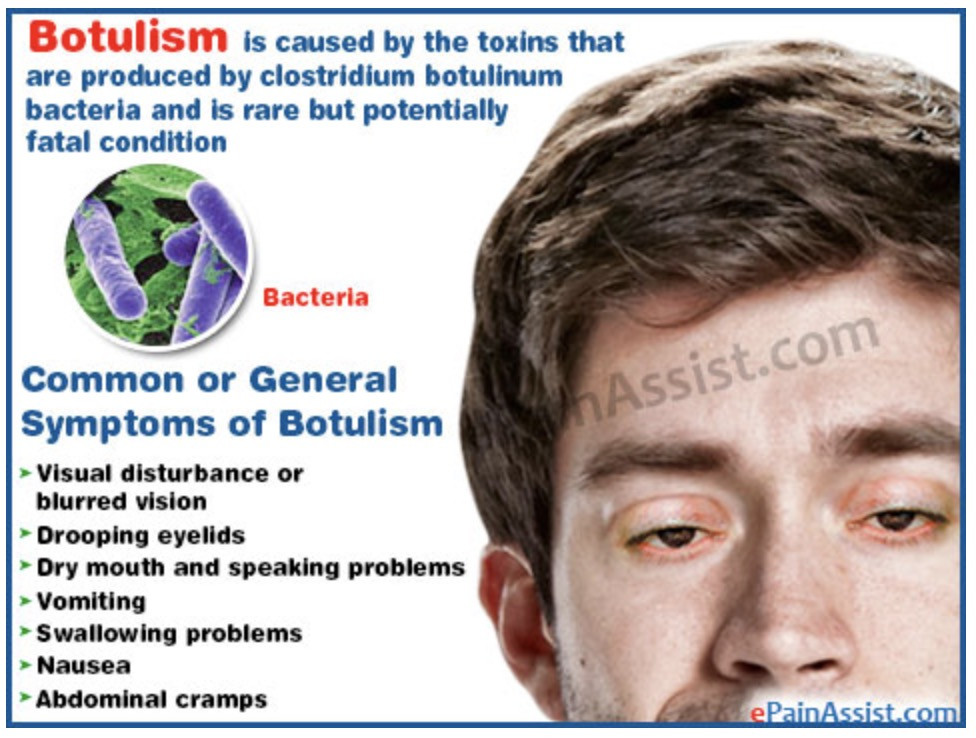
How is botulism treated?
supportive care and ANTITOXIN
What causes HIV?
A retrovirus causes HIV
what body part does HIV target?
CD4 T cells, which are white blood cells
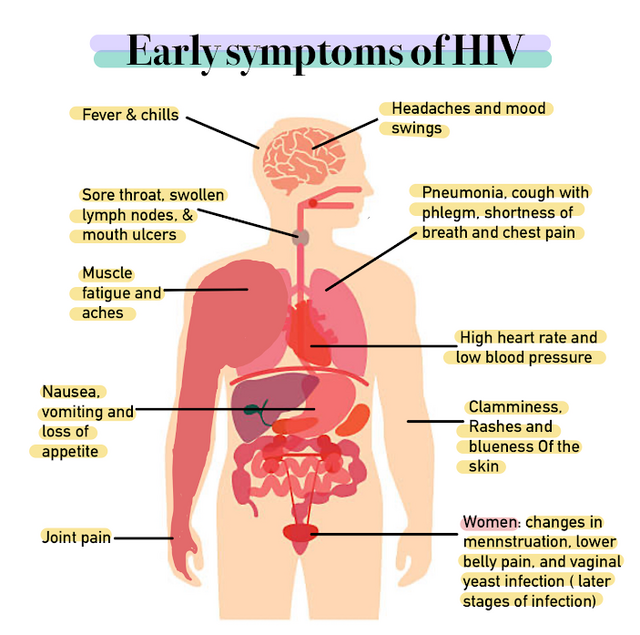
HIV symptoms
Fever and headaches
weight loss
diarrhea
swollen lymph nodes
AIDS occurs at the highest level
Who is most at risk for HIV?
Gay men, people who inject drugs, people with hemophilia, women/infants/children
Pathogenesis of HIV
virus enters the body (remains dormant at first)
injects into the T cells, and then spreads
eventually leads to AIDS when T cell levels are too low.
Influenza A Virus
Most severe and widespread form of Infleunza.
Which kinds of influenza have both animal and human hosts?
A & C
T/F: Influenza is responsible for most outbreaks and pandemics, including the 1918 Spanish flu.
True! Influenza is responsible for most outbreaks and pandemics, including the 1918 Spanish flu.
Infleunza B Virus
Less severe than Infleunza A.
Causes serious illness in weak immune systems.
Causes only epidemics, no pandemics.
Does Influenza B cause pandemics?
No, but it can lead to seasonal flu epidemics.
T/F: Influenza B only infects humans.
True, Influenza B only has human hosts!
Influenza C
Mildest strain of Influenza that only causes mild respiratory illnesses.
Does Influenza C cause epidemics/pandemics?
NO, Influenza C does not cause epidemics or pandemics.
It only causes mild respiratory illnesses.
Spanish Flu
Caused by H1N1 A Influenza virus.
Pandemic that spread around the world in 1918, killing more than 50 million people.
Influenza haemagglutinin (HA)
transmembrane protein that forms the spikes on the viral surface.
binds to N-acetylneuramic (sialic) acid on the surface of respiratory cells to gain entry.
viral entry (ha, i let her in!)
Influenza Neuraminidase (NA)
allows for viral release by removing sialic acid, enabling newly formed virions to infect other cells.
viral release (na, i kicked her out!)
What causes bubonic plague?
Yersinia pestis (gram negative bacteria)

Is bubonic plague zoonotic?
Yes, bubonic plague is a zoonotic disease.
How is the bubonic plague transmitted?
it is transmitted by flea bite (vector) or by contact with infected rodent (esp. rats) or flea feces
Black Death
the epidemic form of bubonic plague experienced during the Middle Ages when it killed nearly half the people of western Europe
What systems are affected by the bubonic plague?
The lymphatic system, as it causes painful swollen lymph nodes
bubos!
Virulence factors of bubonic plague
F1 capsule antigen (inhibits phagocytosis)
pla protease (promotes spread and invasion)
type 3 secretion system (bacterial invasion)
What causes rubella (German measles)?
Rubella virus
How long is the incubation period of rubella?
2-3 weeks
T/F: rubella only infects humans
True, rubella only infects humans
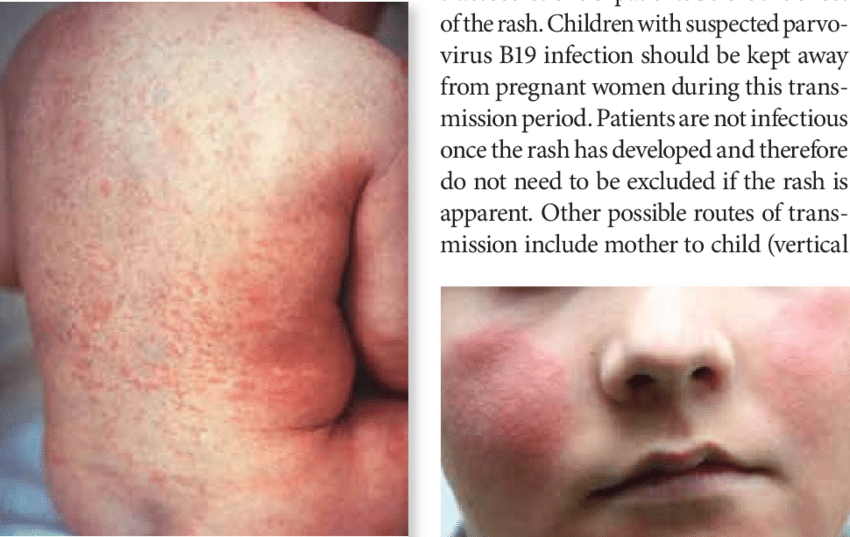
Rubella exanthem
macular rash 1-2 days after onset of prodromal fever -> lasts 1-3 days, head, neck and trunk
What causes strep throat?
Streptococcus pyogenes (Group A Strep bacteria)
How is strep throat transmitted?
Strep throat is transmitted through respiratory droplets
How is strep throat treated?
antibiotics like penicillin
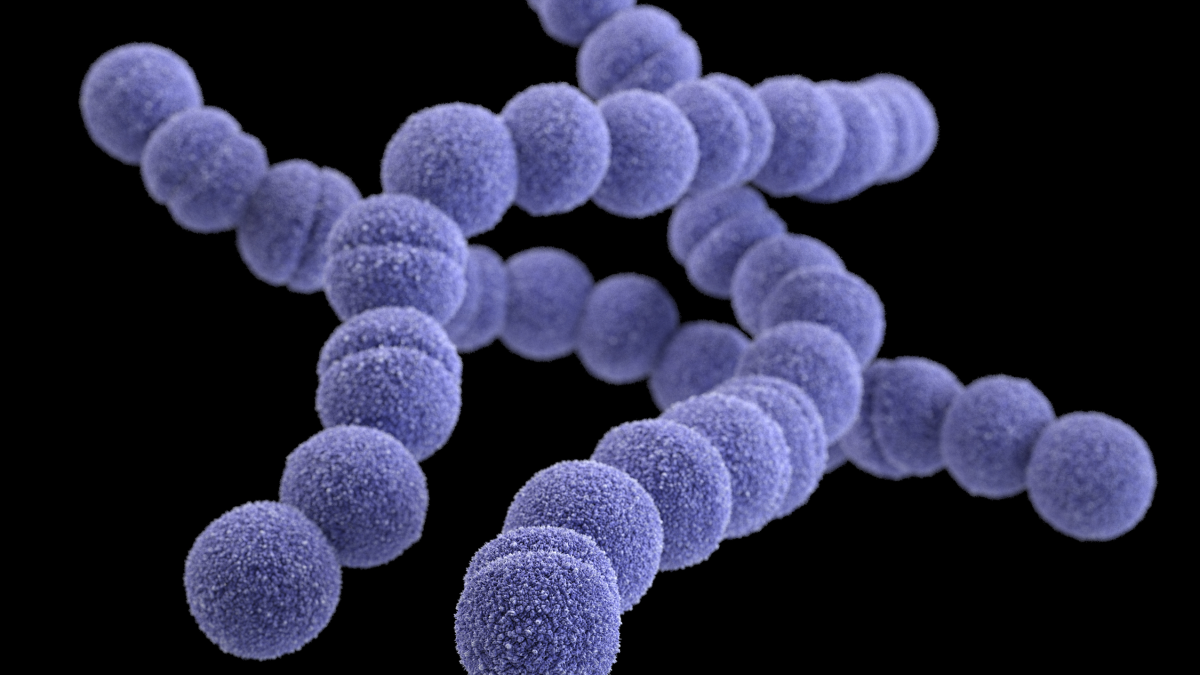
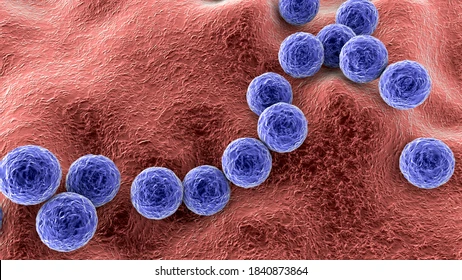
What does streptococcal bacteria look like?
It looks like a purple chain of cocci
Characteristics of s. pyogenes
Gram-positive
non-motile
cocci
facultative anaerobe
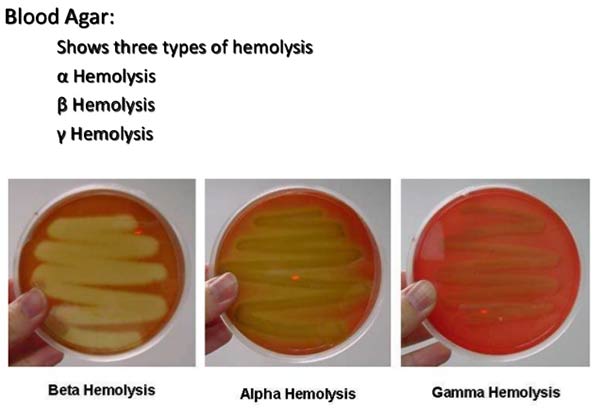
BETA HEMOLYTIC (remember s. pyogenes was your bacteria and b comes before a in ur name)
What does it mean if a bacteria is beta hemolytic
It forms a transparent hemolytic zone on blood agar plates because its antigens lyse red blood cells
How is strep throat diagnosed?
rapid strep test (rapid immunoassay technology that is highly specific for S. pyogenes, detects antigens)
uses a swab from the back of the throat, and results are typically available within 10-20 minutes
What causes tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (bacteria)
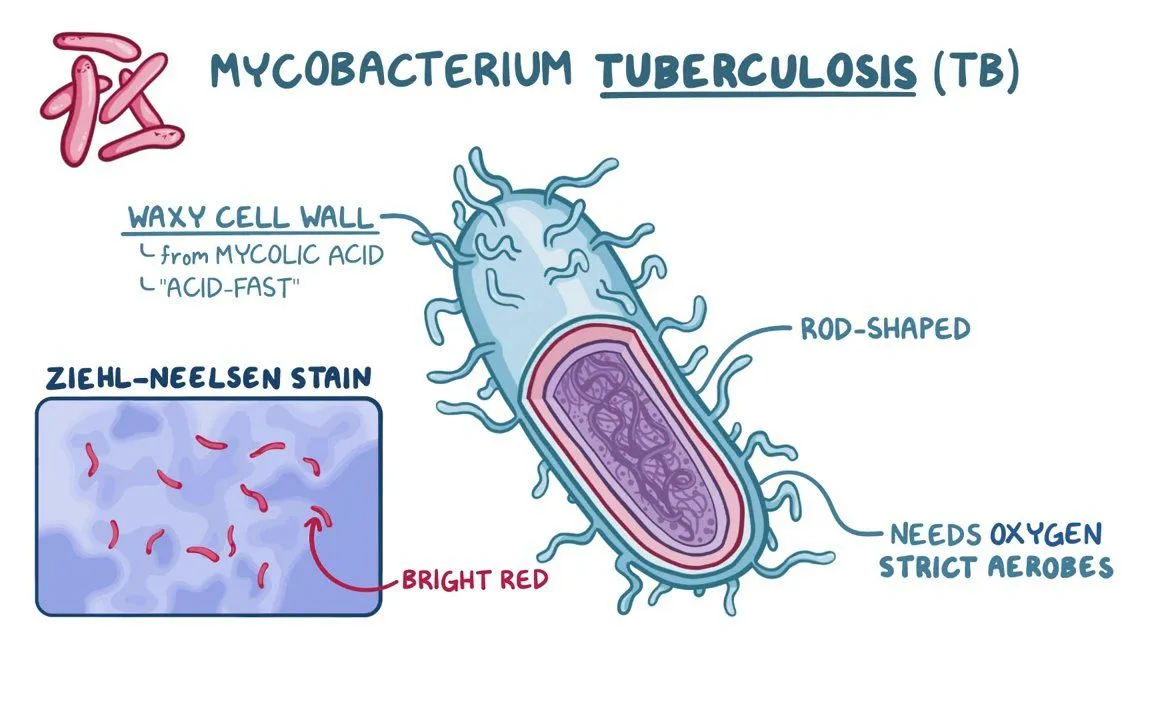
How is TB transmitted?
TB is transmitted through respiratory droplets.
TB virulence factors include what?
antigen 85 complex (triggers strong immune response)
immunity evasion
cord factor (protects from macrophages)
LAM
ESX-1 secretion system
heat shock proteins
Iron Acquisition Systems
How is tuberculosis treated?
long course of antibiotics (streptomycin and isoniazid)
Ghon complex
Nodules in lung tissue and lymph nodes that occur as a result of TB
Is there a TB vaccine?
Yes: BCG
but it is not effective and is not recommended as a part of routine vaccination schedules.
It's only readily available in TB-endemic countries.
T/F: Gardasil vaccine is used against the Herpres infection
False. Gardasil is used against HPV (warts)
T/F: Warts on the skin are formed as a result of HPV infection.
True, Warts on the skin are formed as a result of HPV infection.
T/F: chlamidya can cause both eye and reproductive system infections in humans
True, chlamidya can cause high eye and reproductive system infections.
What type of environment does legionella pneumophilia like?
moist environments, air conditioning systems, refrigerators
What is the shape of the bacteria that cause whooping cough?
Bordetella pertussis is rod shaped
Which of the following is NOT used against Influenza virus infections?
Amantadine
Tamiflu
Relenza
Penicillin
Pencillin. It’s an antibiotic, so it’s ineffective against influenza, which is a virus
T/F: lactobacillus acidophilus, a resident organism in female urogenital tract, is responsible for the majority of UTIs in females.
False, lactobacillus acidophilus is common in the female urogenital flora and it DOESNT CAUSE DISEASE.
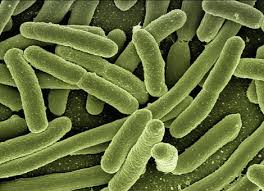
What are helminths?
Parasitic worms
can be seen with the naked eye
Infect GI tracks
What causes Legionnaires' disease?
Legionella pneumophila
gram (-) bacteria
How is Legionnaires' disease transmitted?
inhaling contaminated water droplets, often in the form of mist