Bacteriology Lab Final
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
127 Terms
Bacteria are in Domain ___________, and composed of ___________ cells.
a. Bacteria, eukaryotic
b. Bacteria, prokarytic
c. Archaea, eukaryotic
d. Archaea, prokaryotic
b. Bacteria, prokarytic
The microorganisms that do not have a nucleus in their cells are called
a. eukaryotes
b. decomposers
c. fermenters
d. pathogens
e. prokaryotes
e. prokaryotes
Which of the following is a scientific name?
a. bacteria
b. bacilli
c. Protista
d. species
e. Bacillus subtilis
e. Bacillus subtilis
Streptococcus salivarius BLIS K12 is a probiotic strain against bacterial pharyngo-tonsillitis in the human oral cavity.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Bacteria chromosome are inside nucleus.
a. True
b. False
b. False
Lipopolysaccharide is an important cell wall component of
a. gram-negative bacteria
b. acid-fast bacteria
c. protoplasts
d. mycoplasmas
e. gram-positive bacteria
a. gram-negative bacteria
Example of Biosafety Level 4 agent is
a. Ebola virus
b. E. coli
c. Mycobacteria tuberculosis
d. Steptococcus mitis
a. Ebola virus
Which bacteria is typically found on your skin and may form biofilm on plastic devices?
a. Staphylococcus epidermidis
b. Streptococcus salivarius
c. Bacillus megaterium
d. Escherichia coli
a. Staphylococcus epidermidis
Bacteria are commonly found in your throat include
a. Streptococcus mitis
b. Corynebacterium pseudodiphthericum
c. Moraxella catarrhalis
d. All of these
d. All of these
E. coli is a Gram-positive bacteria.
a. True
b. False
b. False
Peptidoglycan is a unique macromolecule found in bacterial
a. slime layers
b. capsules
c. cell walls
d. cell membranes
e. inclusions
c. cell walls
Neisseria lactamica in the human oral cavity may prevent meningococcal meningitis.
a. True
b. False
a. True
All bacterial cells have
a. fimbriae
b. capsules
c. endospores
d. flagella
e. a chromosome
e. a chromosome
Which following are gram-positive bacteria?
a. Neisseria lactamica
b. Serratia marcescens
c. Moraxella catarrhalis
d. Staphylococcus aureus
d. Staphylococcus aureus
c. streptococcus
The following image is an example of _____
a. diplococcus
b. staphylococcus
c. streptococcus
d. streptobacillus
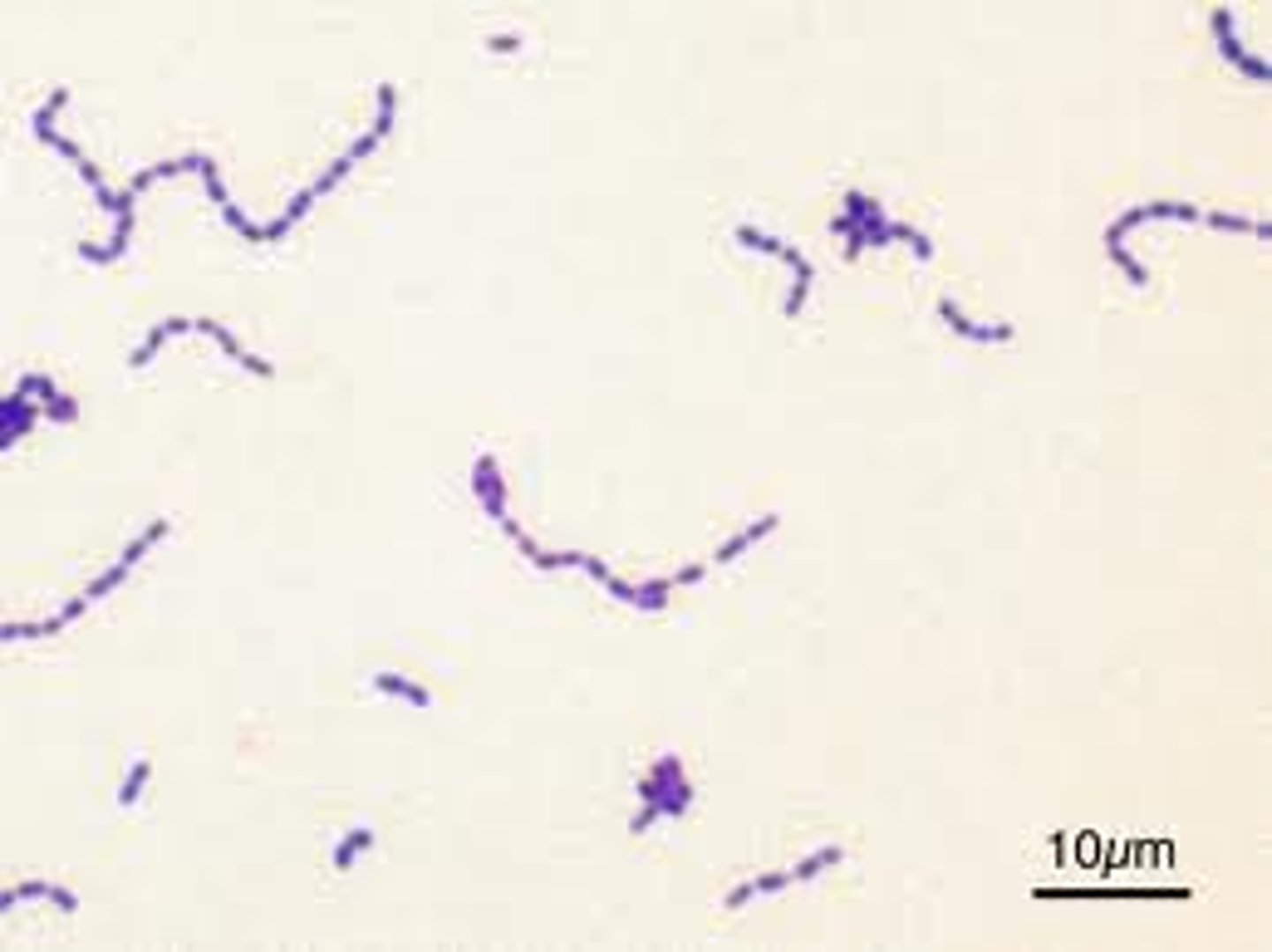
a. True
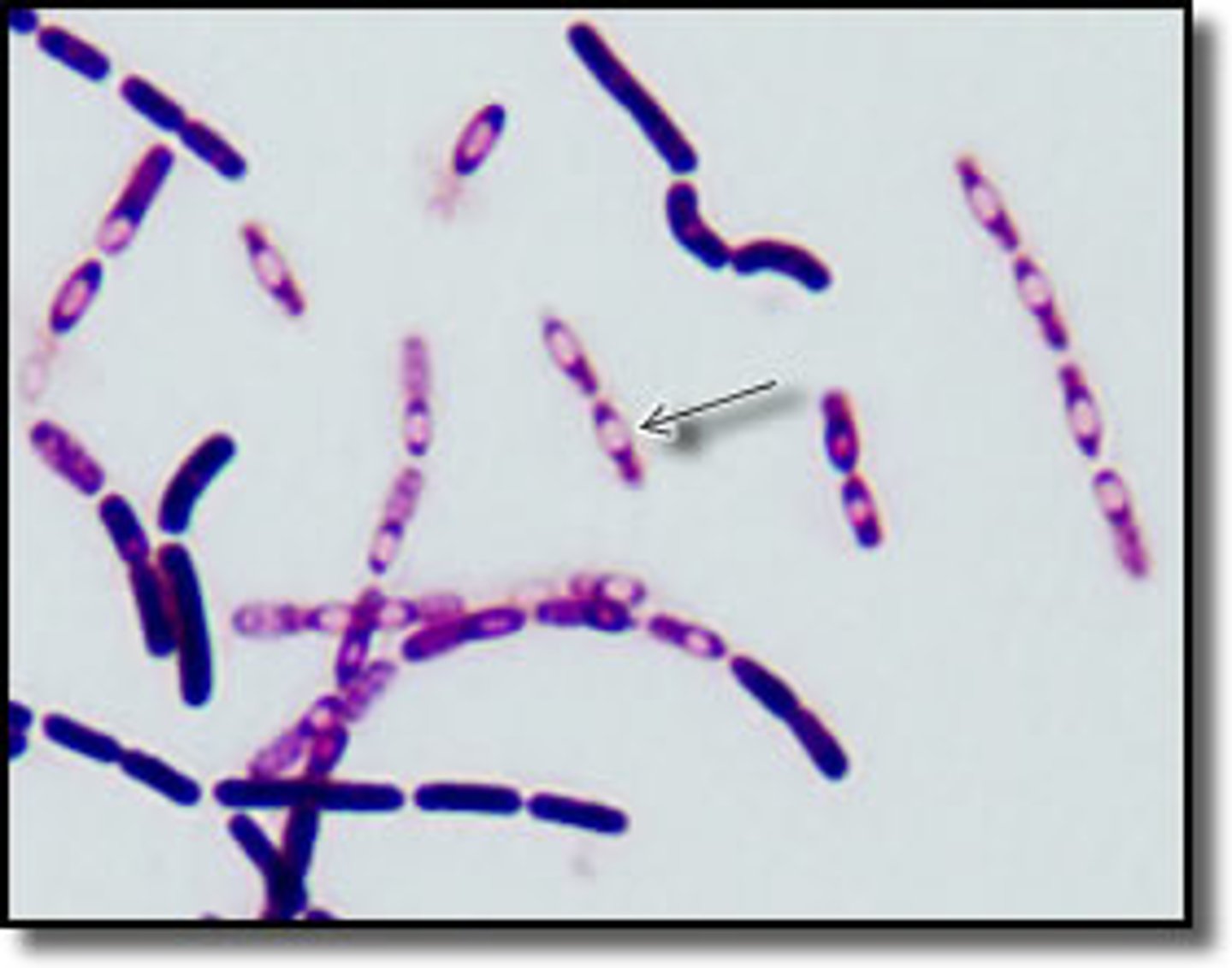
The following image is an example of bacillus bacteria forming endospores.
a. True
b. False
a. diplococcus
The following image is an example of __________
a. diplococcus
b. staphylococcus
c. streptococcus
d. streptobacillus
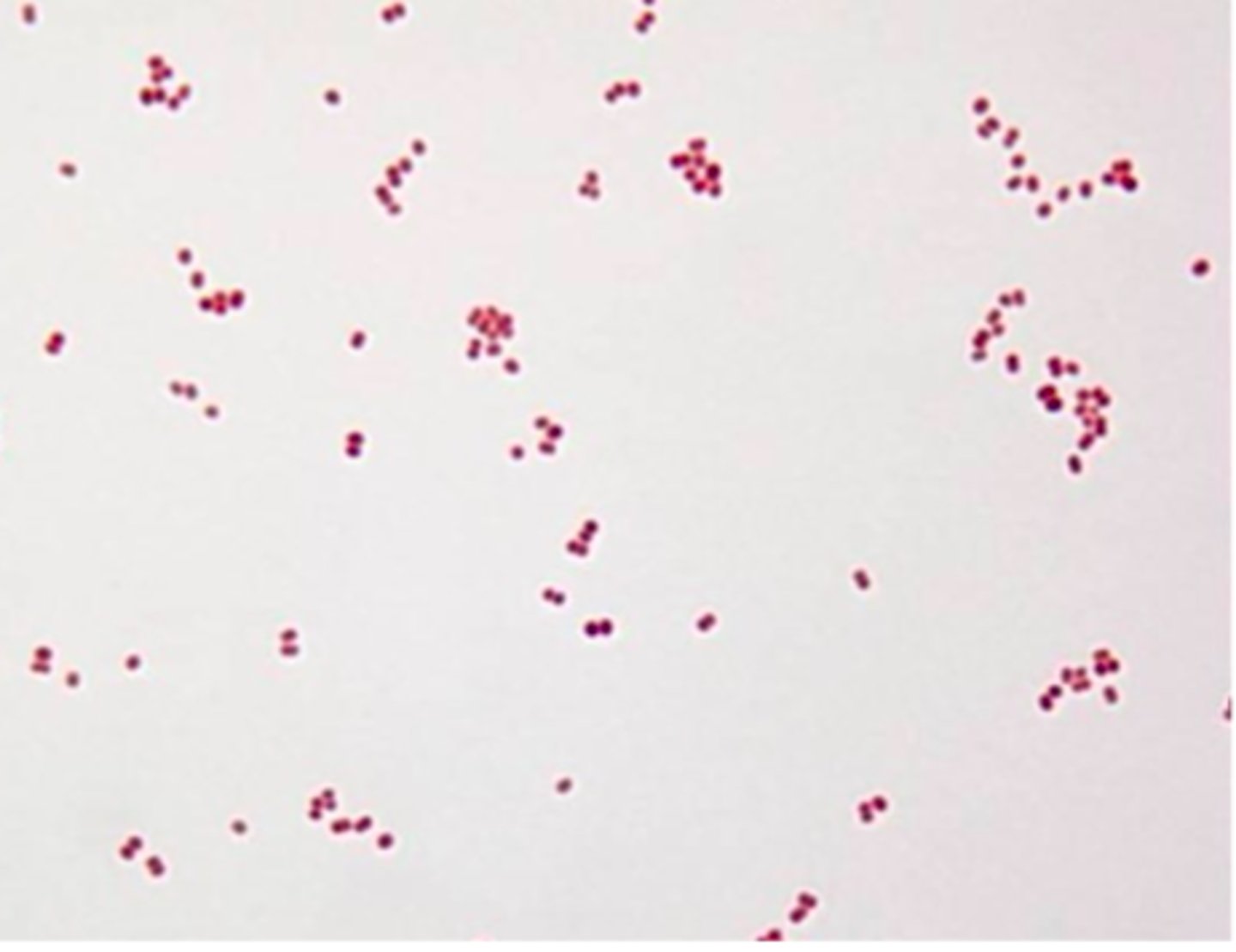
b. bacillus, palisade
The following image is an example of ________ shaped bacteria with __________ arrangement
a. coccus, clustered
b. bacillus, palisade
c. rod, chain liked
d. coccus, chain liked
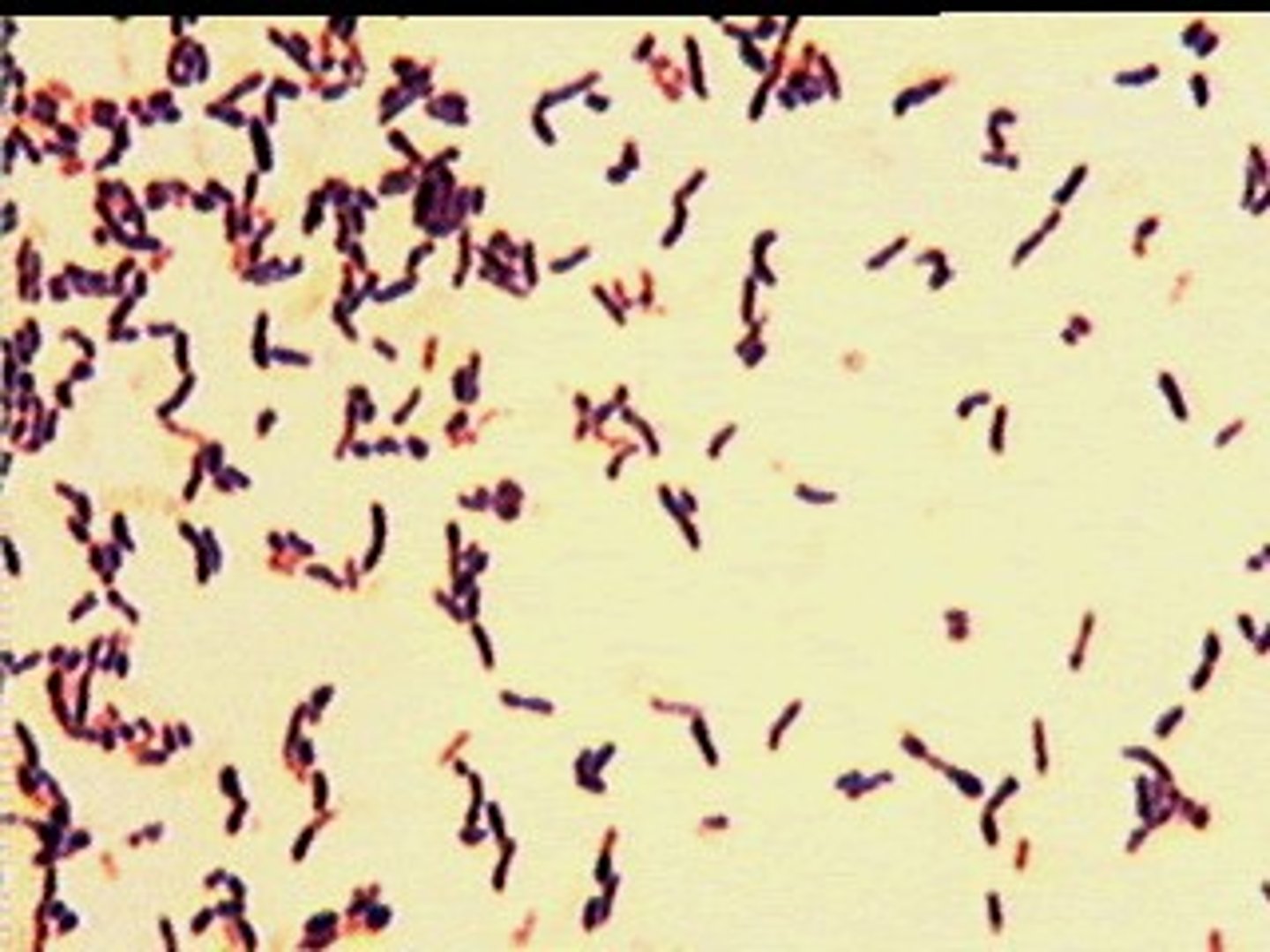
a. spiral
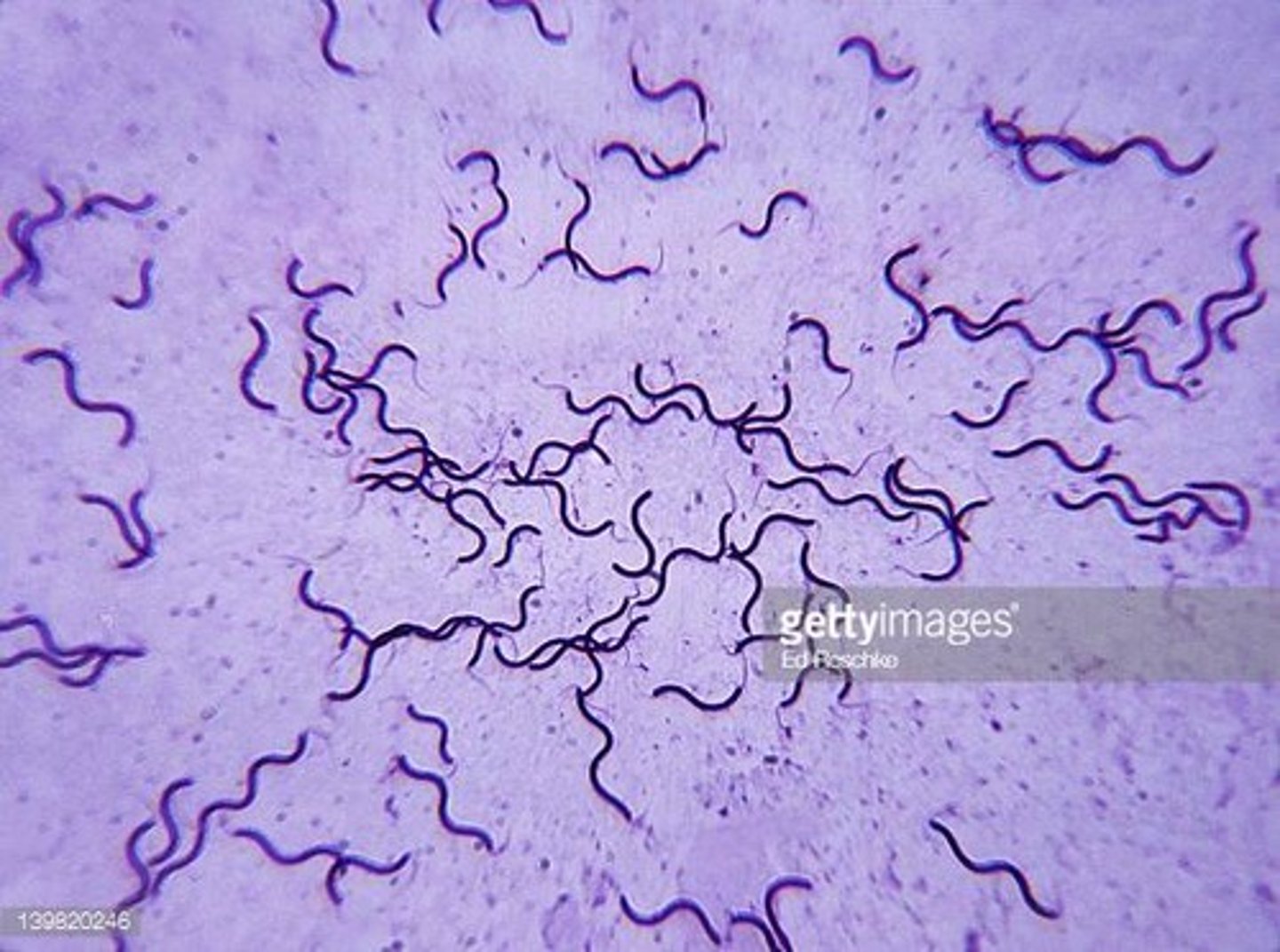
The following image is an example of ________ shaped bacteria.
a. spiral
b. coccus
c. baccilus
d. vibrio
d. division plane during binary fission
Which following process contribute to arrangement of bacteria?
a. division plane during mitosis
b. division plane during meiosis
c. division plane during budding
d. division plane during binary fission
b. the refractive index of mineral oil is the same as glass
Mineral oil is added to the slide when using 100x objective lens to observe the bacteria because
a. adding mineral oil decrease the light entered in the lens
b. the refractive index of mineral oil is the same as glass
c. mineral oil prevents the slide to dry
d. mineral oil perserve the sample
d. tetrad
Which term is not used to describe bacterial cell shapes?
a. vibrio
b. spirochete
c. coccus
d. tetrad
e. rod
c. Bacteria stain differently based on differences in their cell wall composition.
Which of the following statements about Gram-staining is true?
a. Only Gram-negative bacteria cause diseases in human
b. After staining is complete, Gram-positive bacteria will appear pink and Gram-negative bacteria will appear purple.
c. Bacteria stain differently based on differences in their cell wall composition.
d. The primary stain will stain both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria pink.
c. purple; colorless
After the decolorizer has been added, gram-positive organisms are stained __________ and gram-negative organisms are stained __________.
a. purple; pink
b. purple; purple
c. purple; colorless
d. pink; pink
b. Corynebacterium pseudodiphthericum
The bacteria with palisade arrangement is
a. Moraxella catarrhalis
b. Corynebacterium pseudodiphthericum
c. Bacillus cereus
d. Serratia marcescens
a. cell wall
Which structure confers bacteria shape?
a. cell wall
b. cell membrane
c. flagella
d. nucleus
e. All of these
Bacteria are commonly found in your throat include
a. Streptococcus mitis
b. Corynebacterium
c. Pseudodiphthericum
d. Moraxella catarrhalis
e. All of these
c. a cuboidal packet of cells
Sarcinae refers to
a. groups of endopsores
b. vibrios in threes
c. a cuboidal packet of cells
d. coffee-bean-shaped rods in pairs
e. cocci in pairs.
b. parfocal
If the objective lenses of a microscope can be changed without losing focus on the specimen, they are said to be
a. equifocal
b. parfocal
c. optifocal
d. totifocal
b. resolution
The ability of a microscope to differentiate between two close objects or points is referred to as
a. magnification
b. resolution
c. contrast
d. refraction
c. 400
If objective lens used is 40X and occular lens is 10x, the total magnification is ___________
a. 40
b. 10
c. 400
d. 1000
c. refractive index
Immersion oil can be used to increase the resolution achieved with some microscope lenses because it has the same ___________ as the objective lens.
a. neither optical density nor refractive
b. index optical density and refractive index
c. refractive index
d. optical density
Please match the bacteria with the disease they cause:
Salmonella typhimurium
Bartonella Henselae
Yersinia pestis
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Yersinia enterocolitica
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Yersiniosis
Typhoid fever
Plague (black death)
Cat scratch disease
Salmonella typhimurium: typhoid fever
Bartonella Henselae: cat scratch disease
Yersinia pestis: plague (black death)
Pseudomonas aeruginosa: urinary tract infection
Yersinia enterocolitica: yersiniosis
Why is it possible to use a 16S rDNA sequence to identify bacteria?
a. 16S rDNA sequence is conserved among prokarytes
b. 16S rDNA sequence is highly variable among bacteria
c. 16S rDNA sequence codes for ribosome proteins
d. 16S rDNA sequence is a universal gene for all living things
a. 16S rDNA sequence is conserved among prokarytes
How to identify an unknown bacteria?
a. genetics tests
b. biochemical tests
c. Gram stain
d. Aseptic technique
e. All of these
e. All of these
Why is PCR useful for the bacterial virtual ID lab?
a. a rapid method to amplify specific mRNA sequence
b. a rapid method to amplify specific DNA sequence
c. a rapid method to gain more heat resistant protein
d. all of these
b. a rapid method to amplify specific DNA sequence
How does the DNA sequence work?
a. Chain termination method with fluorescent labeled dideoxynucleotides
b. Chain termination method with radioactive labeled dideoxynucleotides
c. DNA polymerase
d. All of these
d. All of these
Herd immunity could be achieved if:
a. 10 people recovered from COVID 19
b. 100 people recovered from COVID 19
c. 1000 people recovered from COVID 19
d. over 90% population recovered from COVID 19
d. over 90% population recovered from COVID 19
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", which virus only infects bacteria?
a. TMV
b. T4
c. HIV
d. Rabies
b. T4
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", vaccine is available to prevent _______ infection.
a. T7
b. SARS CoV-2
c. Papillomavirus
d. TMV
c. Papillomavirus
Herd immunity could be achieved if:
a. everyone in my home are vaccinated
b. I got flu shot
c. significant large amount of population received vaccine
d. everyone my neighborhood are vaccinated
c. significant large amount of population received vaccine
Basic Reproductive Number (R0) refers to:
a. The amount of a pathogen that is required to establish an infection
b. age structure of a population
c. the number of individuals that can be infected from one single patient
d. the current (recovered/vaccinated) state of the population
c. the number of individuals that can be infected from one single patient
Mucormycoisis among COVID 19 patients are caused by_______ which are cmposed of ____________ cells.
a. fungi, eukaryotic
b. bacteria, prokaryotic
c. fungi, prokaryotic
d. protozoan, eukaryotic
a. fungi, eukaryotic
Small pox virus is eradicated from our general environment due to _______.
a. vaccine is available
b. human is the only host
c. herd immunity
d. all of theses
d. all of theses
Mucormycosis may be caused by _____________ infection. (Mark all that apply)
a. Streptococcus mitis
b. Rhizopus
c. E. coli
d. Absidia
e. Influenza virus
f. Mucor
b. Rhizopus
d. Absidia
f. Mucor
Factors contributing mucormycosis among COVID 19 patients are___________________. (Mark all that apply)
a. increased T cells
b. increased phagocytosis
c. hypoxia
d. usage of corticosteroids
e. diabetes related hyperglycemia
f. diabetic ketoacidosis
c. hypoxia
d. usage of corticosteroids
e. diabetes related hyperglycemia
f. diabetic ketoacidosis
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", which virus contains segmented genome?
a. Influenza A
b. Papillomavirus
c. Rabies
e. Ebola
a. Influenza A
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", which virus contains a circular genome?
a. Adenovirus
b. TMV
c. Papillomavirus
d. Ebola
c. Papillomavirus
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", vaccine is available to prevent _______ infection.
a. Rabies
b. Adenovirus
c. HIV
d. Zika
a. Rabies
The first virus to be discovered was viewed through an electron microscope and infects tobacco plants. This virus is included in the interactive "Virus Explore", Which virus is it?
a. Zika
b. Rabies
c. HIV
d. TMV
d. TMV
Besides mucormycosis, fugal infection such as ___________________________ are also common among COVID patients:
d. Bartenella henselae and Yersinia enterocolitica
b. E. coli and Candida
c. Staphylococcus epidermidis and Aspergillus
d. Aspergillus and Candida
d. Aspergillus and Candida
Based on the interactive "Virus Explore", both Adenovirus and Influenza A cause respiratory tract infection. What is the difference between these virus?
a. genome type
b. structure
c. envelop
d. All of these
d. All of these
In the virtual Kirby-Bauer antimicrobial susceptibility test, zone of inhibition around each disk is measured. Based on the results of virtual lab, which following(s) is/are ture? (mark all that apply)
a. Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to amoxicillin
b. Erythromycin may be used to treat E. coli infection
c. Clear zone around disks indicate no bacterial growth
d. E. coli is resistant to clindamycins
e. Ciprofloxacin is effective for treating Pseudomonas aerogenosa infection
a. Staphylococcus aureus is resistant to amoxicillin
c. Clear zone around disks indicate no bacterial growth
d. E. coli is resistant to clindamycins
e. Ciprofloxacin is effective for treating Pseudomonas aerogenosa infection
The naked viruses generally are more resistant to antiseptics such as soap and alcohol than enveloped viruses because:
a. reverse transcriptase resists enzyme digestion
b. capsomers are easily destroyed by soap and alcohol
c. naked viruses do not cause any disease
d. lipids are easily destroyed by soap and alcohol
d. lipids are easily destroyed by soap and alcohol
Gram-negative bacteria are more sensitive towards antiseptics such as soap and alcohol than Gram-positive bacteria because:
a. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria cell wall contains lipid
b. only Gram-positive bacteria cause diseases
c. Gram-negative bacteria have a negative reaction towards antibiotics
d. flagella help Gram-negative bacteria to swim away from disinfectant
a. The outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria cell wall contains lipid
In the Streak Plate virtaul lab, bacteria pure culture could be obtained by___________.
a. sterilize innoculate loop in a flame
b. RT-PCR
c. successive dilution of original culture in each quadrant
d. taking sample from sputum
a. sterilize innoculate loop in a flame
c. successive dilution of original culture in each quadrant
Taxo-P sensitive bacteria is:
a. Streptococcus pnemoniae
b. Streptococcus mitis
c. Bacillus cereus
d. E. coli
a. Streptococcus pnemonia
Which of the following is/are true of antibiotic usage and the development of antibiotic resistance?
a. synthesis of enzymes that alter drug structure.
b. bacterial chromosomal mutations.
c. alteration of drug receptors on cell targets.
d. prevention of drug entry into the cell.
e. All of these choices are correct.
e. All of these choices are correct.
Which of the following is/are true of antibiotic usage and the development of antibiotic resistance?
a. Antibiotics increase the rate of bacterial transformation, conjugation, and transduction, and thus increase the spread of antibiotic resistance.
b. Antibiotics select for resistant mutants and bacteria possessing R-plasmids, increasing their frequency in the population.
c. Antibiotics cause R-plasmids to form and cause their transfer, spreading antibiotic resistance.
d. Antibiotics cause mutations (antibiotics are mutagens), thus resulting in increasingly resistant bacterial populations.
e. All of these choices are correct.
b. Antibiotics select for resistant mutants and bacteria possessing R-plasmids, increasing their frequency in the population.
Which is the best guide for selecting an effective antibiotic?
a. results of Kirby-Bauer antimicrobial susceptibility testing
b. history of prior antibiotics prescribed for the patient
c. location of the patient's infection
d. identification of the microbe causing the infection
a. results of Kirby-Bauer antimicrobial susceptibility testing
In lab, Tom was given a mixed culture. His objective is to isolate single colonies. What should be used to accomplish this goal?
a. sterile swab, loop dilution, TSB
b. sterile swab, streak plate method, 37 degree Celsius incubator
c. hockey stick, spread plate technique, and 4 degree Celsius incubation temperature
d. loop dilution, TSA, hockey stick, 37 degree Celsius incubator
e. inoculating loop, incinerator, streak plate method, 37 degree Celsius incubator
e. inoculating loop, incinerator, streak plate method, 37 degree Celsius incubator
Which method of microbial control destroys microorganisms by oxidation of cells?
a. steam autoclave
b. use of UV radiation
c. use of glutaraldehyde
d. incineration
d. incineration
The cellular basis for bacterial resistance to antimicrobics include:
a. synthesis of enzymes that alter drug structure.
b. bacterial chromosomal mutations.
c. alteration of drug receptors on cell targets.
d. prevention of drug entry into the cell.
e. All of these choices are correct.
e. All of these choices are correct.
A pure culture contains only:
a. bacteria.
b. one species of microorganism.
c. a variety of microbes from one source.
d. All of these choices are correct.
b. one species of microorganism.
The use of chemical agents directly on exposed body surfaces to destroy or inhibit
vegetative pathogens is:
a. Antisepsis
Diseases that suddenly become prevalent are referred to as ____ diseases.
a. Emerging
Which organ is responsible for metabolizing and detoxifying foreign chemicals in the
blood, including drugs?
a. Liver
All of the following could be reasons why antimicrobic treatment fails except..
a. A disk diffusion test showing pathogen sensitivity to the antimicrobic
Drug susceptibility testing
a. Determines the pathogens response to various antimicrobics
Why has the US and Europe banned the used of human drugs in animal feeds?
a. Because it contributes to growing drug resistance problem
The outcome of the Gram stain is based on differences in the cell's:
a. flagella.
b. ribosomes.
c. cell membrane.
d. inclusions.
e. cell wall.
e. cell wall.
Where can you find bacteria that are able to grow on MSA agar?
a. skin
b. intestine
c. bone
d. throat
a. skin
A halophile would ________ in a high salt environment.
a. thrive
b. become crenated
c. undergo osmotic lysis
d. form endospores
e. undergo plasmolysis
a. thrive
Coagulase test may be used to identify __________________. (Mark all that apply)
a. Staphylococcus epidermidis
b. fibrin formation
c. Staphylococcus aereus
d. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. fibrin formation
c. Staphylococcus aereus
_____________ line indicate positive for the Virtual Rapid Strep Test.
a. Green vertical line over pink horizontal line
b. Pink vertical line over blue horizontal line
c. Yellow vertical line over blue horizontal line
d. Purple vertical line over green horizontal line
b. Pink vertical line over blue horizontal line
CAMP test is useful to identify _______________ infection.
a. Streptococcus agalactiae
b. Streptococcus mitis
c. Streptococcus pyogenes
d. Streptococcus pneumoniae
a. Streptococcus agalactiae
Staphylococcus aereus may be identified with_____________ tests. (Mark all that apply)
a. Rapid Strep test
b. coagulase test
c. Catalase test
d. Mannitol Salt agar
b. coagulase test
c. Catalase test
d. Mannitol Salt agar
The Virtual Strep Test may be used to identify _______________ infection.
a. Streptococcus pneumoniae
b. Staphylococcus aereus
c. Streptococcus agalactiae
d. Streptococcus pyogenes
d. Streptococcus pyogenes
Which following(s) is/are true regarding the catalase virtual lab? (Mark all that apply)
a. Oxygen is the product of catalase
b. Hydrogen proxide is the product of catalse
c. Staphylococcus is catalase positive
d. Streptococcus is catalase positive
a. Oxygen is the product of catalase
c. Staphylococcus is catalase positive
The positive CAMP test is an example of synergistic effect of two exotoxins.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Hydrogen peroxide is an effective antiseptic for _______ bacterial infection on the skin?
a. obligate anaerobic bacteria
b. facultative anaerobic
c. acid fast positive
d. aerobic
a. obligate anaerobic bacteria
Which bacteria are Beta-hemolytic? (Mark all that apply)
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
b. Staphylococcus epidermidis
c. Streptocuccus agalactiae
d. Staphylococcus aereus
a. Streptococcus pyogenes
c. Streptocuccus agalactiae
d. Staphylococcus aereus
The function of bacterial endospores is:
a. to convert gaseous nitrogen to a usable form for plants.
b. for protection of genetic material during harsh conditions.
c. the storage of excess cell materials.
d. for reproduction and growth.
e. to have sites for photosynthesis.
b. for protection of genetic material during harsh conditions.
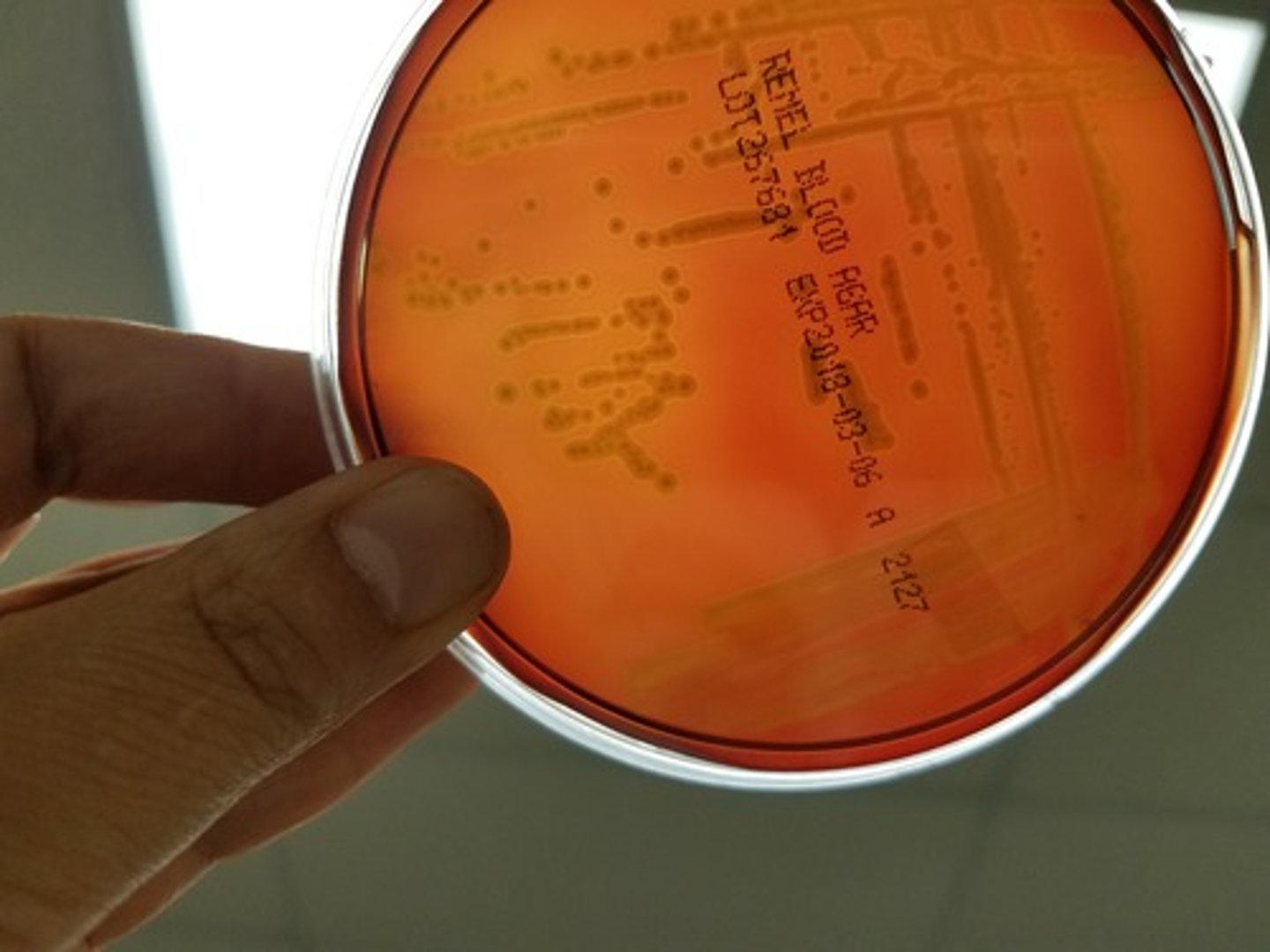
The following image is an example of _________ hemolysis.
a. Beta
b. Alpha
c. Non
d. Gamma
b. Alpha
The purpose of streaking plate is to
a. Isolate pure colonies
What is the product of catalase
a. Oxygen
If a microorganism grows on Mannitol Salt agar, and there are yellow color around
bacterial colony, this bacteria is _____ which _____ salt and ferments mannitol.
a. S aureus, tolerates
Hemolysin is an endotoxin
a. False
Shiga toxin is a(n)
a. exotoxin
b. neurotoxin
c. exoenzyme
d. endotoxin
a. exotoxin
Only Gram-negative bacteria produce endotoxin
a. True
b. False
a. True
If you see the purple black color after the virtual oxidase test, it means the sample is oxidase ____________.
a. positive
b. false positive
c. negative
d. false negative
a. positive
Enterotube may be used to rapidly identify G - baccili.
a. True
b. False
a. True
After decolorization step, G + bacteria are ____.
a. colorless
b. purple
c. pink
d. brown
b. purple
Which tests may be useful to differentiate Gram negative bacilli? (Mark all that apply)
a. lactose fermentation
b. H2S production
c. blood agar
d. oxidase test
a. lactose fermentation
b. H2S production
d. oxidase test
The oxidase test is to identify the presence of __________________.
a. hemolysin
b. cytochrome C oxidase
c. coagulase
d. catalase
b. cytochrome C oxidase
Iodine serves as __________ in Gram stain.
a. primary stain
b. mordant
c. counter stain
d. decolorizer
b. mordant
Coagulase is ___________ (Mark all that apply)
a. an endotoxin
b. a neurotoxin
c. an exoenzyme convering fibrinogen to fibrin
d. produced by S. aureus
c. an exoenzyme convering fibrinogen to fibrin
d. produced by S. aureus
Oxidase test may be used to ____ (Mark all that apply)
a. differentiate E. coli and Pseudomonas spp.
b. identify the presence of cytochrome C oxidase
c. differentiate E. coli and Neisseria spp.
d. differentiate Pseudomonas spp. and Neisseria spp.
a. differentiate E. coli and Pseudomonas spp.
b. identify the presence of cytochrome C oxidase
c. differentiate E. coli and Neisseria spp.
Which following is Category A NIAID emerging infectious diseases/pathogens? (Mark all that apply)
a. Yersinia pestis
b. Francisella tularensis
c. Burkholderia pseudomallei
d. Severer acute resoiratory syndrome associated coronavirus
a. Yersinia pestis
b. Francisella tularensis
Viral hemorrhagic fevers pose_________
a. 2nd highest risk to national security and public health
b. no risk at all
c. the highest risk to national security and public health
d. 3rd highest risk to national security and public health
c. the highest risk to national security and public health