BIOA 2006 - Lecture 11: Endocrinology
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Secretory glands of the endocrine system
Adrenal medulla, adrenal cortex, pineal gland
hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, posterior pituitary
parathyroid gland, thyroid gland, pancreas
Long distance hormones travel through the
blood stream
Local hormones travel through the
interstitial fluid
the pancreas has both
endocrine and exocrine cells
Communication between cells in the body occurs by means of these two systems
nervous (quick) and endocrine (slow, like digestion, growth, development, and reproduction) systems
Cells will only be affected by the hormones if they have
receptors that recognize the hormone
Hormones are
chemical messengers that regulate the activity of target cells
Target cells have
receptors for specific hormones
Endocrine cells release hormones into
interstitial fluid then into blood
exocrine cells release secretions via
a duct to the epithelial surface
Neurohormones are produced by
neurons in hypothalamus called neuroendocrine cells
Endocrinology definition
the study of internal secretions and of the hormonal controls of bodily function
Paracrine (endocrine) glands
glands that secrete chemicals that diffuse through the interstitium to affect other cells in a very localized fashion.
ex: leydig cells of the testes secrete testosterone to the seminiferous tubules for spermatozoa development
The "traditional" endocrine glands are
pituitary
thyroid
parathyroid
adrenal gland
pancreas
gonads (ovary or testes)
Classic hormones are those that communicate
over long distance
autocrine glands
secrete substances that act on themselves
-ex: immune cells that secrete chemicals called interleukins, which in turn affect that cells function
Classical vs Local hormones reach target cells by
Local: diffusion through interstitial fluid
Classic: long distance, blood
What is the difference between neurohormones and neurotransmitters
NTs act locally and quickly at a synapse while neurohormones travel long distances to make a longer term impact travelling through the blood
Endocrine, paracrine, autocrine, neural, and neuroendocrine regulation diagrams
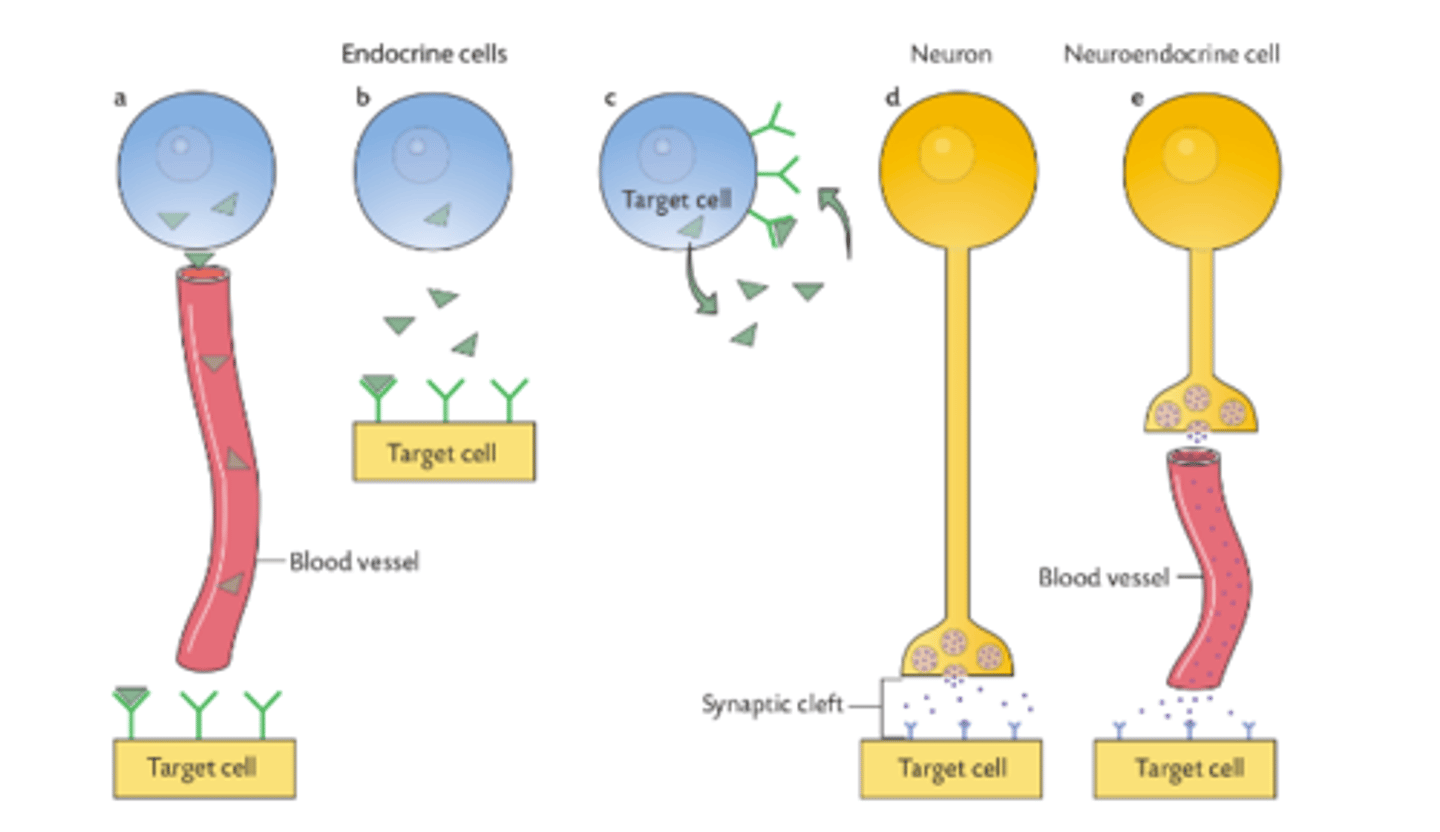
What do hormones regulate?
-energy and metabolism
-electrolyte and fluid balance
-growth and devel
-reproduction
-digestion
-immune functions
-biological rhythm
Hormones circulate at ______ levels in the blood
low
though all cells are exposed to hormones, which can respond?
those with receptors
generally, the greater amount of hormone, the
greater the response
classical hormone example
insulin
neurohormone ecample
oxytocin
local hormone example
prostaglandins (paracrine/autocrine)
Tropic hormones are those which
regulate the secretion of other hormones (eg., thyroid stimulating hormone) as well as the growth of the target endocrine gland (eg., thyroid stimulating hormone supports growth of the thyroid gland)
Thymosin
stimulates the maturation of lymphocytes into T cells of the immune system
Neuroendocrine regulation
neurohormones are released from nerve endings of neuroendocrine cell and transported as classical hormone in the blood stream to the target cells