Light-independent reaction
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
The light-independent reaction uses what from the light-dependent reaction?
NADPH to form a simple sugar
ATP is hydrolysed to provide the additional energy for this reaction
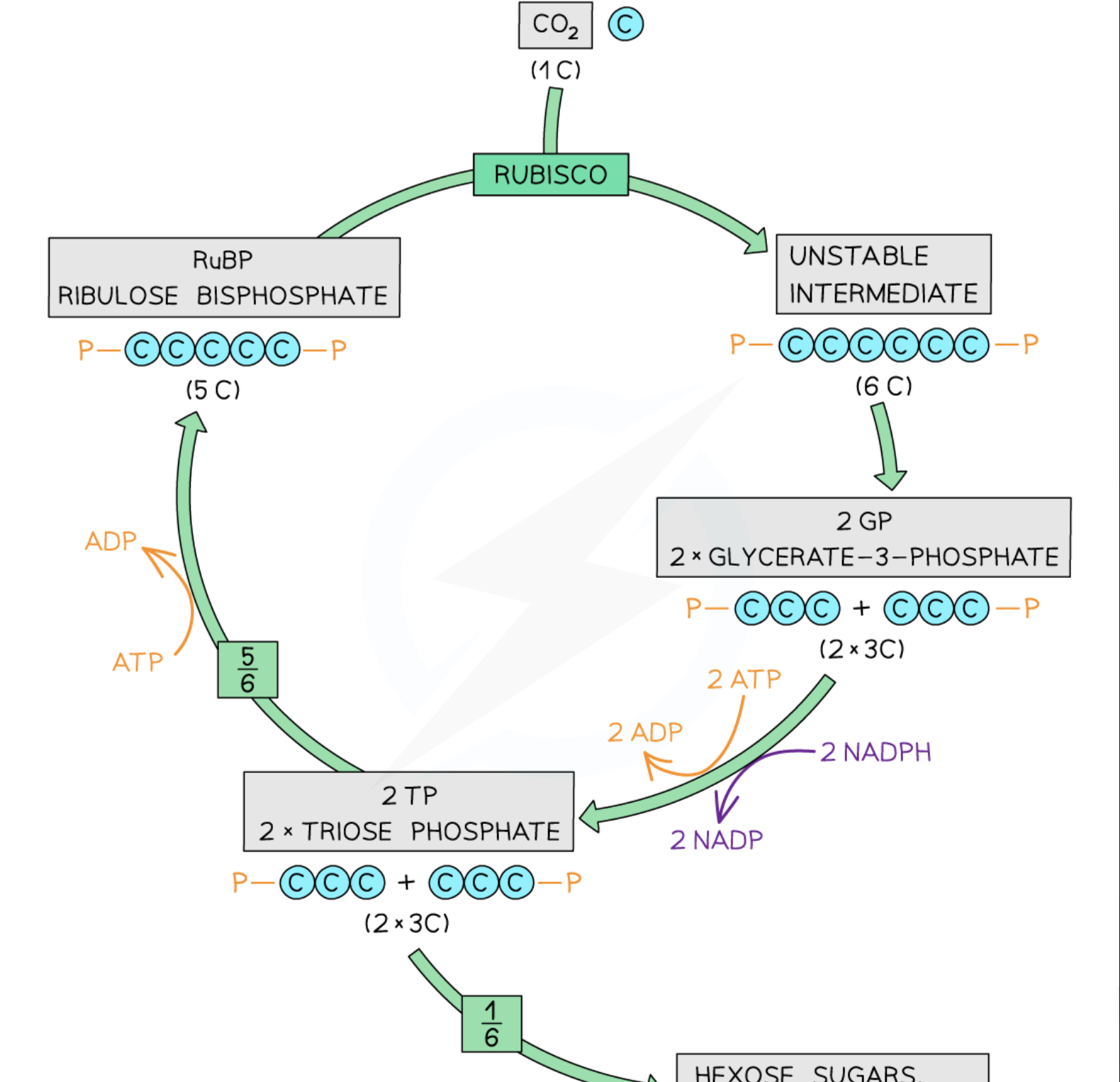
What is the first step of the Calvin cycle?
Carbon dioxide diffused into the leaf through the stomata and then diffuses through into the stroma where it combines its RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate)
Reaction is catalysed by enzyme, rubisco
What happens in the second stage of the Calvin cycle?
The reaction between CO2 and RuBp produces 2 molecules of glycerate-3-phosphate (GP)
What happens in the third stage of the Calvin cycle?
Reduced NADP is used to reduce GP to triose phosphate using energy supplied by ATP
What happens in the fourth stage of the Calvin cycle?
NADP is re-formed and goes back to the light-dependent reaction to be reduced again
What happens in the fifth stage of the Calvin cycle?
Some triose phosphate is converted to organic substances (such as starch, cellulose, lipids, glucose, amino acids etc.)
Some triose phosphate is used to regenerate RuBP using ATP from the light-dependent reaction
What organic substance can you NOT shorten?
Triose phosphate
Where does the light-independent reaction take place?
The stroma of the chloroplasts
What are some adaptations of the stroma for the light-independent reaction to occur?
The fluid of the stroma contains all the enzymes needed and is membrane-bound so high concentration can be maintained
The stroma fluid surrounds the grana and so the products from the light-dependent reaction can easily diffuse
Contains both DNA and ribosomes so proteins needed can be manufactured quickly and easily
What is a summary of the Calvin Cycle?