Assessment Techniques
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the 4 basic techniques of physical examination?
Inspection, Palpation, Percussion, Auscultation
What should be done first during inspection?
Begins when you first meet the person with general survey
Start with assessment for each body system!
ALWAYS THE FIRST THING YOU DO!!!!
General inspection
Observing the pt from front to back and from each side, checking for symmetry of body parts, obvious injuries, abnormalities, overall appearance
Systemic inspection
inspecting each body area systemically from head- to-toe; AKA HEAD TO TOE ASSESSMENT !!!!
Focused inspection
Perform general inspection and then only perform inspection on affected body system (think: ER; they don’t do a full Head to Toe. They only focus on your Chief Complaint
What are the inspection guidelines?
Make sure you have good lighting– can be daylight or artificial
Conduct an unhurried and careful inspection
Expose only what you want to inspect (don’t completely uncover them)
Validate findings with the pt
It’s okay to ask your patient questions. Makes sure you’re getting correct info while also making sure they’re aware of their own health
Ensure you have appropriate equipment to perform assessment
HAND HYGIENE!! Use glovesssss!
Applies sense of touch to assess:
Applies sense of touch to assess the following
Texture, temperature, moisture
Organ location and size
Swelling, vibration, pulsation, crepitation
Rigidity and spasticity
Presence of lumps or masses
Presence of tenderness or pain
Should be performed slow and systematic
start with light palpation and then go deep
Bimanual palpation is used for certain body parts or organs
What are the guidelines for palpation?
Palpation is a technique using the hands and fingers to gather information through the sense of touch.
Keep fingernails short
Have warm hands and be gentle
Use correct palpation depth and the appropriate part of the hand to correctly identify findings without producing unnecessary discomfort to the patient.
Palpation considerations
Typically follows inspection
When assessing the abdomen, always perform palpation after inspection and auscultation
palpation may increase the pt’s intestinal activity, causing misleading auscultation findings, like increased bowel sounds
Gloves should be worn
Touch can also have cultural significance
If pt’s culture views touch as not acceptable, nurse has to respect this and gather what they can w/o touching
Areas of the hand:
Palmar surface of the fingers and finger pads
Position, texture, size, consistency, fluid, crepitus, form of a mass, or structure
Areas of the hand:
Ulnar surfaces of hand and fingers
Vibration
Areas of the hand:
Dorsal surface of hand
Temperature
Areas of the hand:
Entire hand
Muscle strength
Fingertips
best for tactile discrimination of skin texture, swelling, pulsation, determining presence of lumps
Fingers and thumb
detection of position, shape, and consistency of an organ or mass
Dorsa of hands and fingers
best for determining temp b/c skin is thinner here than the palm
Base of the fingers or ulnar surface of the hand
best for vibration
Light palpation
pressing down 1 cm. Used to assess moisture, texture, temp, pulsations, tenderness, superficial masses and lesions
Deep palpation
press down 4 cm with 1 or 2 hands to determine organ size and contour (liver)
Percussion
Uses sound waves to gather info about the density of tissue
Other Percussion tips
Can be direct or indirect and is used to evaluate the size and borders of internal organ
Can also provide info about tenderness or the amount of fluid w/in a body cavity
Tapping person’s skin with short, sharp strokes to assess underlying structures
Sound waves arise from vibrations and produce percussion tones
Has the following uses:
Mapping location and size of organs
The tone/note heard is related to density of underlying tissue
Detecting a superficial abnormal mass (deeper masses would give no change in percussion)
Pain if underlying structure is inflamed
What are the characteristics of sounds?
Amplitude (intensity)- loud or soft
Pitch (frequency)- number of vibrations per second
Quality- subjective difference
Duration- length of time sound lingers
What are the basic principles of sound?
Structure with more air produces louder, deeper sound compared with denser structure
There me variations because of anatomical differences between everyone
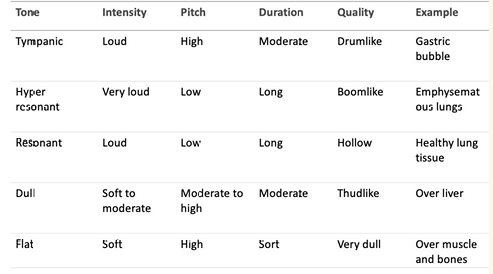
Remember this chart
Select this for freebie
What are the basic principles for auscultation?
Stethoscope does not magnify sound but blocks extra sounds
Eliminate extra sound (touch stethoscope to skin). NEVER ON THE GOWN
Listen to one sound at a time and distinguish the sound you are auscultating
Make sure environment is quiet
Do not anticipate the next sound or what you expect to hear next
How to distinguish sound for auscultation?
Take time to identify, including the intensity, duration, pitch, quality
Intensity- loudness of the sound (soft, medium, loud)
Pitch- frequency of the sound waves generated per second
High pitched- high frequencies
Low pitched- low frequencies
Duration- length that sound is heard (short, medium, long)
Quality- description of the sounds. Also includes murmur or crackles