imaging final exam
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
osteochondritis dessicans (elbow)
- most common in capitulum
- separation of cartilage segment and subchondral bone from articular surface
- common in adolescent athletes
- USE MRI
epicondylitis
- medial = flexors
- lateral = extensors
- diagnose with US
monteggia fx of elbow
proximal 1/3 of ulna w dislocation of radial head
nightstick fracture of elbow
fracture of ulnar shaft
galeazzi fx of elbow
fx of distal 1/3 radial shaft and distal radioulnar joint dislocation
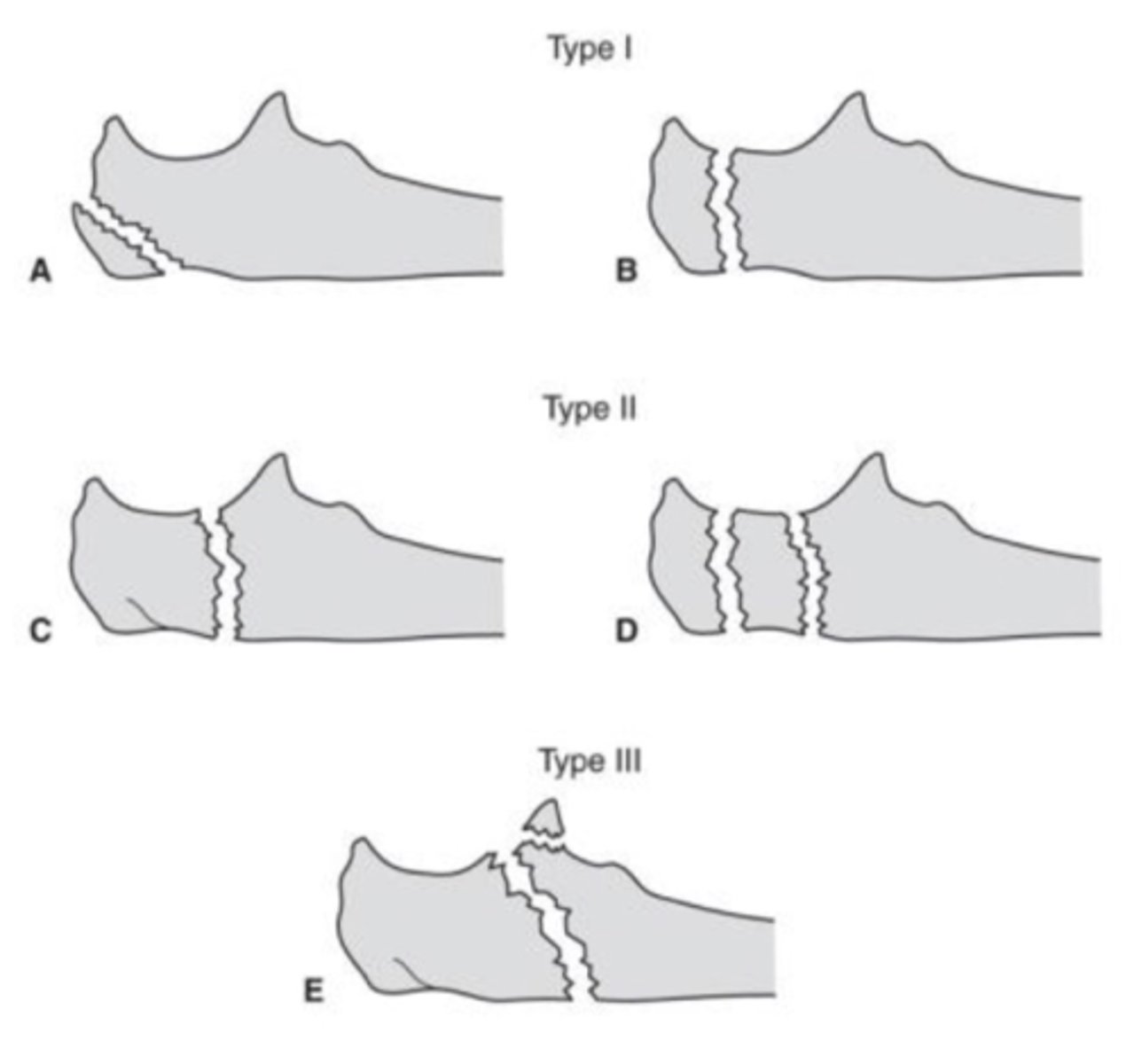
proximal ulnar fx
3 types
- type 1: proximal 1/3 olecranon
- type 2: middle 1/3 olecranon (most common)
- type 3: distal 1/3 olecranon (closer to ulnar shaft)
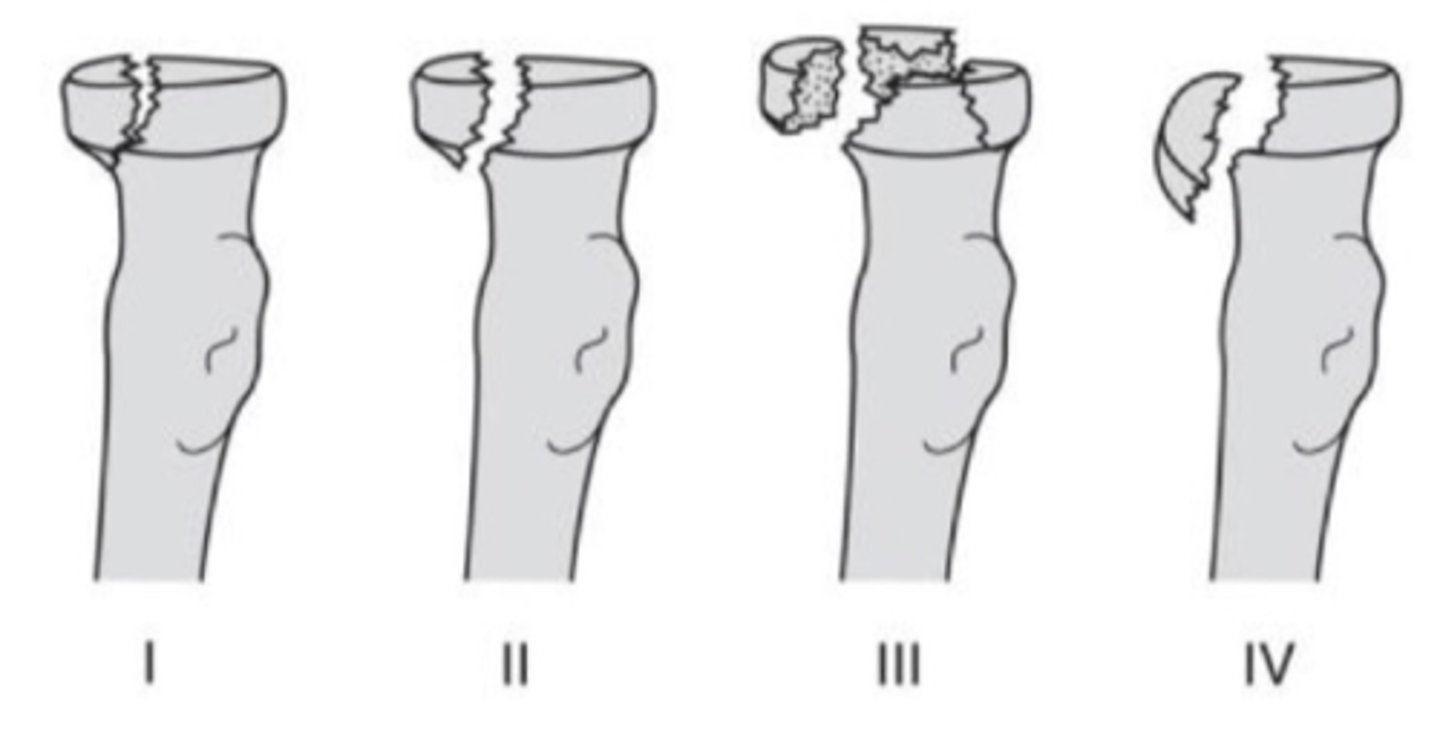
radial head fracture
4 types
- type 1: undisplaced
- type 2: marginal fx w displacement
- type 3: comminuted fx
- type 4: radial head fx and dislocation
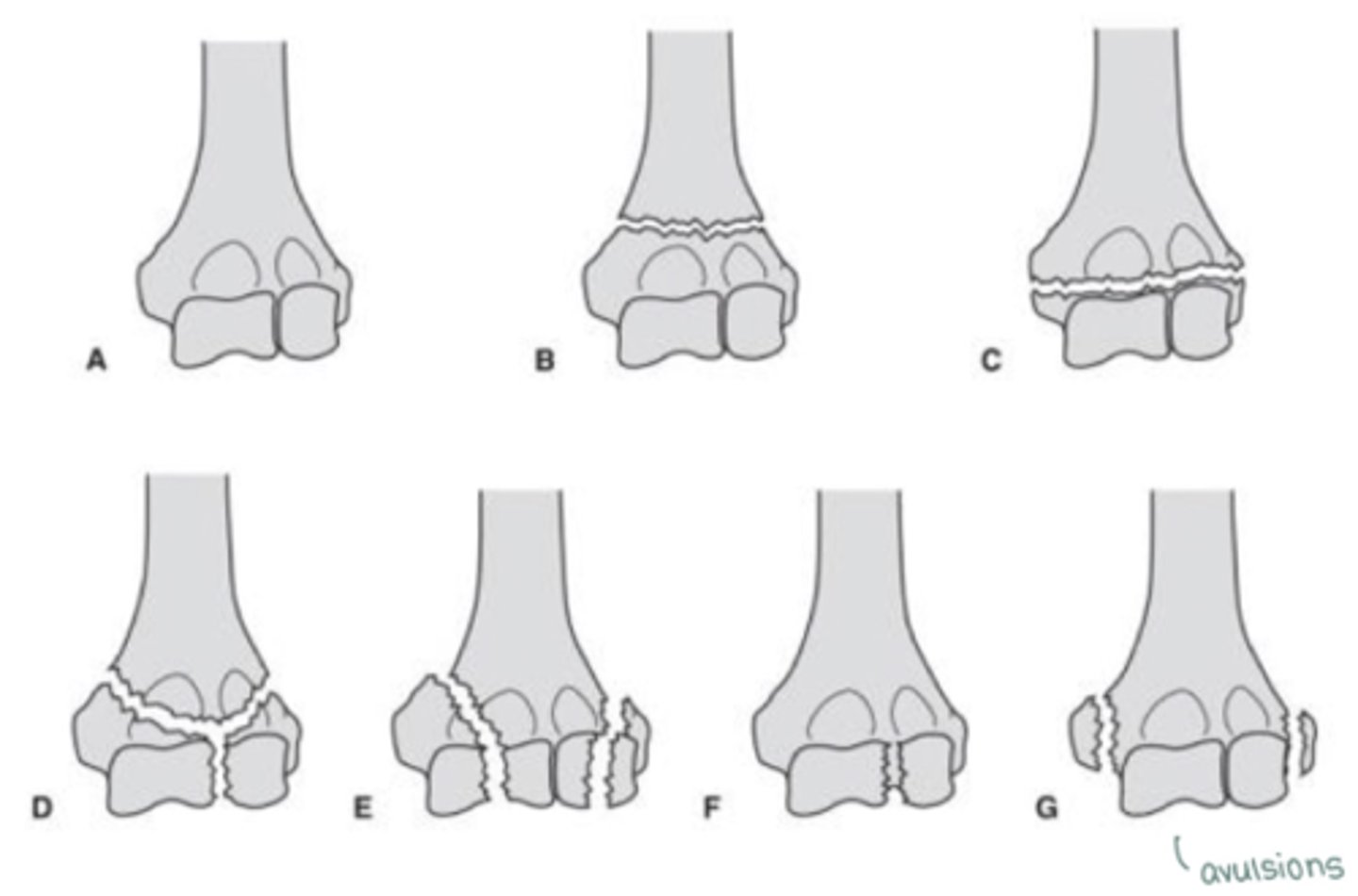
distal humerus fracture
- supracondylar fx (above condyles)
- transcondylar fx (transverse line through condyles)
- intercondylar fx (fx IN BETWEEN condyles, vertical line)
- condylar fracture (condyles broken off)
- articular fx (fx of articular surfaces)
- epicondylar fx (avulsion fx)
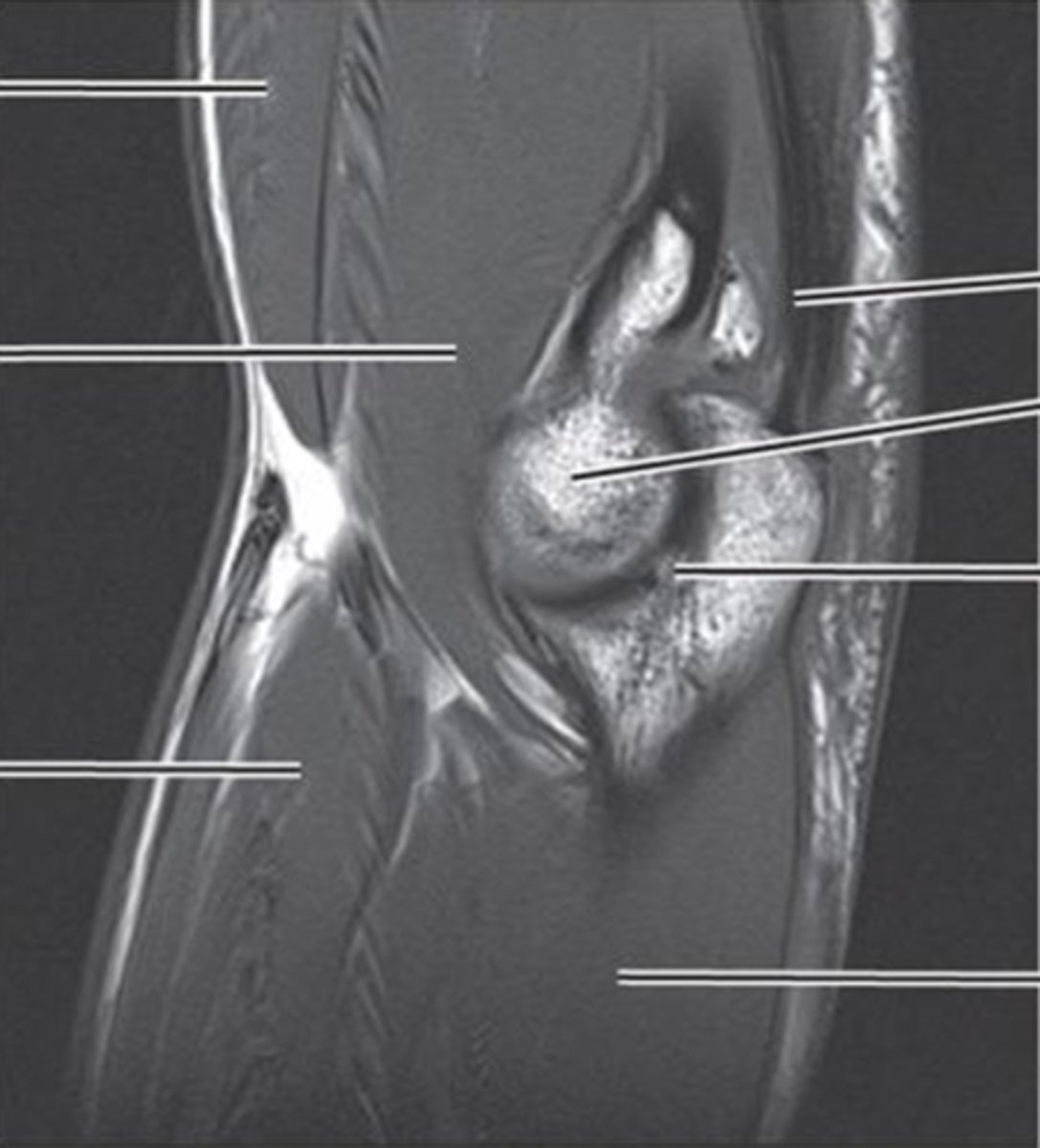
what can u see in coronal plane MRI/CT of elbow
- medial and lateral collateral ligaments
- common flexor and extensor tendons
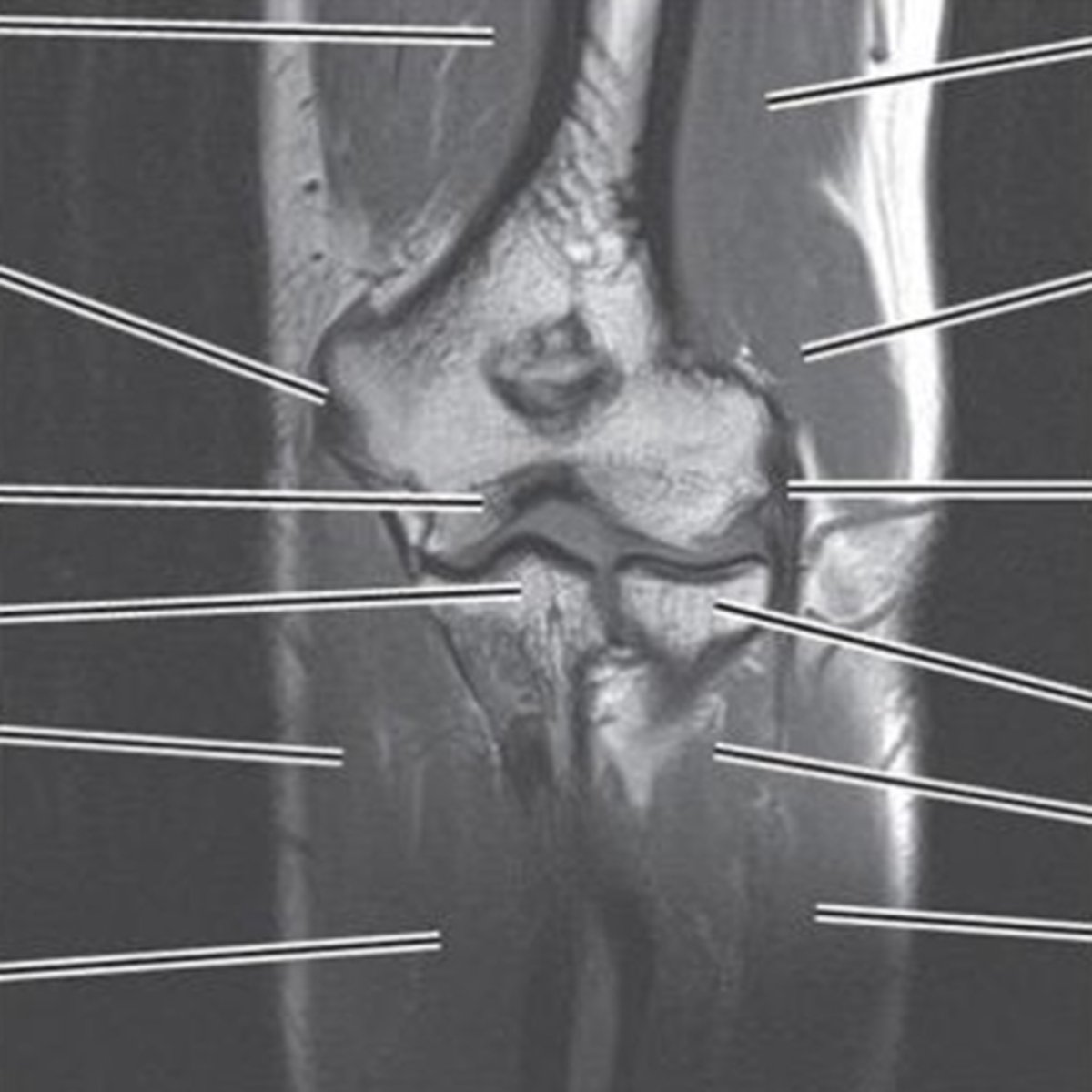
what can you see in saggital plane MRI/CT elbow
- radial head
- humerradial joint
- humeroulnar jt
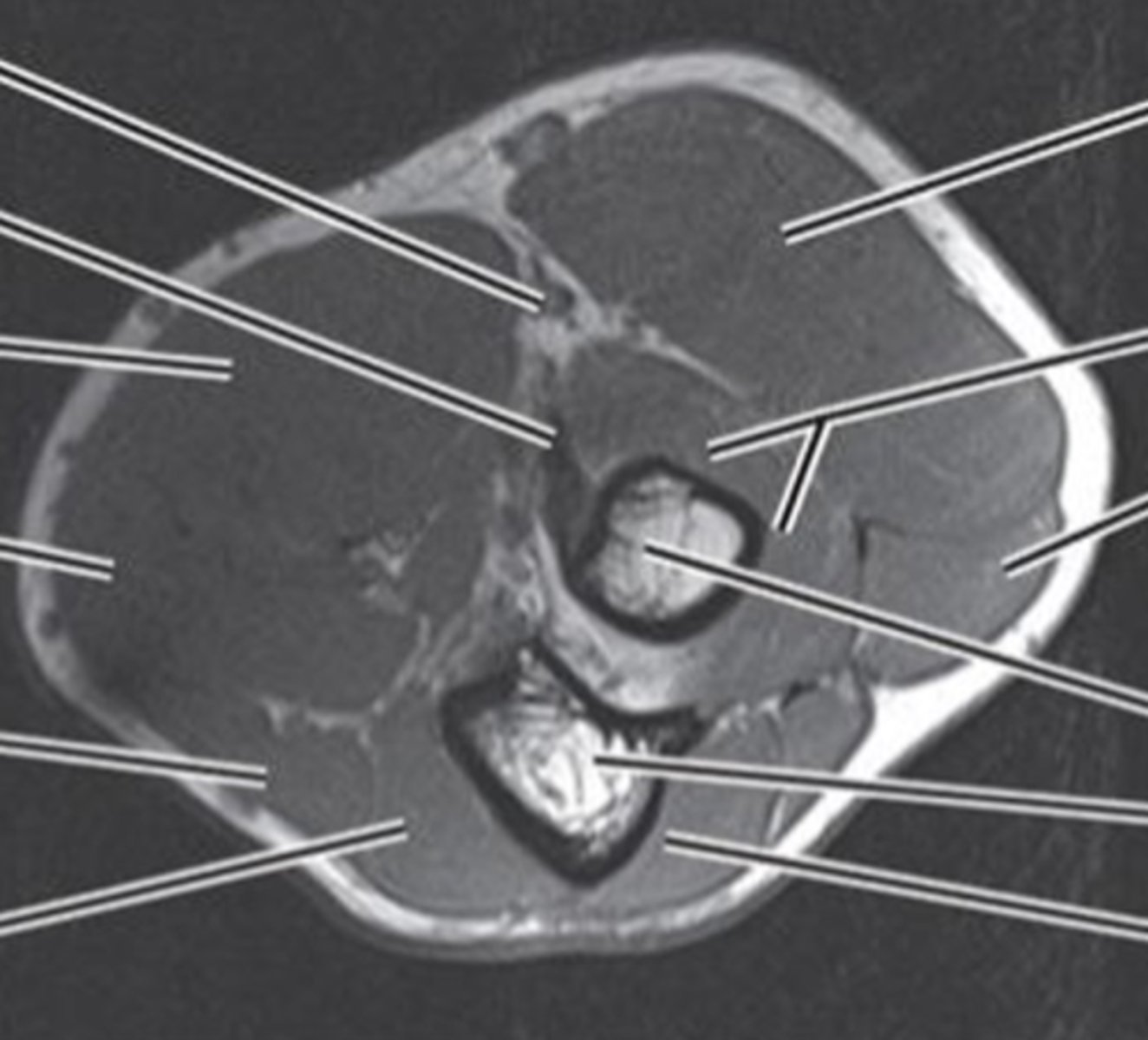
what can you see in axial plane MRI/CT elbow
- biceps tendon
- triceps tendon
- brachial artery
- radial/ulnar N
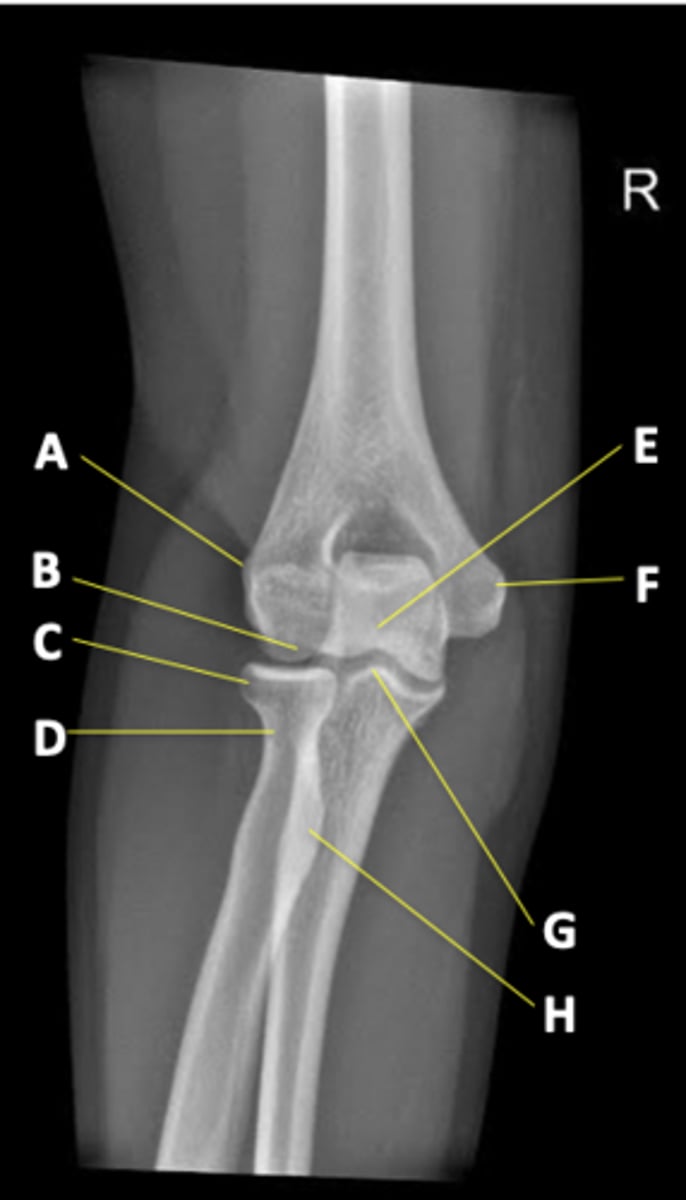
AP elbow radiograph elbow
anatomical position
lateral elbow radiograph elbow
articulations with humerus
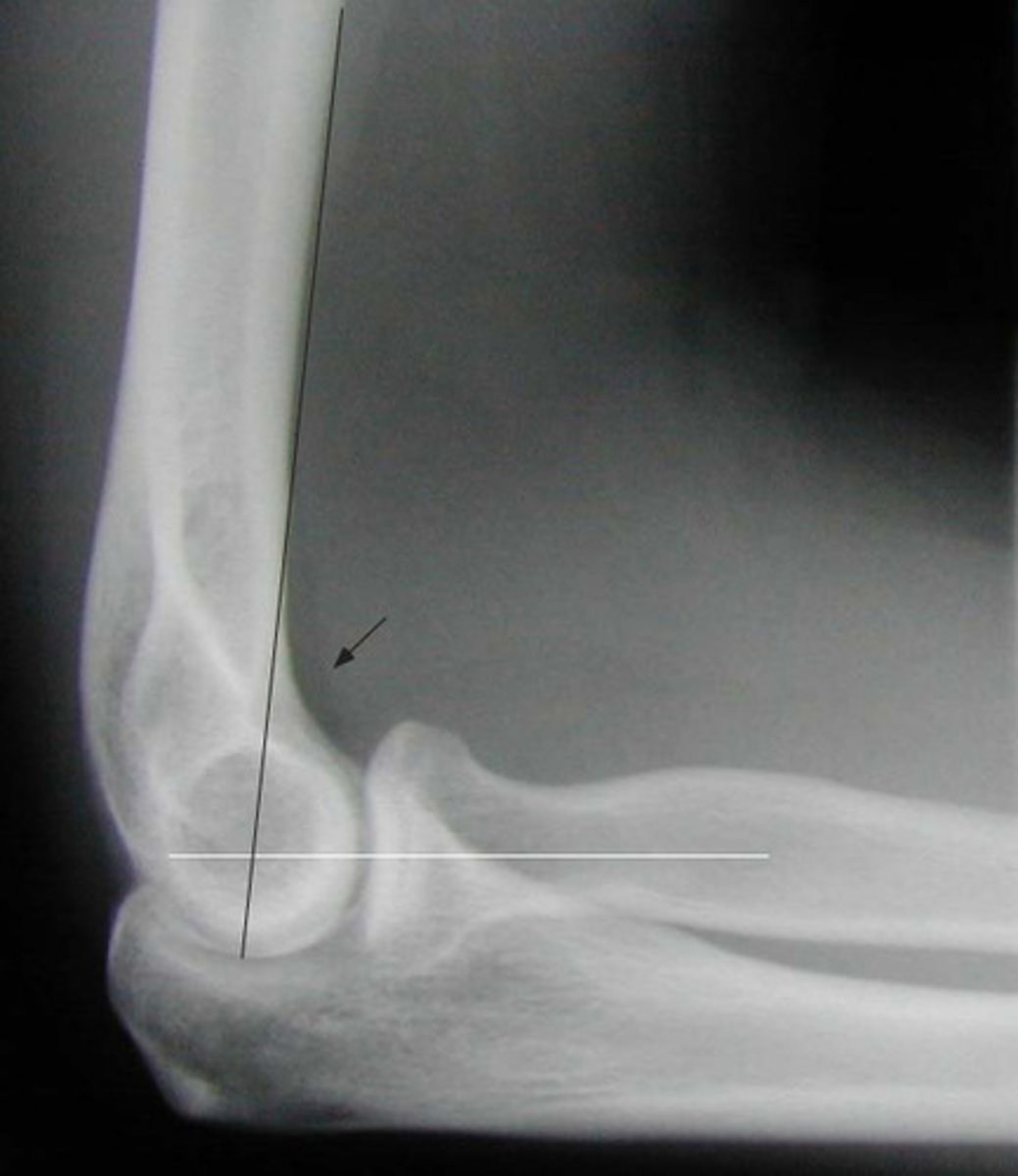
oblique IR radiograph elbow
medial epicondyle
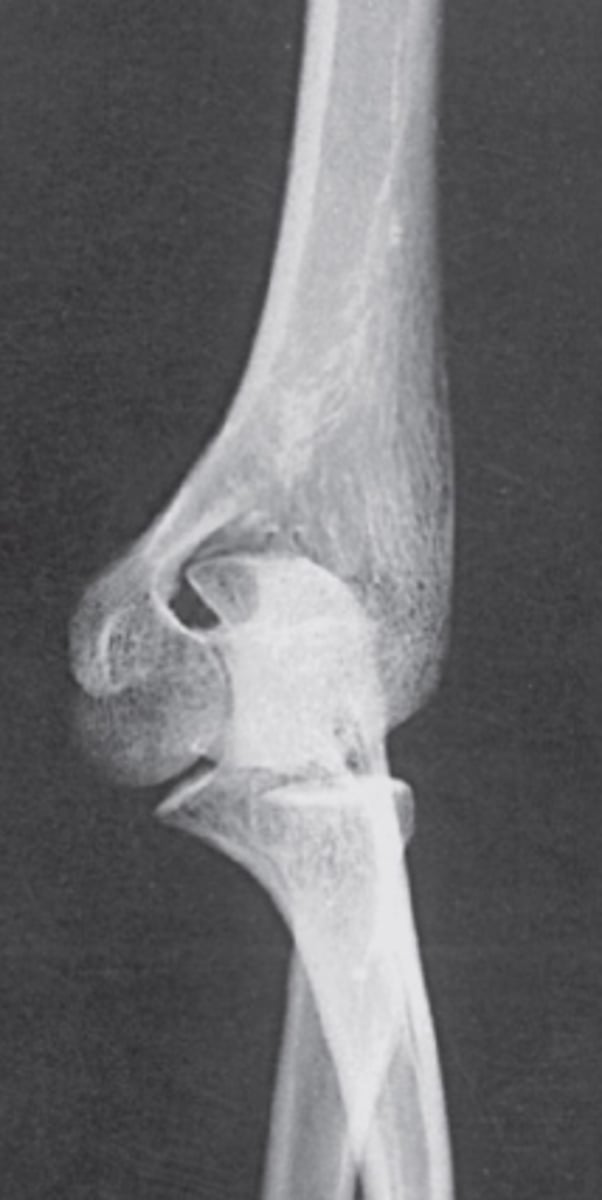
oblique ER radiograph elbow
radial head articulation with humerus
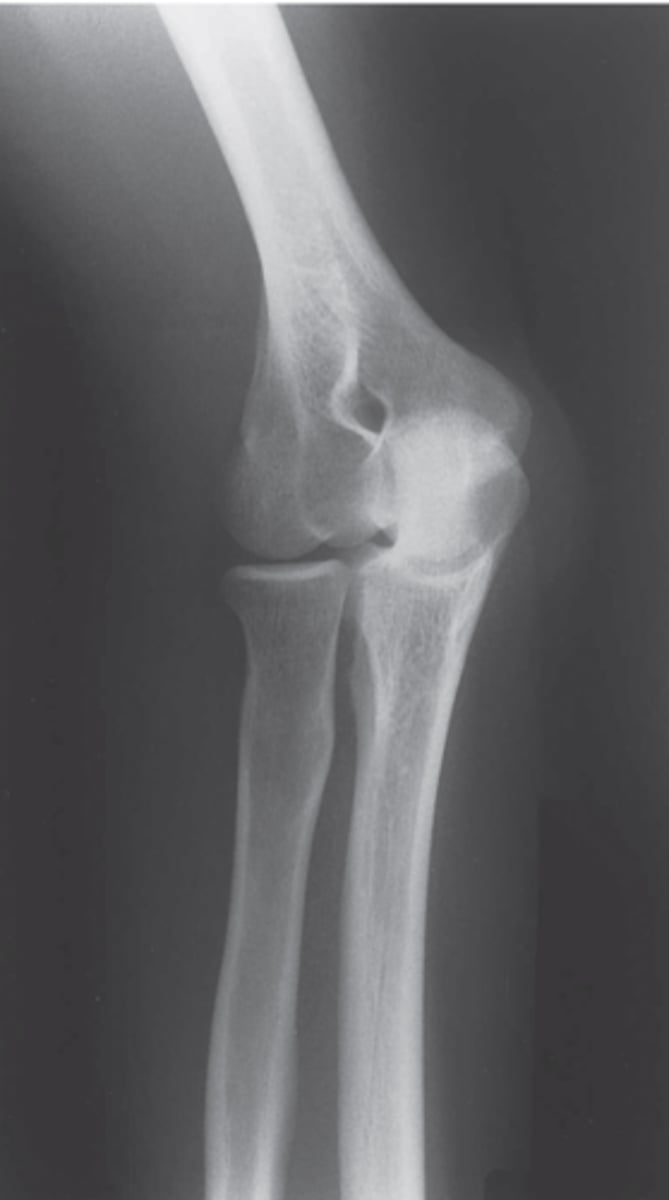
AP forearm radiograph
more focus on radius and ulna
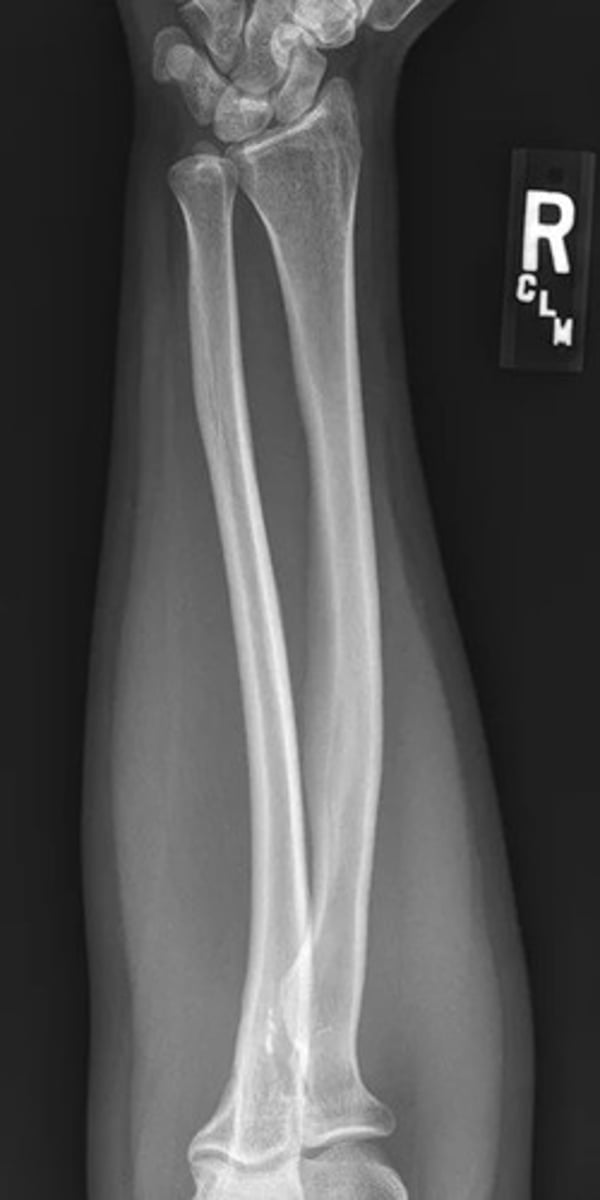
lateral forearm radiograph
ulnar head at wrist
radial head at elbow
labrum tears
image with MRA
- associated with dislocations, 3 types
- avulsion off glenoid rim (bankart fx)
- terar in substance of labrum
- SLAP lesion /biceps tendon
rotator cuff tears
use MRI to image
- can be complete or partial
- treatment depends on degree of tear
- surgery when >3 cm
AC joint laxity/sprain
image with AC radiograph with/without weights to image
- grade 1: mild sprain AC
- grade 2: AC torn and CC stretched
- grade 3: AC and CC torn
shoulder trauma neer classification
1 part: non displaced
2 part: displaced (2 pieces)
3 part: displaced (3 pieces)
4 part: displaced (4 pieces)
GH dislocation
mostly anterior (aB and ER)
- can cause hill sachs lesion (compression fx posteriolateral humeral head)
- bankart elsion (avulsion fx ant/inf labrum)
scapular fx
very rare
- caused by direct blow
clavicle fx
- classified by location (middle 1/3 most fragile)
- can be birth related
- seatbelt in car accident
- treated by immobilizing
- complications: malunion, nerve/vascular concern
proximal humerus fx
- humeral head (anatomical neck)
- greater tuberosity (supra, infra, teres minor)
- lesser tuberosity (subscap)
- shaft at surgical neck
what imaging should you use for proximal humerus fx
AP scapular and y-view
- treatment depends on stability and displacement
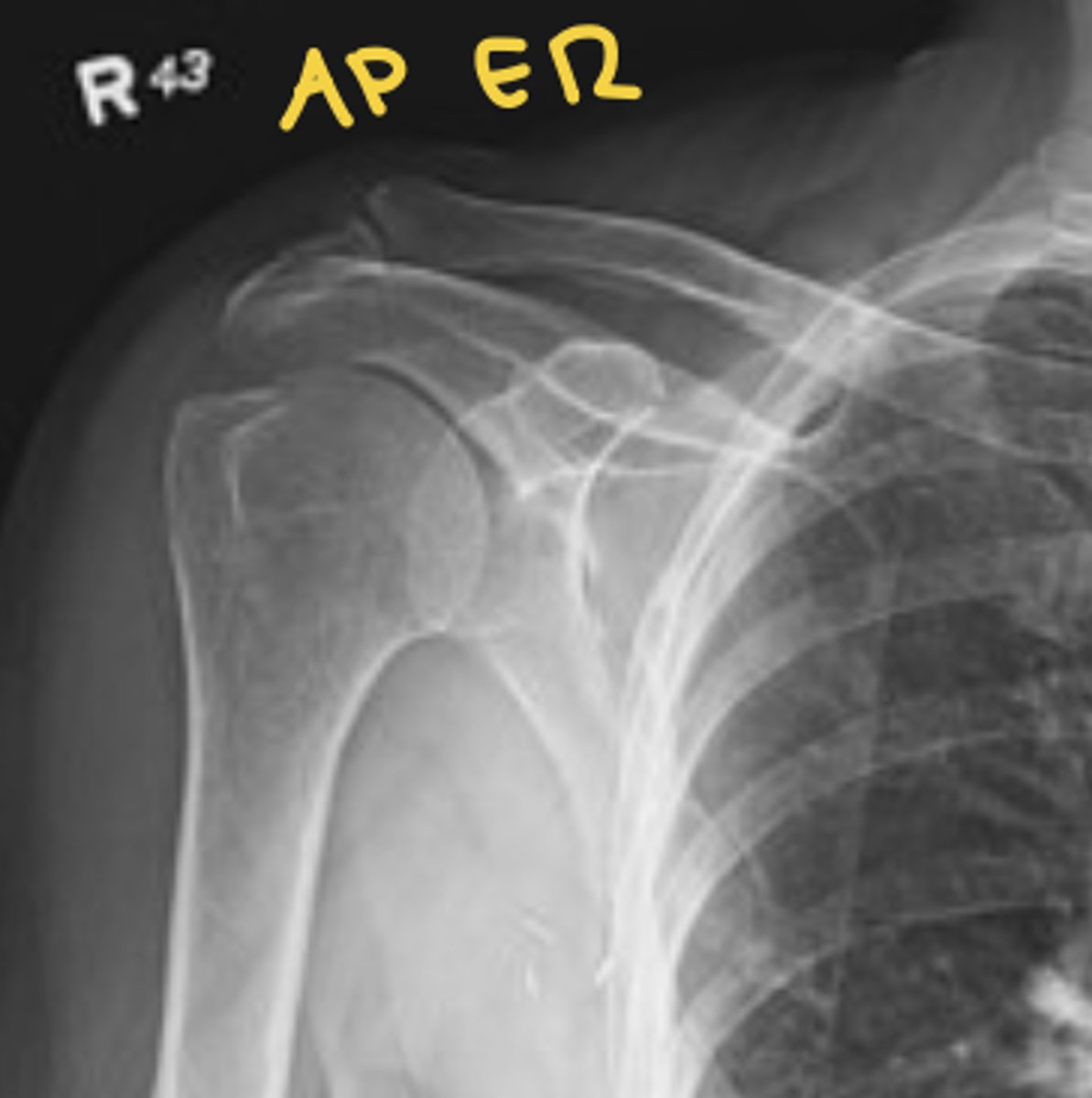
shoulder AP ER radiograph
see greater tuberosity
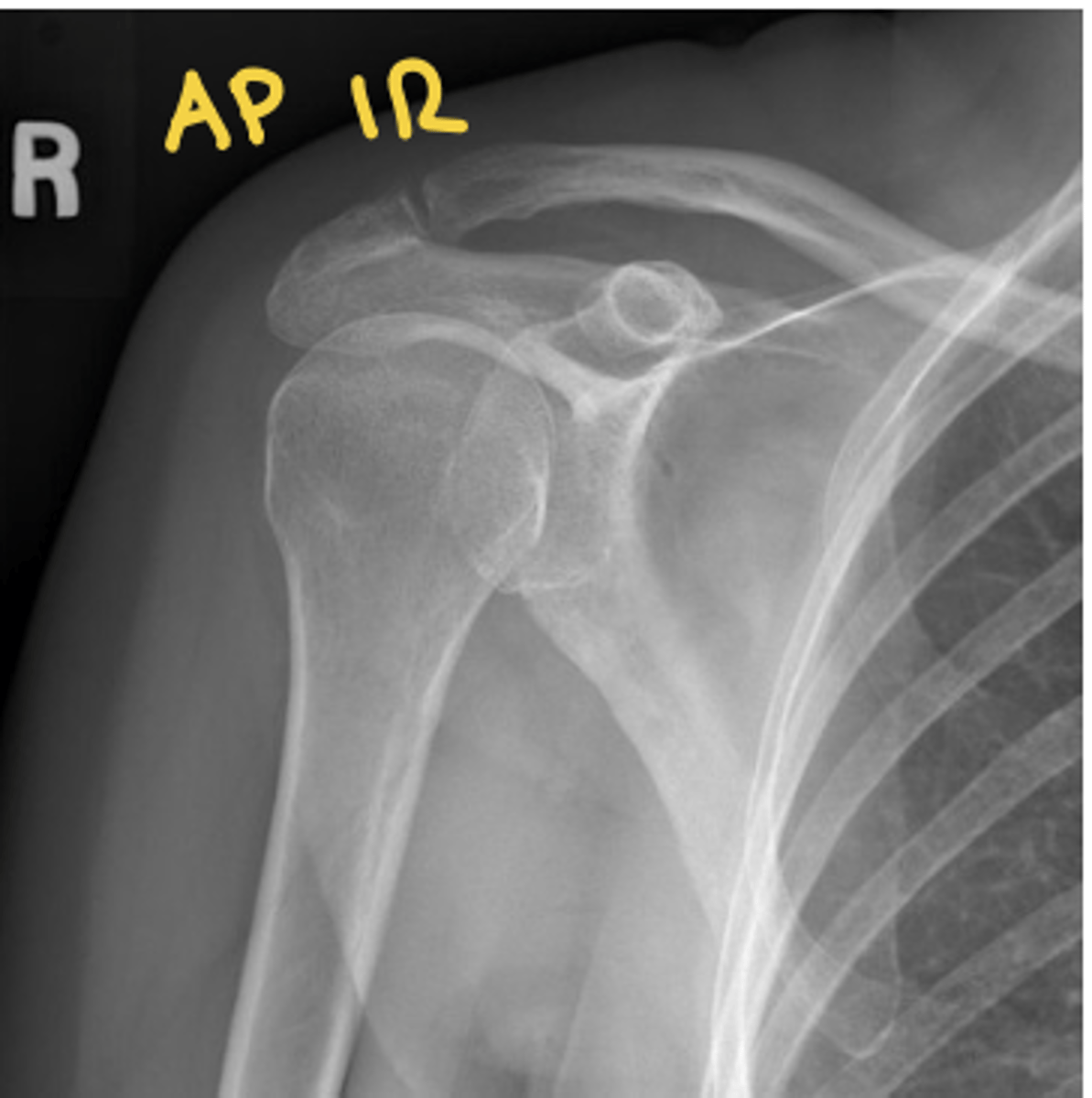
shoulder AP IR radiographs
see lesser tuberosity
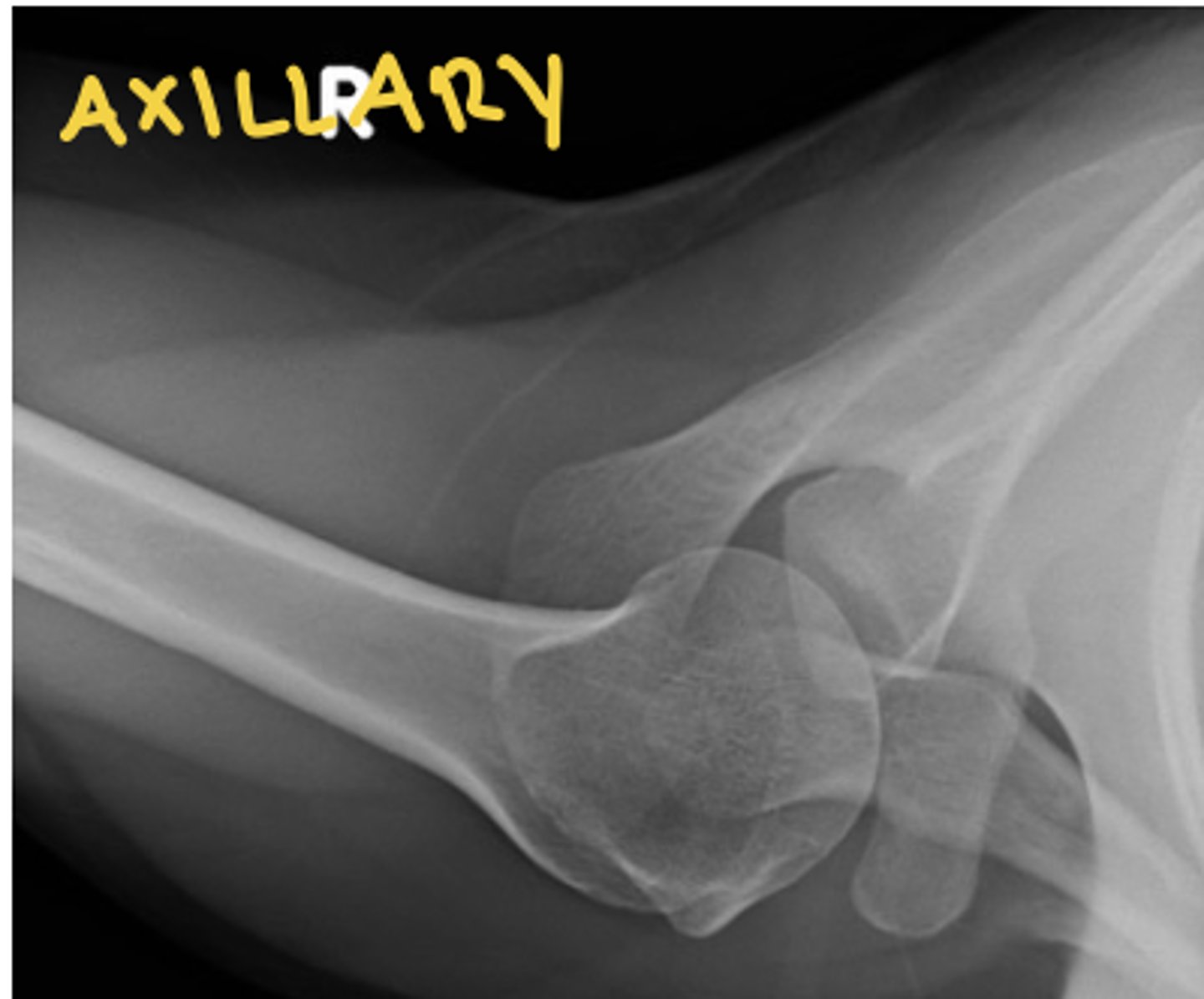
shoulder axillary view radiograph
see acromion, glenoid, and coracoid
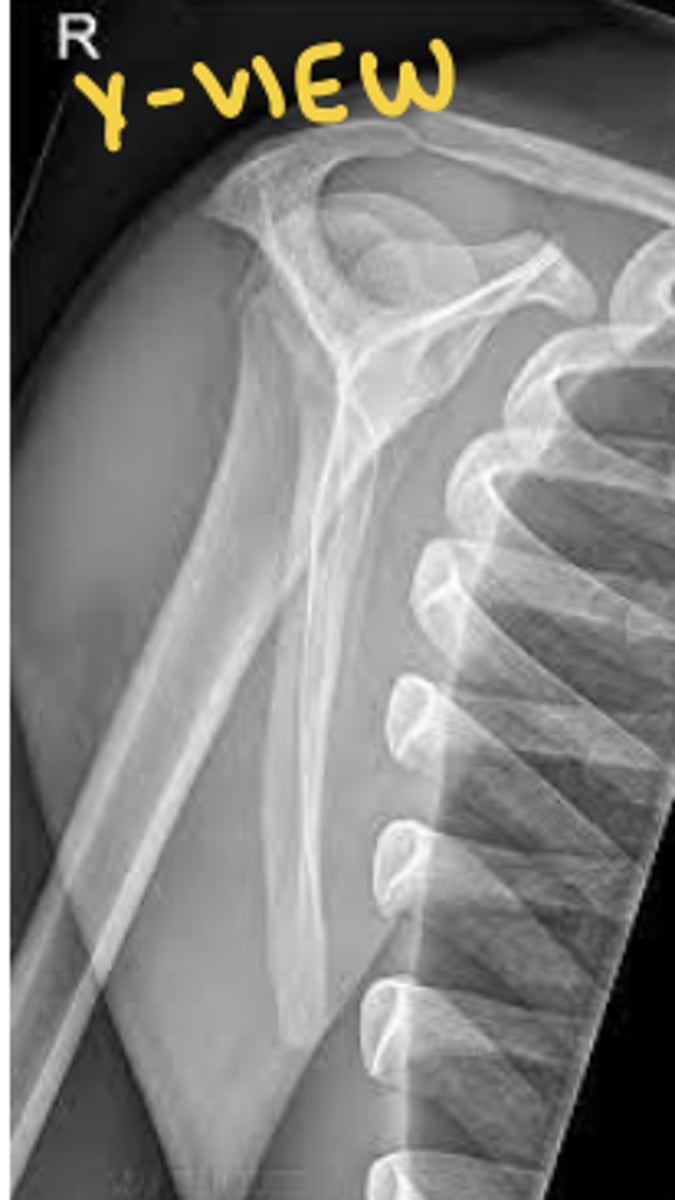
shoulder anterior oblique (y-view) radiograph
still see humerus and lateral scap
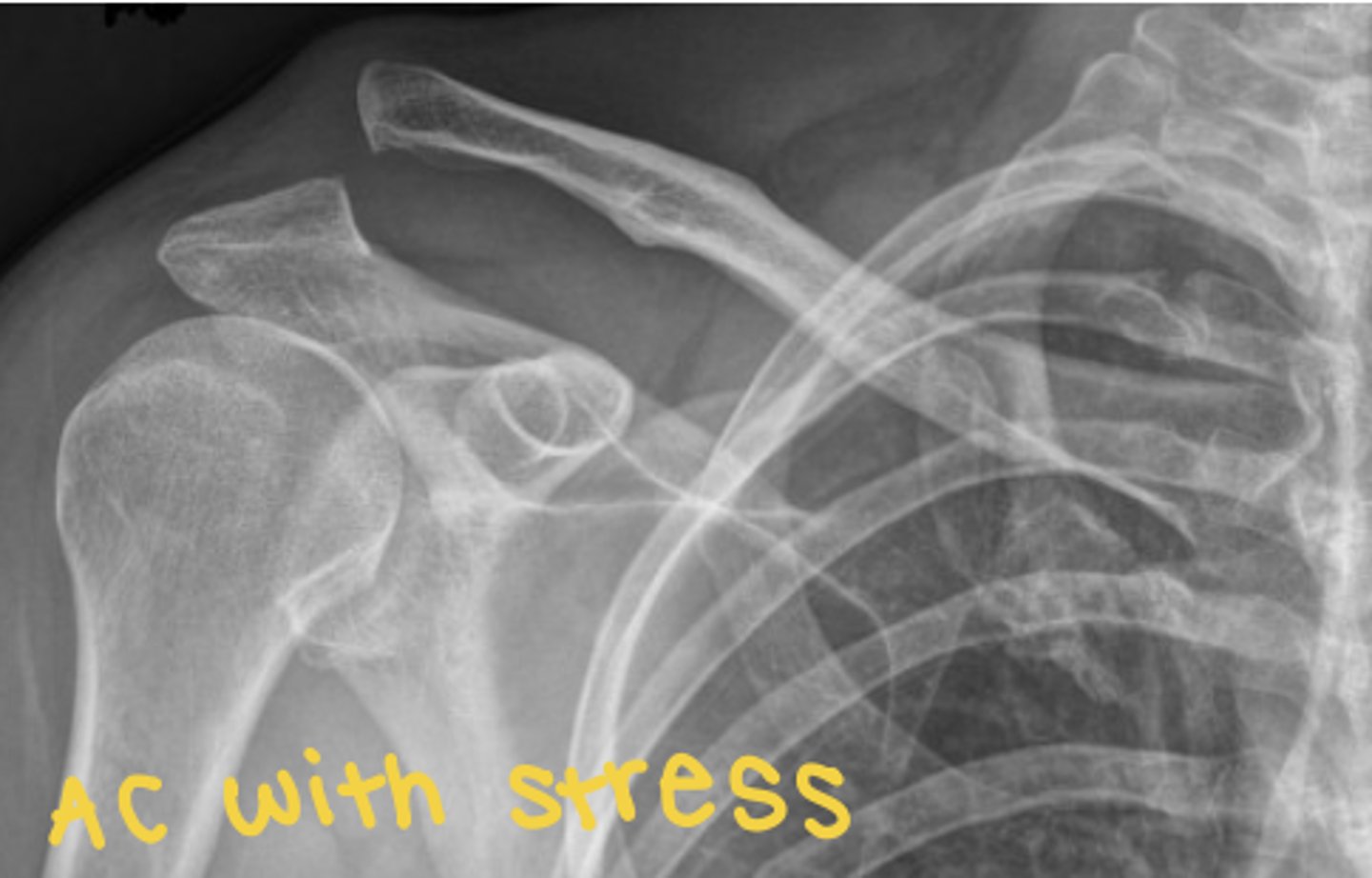
AP with and without stress (AC stress) radiograph
separates AC joint slightly
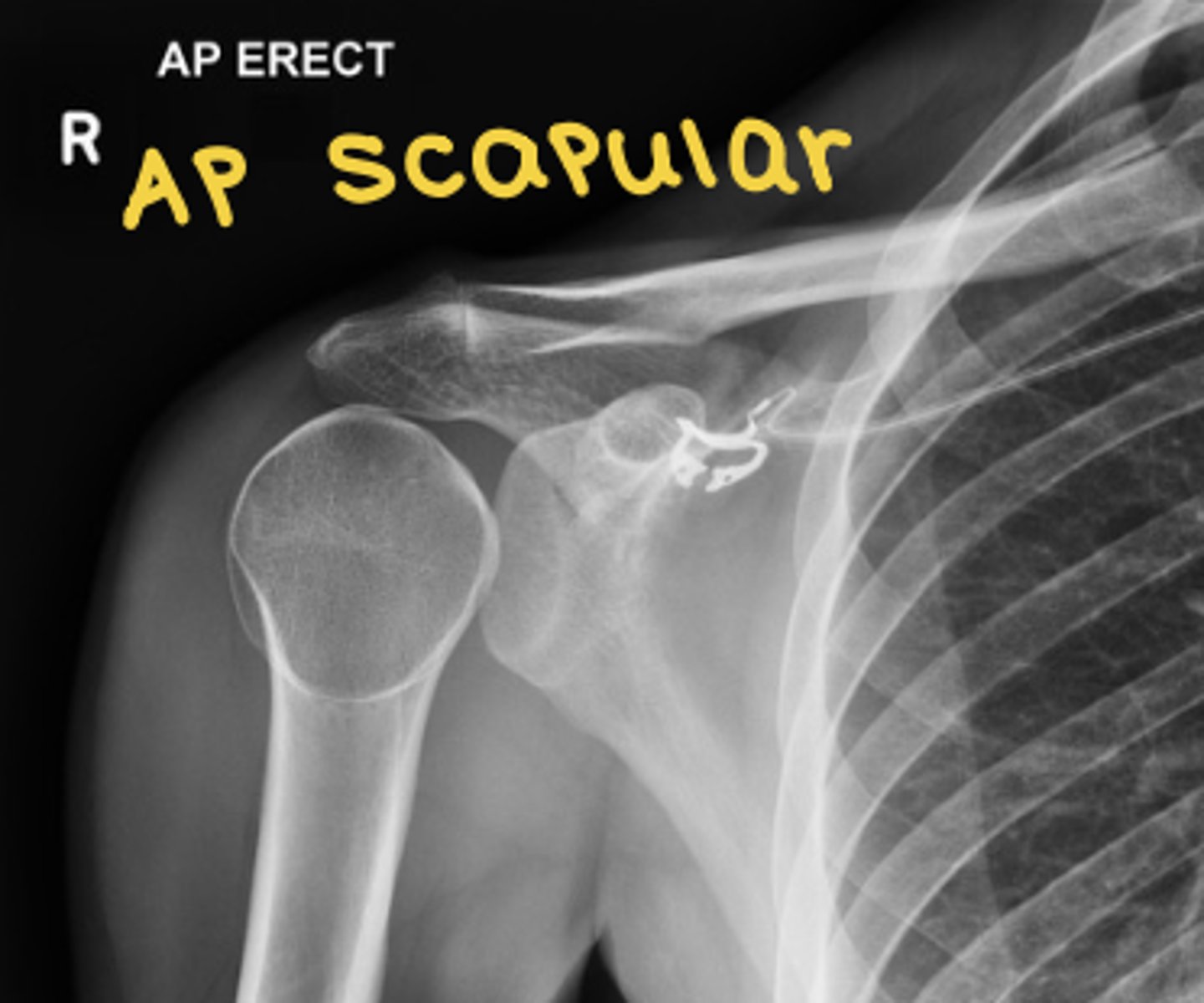
AP scapular view radiograph
clearest view of scapula
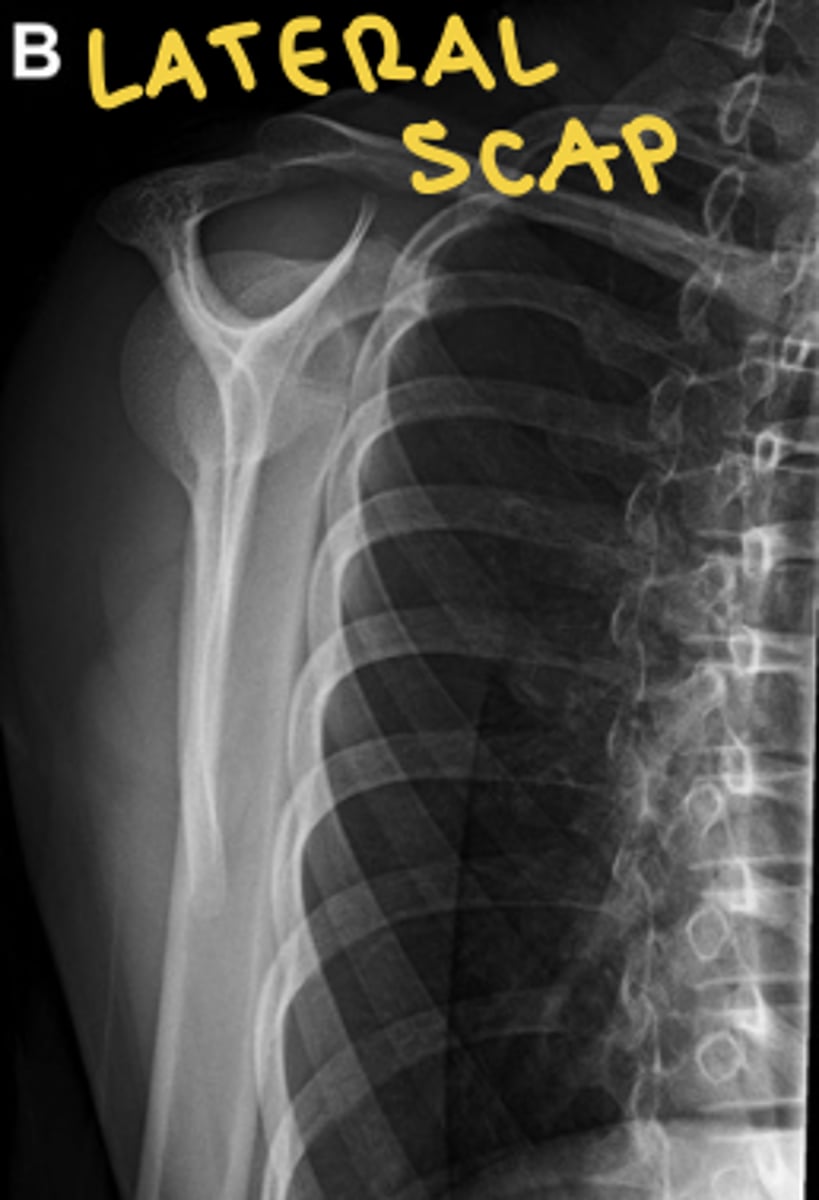
lateral scapular view radiograph
space between scapula and ribs
when should u take an MRI of the shoulder
- muscle/tendon injury
- long head of biceps disorders
- labral injuries
- ligament injuries
axial plane MRI/CT of shoulder
see biceps tendon and labrum
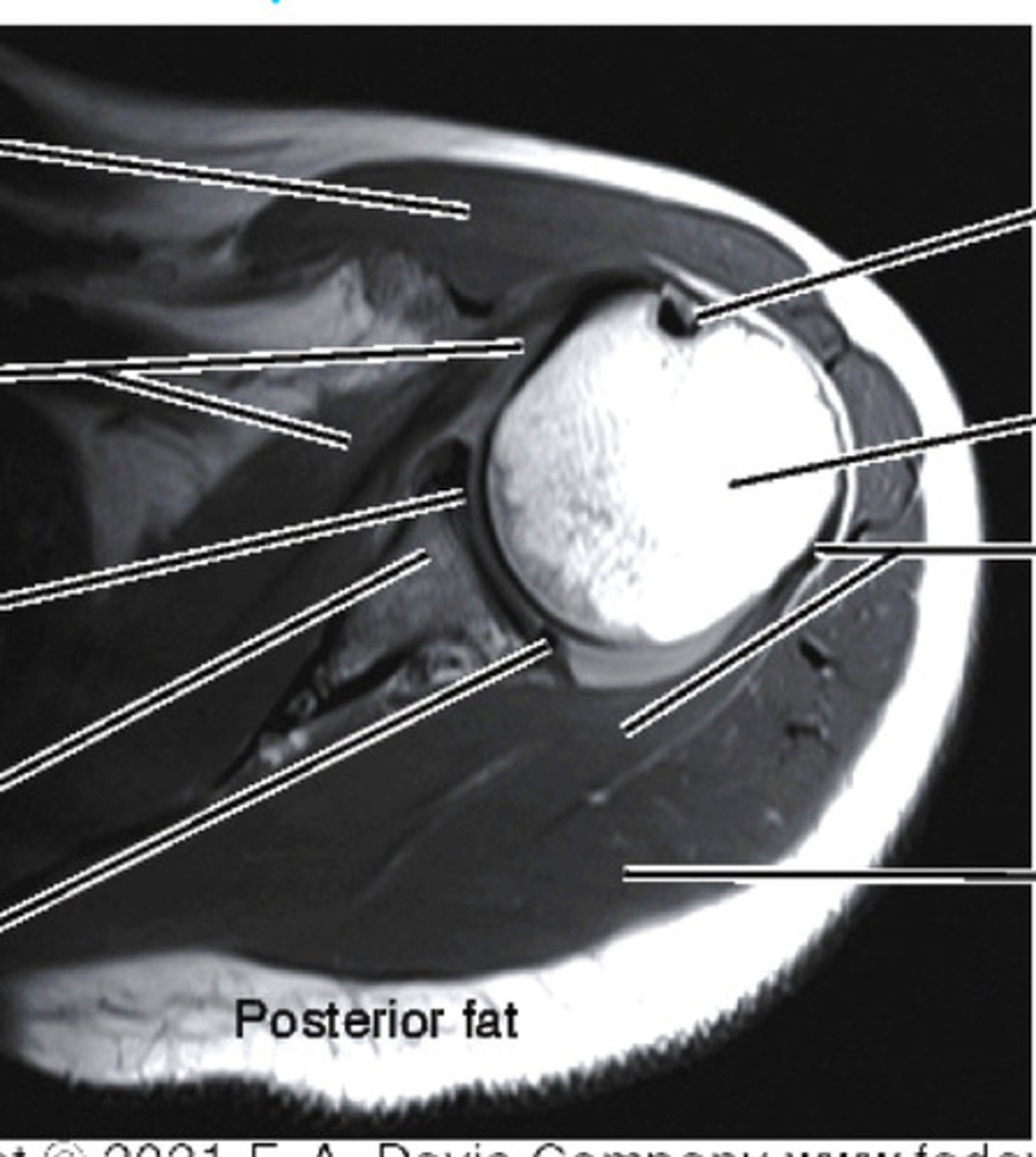
saggital plane MRI/CT of shoulder
- supra/infraspinatus
- acromion
- coracoacromial site
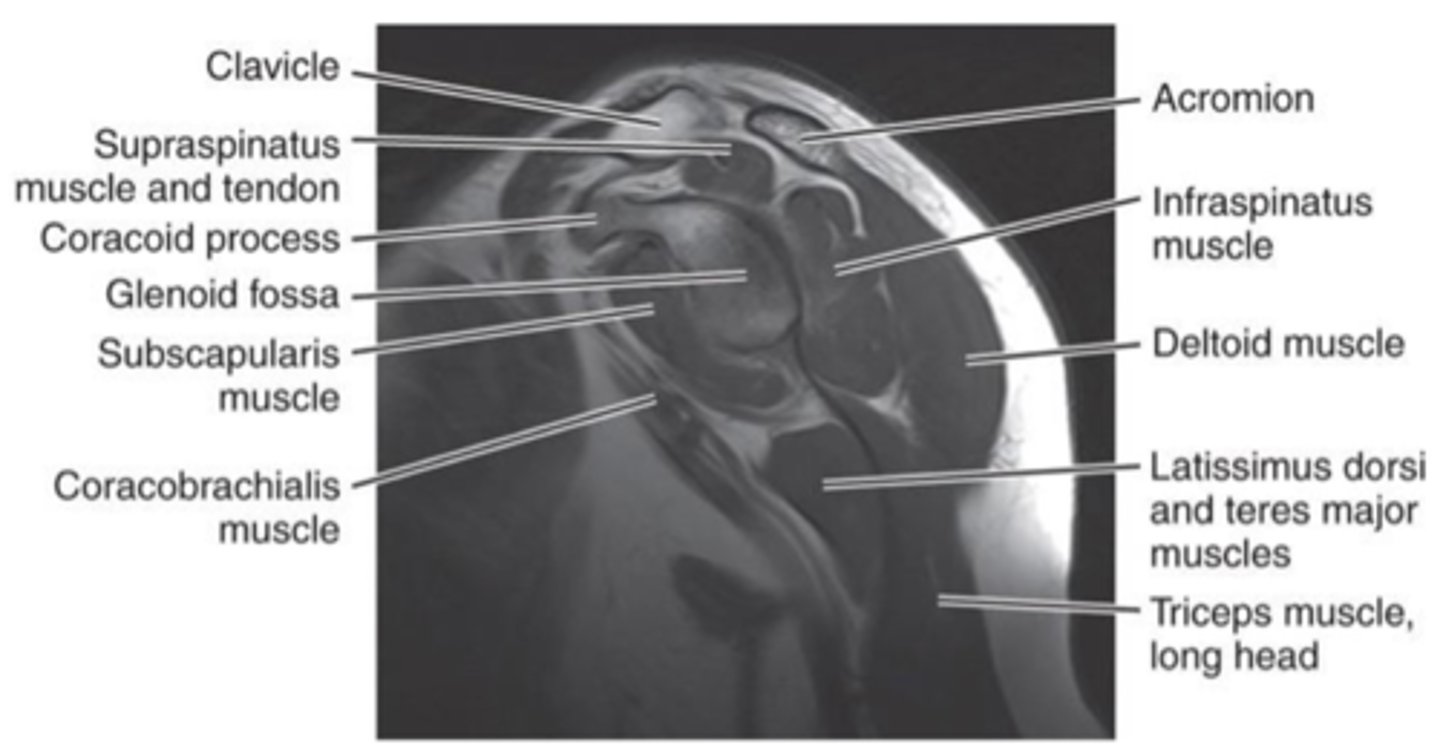

coronal plane MRI/CT of shoulder
see GH joint and AC joint
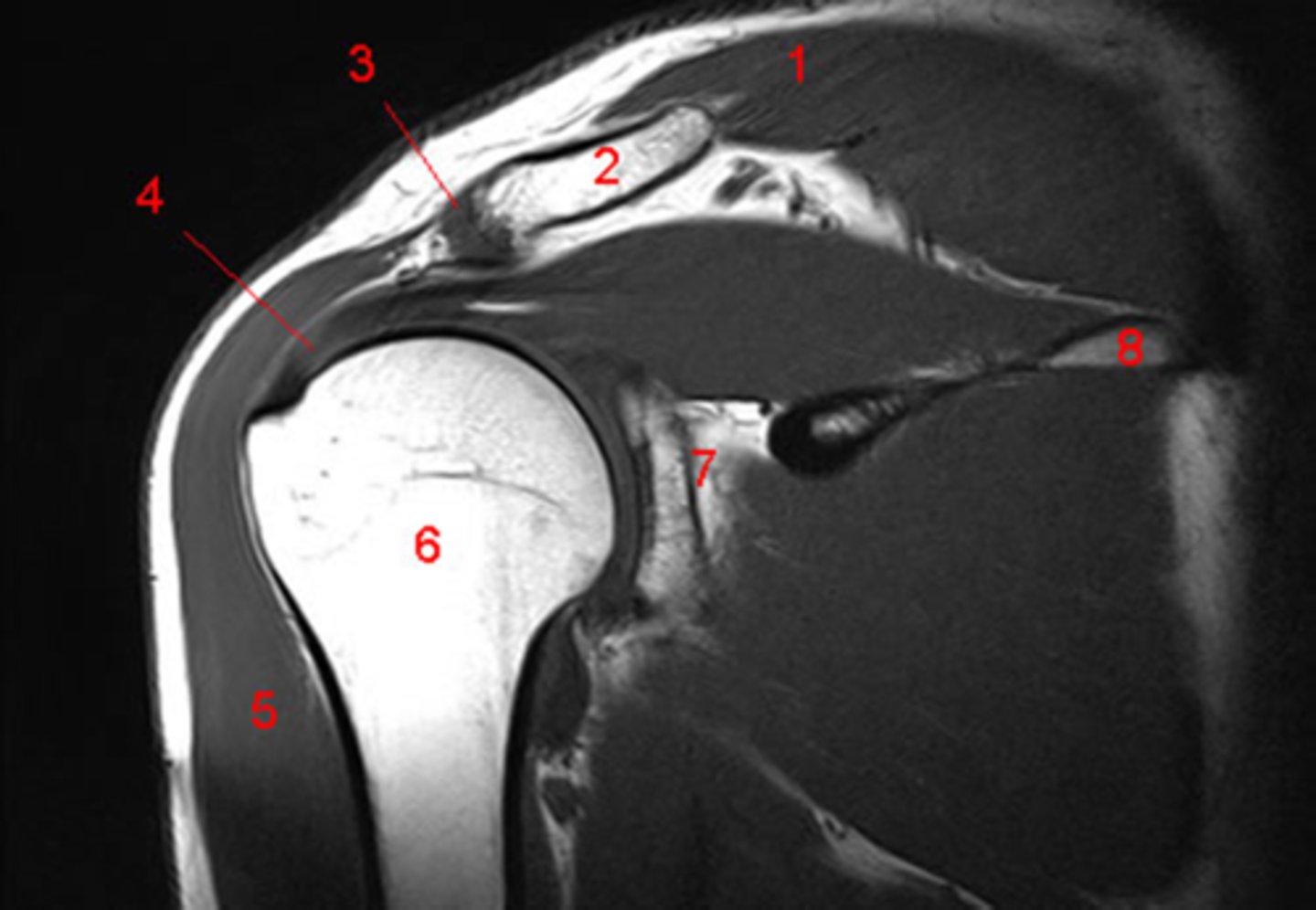
types of foot fractures
- talar fx (poor blood supply, concern for necrosis)
- calcaneal fx (long rehab process)
- midfoot fx (lisfranc or navicular)
- forefoot fx (metatarsals or phalanges)
ankle fx
- unimalleolar
- bimalleolar
- trimalleolar (malleoli and posterior rim tibia)
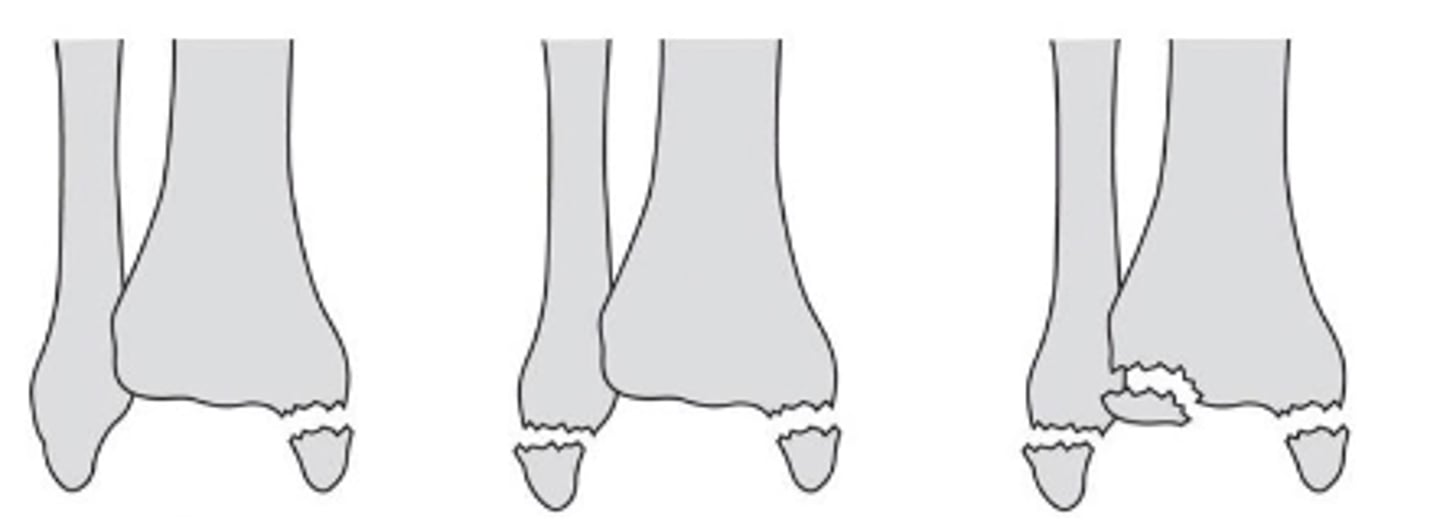
foot deformities
- hallux valgus (1st met deviates medially >10 degrees)
- pes cavus (high arch)
- pes planus (flat foot)
- talipes equinovarus (clubfoot)
talometatarsal angle
intersection of midshaft 1st met and talus (use WB radiograph to view)
- normal angle = 0 deg
tendon pathologies of the foot
use MRI to image
- achilles tendon
- tendons of fibularis longus/brecis after inversion stress injury
ankle sprain
inversion most common
- usually dont need imaging, can be used for avulsions due to pull of ligament
ottowa foot rules
tenderness at navicular or base of 5th met
- inability to WB
ottowa ankle rules
tenderness of medial or lateral malleoli
- inability to WB
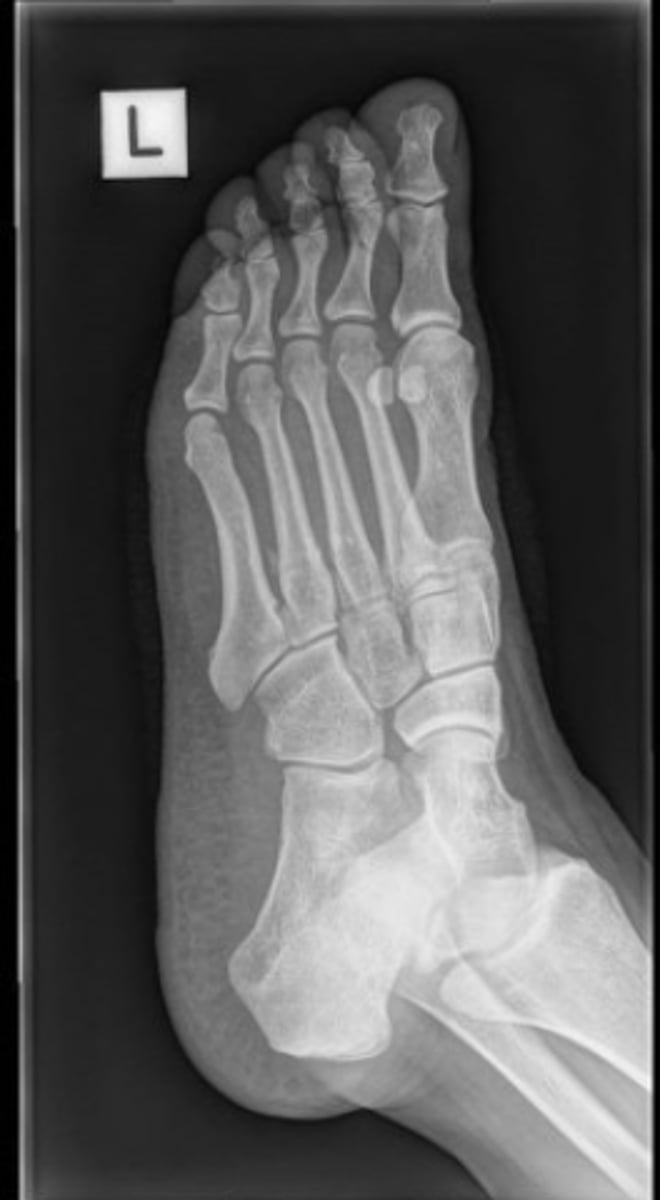
AP foot radiograph
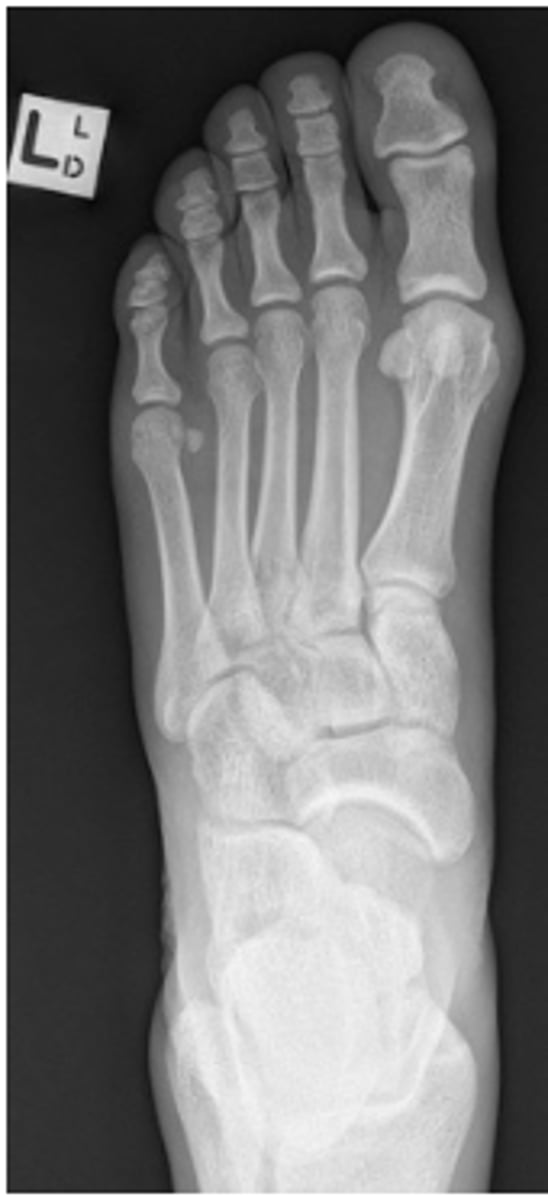
lateral foot radiograph
oblique foot radiograph
AP ankle radiograph
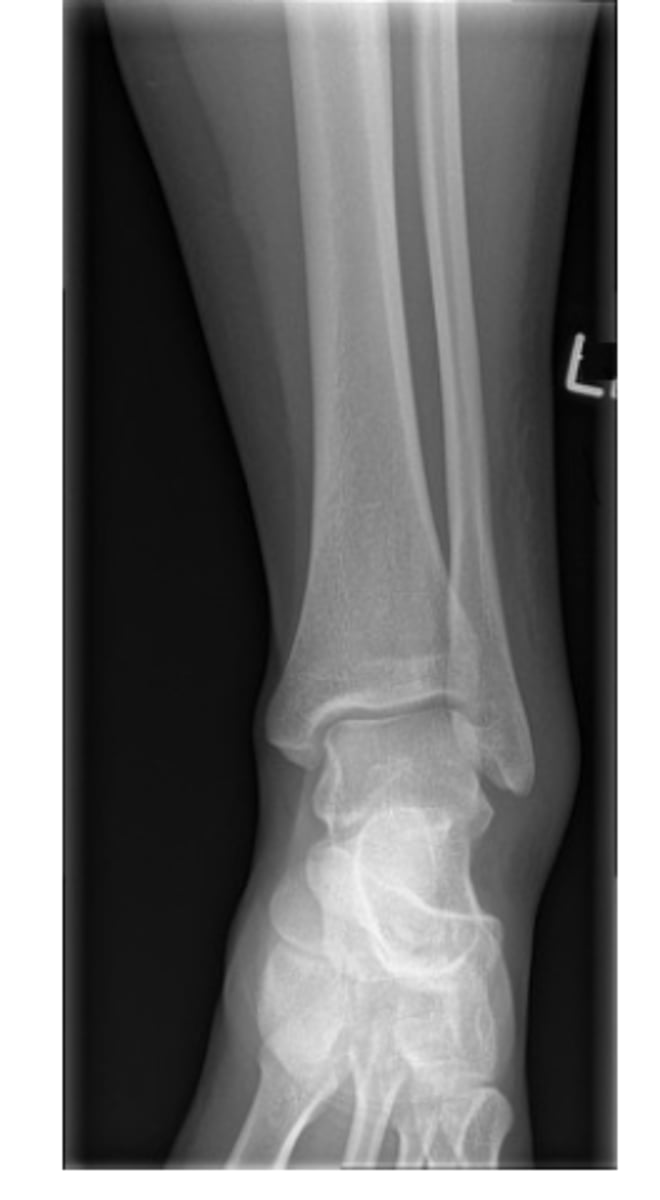
AP oblique/mortise ankle radiograph
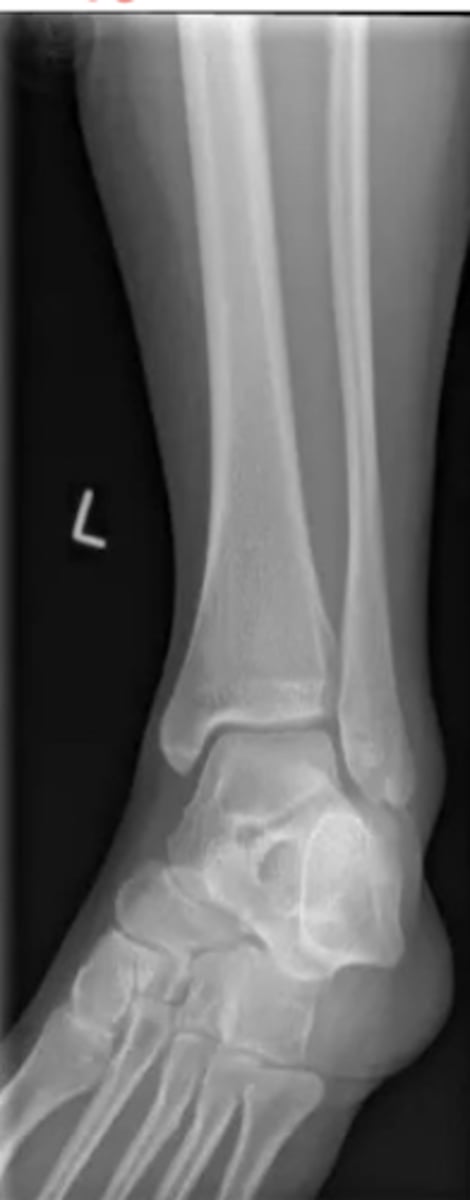
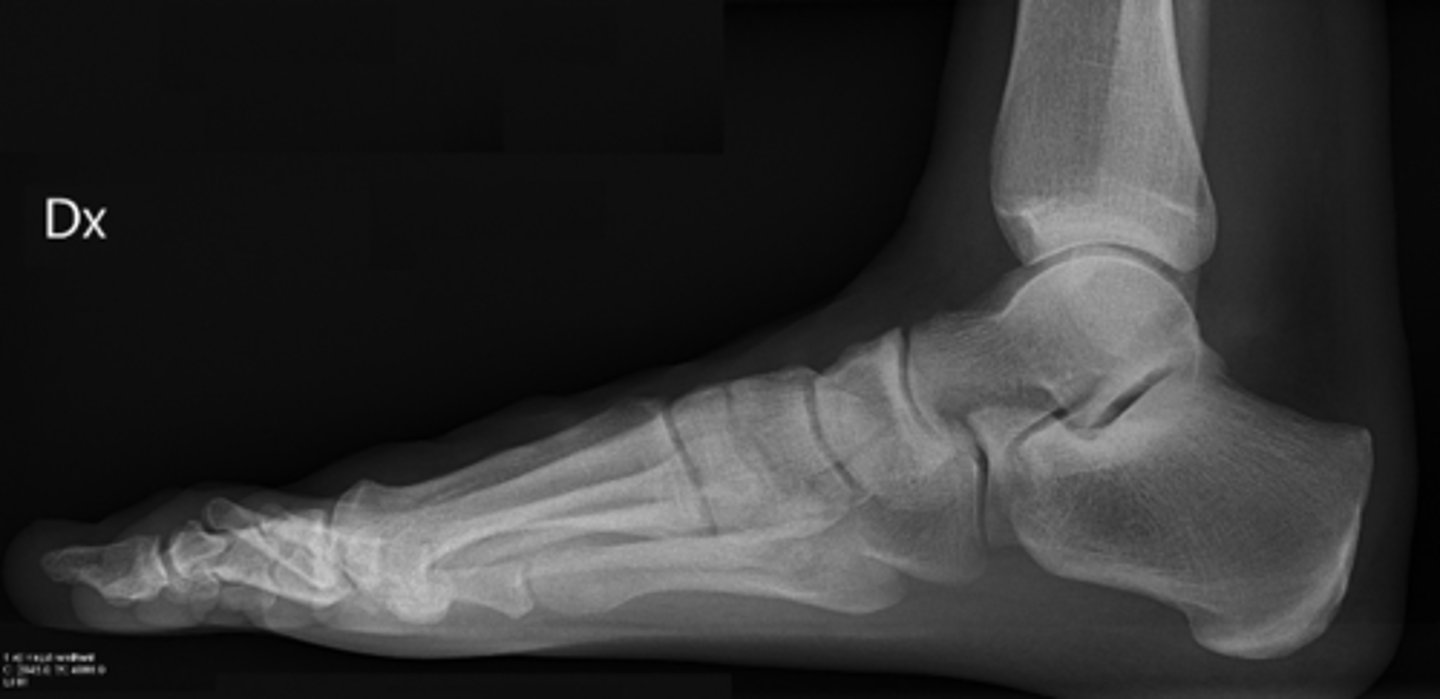
lateral ankle radiograph
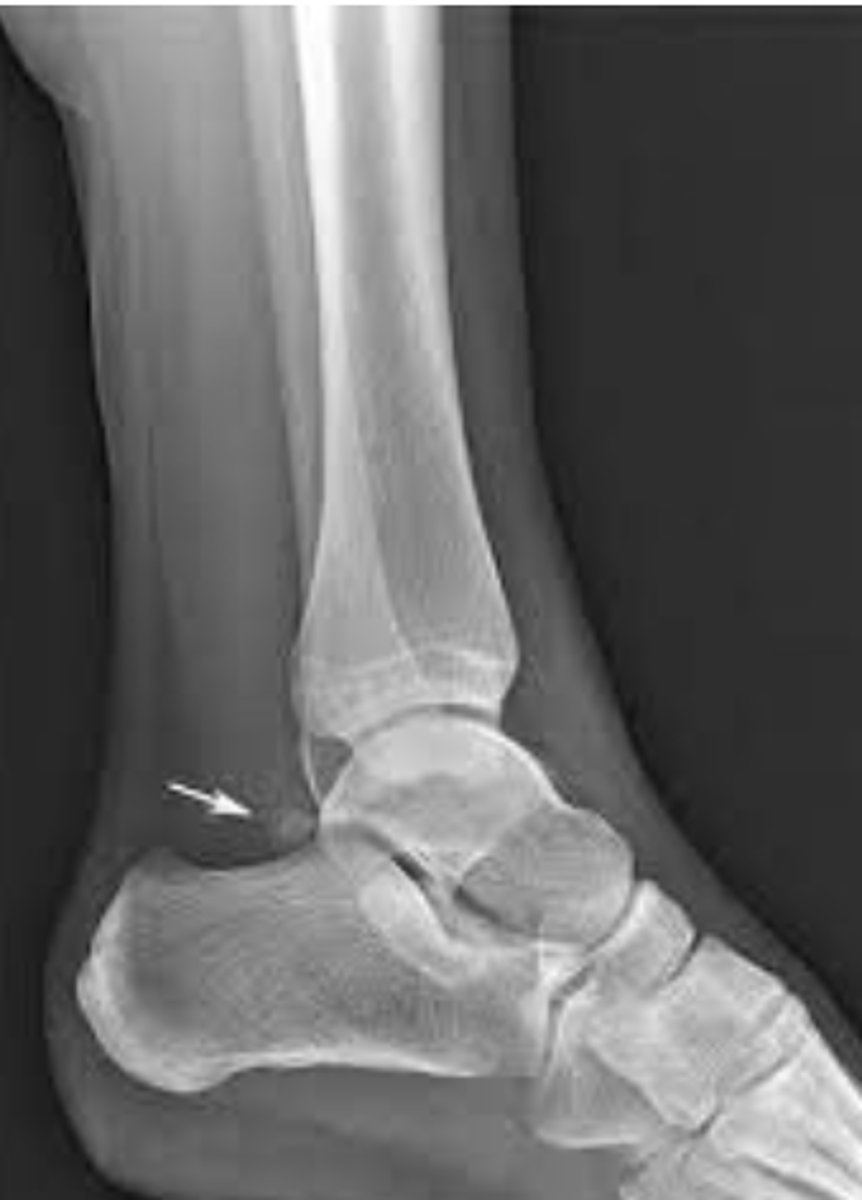
stress view ankle radiograph
for alignment/positioning
- use eversion/inversion
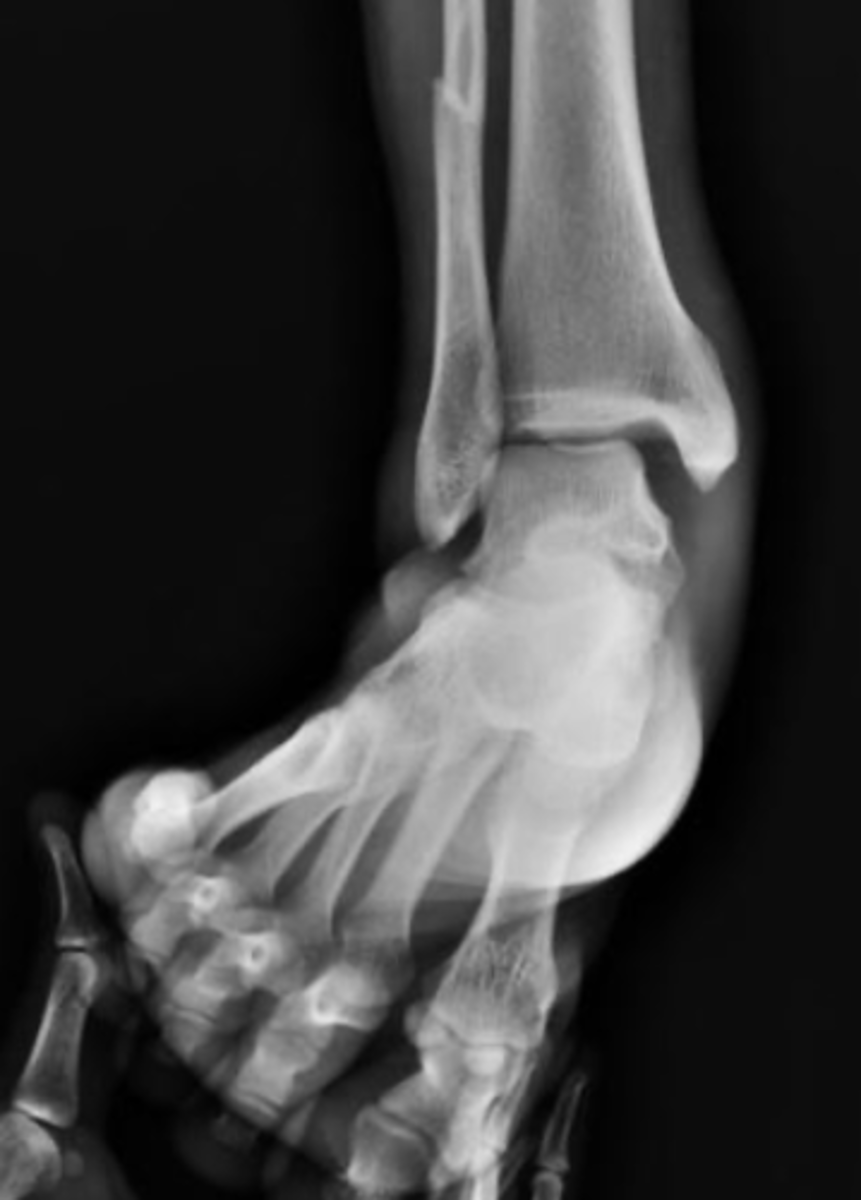
patellofemoral dislocations
acute or chronic
- medial/lateral dislocation = tangential view
- superior/inferior dislocation = lateral view
patella fx
- transverse (displaced or nondisplaced, use lateral x-ray to see)
- vertical (displaced or non displaced)
- comminuted (displaced or nondisplaced)
- avulsion
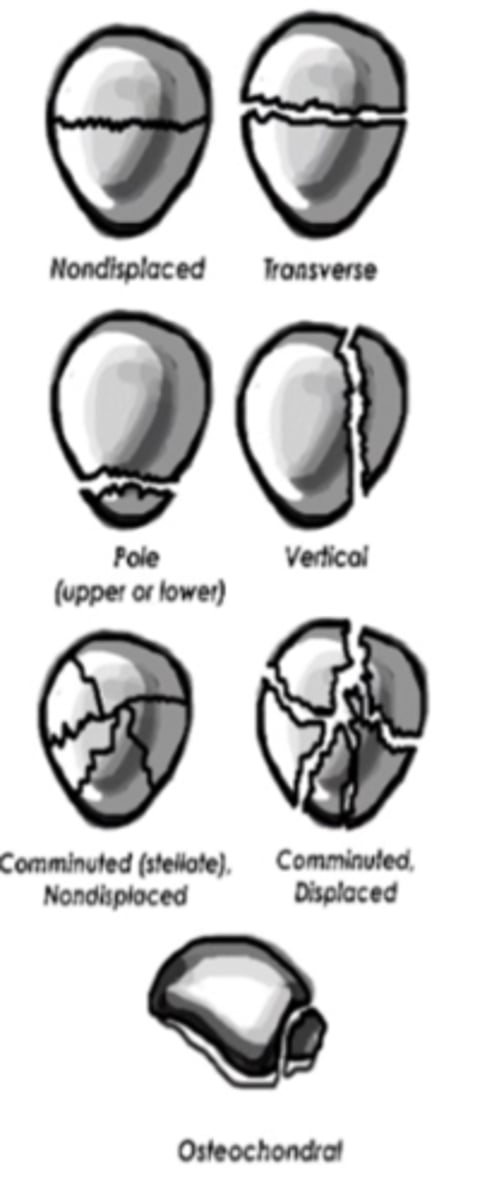
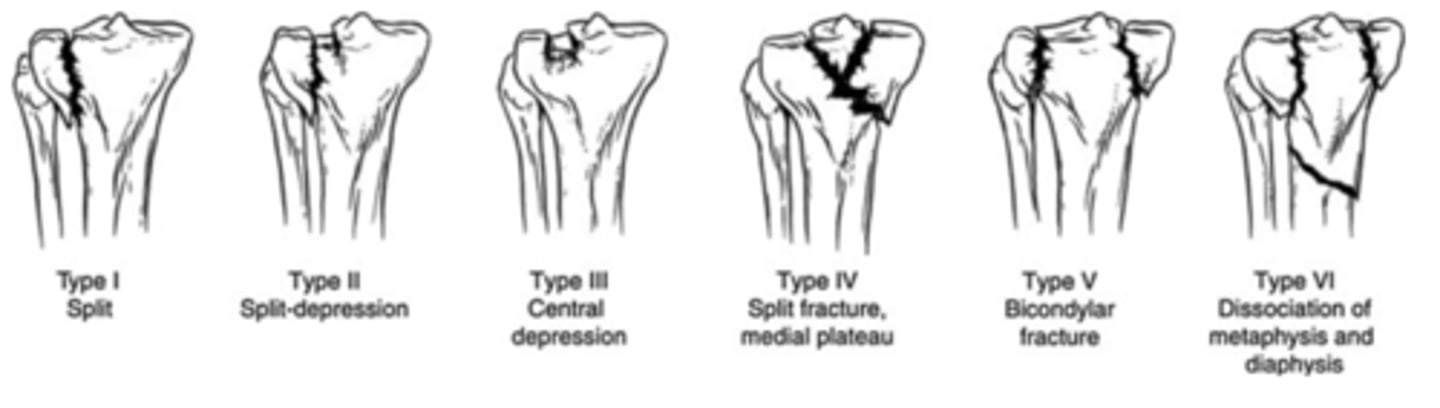
proximal tibial fx
6 types
1: wedge/split of lateral aspect of plateau
2: lateral wedge or split fx
3: pure compression fx lateral plateau
4: involves medial plateau
5: split fx of both condyles
6: complete bicondylar fx
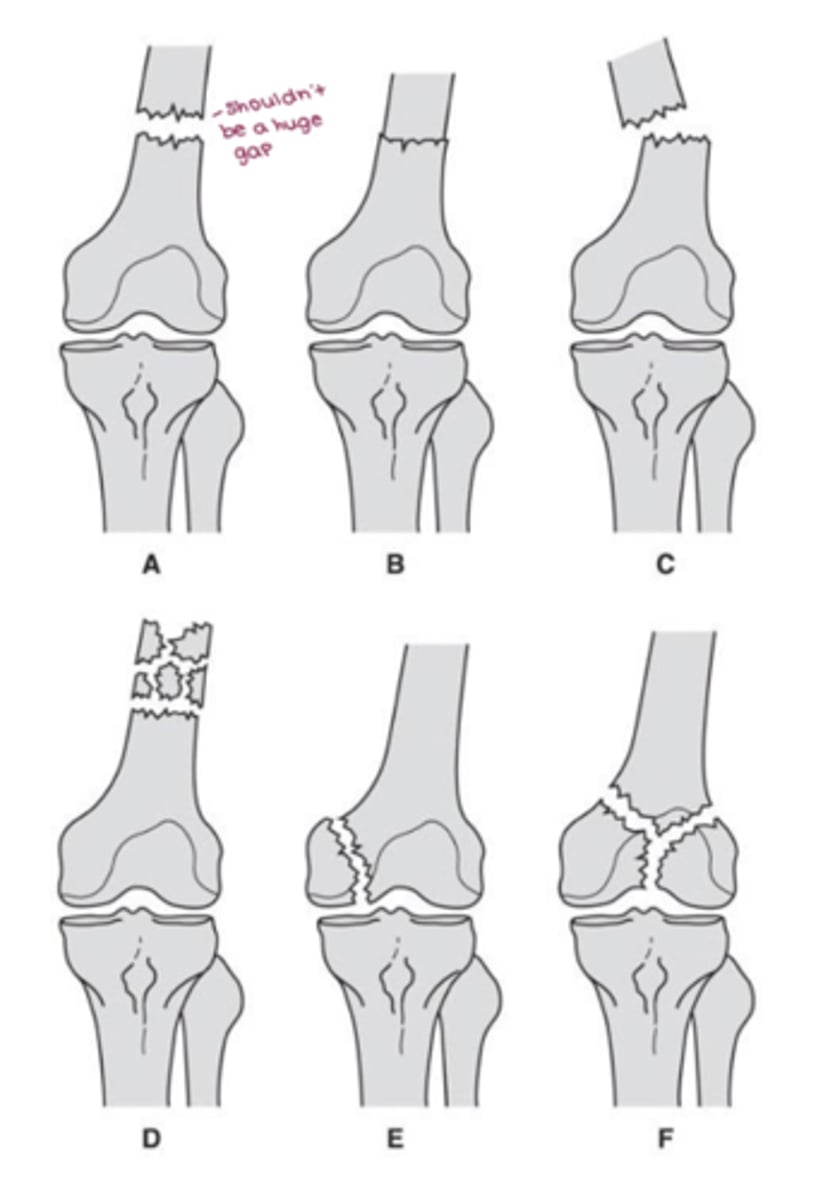
distal femur fx
- supracondylar (nondisplaced, impacted, displaced, comminuted)
- condylar (fx at condyle)
- intercondylar (between condyles)
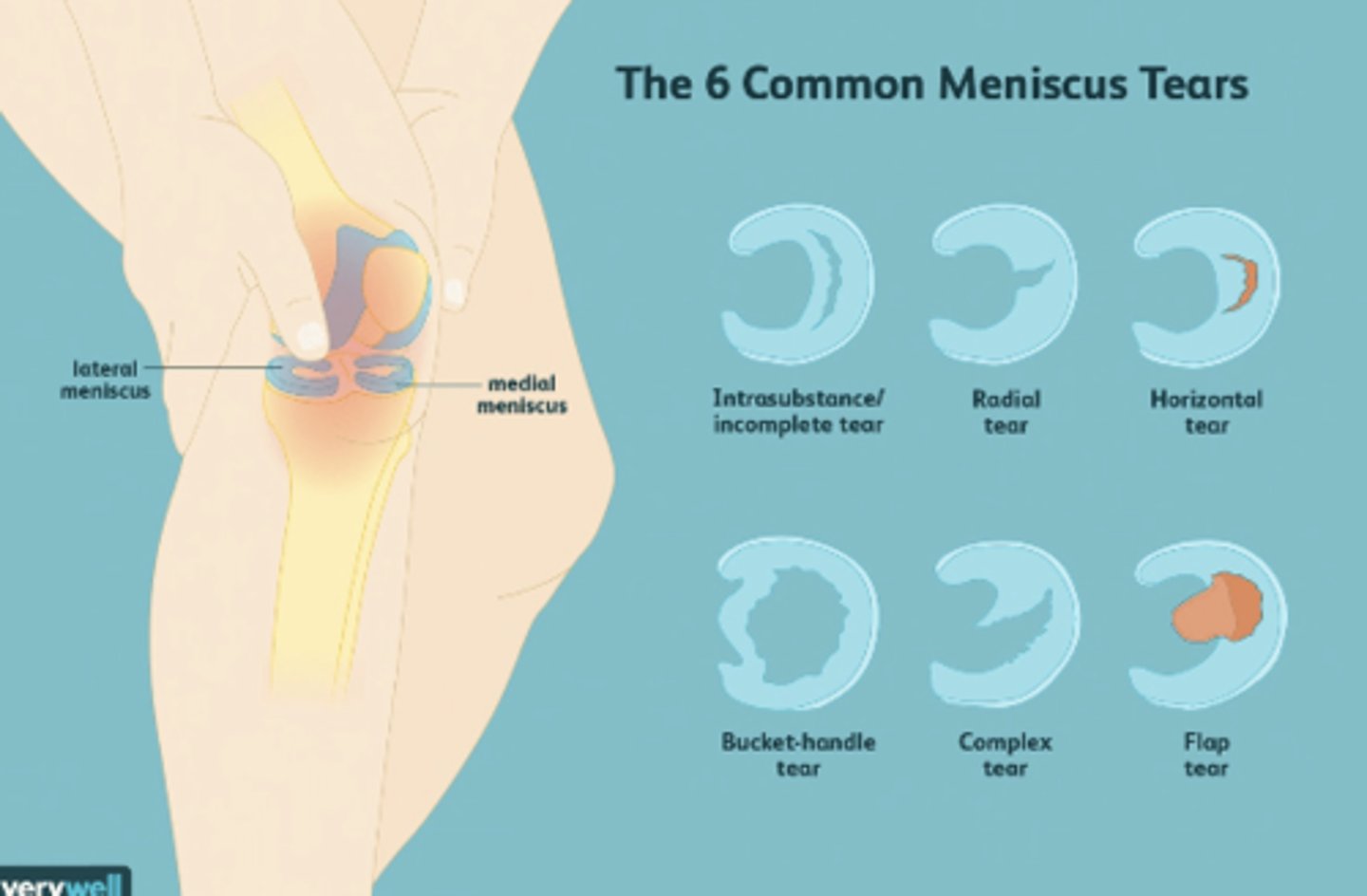
meniscal tears
use MRI fofr imaging
- soft tissues
knee cartilage injuries
- osteochondral fx (young atheltes)
- osteochondritis dessicans
- spontanous osteonecrosis (older adults)
rules for knee radiograph
- joint effusion after direct blow/fall
- mobility to walk without limping
- palpable tenderness over patella or fibular head
- inability to flex knee to 90 deg
- age >55
knee fxs
- distal femur fracture
- patellar fracture
- patellar dislocations
- proximal tibial fx
DJD/OA of the knee
- reduction in joint space
- sclerosis of subchondral bone
- osteophytes at joint margin
- subchondral cysts
- could have varus or valgus deformities
osgood schlatter disease
- enlarged tibial tubercle
- repetitive trauma at distal tendon attachment
- common in adolescent boys
- USE LATERAL RADIOGRAPH
imaging for ligament injuries in the knee
- cruciate ligament tears: MRI
- collateral ligament tears: stress x-ray
- avulsion fx: x-ray
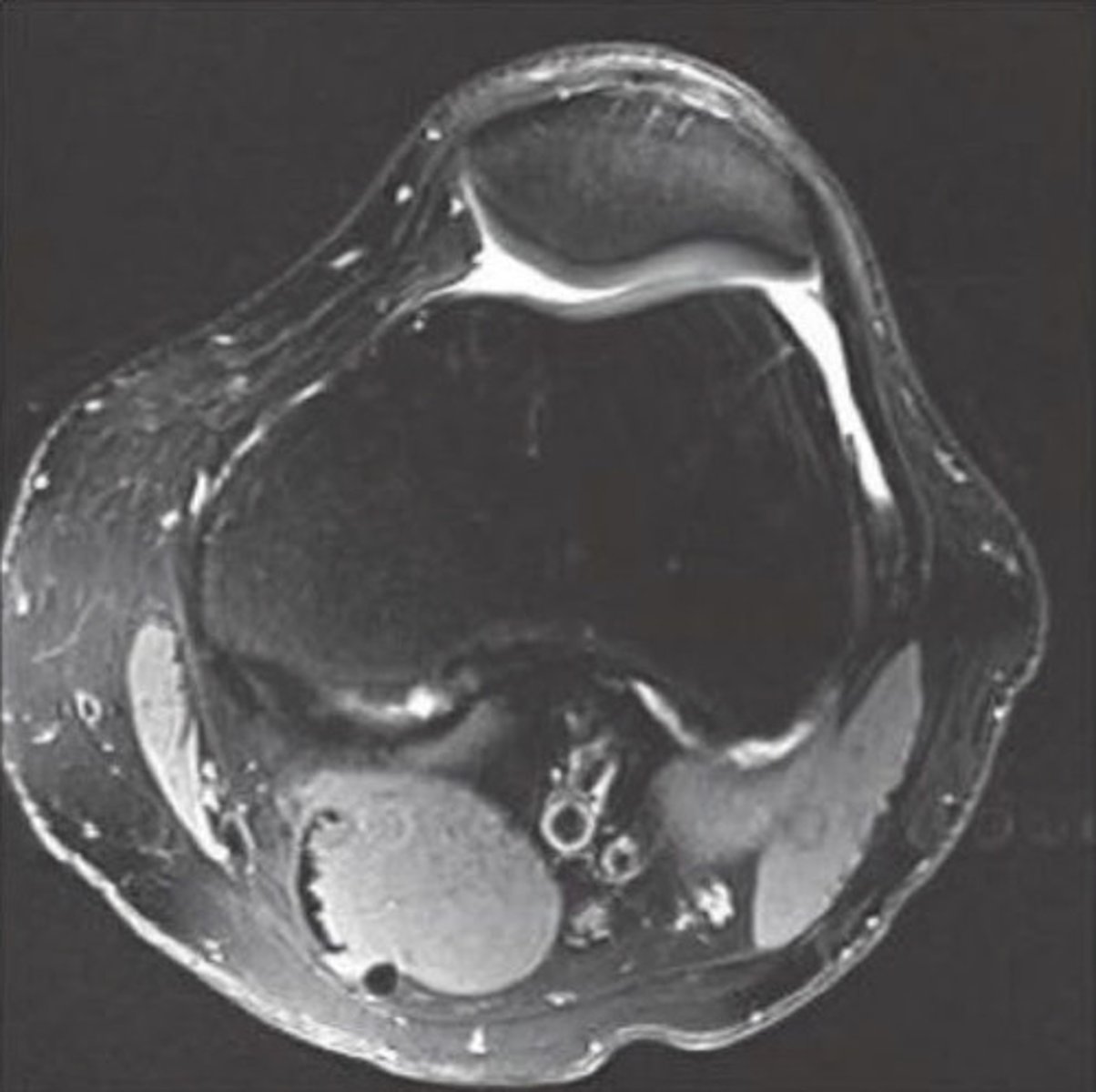
knee MRI/CT axial view
looks like tangential x-ray
- see tibial plateau
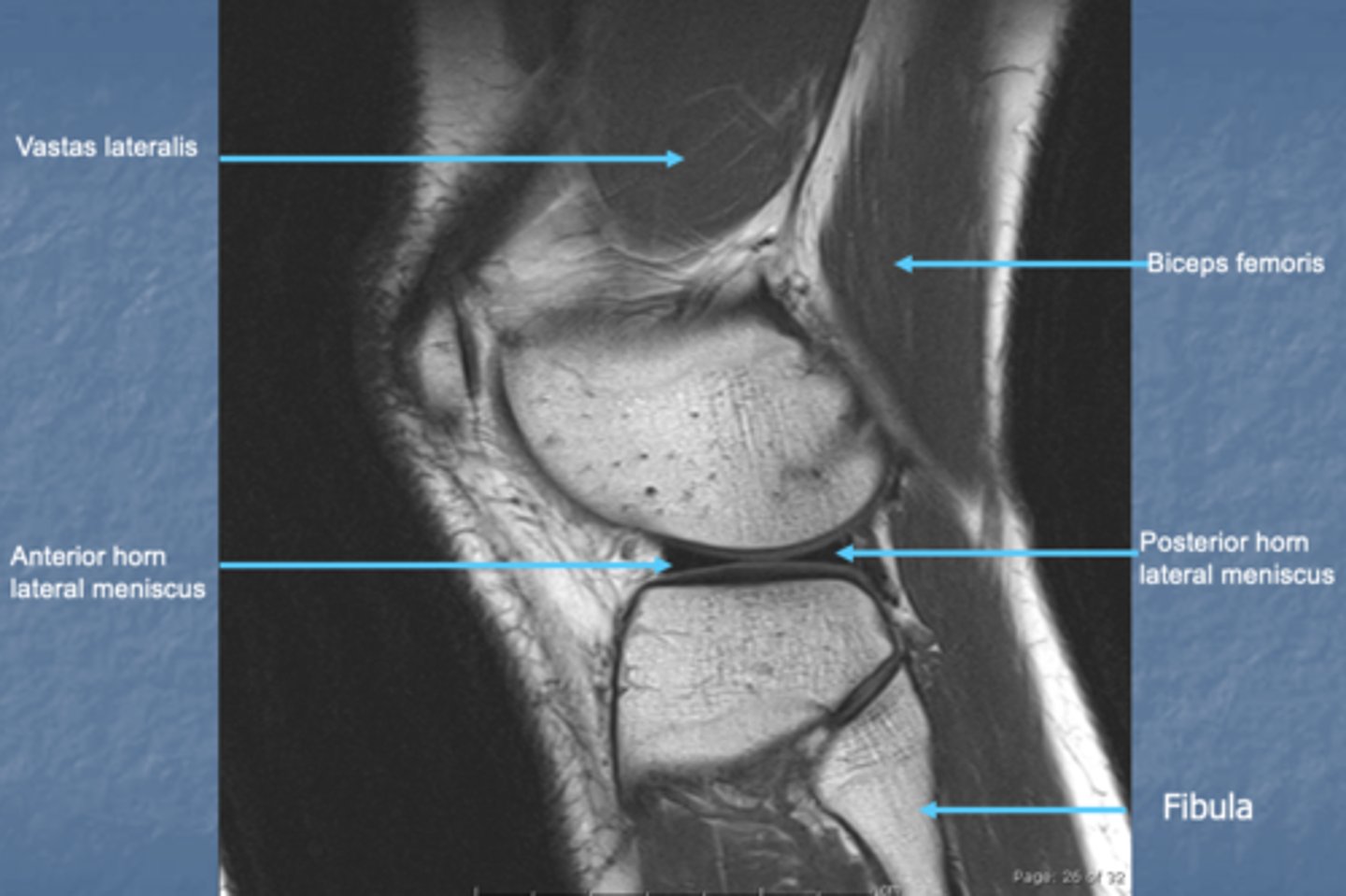
knee MRI/CT saggital view
looks like lateral radiograph
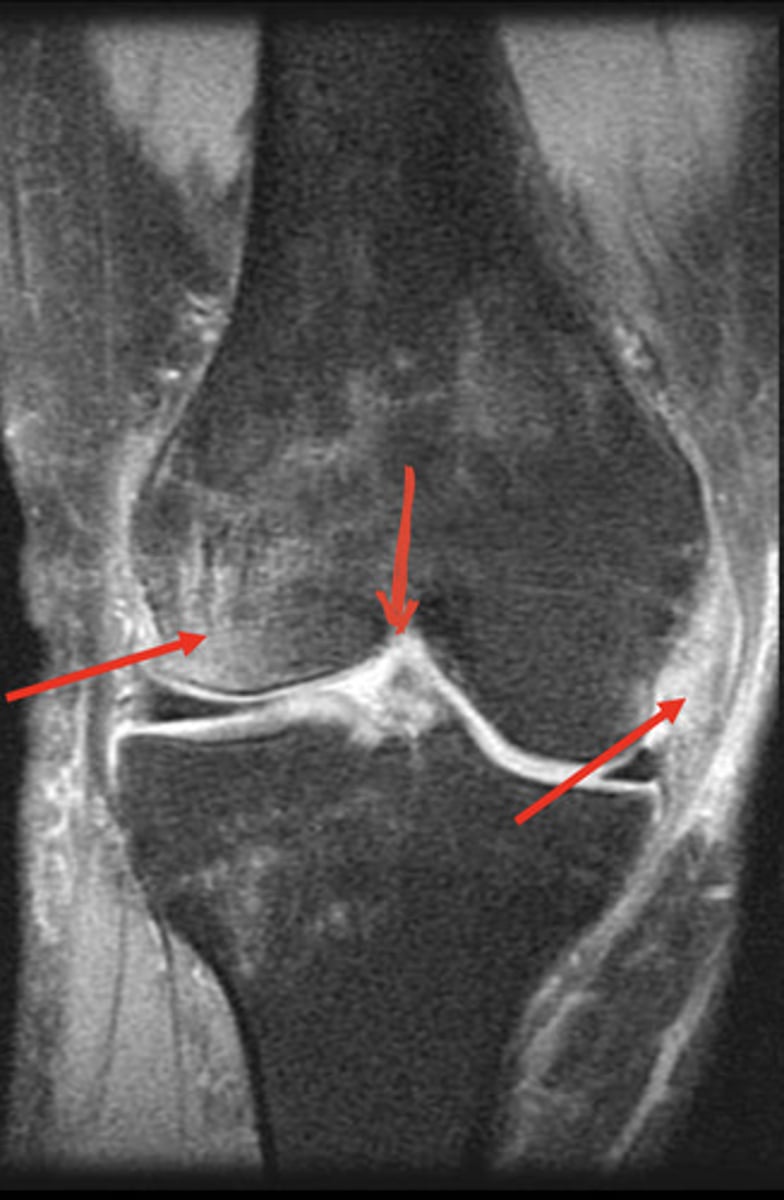
knee MRI/CT coronal view
looks like AP radiograph
when should you use an MRI for knee
- meniscus lesions
- ligament injuries
- soft tissue injuries
- osteochondral abnormalities
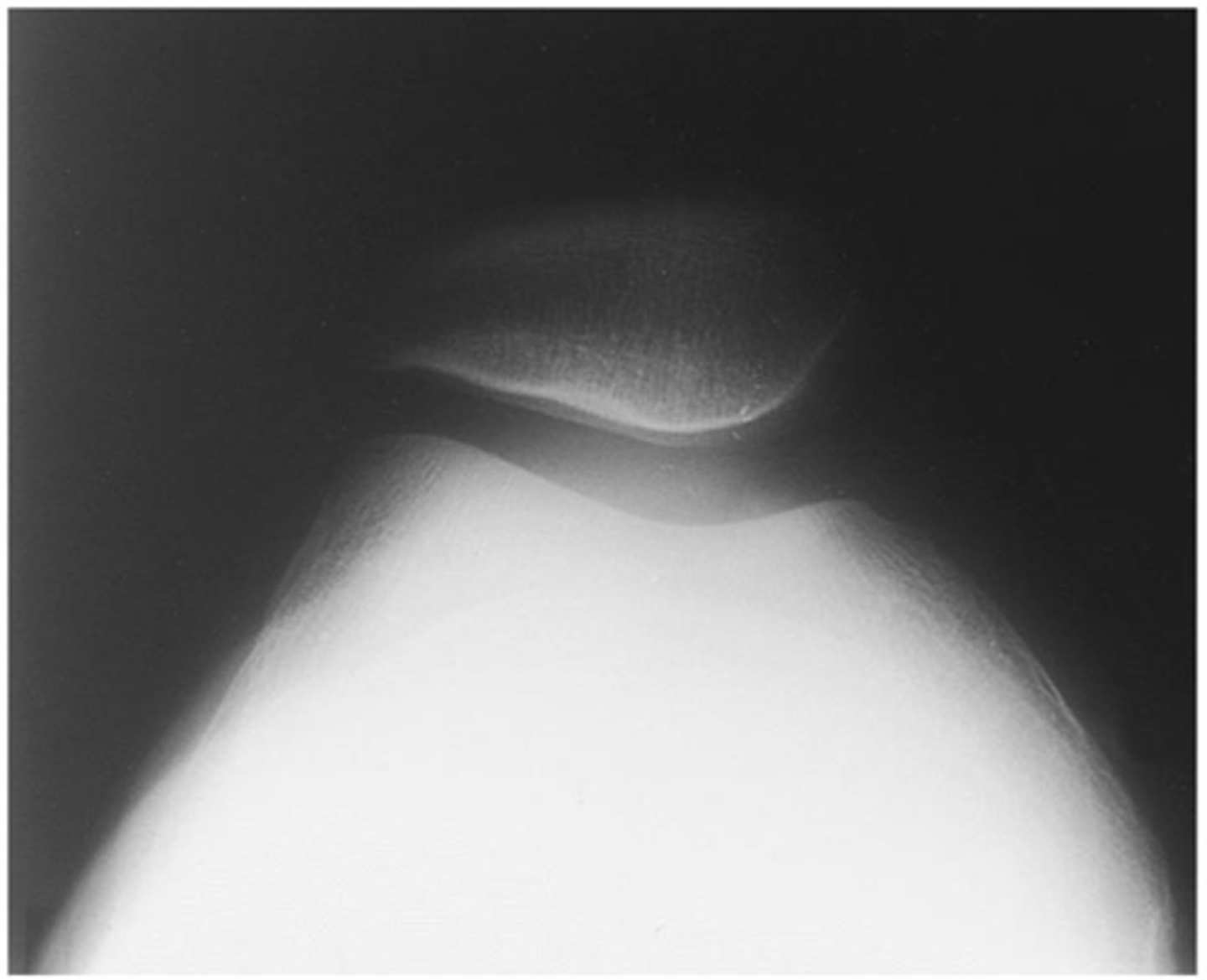
tangential knee radiograph
see patella and distal femur
- use if alignment slightly off
- use for vertical fx of patella
PA knee radiograph
see intercondylar eminence
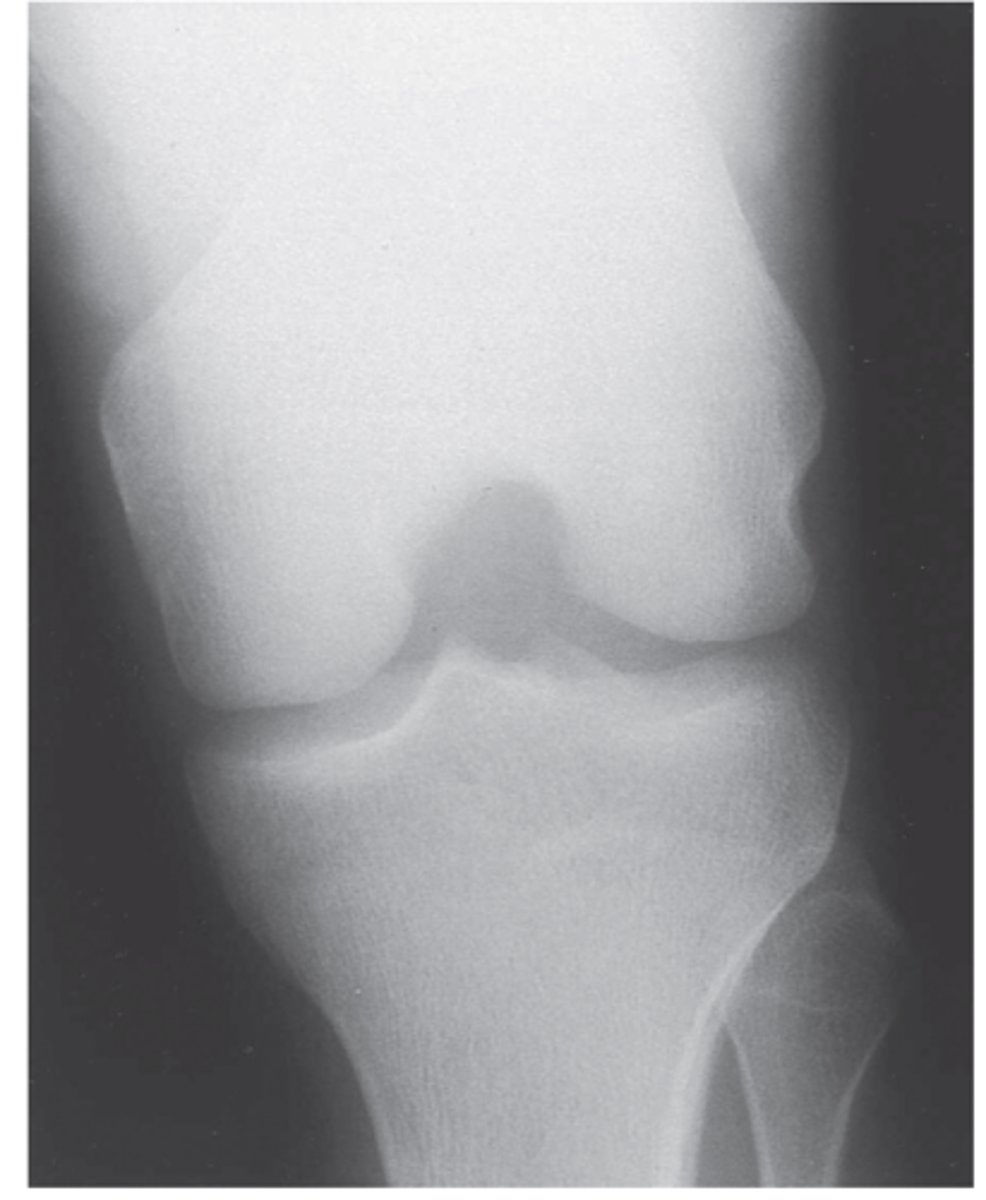
lateral knee radiograph
can see patella tracking superiorly/inferiorly
- alta = high
- baja = low
- use for transverse fx patella
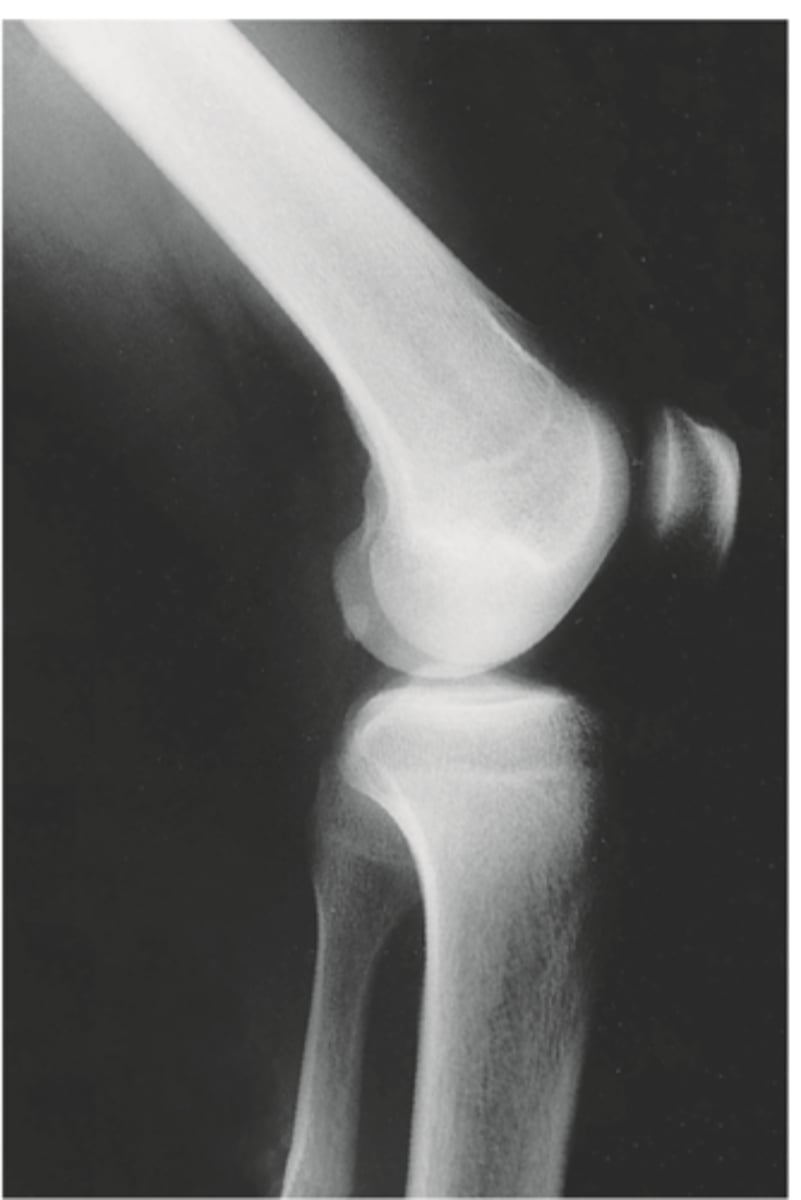
AP knee radiograph
- distal femur
- proximal tibia and fibula
- no patella or tibial plateau
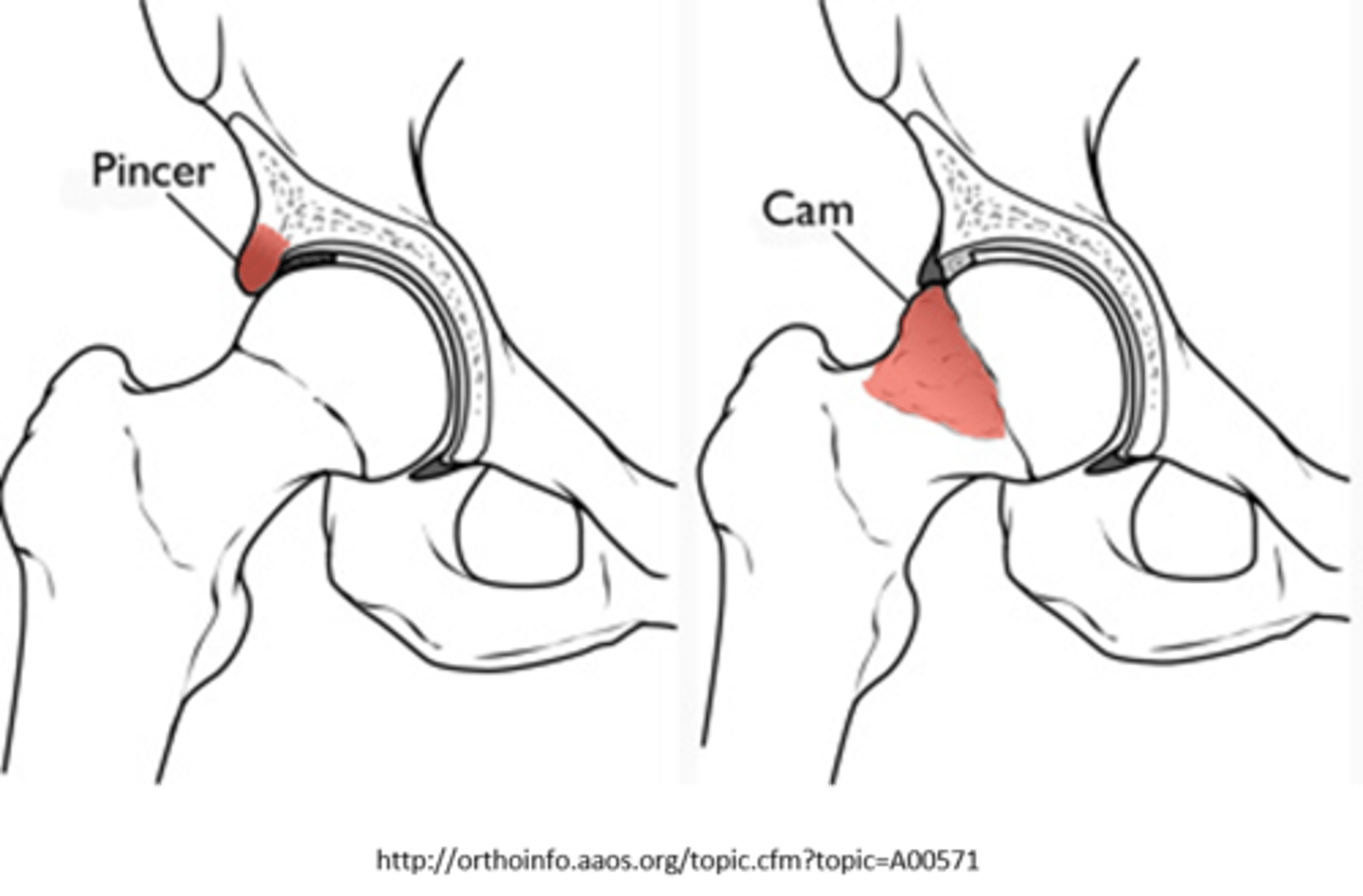
FAI
femoroacetabular impingement
- cam: outgrowth on femoral head
- pincer: outgrowth on acetabulum
slipped capital femoral epiphysis
- femoral epiphysis slips posteriorly
- blurring of physis on AP pelvis view
- use lateral frog view
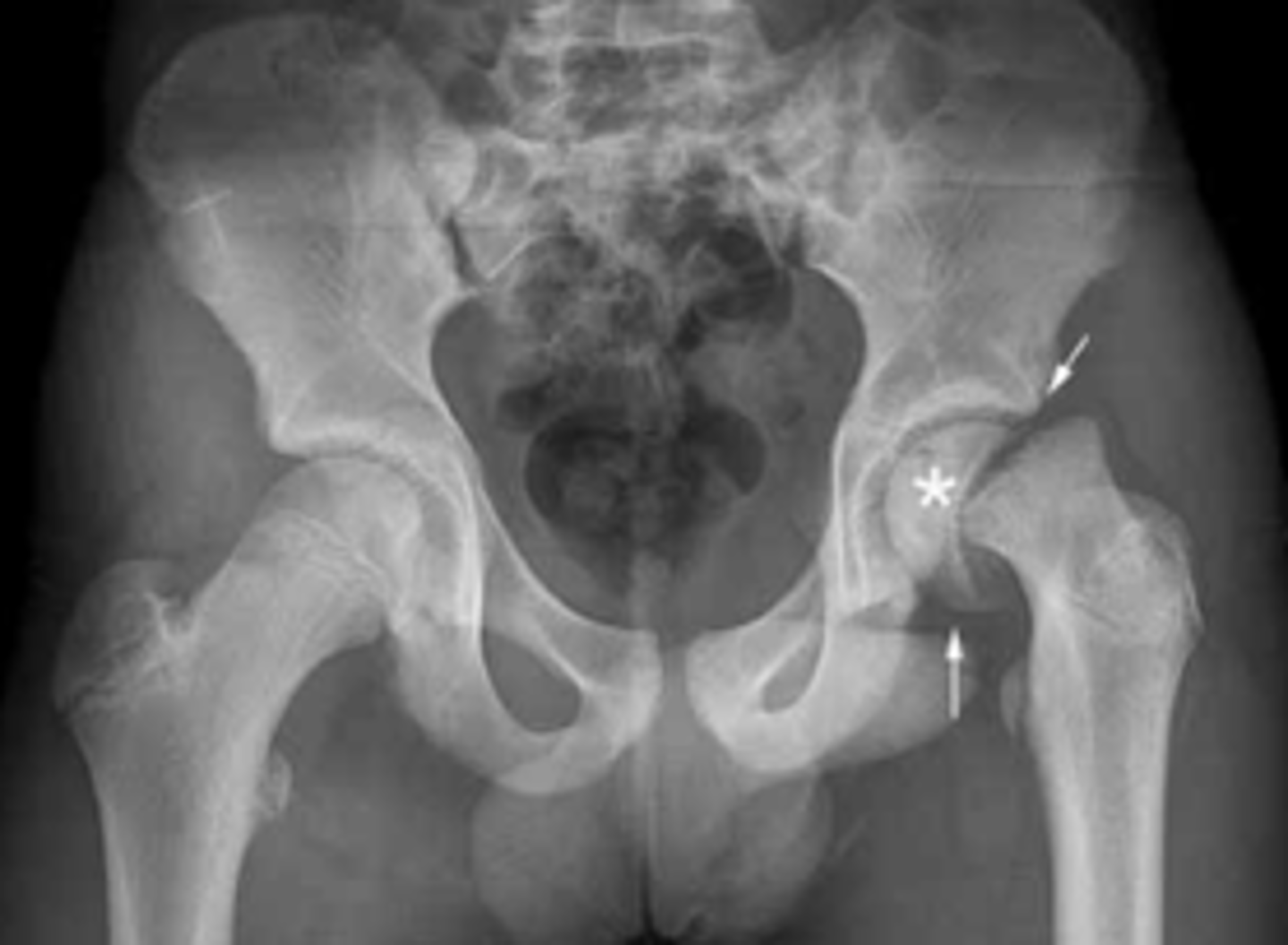
Legg-Calve-Perthes Disease
epiphyseal ischemic necrosis at femoral head
- 3-12
- femoral head looks squished
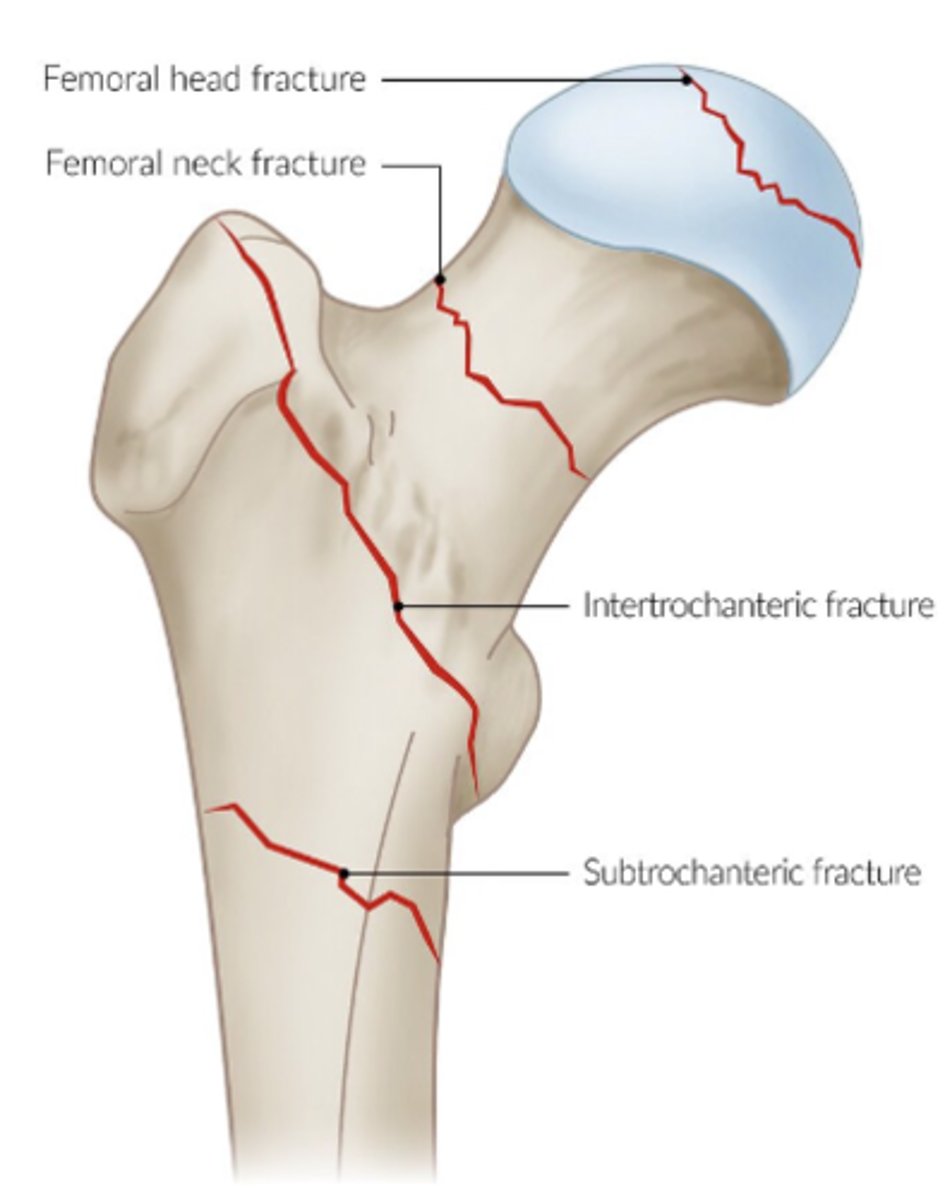
trochanteric fx
fx of greater or lesser trochanters
- typically avulsion
- AP hip (greater) or frog leg (lesser)
subtrochanteric fx
- proximal femur fx
- elderly or young pt
- image using AP hip
- treat w cephalomedullary nail fixation
intertrochanteric fx
extracapsular
- seen w AP hip view
- compare w AP pelvis
- treat w ORIF
femoral neck fx
intracapsular
- increased risk for AVN
- AP radiograph
- treat w ORIF or arthroplasty
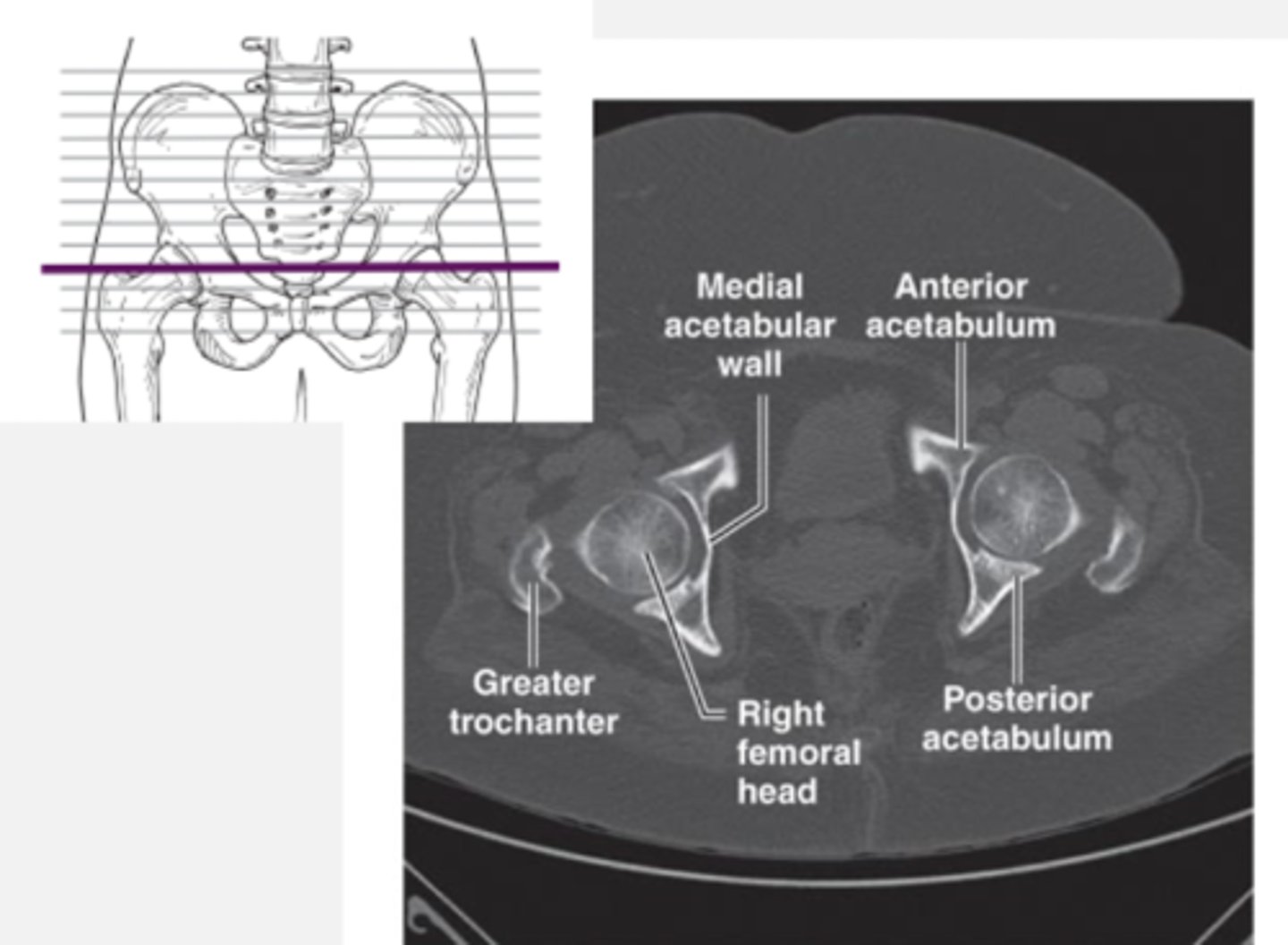
acetabular fx
due to femoral head driving into acetabulum
- REQUIRES CT SCAN bc of bony overlap
hip fx
high rates of morbidity and mortality
- femoral neck
- intertrochanteric
- trochanteric
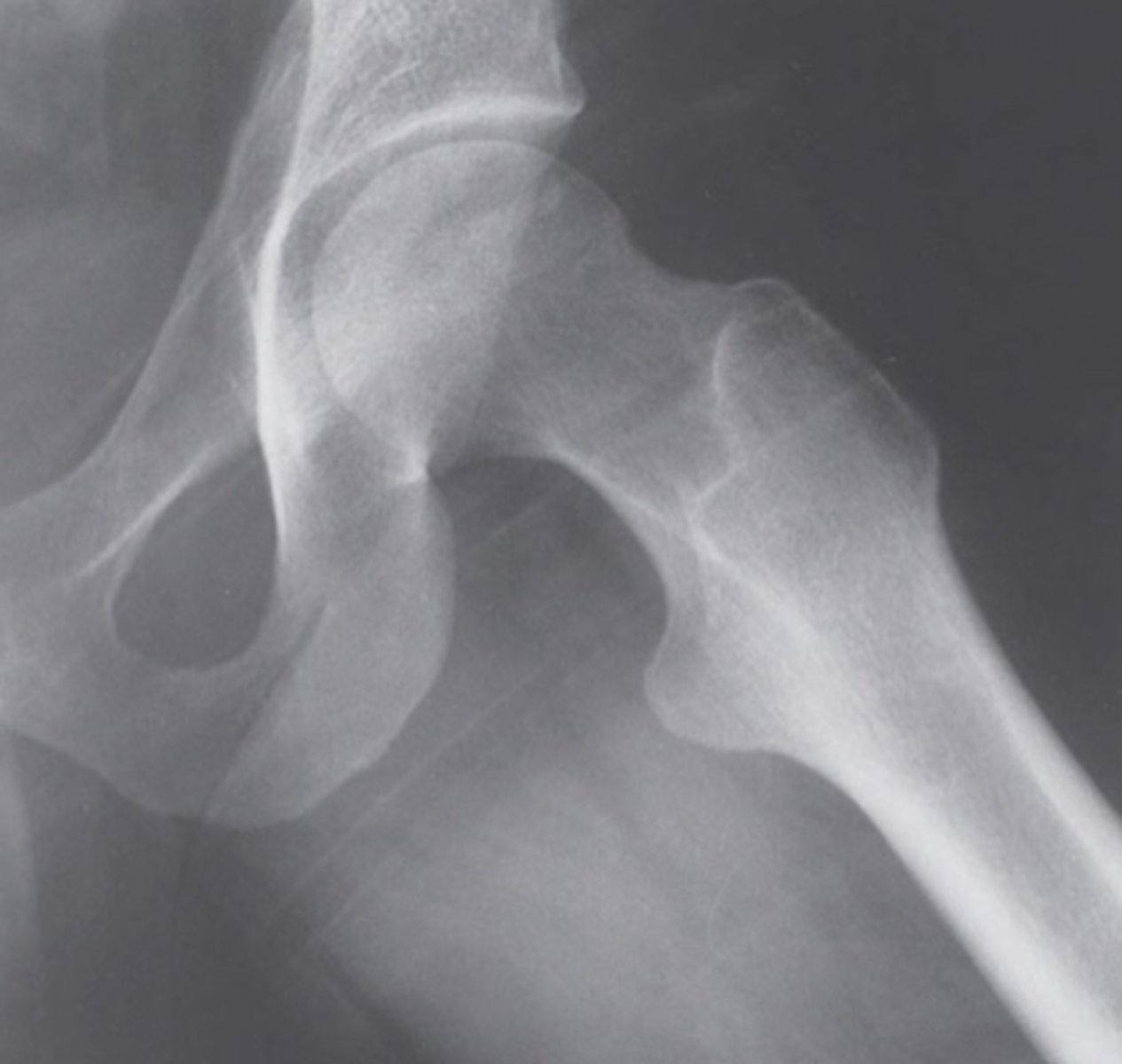
frog leg radiograph
FABER
- LE in ER
- better view of trochanters
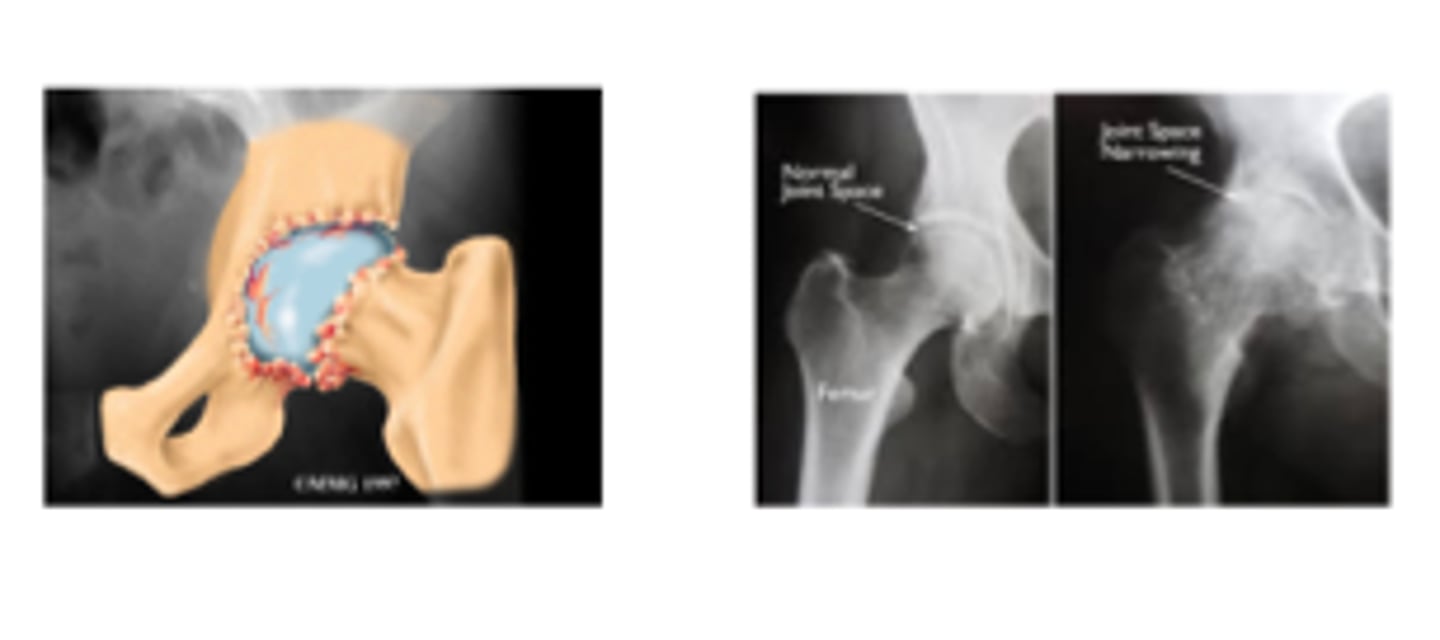
DJD/OA hip
- joint space narrowing
- sclerotic subchondral bone
- osteophyte at joint margins
RA hip
- symmetrical joint space narrowing
- loss of bone density
- joint effusion
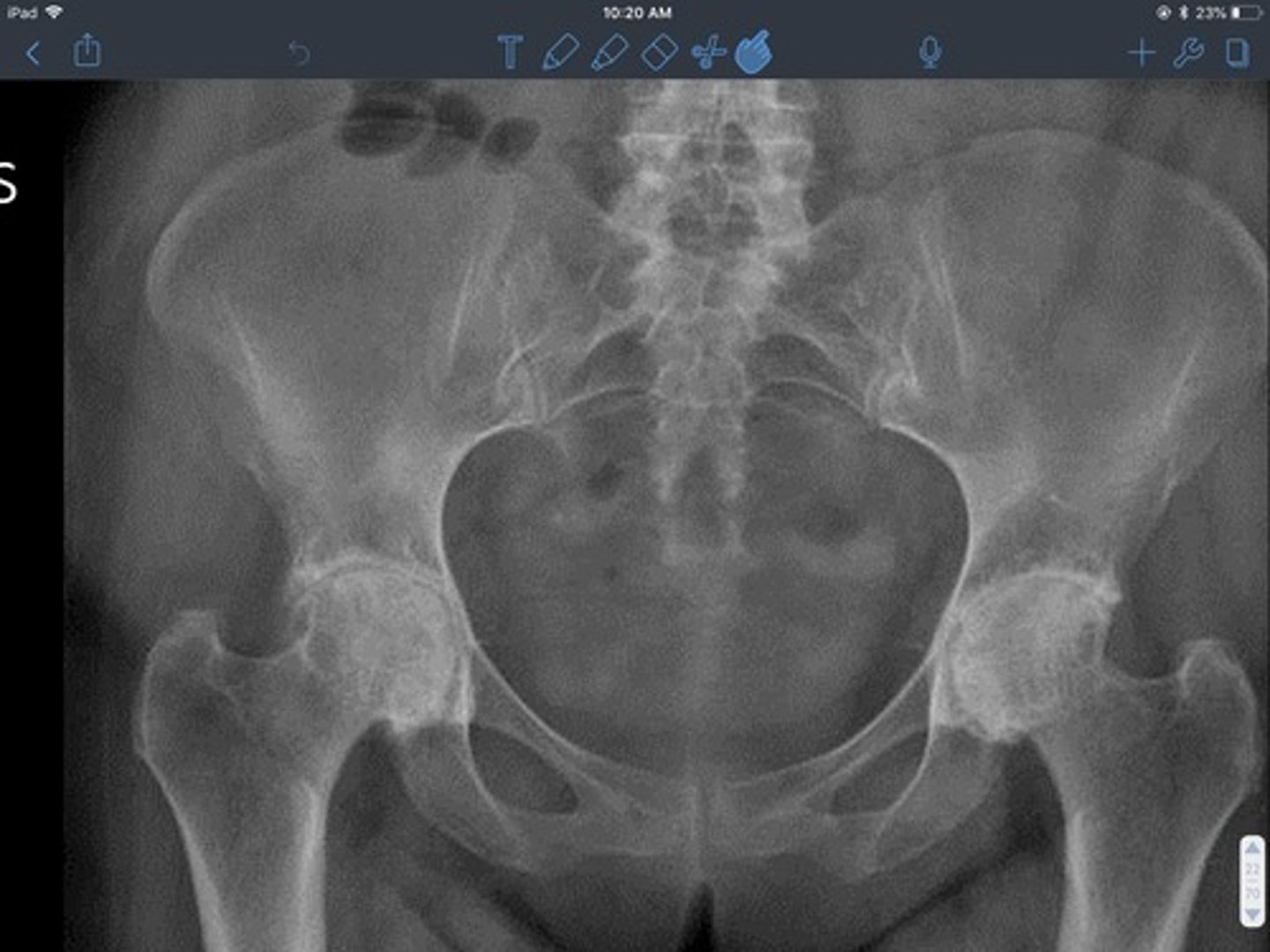
AVN hip
- femoral neck fractures increase risk
- preserved joint space
- MRI detects changes in bone marrow, bone tumors, stress fx and AVN
- CRESCENT SIGN
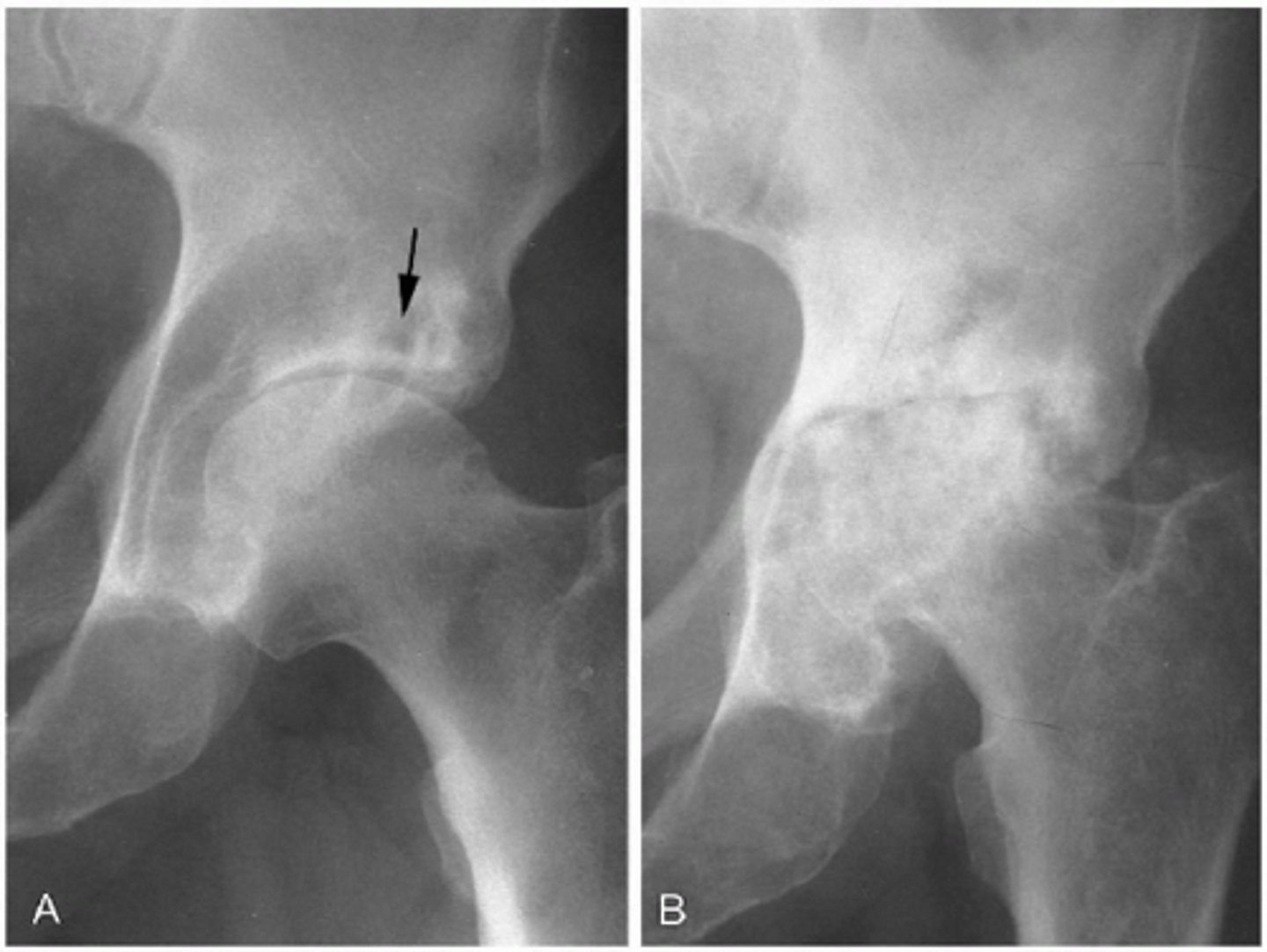
arthography hip
evaluates carticalge, labrum, and presence of FAI
hip MRI/CT coronal view
- bilateral comparison hip joints
- acetabulum
- femoral head neck and shaft
- SI joints, sacrum, greater and lesser trochanter
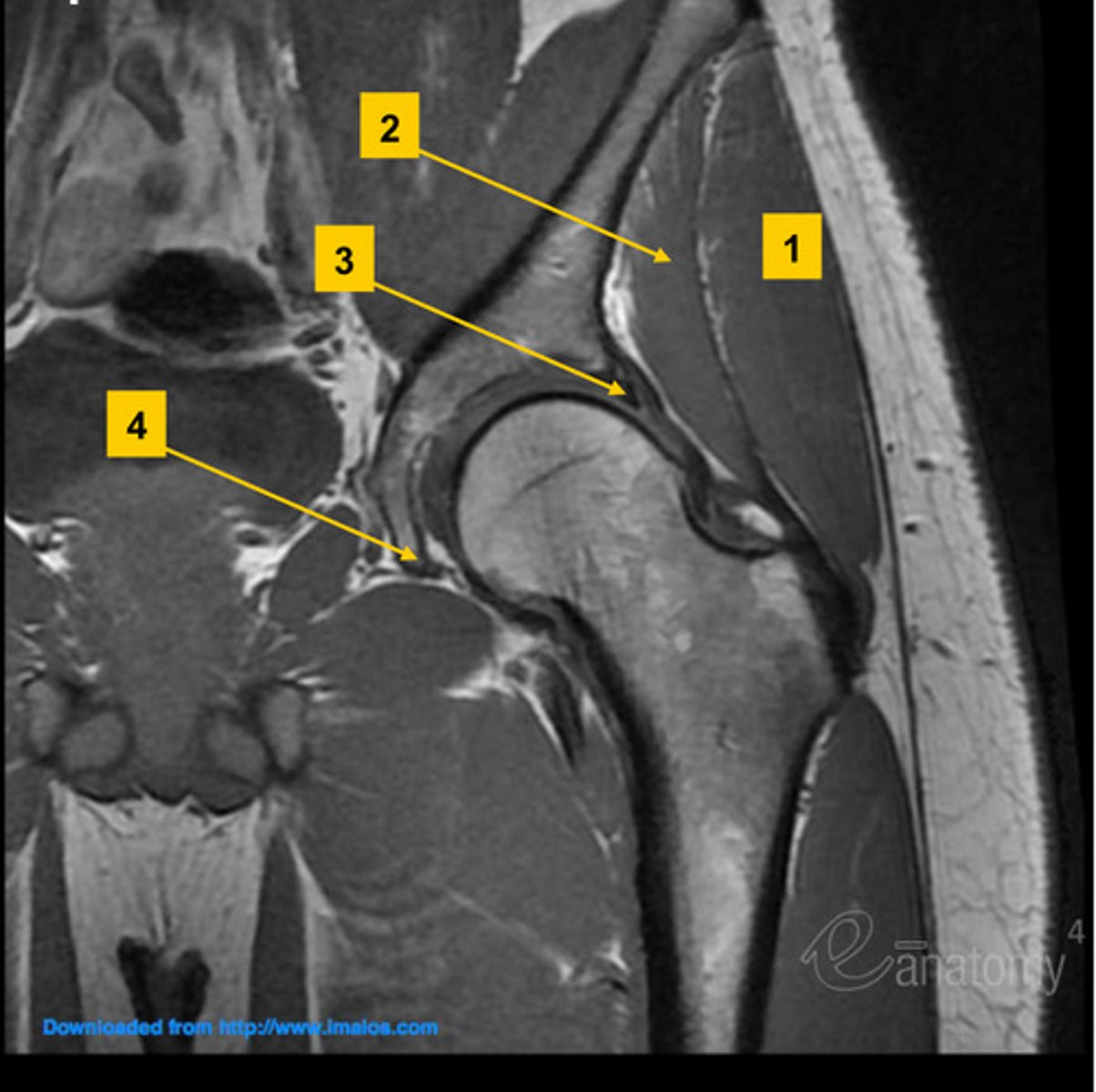
hip MRI/CT saggital view
- acetabular rood
- iliopsoas muscle
- SI joints
- pubic symphysis
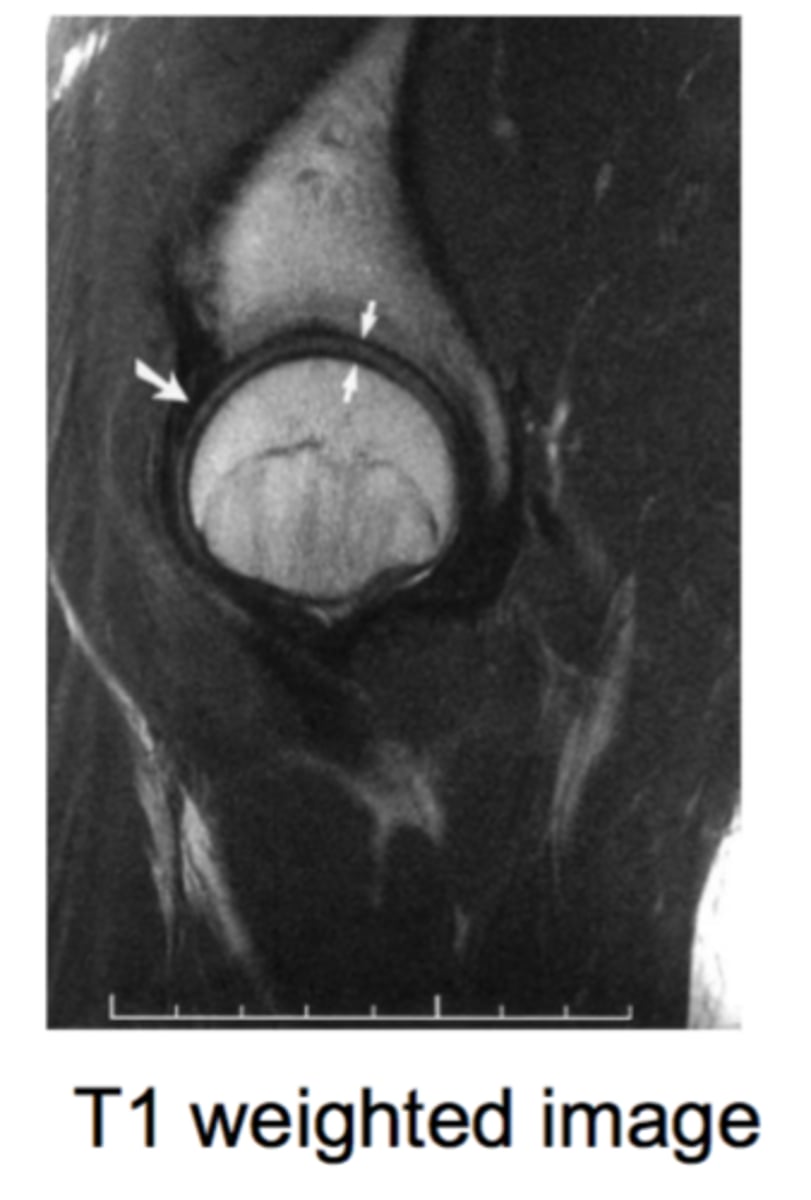
hip MRI/CT axial view
- femoral head in acetabular fossa
- sacrum
- greater and lesser trochanter